- home
- Articles
- Schedule of illnesses
- Do they take you into the army with tachycardia?
»
»
»
Updated: September 12, 2021
Military service requires excellent health. Conscripts are checked by a whole commission of doctors who, based on the results of the examination, give a conclusion on their suitability for service or issue a certificate of deregistration. But not everything is so simple; the presence of a deviation from the norm does not guarantee a deferment. Before going to the military registration and enlistment office, it is better to find out in advance whether a person with heart tachycardia is accepted into the army if such a disease is diagnosed in a person.
Types of tachycardia
Tachycardia is a rapid heartbeat when the heart rate is higher than the general norm. Ideally, the heart should beat in the range of 60 to 90 beats per minute. If the frequency is higher, it is considered a deviation. But the diagnosis of tachycardia is made only if the number of beats is above 100 beats per minute. If the beat rate is below 60, bradycardia is diagnosed.
The disease is divided into two main categories:
- Paroxysmal tachycardia. Appears in the form of flashes. Heart palpitations increase in attacks that cannot be predicted or appear under special circumstances. In this case, the frequency of impacts can be different and varies from 120 to 220 times per minute.
- Non-paroxysmal tachycardia. Unlike paroxysmal, it is characterized by constant accelerated heart function. Such a diagnosis can also be made for those who do not have arrhythmia diagnosed all the time, but often, at least 50% of the time.
The disease is usually divided not only into types, but also into forms. In total, there are three main generalized concepts in tachycardia:
- sinus;
- supraventricular;
- ventricular
In turn, supraventricular is divided into sinoatrial reciprocal tachycardia, atrial, AV nodal reciprocal and WPW syndrome.
Sinus tachycardia is not considered a pathology. It can be registered in people of any age and gender with an absolutely healthy sinus node. Typically, an acceleration of the heart rate to 100 or higher is recorded as a normal response of the body to physical or emotional stress.
ATTENTION. Rapid heartbeat can occur as a concomitant symptom of various diseases, for example, flu or fever. The higher the body temperature, the greater the number of heart contractions.
Cardiac arrhythmia can also be a sign of increased levels of thyroid hormones or decreased hemoglobin levels, as well as other pathologies. The diagnosis of sinus tachycardia is made on the basis of an ECG.
Along with tachycardia, extrasystole can be diagnosed. This is an extraordinary contraction of the atria or cardiac node. This diagnosis is made most often.
Pathological extrasystoles lead to impaired blood circulation, which in turn negatively affects cerebral and cardiac blood flow.
Will they be drafted into the army or exempt from conscription?
The army does not accept conscripts with the following diseases of the cardiovascular system:
- acute heart failure, stable chronic disorders of cardiac muscle contractions;
- paroxysmal tachycardia, cardiac conduction failure, sinus node deficiency, prolonged heart rate disturbances;
- cardiosclerosis, mitral valve prolapse, heart disease;
- heart surgery;
- primary prolapse, a mild form of heart failure.
If sinus tachycardia is not accompanied by other diseases, the conscript cannot count on the non-conscription category.
If there are signs of heart failure and other disorders of the heart that arise as a result of physical exertion, non-compliance with a special diet, stressful situations, disturbances in sleep and rest, a young man of military age can receive a deferment for treatment of the pathology or be released from military service and enlist in the reserve.
The decision to grant a deferment or release from service is made by the medical commission after determining the nature (physiological or pathological) of the occurrence of sinus tachycardia. The cause of a rapid heartbeat can be diseases of the nervous and endocrine systems; if there is evidence of them, the conscript is released from the army.
Another serious symptom for exemption from military service is a constant increase in heart rate. To receive a non-conscription category, a young man must submit a diagnosis and the necessary medical certificates for examination at the military registration and enlistment office.
Exemption from the army due to pathological tachycardia
When determining the degree of suitability, the medical commission at the military registration and enlistment office is guided by Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 53-FZ “On Military Duty and Military Service” dated March 28, 1998.
A conscript is released from military service only if the diagnosed disease is included in the list approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 565 of July 4, 2013. It includes dozens of different diseases, ranging from deafness to flat feet. But there is no definition of “pathological tachycardia” in it. But this does not mean at all that a sick person will be obliged to serve.
