A pathological condition in which a person’s heartbeat rhythm is disturbed is called arrhythmia. Arrhythmia is divided into two types - tachycardia (increased rhythm) and bradycardia (slowed rhythm). It is often difficult for a non-specialist to understand from his own feelings how tachycardia and bradycardia differ.
What do these terms mean?
Arrhythmia is a disorder of the conduction system of the heart with disruption of the formation and conduction of electrical impulses.
As a result, irregular contractions of the myocardium occur. Tachycardia is characterized by a uniform frequency, but at the same time the heart rate increases, reaching 90 or more beats per minute. Normally, such a reaction of the body can occur in response to stress or physical overload. Depending on the location of the impulse during arrhythmia or tachycardia, they can be:
- sinus;
- atrial;
- ventricular;
- atrioventricular.
Any deviation from the normal frequency and uniformity of heart contractions is considered an arrhythmia. This broad concept includes:
- increase or decrease, as well as uneven generation of impulses from the main source (sinus bradycardia, tachycardia and arrhythmia);
- extrasystole;
- flutter, atrial or ventricular fibrillation;
- ectopic rhythms;
- conduction disturbances (asystole, blockades, premature excitation of the ventricles);
- sick sinus syndrome.
The concept of arrhythmia is broader and includes all types of heart rhythm disturbances, including tachycardia.
Difference in origin
Arrhythmia and tachycardia have a similar origin, so the reasons why they occur are usually the same. Physiological rhythm disturbance occurs in the following cases:
- strong emotional shocks;
- hard physical labor;
- playing sports;
- eating disorders;
- lack of sleep;
- use of caffeinated drinks;
- lack of microelements;
- sudden changes in ambient temperature.
All pathological causes of arrhythmia or increased myocardial contractions can be divided into cardiac and extracardiac. In the first case, the main disease is:
- Inflammatory processes (myocarditis, pericarditis).
- Ischemic disease (angina pectoris).
- The appearance of scars as a result of post-infarction or cardiomyopathic sclerosis.
- Valve defects.
- Chest injuries.
Deviation from normal sinus rhythm can also occur in the case of other diseases or conditions:
- Excessive consumption of cardiac glycosides, diuretics and antiarrhythmic drugs.
- Diseases of the endocrine system with increased production of adrenaline, thyroid and adrenal hormones.
- Poisoning with heavy metals and other toxic substances.
- Severe infections with severe fever and intoxication.
- Excess of harmful substances in the blood due to kidney or liver failure.
- Consumption of drugs, alcohol, smoking.
In some cases, a violation of the rhythm of contractions occurs for an unknown reason, then they are considered idiopathic.
The main difference between arrhythmia is the unevenness of the intervals between contractions of the heart muscle. With tachycardia, the intervals are the same, but their frequency reaches 90 or more beats/min.
Signs and complaints
The patient’s subjective sensations during the development of both pathologies usually do not differ; he makes the following complaints:
- shortness of breath, lack of air;
- fatigue, darkening of the eyes, dizziness;
- pain behind the sternum on the left.
With arrhythmia, some patients feel separate beats or beats on the heart. Tachycardia is perceived as strong and frequent tremors. In many cases, deviations occur without obvious symptoms and can only be determined with additional research methods.
Signs of violations usually include:
- uneven and (or) rapid pulse;
- paleness of the skin;
- blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle;
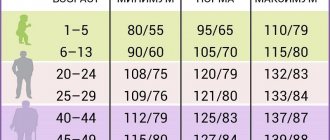
- decrease or increase in pressure.
The most objective way to detect pathology is an ECG. In the case when a person’s rhythm is disturbed episodically, Holter monitoring is used to record an attack.
Tachycardia from the sinus node on the cardiogram looks like this:
You can read a detailed description of the signs and symptoms of sinus tachycardia, as well as get specialist recommendations for this disorder here.
