Tonometer indicators are considered one of the most important in identifying the quality of human health. There are two main meanings. Systolic blood pressure is noted at the moment of cardiac output, that is, the maximum contraction of a muscular organ. Diastolic or inferior - when the cardiac structures relax.
110/80 mm Hg. Art. blood pressure itself is normal, if you look at purely formal calculations. According to the World Health Organization, an adequate blood pressure level is considered to be between 100 and 139 per 60 to 80 or so. All other numbers are pathological.
This scheme does not take into account one point, it is called pulse pressure (abbreviated as PP). The indicator is calculated as the difference between systolic and diastolic levels.
According to national cardiology societies, a value between 40-50 mmHg is considered acceptable. In the case described, we are talking about 30, which is slightly below the norm.
The condition is often caused by dangerous diseases of the cardiovascular system, there are exceptions. A differential, thorough diagnosis puts an end to the issue.
What does 110 to 80 mean?
The blood pressure level itself within the specified limit is considered normal. Doctors proceed from this when checking a patient’s health status as part of a diagnosis or preventive examination. PD remains on the sidelines, which is fundamentally wrong.
With a formally acceptable tonometer value, an organic process is observed. Low pulse pressure indicates that the heart is unable to function normally. Myocardial contractility falls within moderate limits.
This may be due to insufficiency, coronary disease, or defects. In some cases, the reasons have nothing to do with the heart at all and affect it indirectly.
Thus, a pressure of 110 over 80 is not normal due to an indication of myocardial dysfunction. This leads to complications: decreased hemodynamics, tissue ischemia and hypoxia, problems with organs and distant systems, including the brain, kidneys and liver.
With pulse 80-90
A heart rate of up to 90 beats per minute is considered normal. It does not require any correction.
With an adequate heart rate against the background of a drop in pulse pressure within 30 mm Hg, there are most likely no pronounced functional changes in the myocardium.
The pathological process is in early, not yet advanced stages. This means that the prospects for a cure or at least partial correction to ensure life expectancy are good.
There are exceptions; you need to look at the data of ECG, ECHO-CG and 24-hour Holter monitoring.
With a pulse of 100 or more
Tachycardia indicates the development of pronounced changes in cardiac structures. A pressure of 110 over 80 with a pulse of 100-110 may indicate a malfunction of the sinus node or paroxysms due to blockade of the His bundles.
Recovery is difficult. This is a relatively rare variant of the clinical picture. The reverse process is more common.
Less than 80 beats per minute
The so-called bradycardia. Makes it clear that the myocardium cannot cope with the load or is not receiving enough nutrition or oxygen.
A decrease in heart rate poses a great danger to life, sudden death is possible. There can be a lot of clinical options: from bundle branch block to severe insufficiency.
Drugs to normalize low blood pressure
If a cup of strong coffee or tea does not normalize blood pressure, doctors can prescribe a number of medications that will quickly and effectively cope with their duties and normalize blood pressure. The following drugs deliver a strong and quick effect:
- Ditamin.
- Caffeamine.
- Ondansetron.
- Metoclopamide.
- Domperidone.
Each drug helps increase blood pressure to optimal levels without causing side effects or consequences. Only a specialist will be able to correctly select the right dosage and nature of the drug in order to have an extremely positive effect on the body, stabilizing blood pressure. The above drugs contain substances that have a beneficial effect on the heart, helping to normalize blood pressure.
Are such numbers dangerous?
Yes, these indicators pose a threat to life and health. Close to them, 110 to 85, 105 to 75, when the pulse pressure is identical, have the same forecasts. But the others, 105 to 80 as an example, are much more serious, since the PD is even lower.
What are the possible consequences:
- Heart failure. In the event of urgent resuscitation, there is still a chance to return the patient.
- Heart attack. Acute death of muscle organ structures.
- Stroke. Brain nutritional disorder. Necrosis of nerve tissue leads to severe neurological deficits. The prospects for recovery depend on the extent of the damage.
