Your blood pressure is constantly 120 over 60, but you don’t feel any discomfort, then don’t worry about the reduced readings. For some people, low diastolic blood pressure is normal and does not mean hypotension. But if, with a pressure of 122 over 66 or 119 over 59, you feel weak and dizzy, then do not ignore the symptoms of a drop in blood pressure. The development of hypotension occurs slowly, but it is better to identify it at the beginning and find out what it means if the pressure is 120 over 60. Delaying diagnosis will not benefit the heart and blood vessels.
Is 120 over 60 normal?
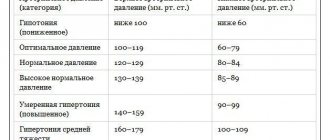
Blood pressure should not go beyond 110-130 to 70-85. Pulse pressure - the difference between the upper and lower - 30-40 units. With tonometer readings of 121 to 61, an anomaly in diastolic and pulse pressure is already noted; even readings of 117 to 67 are not much better, although here the lower pressure is close to the border.
Is blood pressure 120 over 60 normal for a person? Only in the case of genetic, chronic diseases or congenital abnormalities that do not require treatment, but cause hypotension. For everyone else, such indicators are a clear deviation, and you need to find out what this means in an adult or child.
For a child who has not reached puberty, such tonometer readings are completely dangerous. Find out what the indicator says by consulting your doctor.
In young people, the indicators are within the range of 123 to 63, with a short-term decrease due to hormonal imbalances during puberty. If such blood pressure does not provoke side symptoms in a teenager, then there is no reason to worry. But if at 20 years of age and older a person has a large difference between systolic and diastolic pressure, then you need to understand why lower blood pressure does not increase for a long time.
Is blood pressure 120 over 60 normal or not for an elderly person, middle-aged men and women? No, such indicators indicate malfunctions in the cardiovascular system. If you do not notice any abnormal conditions, then monitor your blood pressure and consult a doctor at the first problem.
Diagnostic methods
The reason why low blood pressure decreases can be determined through comprehensive diagnostics. The list of survey activities includes:
- General blood analysis. Biochemical research allows us to identify anemia, which often causes low blood pressure, especially in young women.
- ECG. An echocardiogram gives a complete picture of the structure of the heart and whether its functioning is normal. In this way, it is possible to determine heart valve disorders and other severe pathologies in a person of any gender and age.
- X-ray. Through X-ray examination, it is possible to identify a number of diseases that can lead to fluctuations in blood pressure, accompanied by an increase or decrease in heart rate.
Reasons for a persistently low diastolic reading
A blood pressure of 120 over 60 is not normal unless a person suffers from diastolic hypotension all his life. For people who notice a decrease in their lower pressure for the first time, they need to look for the reasons for the failure.
If you are not at rest, and the tonometer shows 124 to 64 or lower, then first calm down and measure the pressure. The tonometer may be wrong, or the body may simply have reacted violently to an external factor.
There are certain environmental factors that can cause a drop in diastolic blood pressure. But if this is not your option, then look for the reason for the pressure of 120 to 60 in pathological conditions of the body.
Natural
Isolated diastolic hypotension is not always caused by severe illness or pathogens entering the body. There are also natural factors that contribute to a temporary or long-term decrease in lower blood pressure down to 62-68:
- In boys and girls, blood pressure jumps during adolescence, which does not require treatment, but needs to be monitored.
- Pressure 120 over 60 during pregnancy is a variant of the norm in the absence of poor health of the woman.
- For a man, a sharp drop in diastolic pressure is typical after intense physical activity, when the body’s strength runs out.
- Emotional overload, stress and lack of sleep together have a bad effect on the circulatory system.
- A change in weather causes a violent reaction in the body in 20% of people. For some this manifests itself as a jump to 150 to 100, for others a decline to 126 to 65. If after a couple of days the indicators do not recover, then the problem was not due to weather dependence.
- The body's reaction to medications. The drugs often have associated side effects, and diastolic blood pressure may drop.
- In athletes, drops in blood pressure are rare, but each body reacts differently to stress.