Diagnosis of tachycardia and bradycardia
When visiting a therapist, the doctor will prescribe a number of tests. The main type of diagnosis of arrhythmia is an ECG. There are many ECG signs to identify one or another type of arrhythmia. After the doctor determines what type of arrhythmia is developing in the patient, he will prescribe the optimal treatment.
The Medicenter clinic network employs qualified cardiologists and has modern equipment installed. With us you can undergo a comprehensive examination, establish or confirm your diagnosis and receive treatment recommendations.
Action tactics: what's the difference
If abnormalities of a physiological nature occur in the functioning of the heart, treatment is usually not required. It is enough to eliminate the cause of their appearance, and everything returns to normal. It’s another matter if the etiological factor is a disease. In this case, it is necessary to carry out full-fledged treatment, the goal of which is to completely eliminate the disease or transfer the pathology to a state of stable remission.
We remove provoking factors
To normalize the rhythm, it is recommended to remove factors that contribute to the appearance of tachycardia or arrhythmia:
- Review your diet. Eat often and in small portions, exclude spicy, salty, and caffeinated drinks from your diet.
- Try to avoid physical and psycho-emotional overload.
- Observe the work and rest schedule.
- Take walks at an average pace and breathe clean air.
- Stop drinking alcohol and quit smoking.
Paroxysmal tachycardia can be stopped by acting on the vagus nerve. For this purpose, pressure on the eyeballs and massage of the sinocarotid zone are used.
You can get more detailed information about what tachycardia is, what its types are, and also find out how to eliminate the pathology here.
We use medications
Medicinal methods include the use of the following medications:
- sedatives (motherwort, Valocordin);
- beta blockers (Atenolol, Bisoprolol);
- calcium antagonists (Amlodipine).
You can add herbal decoctions to general therapy. Chamomile, valerian, and hawthorn are used to improve cardiac activity. But they should not be used as the main means of stopping an attack.
A detailed description of tablets and other medications, as well as the features of their use for tachycardia, can be seen by going here.
Surgical treatment of severe pathology
Severe forms of rhythm and conduction disorders require the use of surgical treatment methods. Depending on the cause, the specialist recommends the following radical methods:
- radiofrequency ablation;
- installation of an artificial pacemaker;
- implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator;
- valve restoration;
- shunting for blood flow problems.
The prognosis for arrhythmia depends on the etiological factor of its occurrence. But in general, compared to tachycardia, it is more severe and more often leads to various complications and even death.
If you want to know everything about tachycardia, we recommend watching the video below at the link. Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and signs that it’s time to see a doctor - talk about all this in 7 minutes. Enjoy watching!
Heart pounding (cardiac arrhythmia)
It happens that “the heart beats in the chest like a bird” or “like an autumn leaf trembles.” And sometimes “it will clog up, then it will freeze.” In medical language, all this is called cardiac arrhythmia. Heart contractions become irregular and irregular. There are different types of arrhythmias, but one of the most common is atrial fibrillation. It is known that with each heartbeat there is a sequential contraction of its parts - first the atria, and then the ventricles. Only such alternation ensures efficient functioning of the heart. With arrhythmia, which has received the beautiful name “atrial fibrillation,” one of the phases of the cardiac cycle disappears, namely, atrial contraction. Their muscle fibers lose the ability to work synchronously. As a result, the atria only twitch chaotically - flicker. As a result, the ventricles begin to contract irregularly.
Why does atrial fibrillation occur?
There are many reasons that can lead to this disease. For example, various heart diseases: hypertension and some heart defects, infectious heart disease and heart failure, coronary heart disease (CHD) and its dangerous complication - myocardial infarction. In young people, the cause of arrhythmia is often mitral valve prolapse, that is, sagging, weakness of one of the valve leaflets between the left atrium and the left ventricle. This pathology usually occurs latently and is detected accidentally. Atrial fibrillation may be its first manifestation.