- Shock resulting from a sharp drop in blood pressure and blood output.
- Impaired cognitive and mnestic functions as a result of insufficient supply to the brain. May result in vascular dementia.
- A general decrease in the quality of life, a decrease in working capacity and other important biological and social indicators.
However, the risks are at an average level. This is not a critical condition yet, but it is not the first phase either. Most likely, the pathological process is already underway, and it will be noticeable in instrumental diagnostics and even to the patient himself. If you listen to your own body.
What is the danger?
A low pulse difference between systolic and diastolic pressure of 30 units can pose a threat to human health and life. Since lower pressure does not deviate from the norm, all negative consequences are associated with the functioning of the heart and blood vessels. The following complications are most likely to develop:
- the most serious is sudden cardiac arrest with a fatal outcome;
- AMI;
- ONMK;
- cardiogenic shock due to a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- malnutrition of cerebral structures with symptoms of dementia, loss of cognitive functions;
- decreased quality of life and ability to work.
The trouble is that complications with a blood pressure of 110/80 develop gradually, amid apparent well-being, so a person is not ready for such a development of events and does not know how to behave in this case. The essence of what is happening is organic disturbances in the myocardium, a gradual loss of contractility.
Reasons for reduced PD
Low pulse pressure does not always develop due to damage to the cardiovascular system. But more often than not it turns out that way. An approximate list of development factors:
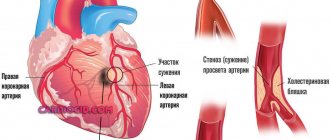
Heart attack
Especially if the left ventricle is affected. Usually we are talking about a slight extent of damage to cardiac structures (microinfarction). Therefore, the indicator drops insignificantly, being within 25-30 mm Hg or a little more.
Contractility is still present, so the body is supplied with blood to an acceptable extent.
With a large area of damage, intense disruption of the release into a large circle occurs. Cardiac shock and death are possible. In such a situation, pulse pressure drops to critical levels.
The pathological process needs to be viewed in exactly this way. Accordingly, a slight decrease in PP is associated with a relatively favorable prognosis for recovery after an emergency condition.
Aortic stenosis
Usually at valve level. There is an impossibility of normal blood ejection into the largest artery. Blood stagnation occurs in the left ventricle. This leads to constant overstrain of cardiac structures.
As it progresses, dilatation (expansion) of the organ chambers occurs. Contractility is insufficient, the volume of liquid connective tissue drops significantly for a whole group of reasons: not only stenosis is to blame, but also changes in the anatomy of the heart.
Pulse pressure decreases as a result of incomplete contraction, with short periods of rest between each cycle. Over time, the process only gets worse, so the likelihood of recovery depends on the moment the defect is discovered. The later, the worse the prognosis.
Neurological abnormalities
To a small extent, cardiac activity is controlled by the brain. If the functioning of cerebral structures is impaired, arrhythmias and insufficiency of myocardial contractility may develop.
This is a characteristic feature of vegetative-vascular dystonia. In origin it is a symptomatic complex, and not an independent diagnosis.
The diagnostic task becomes more complicated: when identifying VSD, it is also necessary to discover its cause.
Mitral valve insufficiency
It delimits the left atrium and ventricle, passing blood in measured quantities strictly in one direction. When an anatomical structure is disrupted, a reverse current or regurgitation occurs, which ends in a well-known manner.
Dilatation occurs, followed by cardiomyopathy, a decrease in myocardial contractility, a drop in blood output, and therefore pulse pressure. And there is already one step before progression, cardiac arrest and death.
The scenario is excluded with timely surgical treatment with restoration of the integrity of the mitral valve or prosthetics (preferably).
Heart failure
Both in the first and second stages. The patient feels minimal discomfort, but the process actively continues, destroying the system. Diagnostics is carried out using instrumental methods.
Recovery requires combating the root cause, as well as symptomatic therapy to eliminate manifestations.