According to the rules of military medical examination, exemption is issued not on the basis of tachycardia, but on the reasons that caused it. The fact is that an elevated heart rate is only a symptom, and the diagnosis is usually completely different.
If the illness resulted in a violation of cardiac function, then the person will be exempt from conscription.
If the conscript has not previously complained about health and has not been registered with a doctor, then the detected deviations will not become a reason for evading service in the armed forces of the Russian Federation. REFERENCE. Diagnosis of minor deviations will only lead to a note in the personal chart and a doctor’s recommendation about the need to send the guy to serve in the troops with less physical activity.
Eligibility criteria for a conscript with tachycardia
You can talk about tachycardia if your heart rate (HR) is more than 90 beats within one minute when lying down and 100 when sitting or standing. The condition is not an independent diagnosis; it is sometimes considered as a variant of the norm.
Types of tachycardias and their features
A rapid heartbeat can occur in an absolutely healthy person after several cups of coffee, intense physical activity, or during severe anxiety. Doctors consider such conditions to be physiological, and those with such tachycardia are recruited into the army.
Pathological heart rhythm disturbances are distinguished:
- For the reason: caused by cardiac diseases and non-cardiac diseases - as a complication of the pathology of other organs and systems (thyroid gland, lack of oxygen, low level of potassium in the blood, hypoglycemia, anemia).
- By type: paroxysmal (suddenly beginning and just as abruptly passing) and non-paroxysmal (constant, sometimes alternating with a normal or moderate rhythm).
- According to the form (depending on the location of the source of disturbance in the excitability of the myocardial pathways): supraventricular (supraventricular) and ventricular.
Tachycardia threatens health and life because an incorrect rhythm leads to inadequate blood ejection. Overstretching of the myocardium occurs, and this can cause heart failure. When an arrhythmia is detected in a conscript, the medical commission of the military registration and enlistment office decides strictly individually whether the young man is subject to conscription or not.
If you want to know everything about tachycardia, we recommend watching the video below at the link. Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and signs that it’s time to see a doctor - talk about all this in 7 minutes. Enjoy watching!
Eligibility criteria for service
The requirements for the health of those liable for military service are set out in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 4, 2013 No. 565; for simplicity, we will call it Decree 565. I advise you to carefully read this document. It details the criteria by which a medical commission determines suitability for military service.
I advise you not to limit yourself to studying only the cardiology section. The list of diseases of Decree 565 includes diseases that can cause tachycardia of non-cardiac etiology. For example, Article 13, which lists diseases of the endocrine system, indicates that if a conscript’s heart rate is more than 120 beats per minute, a medical commission will consider assigning him category D or B.
If you are categorized as:
- A or B – you won’t be able to avoid service. Category B provides only some restrictions on the type of troops.
- B or D – limited fit and temporarily unfit. You may be given a delay of a couple of months to treat the disease. Perhaps they will not be drafted in peacetime, but they will issue a military ID and enroll in the reserves.
- D - the army does not threaten you. A military ID is still issued, but a note is made on it and in your passport that you have contraindications for serving.
In Decree 565 in the section “Diseases of the circulatory system” you will not find the diagnosis “tachycardia”. Carefully review the list of diseases that cause arrhythmias. The table below will make your search easier:
| Article in the disease schedule | Main diagnosis | Type of tachycardia as a complication of the underlying disease | Suitability category |
| 42 | Rheumatism, other rheumatic and non-rheumatic heart diseases | Paroxysmal ventricular tachyarrhythmias | D |
| If palpitations continue for more than 7 days and return after a course of antiarrhythmic drugs | D or B | ||
| 44 | Cardiac ischemia | ||
| 45 | Congenital anomalies of the heart and blood vessels | ||
| 47 | Neurocirculatory asthenia | Persistent tachycardia, not corrected by treatment, significantly reducing ability to work | B or C (the medical commission decides individually) |
| 48 | Circulatory dysfunction after illness, injury, surgical treatment | Tachycardia persists as a complication | G (a decision is made to postpone) |
Sinus tachycardia and the army
This type of rhythm disorder is most common in young people. Conscripts and their parents mistakenly believe that this diagnosis entitles them to exemption from military service or a deferment. I will try to explain why this is not entirely true. The sinoatrial node is located inside the wall of the right atrium. It is the main pacemaker, the generator of the excitation impulse, due to which contraction of both the atria and ventricles occurs.
