Tachycardia - an increase in heart rate from 90 beats per minute. This form of arrhythmia causes frequent visits to cardiologists. Often, after conducting a series of diagnostic studies, the doctor refers the patient to a neurologist or vertebrologist for further treatment. In such patients, thoracic or cervical osteochondrosis is detected, in which tachycardia and accompanying symptoms often occur. This is a rapid heartbeat, discomfort, a feeling of heaviness or pain in the heart area.
Features and causes of tachycardia in osteochondrosis
Pathologies of the musculoskeletal system and rapid heartbeat are interconnected either through pinching of the spinal nerves (spinal roots), or through their mechanical damage. In all cases, the cause of tachycardia is destructive and degenerative changes in the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs.
Vertebral displacement.
As a result of instability of the cervical vertebrae due to their displacement relative to each other, the vagus nerve is affected. The following signs of damage are observed:
- irritation of nerve tissue;
- development of a secondary inflammatory process;
- degenerative changes at the cellular level.
All this provokes a disorder of myocardial innervation, leading to a disruption of the rhythm of contractile activity. But most often, tachycardia occurs with thoracic osteochondrosis, when the patency of the radicular nerve changes. In addition to rapid heartbeat, patients complain to the doctor of severe pain in the cardiac region, radiating to the left arm.
How is cervical osteochondrosis related to tachycardia?
The myocardium or coronary circulatory system is directly innervated by nerves that are absent in the cervical spine. However, osteochondrosis often provokes tachycardia. This is explained by the location in the neck of the tenth pair of cranial nerves and the vagus nerve, which innervates the internal organs. Therefore, the following factors predispose to the appearance of tachycardia in cervical osteochondrosis:
- thinning, compaction of the intervertebral discs, which leads to their displacement, narrowing of the spinal canal and disruption of the patency of the nerves emanating from the brain;
- compression by bone growths, displaced discs or muscle spasms of the vertebral artery, leading to a deterioration in the blood supply to the brain with oxygen and nutrients;
- deformation of the neck as a result of the formation of a hernial protrusion or protrusion;
- tension in the skeletal muscles of the cervical-collar area, provoking persistent infringement of the cranial nerves.
Muscle spasms in cervical osteochondrosis are stable, so there is a constant disruption of the blood supply to all parts of the brain. This leads to disruption of the regulation of all vital systems, including the cardiovascular system. To minimize the effects of narrowing of the vertebral artery, the body requires more effort to maintain blood supply, which leads to increased heart rate.
How are other types of osteochondrosis related to tachycardia?
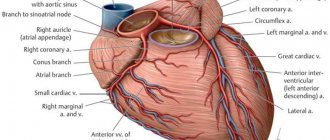
If at the initial stage of development of thoracic osteochondrosis, tachycardia is only one of the symptoms, then in the absence of treatment, damage directly to the myocardium occurs. This is due to the peculiarities of innervation. In the thoracic region there are spinal roots that innervate not only the heart muscle, but also the entire coronary system. Oxygen and nutrients are supplied to the myocytes through the blood vessels. A disorder of innervation can cause deterioration of blood circulation, oxygen starvation of cardiac muscle cells, and subsequently their death.
Infringement of the radicular nerves located in the thoracic region disharmonizes the work of arterial and venous vessels. In the normal state of the spinal column, they function as follows:
- the artery wall contracts;
- a nerve impulse is formed, which travels along the nerve fiber to the vein;
- the venous vascular wall contracts.
Radicular syndrome.
But when blood circulation is impaired, the transmission of nerve impulses is disrupted, so the heart begins to beat faster up to 90-120 beats per minute.
This is how tachycardia develops, which is identified as the primary clinical sign. A secondary manifestation is considered to be the body’s response that occurs during pain. It is characteristic not only of thoracic, but also of lumbosacral osteochondrosis. When pain appears in any area of the back, especially against the background of aseptic inflammation, a large number of biologically active substances are produced in the adrenal cortex. They quickly penetrate the bloodstream, causing frequent contractions of the heart muscle.
Case from practice
A patient came to see me who was constantly tormented by attacks of tachycardia. The heart rate increased at rest, as well as after exercise, and reached 120–160 beats per minute. At the time of the attack, shortness of breath, weakness, and dizziness were observed.
No abnormalities were found on the ECG. X-ray revealed changes in the cervical spine. MRI showed the presence of a hernia between the IV and V vertebrae of the thoracic segment.
I prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, and after achieving remission, I recommended massage of the cervical-collar area and exercise therapy. After 2 weeks there was a significant improvement, the pulse rate was 69–70 beats/min.
How to identify the relationship between diseases
You can detect tachycardia yourself. To do this, take a stopwatch, sit down and relax as much as possible. Now you should squeeze the largest blood vessel (artery), located on the inner surface of the left wrist, note the time and start counting the blows. If their number exceeds 80 in 60 seconds, then this indicates a heart rhythm disorder.
Heart rate measurement.
But it will not be possible to establish a connection between the development of tachycardia and osteochondrosis of any localization at home. Indirect confirmation is its appearance during the period of relapses of degenerative-dystrophic pathology. In such cases, rapid heartbeat is accompanied by acute pain in the neck or back, limitation of movements and other specific signs of osteochondrosis.
How to get rid
Treatment of tachycardia from osteochondrosis begins with eliminating the underlying cause. For this purpose, medications, traction, massage, and physiotherapy are used. Muscle relaxants and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help well; in case of severe pain, it is relieved with novocaine blockade.
When stable remission is achieved, the rhythm disturbance disappears. This result also serves as confirmation of a correctly made diagnosis. The prognosis is usually favorable. It is important to complete the full course of treatment and follow preventive measures.
For such a deviation, I usually recommend muscle relaxants with a sedative effect. They will not only eliminate muscle spasms in the affected area, but will also help normalize the functioning of the nervous system.
If the pulse exceeds 110 beats, and such attacks occur frequently, then the use of antiarrhythmic drugs is required. If treatment is not carried out in time, constant overload of the heart muscle will lead to failure. It is best to use beta blockers for this; they will not only reduce the heart rate, but also help prevent the development of ischemia. Hypotension is a contraindication to their use. At the same time, you can normalize the pulse with the help of drugs containing potassium and magnesium.
Diagnostic methods
The fact that the cause of tachycardia was osteochondrosis cannot be determined through an external examination of the patient or a description of the characteristic symptoms. The doctor makes a diagnosis based on the results of radiography, MRI, CT. An ECG must be performed to determine the frequency and rhythm of heart contractions and differentiate tachycardia from other diseases of the cardiovascular system. Echocardiography (EchoCG) is also prescribed. The results of this diagnostic technique help to identify intracardiac pathologies or exclude them.
An electrophysiological study of the heart is considered highly informative. By studying the propagation of electrical impulses throughout the myocardium, it is possible to determine the mechanism of increased heart rate and cardiac conduction.
Radiography
X-ray examination is the most informative method for diagnosing osteochondrosis. If the doctor suspects that the cause of tachycardia is the destruction of the intervertebral discs, then pictures are taken in two projections. All radiographic signs of osteochondrosis are clearly visible on them. These are formed osteophytes, a decrease in the distance between the vertebral bodies, and thinning of the discs.
Osteochondrosis on x-ray.
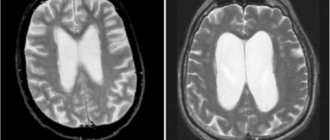
Magnetic resonance imaging
Patients often undergo cardiac MRI to identify destructive changes. And the results of magnetic resonance imaging of the spine are informative in the diagnosis of osteochondrosis, especially its complications. These include protrusions and protrusion of the intervertebral disc beyond the boundaries of the spinal canal. It is hernias that often cause compression of the spinal roots and (or) the vertebral artery, provoking tachycardia.
MRI is also used to evaluate the condition of muscles, ligaments, sensory nerve endings and blood vessels located near damaged vertebral structures. A diagnostic procedure with contrast allows you to identify circulatory disorders in any area of the body.
Osteochondrosis on MRI.
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
The feeling of pain in the sternum with thoracic osteochondrosis is a symptom mistakenly taken by patients for pain in the heart
. Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis are characterized by intensification at night. They manifest themselves especially clearly when trying to straighten your back or, on the contrary, slouch, arch your back into a dome.
The severity of symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis directly depends on the stage of the osteochondrosis disease. At the same time, negative sensations with symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis may manifest themselves weakly (osteophytes often grow on the surfaces of the vertebrae, where there are practically no nerve endings, and the muscle corset compensates for the load for some time).