But the cause of arrhythmia is not only a diseased heart. A variety of diseases can give it a start. And not only diseases. · Very often, an attack of atrial fibrillation is provoked by drinking more alcohol than usual. There is even such a concept - “holiday cardiac arrhythmia.” · On any given day, you can expect arrhythmias to appear in people with thyroid disease (especially those with excessive thyroid function) and some other hormonal disorders. · Arrhythmia often develops after surgery, stroke, or various stresses. · Its development can be provoked by rich food, constipation, tight clothing, insect bites, and some medications. · Taking diuretics to lose weight often lands “your own doctor” in a hospital bed. · There is a high risk of developing atrial fibrillation in people with diabetes, especially if diabetes is combined with obesity and high blood pressure. However, doctors are not always able to determine the cause of the arrhythmia. How to find out about the onset of the disease? It is signaled, for example, by palpitations, when the heart is pounding so much that it seems like it is about to jump out of the chest. There may be a feeling of interruptions in the heart. “It will knock, knock, and suddenly freeze,” or “something will turn inside” - this is how patients describe their condition. But often the arrhythmia goes unnoticed. Only by feeling the pulse can you establish the irregularity of heart contractions. Often the disease is detected only during a clinical examination using an ECG. But it can be worse: the first manifestations of the disease are complications. Why is atrial fibrillation dangerous? It is often accompanied by tachycardia, that is, an increase in heart rate. At the same time, a colossal load falls on the heart. As a result, chest pain may appear - symptoms of angina pectoris or even myocardial infarction. Arrhythmia may reduce the efficiency of the heart. This will lead to another complication - heart failure. At the same time, the person feels suffocated; it seems to him that there is not enough air. Can arrhythmia go away on its own? In principle, it can. But if the arrhythmia persists for several hours or complications arise, you should immediately seek medical help. However, even if the arrhythmia disappears on its own, you should not postpone your visit to the doctor. Repeated rhythm disturbance can occur at any time and end tragically. Therefore, self-medication will not help much. As a good song says: “No matter how much you treat the heart with validol, there are still continuous interruptions.” The fact is that restoration of normal rhythm is best done on the first day from the onset of arrhythmia. It is possible to eliminate arrhythmia later than this period, but then additional preparation will be required. With atrial fibrillation, when the atria do not contract normally, the blood flow in them sharply slows down, and therefore blood clots - thrombi - form. This occurs on the second day after the onset of arrhythmia. When the normal rhythm is restored and the atria begin to contract, fragments of blood clots can break off and clog the vessels of any organ. Typically, blood clots “float” into the vessels of the brain. And this leads to a stroke. That is why anyone who consults a doctor more than 24-48 hours after the onset of arrhythmia is prescribed drugs that slow down blood clotting. Only when the effect is obtained, after about 1-2 weeks, is it possible to restore the rhythm. How is normal heart rhythm restored? There are many techniques. The most effective is restoring the rhythm using an electrical discharge. The procedure is performed under anesthesia, so it does not cause any discomfort. Often doctors are able to eliminate arrhythmia with drug injections. It is much more difficult to select an antiarrhythmic drug to maintain a normal heart rhythm. And here a lot depends on you: strictly following the doctor’s instructions is already half the success, since each new attack of arrhythmia is more difficult to bear than the previous one. Can atrial fibrillation persist for a long time and is it dangerous? There are two main forms of arrhythmia: paroxysmal, which manifests itself in individual attacks, and constant, when atrial fibrillation persists for years or even decades. Of course, persistent arrhythmia threatens great complications, especially if accompanied by tachycardia. But here regular use of medications that slow down the heart rate helps. Is it harmful to take pills all the time? It’s a shame that even in our enlightened age people prefer to get sick so as not to “contaminate the body with chemicals.” It is safe to say that refusing treatment will cause much more harm to the body. You need to take special care of your heart. It is not for nothing that it was called the “heart,” that is, the core, the center of life.
Alexey Erlikh, cardiologist Family doctor