Sinus tachycardia is called tachycardia, in which there are no disturbances in the conduction system of the heart. In other words, the body's main pump is functioning correctly, but too quickly. This does not mean that the condition is not dangerous. A person suffers from “fluttering” inside the chest, shortness of breath, dizziness, and impaired performance.
Mandatory medical supervision and adequate therapy are required. But Resolution 565 does not distinguish the diagnosis of “sinus tachycardia”. Therefore, the number of heart beats per minute matters. If your heart rate exceeds 120, continues continuously for more than a week, and cannot be corrected with medication, you have the right to count on category D, B or G.
Mitral valve prolapse and military service
The second diagnosis that is of interest for obtaining a deferment or exemption from the army is mitral valve prolapse (MVP). The condition is a bulging of its valve at the time of systole into the atrium cavity. It is considered a clinical and anatomical syndrome. It may be either a congenital pathology or a result of heart disease.
One of the complications of MVP is permanent or transient heart rhythm disturbances.
According to Resolution 565, you can avoid military service if your mitral valve prolapse is accompanied by:
- sinus tachycardia more than 120 beats per minute;
- paroxysmal tachycardia;
- atrial fibrillation or flutter;
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
In the first degree of MVP, which proceeds without complications, there is no delay. Some conscripts, wanting to get into the elite troops, try to hide from the medical commission the presence of mitral valve prolapse, which I strongly advise against doing. With excessive physical exertion, a mild degree of MVP can transform into a more severe one and pose a threat to the health and life of a young person.
Will they be accepted into the army with sinus tachycardia in 2021?
The diagnosis of sinus tachycardia is very common in young people. If this syndrome was identified in the hospital and treatment was prescribed, this does not mean that liberation is in your pocket. In 2021, people with this pathology will be accepted into the Russian army.
During active puberty in guys, rapid heartbeat can be caused by an excited nervous system, increased anxiety and other symptoms. This is not a disease as such and goes away over time, although it still poses a health hazard. That is why it is better not to delay therapy until passing a military medical commission, but to start it earlier. The conscript will still be accepted into the army, but if he has the specified condition, he will be subject to mandatory medical supervision.
Procedure for passing a medical examination
The pathological form of tachycardia is one of the common problems encountered in young men of military age.
A conscript who knows that he has health problems must come to the military registration and enlistment office, bringing with him the entire list of documents confirming the presence of the disease. Important documents include certificates, clinical tests, examination results, confirmation of periodic visits to the doctor.
The examination at the military registration and enlistment office is carried out in accordance with the available documents. If controversial issues arise, as well as in the absence of the necessary medical certificates and the conclusion of the attending physician, the conscript is sent for additional examination. The results of the re-examination and examination are considered final for the medical commission to make a verdict.
This is the only way to 100% count on being written off to reserve.
Problems with exemption from the army may arise for those young people who previously, before the medical examination, did not consult a doctor because they had a disease. The position of the conscript against the opinion of the military commissariat may turn out to be weak if the young man does not have documents from the medical institution where he was observed before passing the commission from the military registration and enlistment office.
If this is the case, then it is better for the conscript to seek help from lawyers in order to undergo an examination with doctors recommended by legal experts before the medical examination so that they can make the correct diagnosis. With this diagnosis, the military commissariat will definitely send the conscript for additional examination in order to confirm it and assign the failed recruit a fitness category and write him off to the reserve.
Cases where the rights of conscripts declaring their diagnosis at a medical examination are violated occur in judicial practice. If the interests of a young man are represented by a lawyer, the lack of documents proving early visits to a doctor will not be an obstacle to obtaining a military ID. It is only important to have time to take advantage of this opportunity to protect your civil rights.
Arrhythmia and the army
What are the general eligibility categories?
- G - fit for service;
- GO - fit for service with minor restrictions;
- VN - temporarily unusable;
- GPS - unfit for service in peacetime;
- NGI - unfit for service with exclusion from military registration;
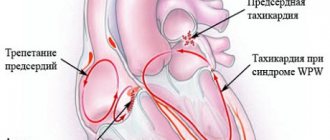
All types of arrhythmias are classified under article 42 of the disease schedule.