In addition to pain in the sternum and between the shoulder blades, patients often complain of the following radicular and reflex symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis:
- a feeling of cold, burning and tingling in the chest, at the base of the neck, in the abdomen;
- muscle tension (difficulty relaxing your back);
- a feeling of pain in the sternum (a symptom of thoracic osteochondrosis, which is one of the first to appear);
- increased heart rate, feeling of pulsation in the chest;
- a feeling of “pins and needles” inside the chest, which is often accompanied by causeless anxiety or increases with stress;
- numbness of soft tissues (skin and muscles) near the spine, in the shoulders, especially noticeable when pressed or in contact with hot and cold surfaces;
- with thoracic osteochondrosis it is difficult to breathe;
- feeling of coldness in the hands and feet, pale or bluish skin on the hands;
- weakness, inhibition of reflex reactions in the affected area;
- disturbances in the functioning of the digestive organs, colic, stool disorders;
- the appearance of areas of skin with obvious nutritional disorders (peeling, pallor, thinning or, conversely, thickening of the skin);
- feeling of a lump in the chest, discomfort when swallowing large pieces of food;
- characteristic cough with thoracic osteochondrosis;
- digestive symptoms (dyspepsia, loss of appetite, nausea, heartburn, bloating);
- increased fatigue, feeling very tired in the morning (“broken” state);
- change in gait (usually stooping, unsteadiness);
- intercostal neuralgia.
The symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis can feel like they are a stomach or intestinal ulcer, angina pectoris, gastritis or a heart attack. Sometimes it is mistaken for renal or cardiac colic, cholecystitis or pancreatitis. Indeed: advanced thoracic osteochondrosis can cause malfunctions in the gallbladder (for example, sediment formation) and intestines, and dysfunction of the heart vessels.
The specificity of the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis depends on the location of the problem:
- 1st-2nd thoracic vertebrae
- pain radiates to the collarbone, armpit, and can reach the shoulders; - 3-6th vertebrae
- patients are bothered by girdling pain above the chest, which is similar to pain in the heart or mammary glands; - 7-8th vertebrae
- pain in the solar plexus, which imitates diseases of the internal organs (stomach, liver, gall bladder, pancreas). There is also inhibition of the epigastric reflex (contraction of the abdominal muscles when passing the instrument along the line of the lower rib); - 9-10th vertebrae
- here osteochondrosis can cause sharp pain in the abdomen and under the ribs, inhibit the mesogastric reflex (when a tool draws a horizontal line at the level of the navel); - 11-12th vertebrae
- can initiate groin pain, diseases of the internal genital organs and intestines. Reduces the hypogastric response (by drawing a line in the lower abdomen parallel to the inguinal fold).
Difficulty breathing
During physical activity (for example, climbing a couple of floors of stairs), patients find it difficult to breathe. With thoracic osteochondrosis, severe shortness of breath is observed. Patients often describe this sensation as “breathless.” Similar symptoms can be observed during sleep: in an unsuccessful position, patients dream of lack of air, their ears may become blocked (a strong pulsation can be heard), and severe chest spasms occur.
Often the feeling that it is hard to breathe with thoracic osteochondrosis is accompanied by girdle pain in the back and ribs, as well as subcostal pain.
Increased heart rate
Even after light exertion, which previously went unnoticed, patients complain of increased heart rate, feeling as if the heart is trying to jump out of the chest. At first, increased heart rate may be caused by spastic contractions of the muscles and chest or a violation of tissue trophism, but over time, this dangerous symptom can actually outgrow angina pectoris, coronary heart disease and even lead to a heart attack.
In addition to increased heart rate, patients often note an accompanying feeling of panic, fear of death, or increased background anxiety. In some cases, against the background of thoracic osteochondrosis, real panic attacks can be observed.
Chest pain
The most telling symptom of thoracic osteochondrosis is a feeling of pain in the sternum
.
These include sharp shooting pains and a feeling of pressure in the chest, as well as intercostal pain when walking. Chest pain tends to intensify after a long stay in one position, hypothermia, turning the body and bending (especially with a turn), raising the arms. Carrying heavy objects, playing sports, taking deep breaths, and sleeping still can also increase pain. It should be remembered that due to the low mobility of the thoracic spine, osteochondrosis in this part of the back is characterized by dull, aching, pressing and throbbing pain. Acute, prolonged pain with thoracic osteochondrosis is very rare, which is why patients tend to ignore the pathology for a long time
.
Vertebral pain
With osteochondrosis of the spine, it is customary to divide into dorsago and dorsalgia.
