Every modern person must know the minimum practical medical actions that can be applied in an emergency situation. It is especially important to understand the location of the main organs, bones, and arteries.
In medical practice, cases are often described when people of any age lose consciousness or simply lie on the ground, without any signs of a normal condition. In this case, the person needs to feel for a pulse in the carotid artery. If it is absent, it is necessary to perform artificial respiration.
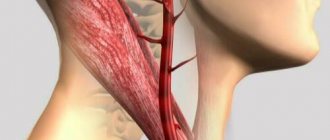
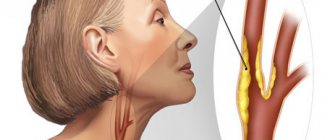
What is the carotid artery? It is important to understand the process that it carries out. The carotid arteries direct blood to the brain, and its amount accounts for 70% of the total volume. The name of these vessels is directly related to their ability to put the human body into a state of sleep, when compressed with a certain force for a period of 10 seconds.
What happens if you press on an artery: instructions
When you squeeze it lightly, you feel discomfort and sometimes mild pain. Strong compression easily puts a person to sleep. Receptors perceive pressure as a stimulus to increase pressure, so they do the opposite - they sharply lower it. A person’s heartbeat calms down on the neck, and due to the minimal supply of oxygen, the body experiences drowsiness. Long-term and severe compression of the carotid artery can be fatal.
Typically, a person's pulse is checked on their arm. But in complex traumatic cases this is not enough. Therefore, the pulse is felt in the neck. It should be noted that the pressing force must be controlled. On a thin body, the pulse will be clearly felt even with weak pressure, but if you have developed muscles, you will have to try.
Postoperative period
The patient is discharged on the 2nd day after surgery with a mandatory follow-up ultrasound scan.
After carotid artery stenting, combination antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel 75 mg/day and aspirin 100 mg/day is prescribed for up to 12 months. Subsequently, aspirin and anti-cholesterol drugs - statins remain.
A control ultrasound scan is performed one month after stenting surgery. The patency of stented segments should be assessed at intervals of 6 months. If signs of restenosis are detected, the patient is prescribed a multislice computed tomography scan with contrast.
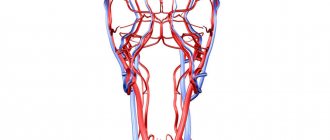
Structure of the carotid artery
The common carotid artery and its branches are divided into two halves: on the right side of the body it passes in the neck from the brachiocephalic trunk, and on the left, it comes from the aortic arch in the thoracic region. To understand where the carotid artery is located in a person, you need to feel the pulse in the neck, you need to press the vertical depression in the neck on the right or left side. Everything is clearly shown in the photo.
Medical students often wonder where the carotid artery is located in the neck? To feel the pulse of the carotid artery in the neck, you need to lay the person down or sit on a chair. Place several fingers, usually the middle and index fingers, in the cavity between the Adam's apple and the lateral neck muscle.
Normal heart rate values are about 60-80 beats per minute. Each of the arteries runs diagonally upward; in the lower part they are connected by the trachea.
Efficiency. Professionalism. Mercy
At yesterday's first aid courses, conducted by the Tyumen Emergency Medical Service, there were at least ten people. The courses are free. Everyone listened with interest to emergency doctor Andrei Rogotnev.
Useful tips based on practical experience
It is immediately worth noting that there is a lot of information on first aid on the Internet. The courses conducted by emergency doctors in Tyumen are valuable because the training is based on practical experience. Let's give a simple example. How long do you think it is possible to clamp an artery on the thigh or shoulder? Many will answer that no more than 1.5 hours. In fact, this recommendation has long been outdated, because after an hour and a half of compression, the blood below the tourniquet will clot in all vessels, and the limb will then have to be amputated. We are not at war, and we not only need to save a person’s life, but also try to save an injured arm or leg. However, first things first.
We find out where the blood is coming from - from a vein or from an artery
Before giving useful tips and recommendations for stopping bleeding, Andrei Rogotnev reminded that bleeding can be venous and arterial. We did not consider ordinary cuts, since they are not life-threatening. In venous bleeding, the blood comes from a vein; in arterial bleeding, the blood comes from an artery. It's generally simple. It is much more difficult for people far from anatomy and medicine to distinguish one bleeding from another. Meanwhile, it is important to understand this before you start saving a person. In fact, everything is simple here: blood from the artery flows like a fountain, but not in a continuous flow, but pulsates in time with the heartbeat, since blood from the heart enters all organs through the arteries. The blood flows back through the veins, so during venous bleeding there is no such pressure, the blood flows in a continuous stream, like water from a tap.
