Arrhythmia is observed in many people suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia. Heart rhythm disturbances may manifest differently in everyone. There is a classification of pathologies that defines different types of cardiac dysfunction.
If you have arrhythmia due to VSD, on this page you will find out what is happening to the body, the causes of the pathology, get acquainted with the symptoms, and receive recommendations for treatment. Do not forget that only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment. The information is presented for informational purposes and not for self-medication.
Why does arrhythmia appear in vegetative-vascular dystonia and neurosis?
Arrhythmia, which manifests itself against the background of VSD and neurosis, like the vegetative and neurotic disorder itself, is of a purely functional nature. At first, a person may not notice interruptions in the functioning of his heart. In the absence of timely and correct treatment, it becomes habitual, and the patient does not pay attention to it.
Normally, the sinus node (SU) is responsible for generating electrical signals that regulate the rhythmic mechanical contraction of the heart. But against the background of the development of VSD and disturbances in the processes of the autonomic nervous system, the intensity and order of “supervising” the work of the sinus node of the vagus nerve and sympathetic influences changes, which leads to various forms of arrhythmia.
To put it simply, the regulation of the heart is ensured by impulse flows coming from the central nervous system (CNS) along the parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves of the ANS.
The vagus nerve, which belongs to the parasympathetic division, slows down its rhythm. Sympathetic nerves, on the contrary, accelerate the impulse responsible for myocardial contractions.
When such a failure occurs in a well-coordinated mechanism, disturbances in heart beats (arrhythmias) appear. An imbalance in the parts of the nervous system, which is functional in nature, becomes the cause of arrhythmic syndrome in VSD.
Other causes of arrhythmia
There are other factors that cause abnormal heart rate (HR)
These include:
- Congenital and acquired cardiac heart defects.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Some diseases of the central nervous system.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Infectious diseases.
- Diabetes.
- Excessive consumption of coffee, strong tea.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Physical and mental overload.
- Binge eating.
- Dehydration.
- Hypothermia or overheating of the body.
- Stress, psychological shocks.
On a note!
Normally, the heart of an adult makes 60-80 beats per minute, in a calm position. For some people the norm is up to 90 beats/min. When walking, the beat frequency ranges from 90-120 per minute. In women, in 1 minute the heart beats 10-12 beats more than in men.
Arrhythmia can occur at any age (including children) and for various reasons. Any pathology in the electrical conduction system causes the development of a failure of heart contractions.
To establish the exact cause, a detailed medical examination is necessary.
Why is arrhythmia dangerous?
The feeling when the heart begins to beat vigorously, as if jumping out of the chest, is not a pleasant one. What types of arrhythmias are there and why they are dangerous, says cardiologist Yulia Shuvalova.
— Yulia Vladimirovna, what is arrhythmia and how does it manifest itself?
— Arrhythmia is a change in the frequency and periodicity of the heart rhythm. There are several types of this disorder. Since heart rhythm disturbances can occur in different parts of the heart, arrhythmias can be ventricular, supraventricular, or from the AV junction. The change in rhythm itself can also be different. A rapid heartbeat is called tachycardia, a slow heartbeat is called bradycardia, but these are only the simplest and most common arrhythmias.
Tachycardia and bradycardia are serious disorders that require constant correction and monitoring. However, if they appear periodically, they may be the result of stress, fever (with uncomplicated ARVI) or vegetative-vascular dystonia, which is not dangerous. In these cases, the heart returns to its normal rhythm.
— In what other cases is arrhythmia not a cause for concern?
— Quite often, based on the ECG results, doctors make a conclusion: sinus arrhythmia. This arrhythmia is caused by the sinus node. It is characterized by slowing or lengthening the intervals between heartbeats and is considered safe. In childhood and adolescence, during the rapid growth of the body, this often happens. In these cases, sinus arrhythmia is the norm, not a pathology, and goes away with age.