Dorsago
is a spontaneous shooting pain that, as a rule, does not last long and goes away with a change in position.
Dorsago is usually caused by accidental root pinching. Dorsalgia
is long-lasting (about 2-3 weeks) and is associated with permanent disruption of blood circulation or nerve conduction. They make themselves felt by burning, stinging pain.
The pain intensifies when coughing and can be mistaken by patients for a spinal hernia. However, with osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, hernias are extremely rare. Don't write off the main symptom
(feeling of pain in the sternum with thoracic osteochondrosis)
to a displacement of the vertebra - its probability is extremely low in comparison with degenerative-dystrophic changes
!
Cough with thoracic osteochondrosis
Cough with thoracic osteochondrosis is often observed in people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, and their work duties involve prolonged sitting (office workers, operators, drivers). Maintaining this posture, which is difficult for the human spine, causes chronic muscle strain, spasms and tightness. Spasticity
is both a cause and a consequence of the fact that the cervical and thoraco-girdle area suffers from insufficient movement. At night, in positions that compress the spine, spasms and irritation of the spinal roots only intensify, causing severe coughing. If the upper thoracic vertebrae are affected, a cough due to thoracic osteochondrosis may be accompanied by pain in the esophagus, a feeling as if something is stuck in the chest.
During coughing attacks with thoracic osteochondrosis, it becomes painful for patients to breathe; It becomes difficult to take a deep breath.
Which doctor should I contact?
Most patients with complaints of palpitations turn to a cardiologist, and sometimes a therapist. These doctors prescribe all necessary diagnostic tests, including x-rays. Based on its results, a diagnosis is made and the patient is sent for further treatment to a vertebrologist or neurologist.
Osteochondrosis is treated by a vertebrologist.
The mechanism of arrhythmias
Does osteochondrosis affect the appearance of heart pain and why?
The clear answer is yes. The main cause is compression of the vertebral or vertebral artery, which runs along the entire spine and cardiac nerve. The vertebral artery supplies blood to 25% of brain cells. It can be compressed by spastically contracted muscles, osteophytes on the vertebral bodies as a result of spondylosis. At the same time, blood pressure increases, and subsequent pumping of blood from the atria to the ventricles occurs with increased effort and rhythm disturbances. In addition, cerebral ischemia develops, i.e. hypoxia, causing spasm of blood vessels and muscles. Because of this, the central innervation of internal organs, including the heart, is disrupted. Thus, a disturbance of cardiac activity occurs with interruptions in rhythm. In this case, tachycardia occurs more often.
The paravertebral tissues become inflamed, the anterior root nerve endings of the spinal cord are irritated. And if these endings innervate the heart, they can cause arrhythmia. Everything is very clearly interconnected. The number of impulses from the endings during inflammatory reactions increases and a zone of pathological impulses appears in addition to the normally functioning sinus node. In this case, the heartbeat with osteochondrosis with its frequency, rhythm and a certain sequence of contractions is disrupted.
Arrhythmias often occur with poor posture:
- scoliosis;
- stoop as a result of physical inactivity;
- long-term monotonous loads;
- sitting in an awkward position.
When such interruptions occur, it is not the heart that is treated, but the spine. Arrhythmias in osteochondrosis differ in some manifestations.
What to treat first
Tachycardia in osteochondrosis is a concomitant clinical manifestation that disappears after adequate treatment of the underlying disease. When the lumbar pathology worsens, “lumbago” occurs, and when the cervical disease recurs, the person suffers from dizziness and surges in blood pressure. Thoracic osteochondrosis, in addition to tachycardia, is clinically manifested by severe pain in the heart, reminiscent of an angina attack. Therefore, the patient’s well-being can only be improved by simultaneous treatment of pathologies.
Dizziness is one of the signs of osteochondrosis.
Expert recommendations
Paroxysmal or constant tachycardia with osteochondrosis requires not only the use of medications. They help in acute conditions, but do not in any way affect the duration of remission. The spine deforms slowly, but with each exacerbation the process gets worse. To prevent the condition from worsening and the attacks to recur, I would like to recommend the following:
- review your diet towards greater consumption of fruits, vegetables and other healthy foods;
- give up coffee, energy drinks, medications and other substances that increase heart rate;
- develop resistance to stress, this is helped by yoga, breathing practices, meditation;
- be sure to get enough sleep and follow a daily routine;
- Perform regular physical exercises to stretch the spine and strengthen the muscles of the back and neck.
