Atherosclerosis is called the most common disease of humanity, but it depends only on ourselves to what degree of destruction we will subject our cardiovascular system. The disease is caused by excess cholesterol accumulating in medium and large arteries. If you watch your diet, don’t give in to stress and exercise regularly, you will most likely avoid serious damage to your blood vessels and be able to keep their walls toned. If you do not have the opportunity to carefully adhere to a healthy lifestyle, and you still notice negative changes in your body, contact a professional specialist as soon as possible. Modern diagnostic methods used in the CBCP clinic will help identify vascular atherosclerosis at an early stage, and doctors will select treatment that will protect you from unpleasant complications.
How does the disease appear?
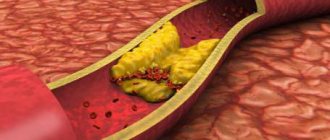
In general, cholesterol (a type of fat) is important for the body, as it participates in the construction of vascular walls and is part of hormones and vitamins. In normal metabolism, cholesterol circulates between the liver and tissues; in excess, it is utilized in the liver. If the circulation is impaired, it accumulates in the form of plaques (together with fibrin and other substances) on the walls of blood vessels. The lumen of the vessel narrows, and the blood pressure on the walls automatically increases. Unfortunately, the process is almost inevitable and is observed in 85% of cases in patients over 50 years of age.
The following phenomena gradually develop:
- the walls of the vessel are subject to ulceration;
- scar tissue grows;
- deposits of lime salts are observed on the vascular walls.
The vessel at the site of plaque formation becomes calcified, and this leads to its destruction.
Reasons for appearance
The appearance of atherosclerosis is associated with metabolic disorders in the body, lipid imbalance and excess cholesterol in the blood.
Mechanical damage to the vessel wall also plays an important role, contributing to atherosclerotic deposits and plaque formation at the site of injury. The risk of developing atherosclerosis is higher in men over 45 years of age, women over 55 years of age or with early menopause, as well as among people with familial hypercholesterolemia and family history, whose relatives already suffer from this disease.
Other factors contribute to it:
- unbalanced diet with an abundance of fatty foods;
- excess body weight;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- cardiovascular diseases – ischemic heart disease, arterial hypertension;
- endocrine pathologies, in particular diabetes.
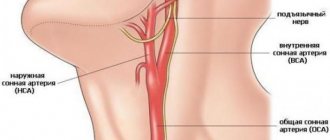
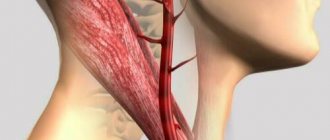
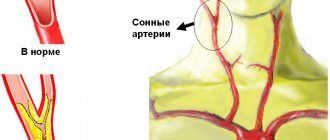
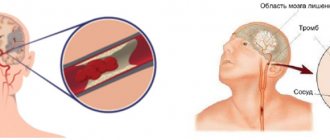
Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels
A form of disease in which atherosclerotic plaques appear in the blood vessels of the brain. The immediate consequence may be a stroke. Various cerebral vessels are affected: brachiocephalic trunk, carotid arteries.
In some cases, atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels occurs without any special symptoms, even if the artery is narrowed by 50%. The patient experiences tinnitus, dizziness, headaches of varying intensity, and sleep disturbances. Gradually, these signs complement hand tremors, memory deterioration, and decreased performance.
Symptoms of cerebral atherosclerosis at a late stage:
- partial memory loss;
- deterioration of thinking abilities;
- numbness of limbs, tongue;
- difficulties in self-care.
The patient periodically experiences conditions similar to a stroke - transient ischemic attacks. When the vessel is completely blocked, an ischemic stroke occurs - brain cells begin to die from lack of oxygen. Another manifestation is a rapid hemorrhagic stroke, which is not expressed by blockage of an artery, but by hemorrhage in the brain. Complications of the disease are extremely difficult to treat: malignant tumors, dementia, etc.
Diagnostics
It is almost impossible to make a diagnosis of “atherosclerosis” only on the basis of patient complaints. This is due to the fact that the pathology has a lot of signs that are characteristic not only of it, but also of a number of other diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Diagnostics is comprehensive and includes:
- Blood test. It is very important to determine cholesterol and sugar levels. A blood clotting test is also performed. It allows you to determine the risk of developing blood clots and stroke.
- Ultrasound examination of blood vessels. Dopplerography provides opportunities to study blood flow.
- CT with contrast. With this study, the specialist receives a three-dimensional image of the arteries. The doctor can collect detailed information about the affected area, its size, location, etc.
- Magnetic resonance angiography. This study allows you to determine the size of existing cholesterol plaques. Usually, it is on the basis of such diagnostics that a suitable treatment method for atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries is selected.
- X-ray contrast angiography. This study is carried out in complex clinical cases.