Many people have at one time or another experienced the feeling of a sinking heart that passes without any consequences. This is a very common type of arrhythmia - so-called extrasystoles. Extrasystoles occur due to premature passage of the impulse. In most cases, they are not dangerous to health and normally amount to 1500 extrasystoles per day. Sometimes a person doesn't even notice them. Extrasystoles appear as a result of psychoemotional arousal, against the background of vegetative-vascular dystonia, or for no reason. However, frequent attacks of extrasystole are a reason to consult a doctor and undergo a full examination, not only from a cardiologist, but also from other specialists.
— Which arrhythmias are the most dangerous?
— The most dangerous arrhythmias are paroxysmal, which occur suddenly, paroxysmally. Paroxysmal arrhythmia can occur against the background of good health, but more often it develops during pressure surges and after psycho-emotional stress. The heart begins to beat either faster, losing its rhythm, or, conversely, too slowly. Heart rhythm disturbances are accompanied by a sharp deterioration in health - sudden weakness, dizziness, even loss of consciousness. Arrhythmia can occur at night, which can cause sudden cardiac arrest.
Atrial fibrillation (a permanent form of atrial fibrillation) is a sign of serious heart disease, often developing as a complication of coronary artery disease, hypertension, heart defects, and also in cases of thyroid dysfunction. People suffering from hypo- and hyperthyroidism are susceptible to arrhythmias if the diseases are not compensated for by medications.
With atrial fibrillation, the conduction of impulses in the atria is disrupted, which is why they seem to “quiver and flicker.” As a result, the heart works unevenly and there is a risk of blood clots, which can lead to the development of a stroke or heart attack. Atrial fibrillation is manifested by very unpleasant symptoms - shortness of breath, weakness, dizziness, and a feeling of lack of air. It requires treatment and constant monitoring by a cardiologist.
— What examinations are necessary to make a correct diagnosis?
— Arrhythmia is quite difficult to diagnose, since heart rhythm disturbances are observed at different times of the day and there may be a long break between them. A comprehensive examination is necessary and, first of all, daily monitoring of ECG and ultrasound of the heart.
General symptoms of arrhythmia
Symptoms vary depending on what type of arrhythmia the patient has. But there are common signs for all types of heart rhythm disturbances.
Since arrhythmia in VSD and neuroses is psychogenic in nature, it is most often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Lack of air.
- Shortness of breath.
- Trouble breathing.
- Feeling of heaviness in the chest.
- Fluttering in the chest.
- Dizziness.
- Increased heart rate.
- Increased sweating.
- Heat in the body or, conversely, chills.
- Weakness, increased fatigue.
- Feelings of anxiety, panic attacks.
Arrhythmia in vegetative-vascular dystonia
Home ->Symptoms of VSD -> Arrhythmia and vegetative-vascular dystonia
The heart is a unique organ that has special cells - pacemakers, capable of independently producing an electrical impulse, due to which the heart muscle contracts. The sinus node, or pacemaker, is located in the wall of the right atrium and therefore the heart rhythm, normal according to the source of its passage, is usually called sinus rhythm.
If the heart functions normally, then with each beat there is a sequential contraction of its parts: the atria, then the ventricles. In healthy people, these contractions follow each other at regular intervals, but with arrhythmia their sequence is disrupted, and the frequency can be either higher than normal or lower than normal. A normal heart rate is considered to be 60-80 beats/minute.
, sinus tachycardia is very often observed . at which the heart rate reaches 90-100 beats per minute or more with the correct rhythm. In this case, tachycardia decreases markedly with breath holding.
This arrhythmia is called respiratory arrhythmia . in which the heart rate increases as you inhale and decreases as you exhale. Typically, respiratory arrhythmia is characteristic of people with increased excitability of the autonomic nervous system, that is, it is neurogenic in nature.
The general condition does not suffer with such arrhythmia. But as soon as a VSD student learns about this problem, almost immediately he experiences a whole range of subjective sensations, such as pain in the heart area not only during physical activity, but also at rest.
With such an arrhythmia, an additional beat or several beats are noted at regular intervals. Respiratory arrhythmia is not life-threatening and does not require special treatment. And yet, if a person suffering from VSD experiences an irregular heart rhythm, then this patient should be consulted by a cardiologist.