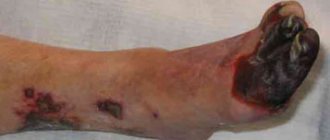
In case of arterial bleeding, you have no more than 3-8 minutes left
With arterial bleeding, the probability of death is greatest; with venous bleeding, death is unlikely; damage to large veins in the neck is dangerous. In case of bleeding from large arteries, those around you have no more than 3-8 minutes left. In such a short period of time, the ambulance will not have time to get there. Therefore, we drive away all fears, put plastic bags or rubber gloves on our hands if they happen to be nearby (so that in case something happens we don’t catch dangerous viruses), and look for points on the body to press the arteries with fingers. There are more than 10 such points on the body at which pulsation is felt on each side of the vertical axis of the body. We need to remember only three main ones: the carotid, brachial and inguinal arteries.
How to clamp the carotid artery
The carotid artery in the neck is to the right and left of the trachea. The pulse is clearly felt in this place. We feel and pinch this artery below the wound with our fingers. We compress the artery until the blood stops gushing out. If this happens, you did everything right. Do not under any circumstances reduce the pressure or remove your hand; the artery will be more difficult to find later.
And only after you have managed to stop the bleeding, Andrei Rogotnev advises you to do everything else: scream, call for help, ask passers-by to call an ambulance. If it is not possible to squeeze the artery with your fingers, you can secure a bandage (tourniquet, belt or piece of fabric) through the arm opposite to the wound. Thus, the artery will be compressed only on the side where the wound is. The most correct option is to compress the carotid artery until the ambulance arrives.
How to compress the brachial artery
We do the same with the brachial artery. The shoulder is the part of the arm from the elbow to the shoulder joint. Press your thumb against the inside of your shoulder to the bone and you will feel a pulsation. This is where you need to pinch the artery, clasping your hand with your thumb and forefinger until you find something to tighten it with. Motorists have a tourniquet in their first aid kit; in all other cases, you can use any available means - a shoe lace, a belt, a charger wire, etc.
How to clamp an abdominal artery
Bleeding from the abdominal artery (internal bleeding) can be stopped by pressing your fist on the abdomen in the navel area. You need to apply pressure towards the spine until the bleeding stops or decreases. Signs of internal bleeding: the person is pale and has a rapid heartbeat.
How to clamp the femoral artery
To stop arterial bleeding when the lower limb is damaged, you need to squeeze the inguinal fold between the thigh and lower abdomen with your fist. Here is another point of pressure on the artery.
The points for applying a tourniquet for injured limbs are the middle of the thigh or shoulder
If a limb is damaged, the artery should be pressed with a tourniquet above the wound. The points for applying the tourniquet are the middle of the thigh and shoulder. There is no point in applying a tourniquet to the lower leg or forearm (from the hand to the elbow), since here the arteries pass between two bones and stopping the bleeding is not guaranteed; significant force will need to be applied, which can damage the tissue.
If you are somewhere far from a populated area - in the forest or on the road - you should clamp the artery with a tourniquet for no more than 15 minutes. No more, otherwise a person risks losing an arm or leg. After 15 minutes, the tourniquet must be loosened without removing the last two rounds (turns of the tourniquet). We rest for the same amount of time as we walked, then tighten the tourniquet again and walk or drive further - to where we will receive medical assistance.
How hard should you squeeze the tourniquet?
Many people have a question: with what force should the artery be clamped with a tourniquet? We tighten the tourniquet until the bleeding stops, then fix it. It's better to try it yourself. The force should be minimal, as when squeezing with a tonometer cuff.
What to use instead of a tourniquet
Instead of a tourniquet, you can use fabric (scarf, shirt sleeve, trouser leg) or lace or bandage, with which you can make a “twist”. We wrap the bandage around the limb twice, tie a knot, but do not press it tightly to the hand, leaving a distance the size of a finger. Then insert a key, a pen or any stick and begin twisting until the bleeding stops.
Well, that’s actually all you need to know about stopping arterial bleeding. The main thing is not to faint at the sight of blood. Of course, you need to be mentally prepared for such situations in advance.
It is much easier to stop bleeding from a vein when the limbs are injured
With venous bleeding everything is much simpler. As soon as we understand that blood is running from the vein, we clamp the wound with a tight bandage, just as ordinary wounds are bandaged. The bleeding must stop.