Other heart defects, congenital and acquired
They require timely surgical treatment. They are not always detected immediately, and therapy is not needed in all cases.
In order not to miss an important point, it is recommended to undergo preventive examinations with a cardiologist every six months to a year, as well as an ECG and ECHO to detect any abnormalities. The need for therapy is decided on an individual basis.
Noncardiac causes
Represented by a group of heterogeneous processes:
- Iron deficiency and megaloblastic anemia. Associated with an insufficient amount of hemoglobin in the blood. Lead to the development of disorders of the cardiovascular system.
Mortality is relatively low, because the process can continue for a long time with the same symptoms, without dynamics. A drop in pulse pressure is a possible option. The sign is not always observed.
- Kidney failure and other diseases of the excretory system. If the filtering function is impaired, an increase in the amount of circulating blood occurs. This leads to increased stress on the heart. Possible drop in PD. This is a response to overstimulation.
- Liver failure. Including against the background of hepatitis, cirrhosis and other pathologies of a destructive nature.
Attention:
Changes in pulse pressure are almost not directly related to bad habits or lifestyle. This is an indirect process. What distinguishes the disease from simple forms of hypertension or hypotension.
Reasons for blood pressure 110/80
Pressure 110/80 has many causes, but all of them can be divided into cardiac and non-cardiac. The latter are represented by a heterogeneous group of initial processes: anemia - iron deficiency or megaloblastic, often against the background of latent internal bleeding, diseases of the genitourinary and biliary system, disorders of the blood clotting system, varicose veins, hormonal imbalances in women, stress, depressive states, pathology of the duodenum, incorrect use of medications.
In this case, the minimum pulse difference is never directly related to bad habits, which distinguishes blood pressure 110/80 from the simple classical form of hypotension.
However, much more often doctors encounter cardiac causes of blood pressure 110/80:
- left ventricular micro- or macromyocardial infarction (the right one is affected significantly less);
- aortic valve stenosis;
- mitral valve insufficiency;
- other congenital or acquired heart defects
- arrhythmias as a result of hypoxia of cerebral structures;
- VSD;
- cardiomyopathies of various origins;
- heart failure of varying severity.
Symptoms that require you to see a doctor
Manifestations of low PP are nonspecific. In the early stages, the patient may not feel any changes at all until the level drops to critical levels. Still, if you listen to your own body, you can detect signals.
- Dizziness. Against the background of a pressure of 110 to 80, vertigo develops as a result of insufficient supply of cerebral structures with nutrients and oxygen. Ischemia (oxygen starvation) of the cerebellum begins. The greater the volume of violation, the more significant the deterioration. There is a decrease in the efficiency of orientation in space.
- Cephalgia. The pain is localized in the occipital region, temples, and parietal zone. The nature of the discomfort is pressing, pulsating. Unpleasant sensations intensify in time with heart contractions. This syndrome can be falsely mistaken for a manifestation of migraine and vice versa. The duration of a headache episode with a pressure of 110 over 80 is from a couple of hours to a whole day.
- Loss of concentration. The result of the same hypoxia. In the early stages it has the form of slight absent-mindedness. Then it becomes more threatening. Patients with a progressive pathological process fall into a state of vascular dementia, which is very similar to Alzheimer's disease. Fortunately, a similar observation occurs when pulse pressure is below 30 mmHg. There are exceptions.
- Change in heart rate. A heart rate of 100 indicates impaired myocardial contractility. The problem can be localized both in the sinus node and in the ventricles, atria (paroxysmal type of tachycardia). A pulse of 80-90 is considered normal, lower indicates heart failure.
- Weakness, drowsiness, decreased performance. Up to the inability to perform everyday duties at home. Not to mention professional activities.
Symptoms requiring an ambulance call
Such signs occur in emergency conditions. Transportation to a cardiology hospital is indicated.
- Intense, unbearable headache.
- Vertigo, in which the patient is unable to navigate in space at all. Respiratory dysfunction. May indicate swelling or other dangerous conditions.