If you want to know everything about tachycardia, we recommend watching the video below at the link. Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and signs that it’s time to see a doctor - talk about all this in 7 minutes. Enjoy watching!
Treatment options
To establish the cause of the development of osteochondrosis, consultations with highly specialized doctors are often required. Rheumatologists, endocrinologists, traumatologists, and surgeons may be involved in therapy. They determine treatment tactics based on the severity of osteochondrosis, the stage of its course, and the characteristics of symptoms.
Drug therapy
Exceeding the heart rate of 110-120 beats per minute becomes an indication for taking the beta-blockers Metoprolol, Atenolol, Bisoprolol and their structural analogues. The drugs do not have a pronounced effect on blood pressure, which is especially important for osteochondrosis.
A course of sedatives - Novo-Passit, Tenoten, Persen, alcoholic tinctures of motherwort, valerian, peony - sometimes helps to normalize heart rate.
| Drugs to eliminate clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis | Therapeutic effect of drugs |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with diclofenac, ketoprofen, meloxicam, nimesulide, ibuprofen | The drugs not only eliminate pain, but also reduce the severity of inflammatory swelling. It is this that often provokes pinching of blood vessels and spinal roots, leading to increased heart rate |
| Muscle relaxants - Mydocalm, Sirdalud, Tolperisone, Baclofen | A course of medications helps relax tense skeletal muscles. As a result, painful muscle spasms that cause tachycardia disappear |
| Ointments and gels with a warming effect - Capsicam, Finalgon, Apizartron, Viprosal, Nayatox | After applying external products to the skin, blood circulation improves, microcirculation is normalized, muscle spasms disappear |
Orthopedic products
Wearing orthopedic collars and other devices helps stabilize discs and vertebrae, preventing their displacement and compression of nerves and blood vessels. For thoracic and lumbosacral osteochondrosis, elastic bandages (corsets) are used. They are equipped with metal or plastic inserts in the form of rings, spirals, and plates. The bandages fit tightly around the body, and some models have a warming effect that improves blood circulation.
Shants collars are usually used to hold the cervical vertebrae in the correct position. They differ in height and degree of fixation, so the size of such a bandage should only be selected by a vertebrologist. Collars are worn for 2-3 hours a day and must be removed at night.
Shants collar.
Ultrasound treatment
In the subacute period and at the stage of remission, patients are shown 5-10 sessions of ultrasound therapy. Under its influence, blood circulation improves in the area of damaged vertebral structures. A sufficient amount of oxygen and nutrients begins to flow into the soft and cartilaginous tissues, which has a positive effect on their regeneration.
And with the help of ultraphonophoresis, the supply of medicinal substances to the affected ligaments, muscles, and discs is ensured in maximum concentration. During the procedures, NSAIDs, anesthetics, chondroprotectors, and preparations with B vitamins are used.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis with ultrasound.
Reflexology
In the treatment of osteochondrosis complicated by tachycardia, acupuncture is often used. The doctor applies small metal, silver or gold needles to acupuncture points. This leads to relaxation of skeletal muscles, improvement of lymphatic drainage, and elimination of compression of arteries and spinal roots.
One of the areas of reflexology is treatment with medicinal leeches. Ringed worms are installed on bioactive points, bite through the skin and inject saliva with a high content of useful substances into the blood.
Hirudotherapy session.
Exercise therapy and massage
For patients with osteochondrosis and tachycardia provoked by it, sessions of classical, acupressure, vacuum, segmental, and Swedish massage are recommended. The procedures not only have a general strengthening and tonic effect, but also become an excellent prevention of the progression of degenerative-dystrophic pathology.
Daily exercise therapy and gymnastics help eliminate all symptoms of osteochondrosis and strengthen the back muscles. The physical therapy doctor selects exercises individually for the patient, taking into account physical fitness and the severity of clinical manifestations.
Surgical intervention
Indications for surgical intervention include the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy for several months and the rapid progression of osteochondrosis. The operation is also performed in case of developed complications - radicular syndrome, discogenic myelopathy, vertebral artery syndrome.
Tachycardia is often provoked by an intervertebral hernia: it is removed by excision of the protrusion, usually together with a destroyed intervertebral disc, with further stabilization of the spine or installation of implants.
Installed implant.
Treatment and prevention of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
Treatment of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis of the spine should be carried out comprehensively. In each case it is necessary to find an individual approach. Medicines, physical therapy, massages and some folk remedies can help cope with the disease.