Very often, as lifestyle improves, this condition goes away on its own without any drug treatment.
But if a doctor, who still needs to be contacted, suspects that a person has a type of arrhythmia that requires diagnosis, then in this case Holter ECG monitoring is used, or recording a cardiogram for a long time, which makes it possible to detect much faster rhythm disturbance.
Causes of arrhythmia
In healthy people, the cause of sinus tachycardia is physical activity and psycho-emotional arousal . If the arrhythmia is the result of emotional stress or increased body temperature, it usually goes away on its own without special treatment. But if the arrhythmia continues for several hours in a row or repeats frequently, you should urgently visit a doctor!
Heart failure, anemia, thyrotoxicosis, heart failure, myocarditis can also cause persistent tachycardia. In a healthy person, arrhythmia can be triggered by tight clothing, constipation, heavy food, and insect bites. Very often, arrhythmia can be caused by a seemingly natural cause - premenstrual syndrome, when the heart rhythm is disturbed, pain appears in the chest, and suffocation occurs.
Predisposition to arrhythmia can be inherited genetically . There are several types of arrhythmias: bradycardia, tachycardia, extrasystole and atrial fibrillation. But with any type of arrhythmia, you cannot self-medicate, and especially if atrial fibrillation is diagnosed. It is imperative to visit a medical institution, where a special study will be carried out and appropriate treatment will be prescribed.
You might also be interested in:
Types of arrhythmia in neurosis and VSD
Cardiac arrhythmia during VSD is divided into several types. They are also divided into functional and organic. In the first case, the pathology develops with a completely healthy heart and is not a complication of the disease. This type of pathology most often occurs with vegetative-vascular dystonia. In the second case, arrhythmia is caused by physiological diseases.
Tachycardia specifically with VSD is divided into two types:
- Intracardial . The etiology is associated with the cardiovascular system. Failure of heart rate indicates impaired functioning of the ventricles, poor blood flow, and heart failure.
- Extracardiac . The non-organic nature of the disease, which is determined by a neurological, psychological factor. Sometimes it may indicate diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
Diagnostics
Any disturbances in the functioning of the heart require immediate examination. Specialized doctor – cardiologist.
To make a diagnosis, the patient is prescribed the following types of diagnostics;
- Measurement of heart rate and blood pressure.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG).
- Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart).
If these studies do not provide a complete picture, then Holter monitoring is used to more accurately identify the causes of arrhythmia. The method is based on round-the-clock analysis of the electrophysiological function of the heart muscle. The patient puts on a special sensor and spends a day or two with it.
Choletron monitoring of the heart allows you to identify many disorders in the functioning of the organ, and not only functional, but organic, for example, spontaneous variants of angina that occur at night, or painless equivalents of myocardial ischemia.
This study is the most accurate, extensive and very useful in preventing serious pathologies.
ONLINE APPOINTMENT WITH A DOCTOR IN ANY CITY IN RUSSIA
Is cardiac arrhythmia dangerous during VSD?
Various types of arrhythmia caused by psychogenic factors are not life-threatening. But only if a person promptly seeks help and accepts treatment.
It is worth understanding that any disturbances in the functioning of the heart that remain unattended can become chronic. Over time, the nervous form of arrhythmia will turn into a physiological one. Irreversible changes may begin in the most important organ, threatening serious diseases, early heart attack, and constant pain.
Of course, it will take a long time for this disorder to develop from a psychogenic to an organic form. Therefore, do not be alarmed if you have recently experienced arrhythmia - just visit a doctor and have your heart checked.
Treatment
If during the examination any physiological diseases of the cardiovascular system were identified, then treatment appropriate to the diagnosis is prescribed. As the pathology is eliminated, the heart rate disturbance itself goes away.
Important!
Other serious diseases may be hidden under the mask of VSD. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment! All information on the site is for informational purposes only and is not a reason for self-diagnosis or self-medication.
But the ways to deal with arrhythmia during VSD have their own characteristics. Since the main provoking factor for disturbances in the functioning of the heart are neuropsychological problems, complex therapy is prescribed.