- Serious illnesses, surgeries, blood loss - such factors often affect the cardiovascular system.
Natural physiological changes in the human body cannot cause harm. But if you do not control your blood pressure, an additional pulse of 80 or more appears, and severe weakness develops, then this is a reason to consult a doctor.
Pathological
Diseases caused by the entry of foreign microorganisms, viruses, etc. into the body, as well as pathological malfunctions of organs, can reduce blood pressure to 120 to 60:
- Pathology of the thyroid gland with reduced production of hormones.
- Adrenal dysfunction, accompanied by a lack of cortisol, a hormone that affects blood pressure. Changes can also be triggered by organ surgeries, long-term therapy, and tumors.
- Diabetes mellitus is a disease that affects all systems and organs, and therefore vascular tone decreases and the heart becomes weaker.
- Pituitary pathologies are another type of hormonal imbalance that provokes a drop in diastolic pressure.
- Anemia due to blood loss or insufficient functioning of the hematopoietic organs. Because of this, the pressure often drops below 100 to 60, hemoglobin changes, and pale skin appears.
- Osteochondrosis of the spine in the cervical region. When nerves are pinched, the brain sends the wrong signals to the organs or they do not reach them. This provokes cardiac dysfunction.
- Kidney diseases. This organ influences the functioning of the cardiovascular system more than others. With a lack of renin, the excretory system deteriorates, causing the tonometer readings to change.
- Any disruptions in the functioning of the central nervous system.
In rare cases, changes in blood pressure cause viral or bacterial diseases, which are dangerous due to their complications.
Home treatment
High blood pressure is sometimes called the “silent killer” because it may not cause any symptoms but can wreak havoc on the body. Therefore, it is very important to follow home treatment to avoid complications such as stroke or heart attack.
Comprehensive home treatment includes:
- Physical exercise. 30 to 60 minutes of activity is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Along with this, blood pressure normalizes and body weight decreases. You need to start training gradually, increasing the load.
- Low salt diet. The basis of the diet should be vegetables, fruits and whole grains. Meat, fish and dairy products should be lean and cooked without salt, preferably steamed or baked. Sweets, carbonated drinks, juices and animal fats are strictly limited.
- Using herbs instead of salt. As a rule, many spices already come with salt, so you should pay attention to the label. Provencal or Italian herbs, as well as basil, oregano, dill and parsley, are well suited for cooking.
- Losing excess weight. Excess body weight affects the heart and other organs, so losing weight is important. This will reduce the risk of serious diseases.
Is there anything I need to do if my blood pressure is 120/60?
You shouldn’t draw hasty conclusions about the cause of the pressure drop on your own. If you notice indicators of 118 to 60 or close to it, then first assess the condition. If symptoms of illness are present, solve problems one by one. Take a headache pill and lie down if you feel weak.
Do not take medications with hypertensive properties. This will increase your systolic pressure, making you feel worse.
If you experience such pressure regularly, but there are no alarming symptoms, then try to strengthen the body and make its work easier:
- Eat nutritiously, do not limit yourself by types of foods, but do not overeat.
- If you are overweight, lose a couple of kilos.
- Start moving actively - walking in the forest, jogging, daily exercises, aerobics and other feasible exercises are useful.
- Get enough sleep, don't overwork, take time to relax during the day.
- Stop smoking, try not to drink alcoholic beverages, especially in large quantities.
During pregnancy, in childhood and adolescence, in case of chronic diseases, self-medication with drugs is not allowed. Strengthen and maintain your body at home, and go to the doctor for medications.
Methods of therapy
Treatment is systematic and comprehensive. It is carried out using several methods.
Use of medications
- Cerebrovascular drugs. Improves cerebral circulation and heart trophism. Piracetam, Actovegin.
- Nootropics. Normalize metabolism in cerebral structures. Glycine.
- Midodrine and its analogs. Constrict blood vessels, increase blood pressure.
- Caffeine and preparations based on it. Including Citramon, but with caution.
The selection is carried out by a doctor; a group of medications is usually prescribed, rather than just one single remedy.