If osteochondrosis is in an acute stage, then its treatment will be aimed at improving blood circulation and eliminating spasms and pinching. The doctor can prescribe medications to the patient that will improve blood flow, as well as relieve inflammation and reduce pain.
Medicines for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
Clinical studies have shown that during exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis, analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs work well. In addition to them, the doctor prescribes chondroprotectors, antispasmodics and drugs that stimulate blood circulation in the tissues.
For complex therapy in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, the following are used:
- Analgesics. Eliminate pain. Some of them can have an anti-inflammatory effect. Most often, analgesics are prescribed for lumbar osteochondrosis, which has a wide localization of pain;
- Antispasmodics. They have an analgesic and antispasmodic effect. Eliminate muscle spasms, block the sensitivity of nerve endings;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Relieve pain, reduce inflammation;
- Vasodilators. Necessary for improving blood circulation. Reduces the recovery time of the body after osteochondrosis;
- Chondroprotectors. Necessary for tissue restoration in damaged cartilage. One of the most effective drugs today is Artadol. It contains chondroitin sulfate, which actively fights the degradation of articular cartilage. The drug stimulates the production of proteoglycans. Improves metabolic processes in cartilage and bone tissue.
Regardless of the stage of the disease and the degree of pain, doctors strongly recommend refraining from self-medication. Only after examination by a specialist, analyzes and tests can the doctor prescribe adequate and effective treatment for cervical osteochondrosis.
Massage for cervical osteochondrosis
Massage is necessary to relieve pain and improve muscle tone. Different techniques are used, which depend on the stage of the disease. In the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, the following are effective:
- stroking;
- squeezing;
- rubbing;
- kneading.
If pain is observed only on one side of the neck, then the massage begins with a healthy part of the body, gradually moving to the sick one. It can be performed at home or in a specialized institution. But you should be extremely careful, since incorrect movements and influences can only aggravate the situation.
Therapeutic exercises for symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
Therapeutic gymnastics is used in complex therapy in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis and gives excellent results. Unlike medications, it has no contraindications or side effects. Exercise therapy aims to improve blood flow to damaged parts of the body. It is important that the patient does not feel pain when performing certain exercises.
Therapeutic gymnastics is designed to strengthen the muscles in the neck area, and also serves as an excellent prevention of osteochondrosis.
Possible complications
With osteochondrosis, the development of ventricular types of heart rhythm disturbances, which include tachycardia, is usually observed. Its atrial paroxysmal form is rarely diagnosed. The pathogenesis is based on organic damage to the heart muscle in combination with osteochondrosis. If left untreated, vertebral artery syndrome develops, which causes cerebral circulation disorders in the vertebrobasilar region. And this leads to a decrease in the functional activity of the cardiovascular system.
How to install a dependency
A careful study of the symptoms allows us to establish a connection between tachycardia and osteochondrosis.
If its cause is degenerative changes in the discs and pinched nerve fibers, the following is observed:
- rhythm disturbance occurs at rest;
- the condition worsens when changing body position, which increases the load on the spine;
- when the heart rate increases, sinus rhythm is maintained;
- improvement occurs after therapy for osteochondrosis.
In my practice, cardiac pathology is often found in combination with problems of the musculoskeletal system.
Therefore, there is a need for additional research:
- ECG (it will not detect ischemic changes);
- radiography (will show deviations in the structure of hard tissues);
- MRI or CT scan of the affected segment of the spine (will give a clear picture of changes at all levels).
Tachycardia is also a symptom of thyroid dysfunction during an allergic reaction. It can be provoked by anemia, fever and intoxication. In some cases, this symptom is observed when using drugs or certain medications.
Which departments should you look for the problem in?
Cervical osteochondrosis and tachycardia are most often associated. Due to the high mobility and weakness of the neck muscles, it is this part of the spine that is affected more quickly. The thoracic region is deformed less frequently, and changes in the pulse are rarely observed when the neurovascular bundle is pinched in the lower part. In the latter case, there is a reflex effect that is transmitted along the nerve fiber of the ridge.
During palpation examination in the affected area, muscle tension will be determined. A sharp turn or bend causes pain. Chondrosis of the cervical vertebrae is often accompanied by deterioration of vision and hearing, and periodic dizziness. With pathology of the thoracic region, pain often occurs when inhaling or exhaling deeply.