If the tension of the tourniquet is weak, the blood flow from the vein will only increase
There are situations when people cannot understand whether blood is flowing from a vein or from an artery. At the same time they are trying to help. It should be remembered that when a tourniquet is applied, the bleeding should stop. If the tourniquet is loosely secured, the blood flow from the vein will only increase.
Yuri Shestak, Medical Information Agency NEDUGAMNET
External carotid artery
The paired organ provides brain tissue with 55 ml of blood per 100 g. tissue, and also saturates with oxygen molecules 3.7 ml per minute. Such provision is considered normal. The external artery in humans is located slightly higher from the larynx, closer to the face, and is part of the front of the head.
In the area of the Adam's apple, the artery diverges to the front and back of the head. The first directs blood flow to the eyeballs, the second to the brain cells. The external artery consists of:
- front end;
- medial part;
- rear end;
- terminal branches - a system of capillaries directed to the eyes and into the oral cavity.
Proof of the presence of a capillary network is the redness of the face. In stressful situations, excessive physical strain, and hot weather, blood rushes to the skin. For some, this effect is practically unnoticeable, for others it is clearly pronounced. This is influenced by genetic predisposition, skin properties, etc.
The external artery directs blood to the following organs:
- thyroid;
- auricles, tympanic cavity;
- eyes;
- facial muscular system, ligaments;
- skin of the face and head;
- some parts of the meninges, the occipital vessel;
- roots of teeth, soft palate, lingual vessels.
The branches of the external artery do not send blood directly to the brain. However, pathologies in the functioning of blood vessels can lead to negative consequences. All that can be done if the external artery is malfunctioning is to contact a neurosurgeon.
In some cases, plastic surgery is required. What diseases can appear if the artery malfunctions:
- Benign tumors in the facial and cervical regions.
- Arteriovenous pathology is the connection between an artery and a vein (blood does not flow into many capillaries).
- Congenital malformation of blood vessels. Signs are external facial defects, migraines and regular pulsation in the head at night, bleeding from large arteries that cannot be stopped.
As a rule, such diseases arise due to dangerous facial injuries, plastic surgery on the nose, ears, throat, etc. Also, there is a high probability of pathologies occurring due to improper implementation of basic procedures.
For example, aesthetic punctures, rinsing the sinuses, tooth extraction, cosmetic injections in the eye area. Rare cases of the disease can cause hypertensive complications.
Atherosclerosis with thrombosis of the anterior cerebral artery
Atherosclerotic deposits in the lower segment of the anterior cerebral artery rarely give pronounced clinical symptoms of neurological deficit, since blockage of the lumen (occlusion) is compensated by collateral blood flow through the anterior communicating artery. The likelihood of a transient ischemic attack (TIA, microstroke) and stroke increases if the path of collateral blood flow is characterized by a congenital fusion (atresia) or if there are atherosclerotic changes in a higher section of the anterior cerebral artery.
Internal carotid artery
The branch of the internal artery is directed through the temporal bone. The strength of blood flow increases due to external and internal factors. The number of oxygen molecules entering the brain with the blood exceeds the norm and a person feels a surge of strength, energy for work and other vigorous activities.
But a long process can lead to the opposite - a person feels a loss of strength, drowsiness and fatigue. Oxygen must be supplied normally - excess or deficiency harms the body. Components of the internal artery:
- cavernous - in the dura mater;
- cervical - located deep under the muscle layer;
- part in a torn hole;
- brain;
- stony - laid in the bone canal.
The artery runs laterally, along the edge of the pharynx, parallel to the ear gland. It is divided into small vessels. The complex system supplies brain cells well with oxygen. In the cranium, the branch of the clivus and the pituitary vessel depart from the internal artery. Small arteries are directed to:
- gray matter;
- nuclei of the medulla oblongata;
- white matter;
- cortical parts.
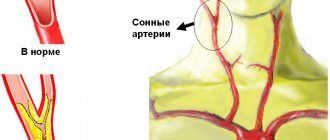
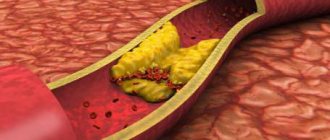
Pathological deformations of the carotid artery Lack of treatment for diseases such as atherosclerosis, syphilis, tuberculosis can lead to deformation of the artery. Against the background of inflammatory processes, internal tissues begin to grow, and the lining of the artery ruptures, letting blood into the area between the walls.