This is interesting :
How life-threatening is VSD?
Drug treatment
Drug therapy includes medications that relieve arrhythmia symptoms:
- Beta blockers - reduce the sensitivity of adrenaline receptors, usually prescribed for tachycardia and extrasystole.
- Calcium channel blockers - used to eliminate atrial fibrillation.
- Sodium channel blockers are effective antiarrhythmic agents.
- Potassium channel blockers - used for angina pectoris, supraventricular arrhythmia.
- Tranquilizers – reduce anxiety, nervous excitability, and help improve sleep.
- Sedatives – have a calming effect, have a positive effect on sleep, and increase stress resistance.
- Antidepersants - reduce anxiety, stimulate neurotransmitters, improving mood and general psycho-emotional state.
- Nootropics - improve cerebral circulation, improve memory, concentration, and have a positive effect on the general condition.
Any medications are prescribed strictly by a doctor. Self-medication of vegetative-vascular dystonia is dangerous because its symptoms can mask organic diseases.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is very useful in the fight against functional cardiac arrhythmia. It acts comprehensively on the entire body, improving metabolic processes, increasing immunity, and also relaxing spasmodic muscles and blood vessels.
Recommended procedures:
- Massage.
- Acupuncture.
- Sharko's shower.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Balneotherapy.
Psychotherapy
In the treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia, neurosis and their consequences - arrhythmia, asthenia, panic attacks, psychotherapy can play a key role.
The specialist helps the patient discover the true causes of the functional disorder. Often these are unconscious and suppressed stress, internal conflicts, hidden depression, and psychological trauma. These factors are quite capable of causing VSD and arrhythmia.
The psychotherapist also teaches the sufferer to react differently to external factors in order to reduce the impact of stress.
Psychotherapy helps a person overcome internal problems, form new views, forms of behavior, thinking and perception.
Today the most effective methods are:
- cognitive behavioral psychotherapy;
- Gestalt therapy;
- hypnotherapy;
- psychoanalysis.
Interesting facts about psychotherapy
- Fact 1
- Fact 2
- Fact 3
Mere presence of the client is not enough. Sometimes, when clients go to a psychotherapist, they think that all that is required of them is to attend sessions. In much the same way, they come to the doctor complaining of a bad runny nose and leave with a prescription for an antibiotic. If a person comes to a psychotherapist with the attitude of “solve my problems,” he will be very disappointed. Psychotherapy is impossible without the cooperation of the client and the therapist; passively waiting for the result will not yield anything.
The psychotherapist is not a psychic. He does not know how to read thoughts and look into a person’s soul. Thanks to special education and knowledge, the therapist can analyze the situation in which the client finds himself. But without information from the patient himself, the specialist will not be able to find out anything and help.
Psychotherapists work not only with mental disorders. Like psychologists, they can help the patient solve various psychological difficulties and problems that many people face in everyday life.
As problems that lie deep in the subconscious are resolved, a person’s inner world changes for the better. The nervous system gradually returns to normal, all symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia weaken and disappear.
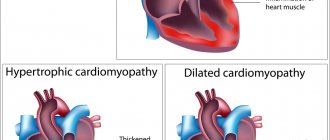
What is atrial fibrillation
Normal heart rhythm (sinus rhythm)
In a healthy person, the phases of heart contraction (systole) and its relaxation (diastole) alternate in a certain rhythm.
During systole, venous blood from the right ventricle is pumped to the lungs, and enriched blood from the left chambers of the heart enters the aorta and then to all other organs. During diastole, the heart fills with blood again. Under normal conditions, this cycle is repeated approximately 60–90 times per minute. The contractile activity of the heart is controlled by the rhythmic formation of electrical impulses and their subsequent conduction through the atria and ventricles. The area of the heart muscle in which impulses are generated that determine the heart rate is called the “heart pacemaker.” Normally, the main pacemaker is a special area on the vault of the right atrium (sinoatrial node). Each electrical impulse arising in the pacemaker, with the help of a special conduction system, spreads throughout the heart muscle and leads to its coordinated contraction: first the atria contract, and then the ventricles. This normal rhythm, controlled by the sinoatrial node, is called the sinus rhythm of the heart.