Folk remedies
- Eleutherococcus (2 teaspoons 2 times a day).
- Tansy decoction (200 grams of raw material per 500 ml of water, drink a glass a day).
- Ginseng tincture (35-40 drops per day).
- Lemon with cinnamon and honey. No more than 6 tablespoons per day.
This is not the main method of therapy, only an addition that should enhance the effect.
Lifestyle change
- Quitting smoking, alcohol and drugs (even more so).
- Walking, physical activity (minor, 2 hours a day).
- Salt no more than 10-12 grams per day.
- Sleep - 8 hours per night.
Proper nutrition.
Can:
- Cereals, porridge.
- Vegetables fruits.
- Berries.
- Kissels, fruit drinks.
- Jelly.
- Natural sweets.
- Nuts, dried fruits, honey.
- Tea.
- Coffee.
- Lean meat and soups.
- Bread.
It is forbidden:
- Fried foods.
- Smoked meats.
- I'll bake it.
- Canned food.
- Semi-finished products.
- Pork, beef.
The diet is adjusted with a nutritionist.
Symptoms
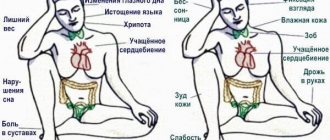
Isolated diastolic hypotension is clinically mild in the early stages. But if in a person’s usual mode the tonometer shows 128 to 85, and then there is a jump, then the symptoms will be:
- Increased heart rate up to 110 beats per minute.
- Dizziness, aggravated by sudden changes in position.
- Aching or shooting headache.
- Fainting against a background of constant weakness and malaise.
- Constant fatigue, inability to perform physical and mental work.
- Increased irritability.
- Pale skin.
- Coldness of the extremities.
Severe symptoms require immediate medical attention or consultation with a doctor. If you have a headache and can’t bear other symptoms of low blood pressure, call an ambulance. Do not take strong medications on your own, as without calculating the dosage you will provoke a hypertensive crisis or a jump in systolic pressure.
How does a person feel?
An increase in blood pressure is always accompanied by a number of symptoms. If the numbers change by 5-10 units, symptoms may be less pronounced or completely absent.
If the numbers change by 10 units or more, then signs appear that can cause serious discomfort or even restrictions on normal life activities.
The main manifestations of pressure 125/80 include:
- chest pain;
- headache, mainly in the back of the head;
- fatigue;
- vision problems;
- labored breathing;
- arrhythmia;
- blood in urine.
A physiological increase in blood pressure does not cause any symptoms. If any disease occurs that causes high blood pressure, the above symptoms will manifest themselves and cause discomfort.
When is it necessary to contact a specialist?
If you are in one of the conditions described below, then you need to see a doctor immediately:
- Migraine for several hours, medications cannot relieve the pain.
- Constant dizziness, accompanied by disorientation and loss of consciousness.
- Difficulty breathing; if shortness of breath, mild or severe suffocation appears in a calm state, this indicates an approaching hypotonic crisis.
- A pressing feeling in the chest area, heart pain.
- Tachycardia on a constant basis or attacks throughout the day. When the heart beats strongly, it puts a lot of stress on it. Inelastic vessels may not withstand such pressure and rupture.
- There is noise in the head and ears, vision is impaired, spots appear before the eyes, it gets dark.
For pregnant women and elderly people, such symptoms are especially dangerous and require a quick response. If you cannot fix the problem yourself, and light medications do not raise your blood pressure above 127 over 65, then this is a reason to call paramedics.
Possible consequences
Among the complications:
- Myocardial infarction. Acute necrosis of cells of the muscular structures of the heart. It begins abruptly and quickly leads to irreversible changes and a fatal decrease in organ activity. Requires treatment. Even if successful, heart failure develops, which leads to death within 3-5 years without complex therapy.
- Stroke. Malnutrition of brain structures. Ischemic type. Hemorrhage is not common. It can also be fatal in the short term.
- Injuries due to falls. Fainting can happen at the most crucial moment. Therefore, patients with uncompensated hypotension should not drive. It is better not to visit potentially dangerous places.