Important! The diagnostic test is adjusted by the doctor taking into account the patient’s condition, the cause of the pathology, the goals of the study, etc. The individual characteristics of the patient must also be taken into account. While ultrasound can be performed on all patients, contrast methods have a number of contraindications. These include obesity, allergies, the presence of heart implants, liver and kidney failure.
Atherosclerosis of heart vessels
Atherosclerotic plaques can also form in the coronary vessels, which are responsible for supplying blood to the heart muscle. As a result, the flow of oxygen and nutrients is disrupted, disturbances in the functioning of the heart are noted - chronic ischemic disease develops.
The patient feels:
- frequent pain in the heart area;
- cold extremities;
- increased blood pressure;
- memory and concentration problems;
- lethargy, drowsiness.
In some cases, atherosclerosis of the heart vessels develops against the background of diabetes mellitus and kidney disease. Diagnosing it is difficult, since the first signs may appear when the vessel is already almost completely blocked by plaque. Therefore, if you feel unwell and observe the symptoms listed above, if there is even the slightest suspicion, consult a doctor. This type of disease is one of the common causes of myocardial infarction.
Prevention
Primary prevention is aimed at eliminating factors that contribute to the deterioration of health and are risk factors; This:
- smoking;
- arterial hypertension;
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- physical inactivity;
- poor nutrition.
Secondary measures for the prevention of cerebral atherosclerosis are aimed at preventing plaque detachment, preventing thrombus formation and preventing the progression of the disease.
Atherosclerosis of the renal arteries
The formation of an atherosclerotic plaque at the mouth of the renal artery is a common cause of the development of renovascular hypertension. The pathology has characteristic symptoms that can help identify the disorder at an early stage:
- high blood pressure;
- headaches and dizziness;
- shortness of breath due to strain on the heart;
- kidney dysfunction;
- Laboratory tests reveal protein in the urine.
The danger of the disease is that vascular thrombosis can develop, and if both kidneys are affected, a malignant tumor can develop. Only timely diagnosis using modern methods will protect you from dangers.
Treatment
Treatment of the disease is carried out using complex therapy, which includes the following groups of drugs:
- antisclerotic drugs;
- antihypertensive drugs;
- hypoglycemic drugs;
- metabolism;
- antihypoxants;
- antioxidants;
- antispasmodics;
- anticoagulants;
- nootropics;
- vasodilators.
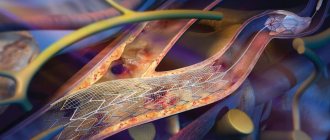
In advanced cases, the disease is severe, and drug treatment does not show high effectiveness. In this case, the neurologist decides to perform surgical treatment. During the operation, the surgeon removes blood clots and atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels that narrow the lumen of the vessel. Stenting, endarterectomy, balloon angioplasty, and extra-intracranial anastomosis can be performed. Such surgical interventions are performed in case of vascular obstruction, severe narrowing of the vessel, to remove atherosclerotic plaques and restore vascular patency.
Atherosclerosis of the mesenteric arteries
Mesenteric arteries are responsible for the blood supply to the intestines, and the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in them leads to serious digestive disorders. As a result, the blood supply needs of the gastrointestinal tract cannot be satisfied.
The signs of vascular atherosclerosis in this case are quite obvious:
- pain in the upper abdomen;
- bloating, constipation, belching;
- nausea and vomiting with bile;
- retention of stool, gases;
- blood in the stool.
This type (popularly called abdominal toad) is similar in symptoms to peptic ulcers, but the pain goes away faster, especially if you take nitroglycerin, and is not relieved with soda. The pain can wander in different areas of the abdomen, often concentrating around the navel. Patients note a general deterioration in their condition, a slight increase in temperature.
Complications include thrombosis of mesenteric vessels, intestinal gangrene with signs of peritonitis.
Atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities
In the lower extremities, plaques most often form in places where large vessels branch. The superficial femoral and popliteal arteries are usually affected.
This type of disease has several obvious manifestations:
- lameness that appears when you start walking and disappears when you stop;
- pain in the calf muscles, thigh, hip joint;
- at the site of joint damage, the shade of the skin changes (cyanosis);
- there is chilliness in the legs, numbness, cramps at night;
- legs get tired quickly when walking even short distances.
Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner can lead to complete blockage of one of the vessels, which is fraught with complications. The most serious is the development of ischemic gangrene (death of tissue near the affected vessel) - in this case, even amputation of the limb may be necessary.
A common complication is also thrombosis of the arteries of the lower extremities, which leads to embolism: part of the blood clot breaks off and blocks one of the large vessels. It is impossible to predict exactly where the blood clot will go and which vessel it will block.
Multiple sclerosis - how it differs from the vascular type
Demyelination is the destruction of myelin in nerve sheaths, which occurs in inflammatory, autoimmune, and prion diseases. The nosology differs from classical vascular thrombosis, embolism, and atherosclerosis in morphological manifestations.