Sinus arrhythmia and pacemaker migration are not grounds for the application of this article.
The NGI fitness category will be assigned if a conscript is diagnosed with paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia, paroxysms (3 times a year or more often) of supraventricular tachycardia.
suitability category includes paroxysm of supraventricular tachycardia based on 24-hour monitoring.
To determine the exact diagnosis and fitness category, you should contact a specialist, and then, in accordance with Article 42 of the disease schedule, the exact fitness category is assigned.
What is tachycardia, its types
In medicine, tachycardia is understood as a rapid heart rate that exceeds 90 beats in 60 seconds if a person is in a lying position, or 100 beats when a person is standing.
There are pathological and physiological tachycardias. The first talks about pathological changes in the body, the nature of which is important to find out in order to help a person in a timely manner. Physiological tachycardia is natural for anyone, because it shows the presence of a reaction to various external stimuli.
Physiological tachycardia does not exempt you from service, but pathological tachycardia provides grounds for a more thorough examination of the health of a young man applying to become a recruit in the army.
The final decision is made depending on what diagnosis is made by cardiology doctors.
What troops can you serve in?
If a conscript with a mild form of arrhythmia is declared fit without restrictions, assignment to the troops will be made randomly.
If limited fitness has been assigned, next to the main category a number must be indicated indicating the group of troops to which this category applies. Categories “B” are as follows: “B-1”, “B-2”, “B-3” and “B-4”.
Arrhythmia almost always falls into the “B-3” category. This is the most extensive category of fitness, because it includes most conscription diseases without significant impairment of functions. With fitness category “B-3” they are called to:
- drivers of infantry fighting vehicles and armored personnel carriers;
- missile launch installations;
- internal troops of the Ministry of Internal Affairs;
- pipeline troops and other chemical work;
- control and operation of anti-aircraft missile systems.
Reviews
Dear readers, was this article helpful? What do you think about the compatibility of sinus tachycardia and military service? Leave feedback in the comments! Your opinion is important to us!
Sergey
“A rapid heartbeat appeared after minor exertion. Walking in the cold air and doing housework caused a lot of inconvenience. I was examined by a doctor: sinus tachycardia was discovered. With the documents I already had, I presented myself to the military registration and enlistment office for examination. Since there were no concomitant diseases, and sinus tachycardia was not considered a reason for exemption, it was not possible to avoid service in the Armed Forces.”
Yuri
“Sinus tachycardia was one of the symptoms of an endocrine system disease. The diagnosis was confirmed, I was given an exemption from peacetime service, and was enrolled in the reserves.”
How does a military medical commission decide on the fitness of a conscript?
The main task of the commission at the military registration and enlistment office is to compare the conscript’s diagnosis with the Schedule of Diseases and provide a fitness category based on this comparison. Doctors from the military medical commission can conduct a visual examination, interview the conscript and study his medical records.
During a medical examination at the military registration and enlistment office, the conscript undergoes electrocardiography, which cannot fully reveal the dynamics of the disease, since tachycardia can be episodic, transient. Monitoring or Holter ECG, which is performed by attaching electrodes to the patient for 12 hours, is effective. The cardiogram will be recorded on a special device. After the monitoring time has expired, the ECG data is transferred to a computer and decrypted. The method allows you to record the slightest episodic or permanent violations, giving the medical board the opportunity to make the right decision and determine whether a conscript with a given complexity of tachycardia can serve in the army.
Symptoms of tachycardia
May manifest itself in diseases of the cardiovascular system: coronary heart disease (CHD), cardiosclerosis, heart failure, arterial hypertension, heart defects, severe angina; disruption of the endocrine system: thyrotoxicosis, hyperthyroidism and nervous system.
Main manifestations:
- Feelings of strong heartbeat;
- Shortness of breath, dizziness;
- Pulsation of neck vessels;
- General weakness.
Pathological forms of tachycardia are classified under article 42 of the schedule of diseases of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Belarus.
What are the general eligibility categories?
- G - fit for service;
- GO - fit for service with minor restrictions;
- VN - temporarily unusable;
- GPS - unfit for service in peacetime;
- NGI - unfit for service with exclusion from military registration;
For contract military personnel
- State Tax Service - fit for service outside the formation in peacetime
- IND is a fitness category determined individually for a conscript.