As a result, medical intervention can lead to narrowing of the artery, as a result, a lack of oxygen molecules provokes an ischemic stroke. The narrowing can also cause other health problems - an internal artery that twists incorrectly, or splits into three, a blood clot, or an aneurysm.
Causes and prevention
The causes of vasoconstriction are being actively studied, but there is still no clear understanding. A hereditary cause is identified, and everything else can be attributed to risk factors. Among them:
- arterial injuries,
- obesity,
- smoking,
- diabetes,
- sedentary lifestyle,
- older age,
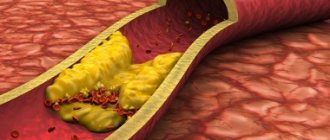
- high level of “bad cholesterol” in the blood (low-density lipoproteins are a combination of cholesterol and protein that do not take excess cholesterol from the vessels, but, on the contrary, attach them to the walls, forming cholesterol plaques).
Prevention of carotid artery stenosis, like any other arteries, consists of maintaining a healthy active lifestyle and a balanced diet to prevent an imbalance in the ratio of low- and high-density lipoproteins, and therefore the development of atherosclerosis.
Concept of carotid artery aneurysm
An aneurysm is an increase in the size of a small area of an artery with an accompanying thinning of its lining. This is a very dangerous disease that can be fatal if the walls of the vessel rupture. Aneurysm can be congenital or acquired, due to muscle atrophy, prolonged inflammatory processes, etc.
What can cause a wall rupture:
- stress, prolonged nervous and physical tension;
- sudden surges in pressure;
- injury to the cervical spine or head.
Blood gradually builds up after the rupture, putting pressure on the surrounding brain tissue. Very often death occurs, but in the case of a small hematoma, the situation can be corrected with surgery.
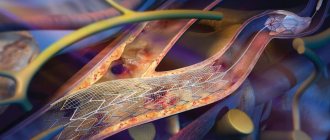
Pain relief during stenting
The intervention is performed under local anesthesia using light sedatives, since it is necessary to assess the patient’s neurological status during stenting. When the balloon is inflated, the patient may experience a slow heart rate (bradycardia) and a decrease in blood pressure (hypotension), so continuous monitoring of cardiac activity during surgery is necessary.
The patient lies on his back, with his arm abducted, on which a blood pressure cuff is attached. The electrodes of the device for taking a cardiogram are glued to the chest. The surgical field is processed and the patient is covered with a sterile sheet.
Artery disease - thrombosis: concept and characteristics
Thrombosis is a disruption of normal blood circulation in the brain. As a rule, a thrombus forms at the site where the artery branches into external and internal. In this area, blood does not move as intensely, which allows platelets to form deposits on the walls of blood vessels. What can affect platelet formation:
- congenital or acquired heart disease;
- brain damage;
- increased blood clotting;
- an autoimmune hypercoagulable state associated with the production of antiphospholipid antibodies;
- a disease associated with heart rhythm disturbances - sudden excitation and slowdown.
How does thrombosis manifest itself, symptoms:
- without any symptoms;
- sharp pain;
- subacute;
- chronic.
The patient experiences tinnitus, migraines in the head, constant pain in the cervical spine, blurred vision, the inability to chew normally due to muscle problems, and possible loss of consciousness.
Thrombosis of the internal carotid artery is characterized by a lack of sensation in the limbs, nervousness, hallucinations, inability to speak normally, and skin pain on the head. If a section of the intracranial artery is damaged, vomiting, lack of sensation in the limbs, and sleep disturbances are possible.
How to identify problems with the carotid artery When visiting a clinic, an accurate diagnosis can only be made based on research:
- Magnetic resonance angiography.
- Rheoencephalography.
- Electroencephalography.
- Computer tomography.
- Ultrasound examination of blood vessels.
Course of the disease
Once atherosclerotic plaques appear, they will no longer be able to resolve, but only gradually progress. The rate of growth of an athersclerotic plaque depends on many risk factors, including cholesterol levels. All people over 50 years of age are recommended to undergo an annual ultrasound of the carotid arteries in order to exclude the development of atherosclerotic plaques and the risk of ischemic stroke.
With the development of complications of atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries, discirculatory encephalopathy quickly progresses. Frequent TIAs, and even more so ischemic stroke, contribute to the death of part of the brain tissue and disruption of brain function. Patients with atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries often develop vascular dementia (dementia).
After restoration of the patency of the carotid artery, the phenomena of cerebrovascular insufficiency are stopped, and the likelihood of repeated cerebrovascular accidents is significantly reduced.