Rice. 1. Conducting system of the heart
Atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation)
The heart of a healthy person beats at a frequency of 60 to 90 times per minute. The concept of “cardiac arrhythmia” combines various deviations from these indicators. What is atrial fibrillation and how does it differ from other heart rhythm disorders?
With atrial fibrillation, control of the heart's work is taken over by other cells of the atria, producing from 350 to 800 impulses per minute. As a result, all muscle fibers (fibrils) in the atria contract chaotically, without leading to a single contraction of the atria (hence the second name for atrial fibrillation - atrial fibrillation).
Despite the excessive frequency of atrial excitations, only a small part of them is randomly conducted to the ventricles. As a result, with atrial fibrillation of the heart, an abnormal rhythm of ventricular contractions is formed, the frequency of which in most patients is above 80 per minute.
Rice. 2. Heart contraction normally and with atrial fibrillation
Prevalence and incidence of atrial fibrillation
1. National recommendations “Diagnostics and treatment of atrial fibrillation”, Minsk, 2010.
Atrial fibrillation, better known as “atrial fibrillation”, is one of the main types of arrhythmias that therapists deal with in their daily practice.
In the USA there are more than 3 million patients with atrial fibrillation, in Western Europe - more than 4.5 million.
2. Stewart S., Hart CL, Hole DJ, McMurray JJ Population prevalence, incidence, and predictors of atrial fibrillation in the Renfrew/Paisley study. Heart 2001; 86:516–521.
The forecast for the future is not encouraging: it is expected that by 2050 the number of such patients will increase by 3 or even more than 4 times.
The prevalence of atrial fibrillation increases with age: before the age of 50, atrial fibrillation occurs in 1-2% of the population, and after 80 years - in 5-15% of people.
3. Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, et al. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: the AnTicoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA 2001; 285:2370–2375.
Atrial fibrillation can go undetected for a long time, and many patients with atrial fibrillation never go to hospital. Therefore, the more realistic prevalence of atrial fibrillation is closer to 2%.
The lifetime risk of developing atrial fibrillation for people over 40 years of age is 25%.
Causes of development of atrial fibrillation
4. Fuster V, Ryden LE, Cannom DS, et al. ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Atrial Conditions. Circulation 2006; 114:e257-354.
There are many reasons that can lead to the development of atrial fibrillation. They are divided into two main groups: cardiac and non-cardiac.
For example, various heart diseases: heart defects; infectious heart diseases; coronary heart disease (CHD) and its complication - myocardial infarction.
| Heartfelt | Not cordial |
| cardiac ischemia | arterial hypertension |
| heart defects | chronic lung diseases |
| myocarditis | thyroid pathology |
| pericarditis | alcohol abuse |
| cardiomyopathy | viral infections |
In 30-45% of cases, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation can develop in relatively healthy people who do not have any diseases. This is the so-called idiopathic (or primary) atrial fibrillation, which occurs in 20-25% of cases.
5. Barold SS, Kalman JM, Tonkin AM. Atrial fibrillation: epidemiology and the risk and prevention of stroke. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 1992;15:1332-1346.
How can atrial fibrillation manifest itself?
There are several types of atrial fibrillation: paroxysmal, sustained and permanent.
With paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, periodic attacks (paroxysms of atrial fibrillation) last from several minutes to 7 days. The main feature of this form is the ability to spontaneously stop paroxysms of atrial fibrillation.
In a stable form, the arrhythmia persists for more than 7 days. However, it cannot stop on its own and medical intervention is always necessary to eliminate it.
In the permanent form, arrhythmia is observed constantly and cannot be eliminated.
In most cases, atrial fibrillation begins with a paroxysm of atrial fibrillation. Over time, the attacks progress: they become more frequent, last longer and gradually become permanent. All of these variants of atrial fibrillation require treatment, which can only be prescribed by a doctor.