- Critical change in heart rate (more than 150 or below 60 beats per minute).
- Paresis, paralysis, sensation of goose bumps running through the body.
- Facial distortion.
- Loss of consciousness, repeated over several hours while symptoms persist.
Normal or pathological?
Blood pressure with indicators of 110/80 theoretically fits into the norm that WHO focuses on. In practice, such figures are typical for the majority of urban residents and people with an asthenic physique. In any case, the criterion of truth should be considered the general well-being of a person, the absence of complaints, negative symptoms. In itself, blood pressure, at which the systolic reading is lowered by 10 units, can cause concern due to a small pulse difference.
Examinations that need to be completed
Diagnosis is carried out on an outpatient or inpatient basis. Depending on the patient's condition.
Full list of studies:
- Orally questioning a person about his complaints.
- Anamnesis collection. Lifestyle, existing diseases, not necessarily those of the cardiovascular system, family history, and other factors are taken into account.
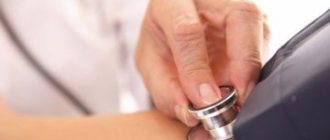
- Measurement of blood pressure and heart rate. Calculating PD does not present any great difficulties. Heart rate will additionally indicate the nature of the activity of cardiac structures.
- Electrocardiography. Allows you to assess the functional state of the myocardium. Makes it possible to identify developmental defects, as well as various types of arrhythmias. The ideal moment for this is the peak of the pathological condition.
- Daily monitoring. Blood pressure and heart rate are to be examined. The only difference is that they are recorded over 24 hours, over time. While the patient lives in familiar conditions, his health status is recorded.
- Echocardiography. Ultrasound research technique. Used to detect anatomical defects. Against the background of defects, congenital and acquired, these are obvious.
- General blood test, hormones and biochemical.
- Urine examination as needed.
- MRI of the brain.
- EEG.
- Scintigraphy.
It is possible to expand the presented list. Not only the cardiologist is involved in the diagnosis. If a cardiac origin of the drop in pulse pressure is excluded, other specialists are involved.
Treatment
Therapy is carried out under the supervision of specialized doctors. The basis is medication. The drugs are applicable in all cases: they stabilize the patient’s condition before possible surgery, relieve symptoms and sometimes the cause, and prevent further aggravation of the process or its relapses.
List of drug groups:
- Cardioprotectors and means for improving metabolism in cardiac structures. Mildronate.
- Beta blockers. As needed, with great care. There may be a drop in blood pressure, and subsequently pulse pressure. Anaprilin or Carvedilol.
- Nitroglycerin for pain in the chest.
- Antiarrhythmic for pulse irregularities. If the change in heart rate is not stopped by other means (for example, the same beta blockers). Quinidine, Amiodarone.
Other groups are prescribed as part of extended individual therapy. Cases vary. The medications described are of symptomatic action.
For etiotropic influence (treatment of the underlying disease), a combination of drugs is required. The question falls on the shoulders of a specialized specialist, not necessarily a cardiologist.
Surgery is required in a limited number of cases. For example, to eliminate heart defects (stenosis, prolapse of the mitral, aortic valves and others).
In the same way, severe atherosclerosis with the deposition of calcium salts on the cholesterol plaque is stopped. This is an extreme measure, sometimes you cannot do without it. The drugs are used as a supportive technique.
Lifestyle changes at the onset of the pathological process do not play a big role. If you give up smoking, alcohol and adjust your diet towards fortification, your chances of recovery are greater. But it all depends on the main diagnosis and the effectiveness of the treatment.
If the pressure is 110 over 80, this means that an organic process is taking place: hormonal or cardiac. We need to figure it out.
The treatment regimen is developed by doctors. What you definitely shouldn’t do is resort to independent actions or take folk remedies.