Multiple sclerosis is characterized by the destruction of myelin. Unprotected nerve sheaths overlap each other, causing damage to signal transmission. Every year, the manifestations of the nosology increase, which leads to muscle paralysis and paresis of the limbs.
Atherosclerosis leads to blockage of vascular patency. The deposition of cholesterol plaques in the artery wall reduces patency. Initially, local changes appear without symptoms. An increase in hypoxic conditions leads to neurological disorders. Doctors will be able to conduct a differential diagnosis of nosologies based on clinical manifestations.
Symptoms
The danger of developing the disease is that it can manifest itself extremely weakly until the plaque blocks two-thirds of the vascular lumen or begins to collapse, and blood clots from it begin to clog smaller vessels. Then the clinical symptoms become noticeable to the patient.
Manifestations of the disease and treatment depend on the location of formation of atherosclerotic plaques. For example, if the vessels of the brain are affected, the symptoms and treatment will differ significantly from atherosclerosis of the lower extremities.
Even the pathology of the same large vessel is not uniform in its symptoms. In particular, atherosclerosis of the thoracic aorta is manifested by burning pain in the chest, which radiates to the neck, back, abdomen and can last for days. The patient has difficulty swallowing, his voice is hoarse, and the patient himself experiences dizziness and faintness.
And atherosclerosis of the abdominal aorta is characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and frequent constipation. If the aorta is damaged at the site of division into branches, the patient begins to limp, feels coldness in the lower extremities, and experiences problems with potency.
Signs and symptoms of stroke and transient ischemic attacks
- Speech disturbances (difficulty).
- Insensibility, weakness, paralysis of one side of the body or face.
- Loss of vision in one eye.
- Problems with balance or coordination.
As noted above, if these changes completely regress within 24 hours, the patient is diagnosed with a TIA, if more than 24 hours, an ischemic stroke.
There is also the concept of “ministroke,” which is not a medical term, but is used to describe a stroke that leads to an infarction of a small area of the brain and, as a consequence, manifests itself with “erased” symptoms with rapid rehabilitation. However, a microstroke can be regarded as a harbinger of an ischemic stroke. Approximately half of patients develop a “major” stroke over the next year.
Variable factors
The development of all types of disease is influenced by our lifestyle. In order to reduce risks as much as possible, you should:
- move more and exercise;
- do not abuse fatty foods;
- try not to expose yourself to stress;
- give up alcohol and smoking.
Potentially correctable causes include:
- diabetes mellitus (glucose levels must be monitored);
- arterial hypertension (pressure);
- hypercholesterolemia (cholesterol levels);
- obesity (waist more than 102 cm in men and more than 88 cm in women);
- frequent infections and intoxications.
Diet
Changing your diet is also a way to improve your well-being and is a great help for other treatment methods. Atherosclerosis very often progresses precisely against the background of poor nutrition and lifestyle, so it is necessary
- follow a certain diet:
- reduce consumption of red and fatty meats and meat in general;
- limit the consumption of confectionery products and baked goods;
- eat as few egg yolks as possible;
- limit solid vegetable fats – margarine – in the diet;
- completely eliminate alcohol, sausages, fast food, and canned food.
Recommended products include vegetables (fresh, pickled, dried), cereals (rice, buckwheat, barley, millet, oats, flax, etc.), dried, fresh and dried fruits, turkey and chicken fillets, river and sea fish.
You need to eat at least 5 times a day at the same time in small portions. It is necessary to avoid fried foods and prepare food using the methods of boiling, steaming, stewing, and baking.
Complications
The main complication is acute or chronic vascular insufficiency of one or another internal organ. It leads to the gradual death or degeneration of part of its tissues. These phenomena are caused by a lack of oxygen and nutrients. Connective tissue grows in the organ, and sclerotic processes develop.
The second important complication is acute blockage of a vessel by an overgrown atherosclerotic plaque or its detached part - a thrombus. Consequences – acute organ ischemia, myocardial infarction.
At the site of plaque formation, an aneurysm may occur - a vascular formation in which the walls of the vessel bulge and become thinner. An increase in blood pressure caused by physical or psychological stress can provoke aneurysm rupture and intense internal bleeding.
In addition, certain types of pathology cause various complications:
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels - stroke, memory loss, dementia;
- atherosclerosis of heart vessels - angina pectoris, arrhythmia;
- atherosclerosis of mesenteric arteries – intestinal necrosis;
- atherosclerosis of the renal arteries - problems with urination and impotence;
- atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities - trophic ulcers, gangrene.
Timely treatment for symptoms of vascular atherosclerosis
Treatment of pathology is especially effective in the early stages. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, you can completely get rid of the symptoms of the disease and minimize the negative consequences.
An important role in treatment is played by the qualifications of the doctor and the class of equipment used in the clinic. Modern diagnostic equipment detects even minor changes in the vascular system, and treatment of complex cases is possible without surgical intervention - using innovative, low-traumatic methods.