Traditional methods of normalizing blood pressure
Various folk methods can normalize blood pressure and improve a person’s condition, which cope with this problem no worse than expensive medications. Hypotension is not a death sentence, which is why you can get rid of frequent drops in blood pressure caused by one reason or another. We use folk remedies, observing all the features and norms.
- Foot baths. We use a temperature no higher than 45 degrees, which will help normalize blood pressure. Add a spoonful of sea salt and 2-3 drops of rosemary essential oil to a bath of water. With the help of hydromassage for your feet, you can normalize your blood pressure and ease the general condition of your body. You can steam in such a bath for no more than 20 minutes.
- Tea infusions. Everyone knows that tea helps normalize blood pressure, relieves headaches and returns to normal functioning. We will use rosemary leaves as a tincture. To do this, you need to take up to 5 grams of dry leaves and fill them with boiled water in a volume of 250 ml. Cover the container with a lid and set aside for 20 minutes for the broth to infuse. You should drink at least 3 cups of this tincture per day. The blood pressure will improve in a few days, and the headaches will go away on the first day of treatment with the tincture.
- Tincture of rosemary leaves. You need to take 80 grams of dry rosemary leaves, pour 500 ml of dry white wine over them. We leave it for 5 days so that our tincture is well saturated and acquires all its medicinal properties. After 5 days, take the tincture one spoon twice a day, preferably before meals.
- Healthy sleep. Most often, poor and inadequate sleep is the main cause of headaches and low blood pressure. During sleep, the head should be positioned higher than the rest of the body, ensuring an optimal level of oxygen flow to the blood. It is this position that can save you from frequent headaches without causing a causal decrease in blood pressure.
Folk remedies have an even greater positive effect than medications. The main thing is to use them correctly, follow all dosages and times of administration. Taking folk remedies should also be carried out after consultation with a specialist, who will determine whether certain methods of traditional medicine will be useful, and whether they can further aggravate the patient’s condition.
Forecast
It is difficult to say exactly what a patient can expect. A group of factors is taken into account:
- Age.
- Floor.
- The nature of professional activity.
- History of somatic pathologies (concomitant).
- Duration of the condition.
- His reaction to the treatment.
- Degree of physical activity.
- Family history.
- Blood pressure level in general, over a longer period of time.
- Main diagnosis.
In general, an indicator of 30 mmHg against a background of blood pressure of 110 over 80 has good prospects in terms of preserving life. This is not yet a critical level, although it is an alarming signal. If treatment is prescribed, there is a high probability of full recovery.
A blood pressure of 110 over 80 in an adult is not normal due to low PP levels. This is an indication of pathology; natural factors do not lead to a decrease in the indicator. Diagnostics will put an end to the issue. Treatment methods and prognosis are determined after.
Characteristics of indicators and their norm
Blood pressure level is 120 at 80 mm Hg. Art. considered normal for an adult. If we look specifically at these numbers, then 120 means systolic pressure (upper). The indicator indicates the pressure with which the blood acts on the vessels when the heart muscle contracts. 80 - lower pressure (diastolic), recorded at the moment of diastole (relaxation of the heart). The difference between the numbers should be from 30 to 40 mm Hg. Art. This indicator is called pulse pressure.
The level of blood pressure in a particular person may depend on the age group he belongs to, his body constitution, gender, weight, climate, emotional and physical state, his level of physical activity, as well as the presence of concomitant pathologies and the state of hormonal balance.
If systolic pressure rises to 140 mm Hg. Art. and higher, experts talk about hypertension, and in the case of a persistent increase - about arterial hypertension. With a stable decrease in upper pressure below 100 mm Hg. Art. We are talking about hypotension. If we talk about the diastolic indicator, then hypertension is diagnosed at numbers above 90 mmHg. Art., and hypotension – below 60 mm Hg. Art. Quite often there is an increase or decrease in only one indicator: either only the upper one, or only the lower one. In addition, the level of blood pressure depends on the force with which myocardial contraction occurs, on the state of the blood coagulation system, the elasticity and tone of blood vessels, as well as the volume of circulating blood.