- Cognitive impairment. Decreased memory, attention. Speed and productivity of thinking. The risk of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases also increases (by approximately 6-8%).
- IHD and dysfunctional disorders.
Prevention of complications is one of the main goals of therapy.
Which doctor should I contact?
First visit to a therapist. He will conduct an examination, measure blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate, and collect anamnesis. Based on the data received, the doctor will refer you to a specialized specialist or issue forms for testing.
Further measures depend on the suspected factor in reducing diastolic pressure. Most often, the diagnosis is carried out by a cardiologist after the initial examination, but if third-party problems are identified, the patient is referred to a neurologist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist or urologist. During pregnancy, a woman is observed by a specialized specialist together with a gynecologist.
In severe cases, the patient is hospitalized in the hospital according to clinical indications, and then the department doctor is involved in diagnosis and treatment.
Necessary examinations
They are carried out under the supervision of a cardiologist. It is possible to involve other specialists: endocrinology, excretory system, etc. Comprehensive diagnostics includes the following activities:
- Recording patient complaints, objectifying symptoms.
- Collecting anamnesis, including family history, to identify the causes of the pathological process.
- Measurement of blood pressure in the arms and legs at intervals of several tens of minutes. It is better to carry out in a hospital to obtain more accurate data.
- Daily monitoring using an automatic tonometer. Allows you to evaluate the dynamics of blood pressure in normal, familiar living conditions.
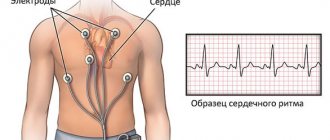
- Electrocardiography. For the diagnosis of heart defects and disorders of the functional activity of the organ.
- Echocardiography. Necessary to detect changes in cardiac structures. This is the most accurate method.
- Study of the state of blood flow in the brain. Dopplerography of blood vessels.
- Blood tests for hormones, general and biochemical.
- If necessary, angiography, MRI, CT.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys.
In the absence of evidence for organic pathology, natural factors are sought. If there is neither one nor the other, we are talking about an idiopathic form of hypotension.
How to increase at home?
Reduced diastolic pressure at the same time as normal upper pressure is difficult to normalize without medication. Drugs should be directed to the source of the pathology, and symptomatic therapy will not help change the tonometer readings. At home, you can drink strong coffee or brew a cup of sweet black tea. If you feel dizzy, drink green tea. In addition to caffeine in its usual form, Citramon will cope with low blood pressure - take 2 tablets.
With a sharp drop in blood pressure, a contrast shower helps improve the condition of blood vessels; changes in water temperature are not strong. Although alcohol is prohibited for problems with the cardiovascular system, if there is a sharp drop in diastolic blood pressure, place 10 drops of cognac on a piece of sugar and dissolve slowly.
If your relative or friend’s blood pressure has dropped, then you can help him with the following measures:
- Lay on the bed, cover with a blanket if you have chills.
- Unbutton your shirt collar and remove all heavy clothing from your chest.
- Open a window for fresh air.
- Start rubbing your legs, moving from your ankles to your knees.
- Give him coffee, strong tea, or another caffeinated drink.
If these measures do not even slightly improve your condition within 30 minutes, call an ambulance.
How to normalize
It is necessary to reduce the pressure from 125 to 80 or 85 only if it is caused by pathological reasons and can lead to complications or is observed in a hypotensive person. And also, if accompanied by unpleasant symptoms that interfere with normal life.
Normalization of pressure includes several stages:
- You need to check the readings again. Perhaps the measurement was taken incorrectly.
- You should relax and lie down. The head should be higher than the level of the heart; a reclining position is ideal.
- Provide oxygen access. Unbutton your collar and open the window.
- Apply a cold compress to the back of your head.
- You can take a hot foot bath, it will improve blood circulation to the periphery.
This is where first aid ends. If the pressure has not decreased within 20-30 minutes after the start of assistance, you should consult a doctor. He will examine the patient and prescribe, if necessary, the necessary medications.
It is very important not to use medications that lower blood pressure on your own, as they can lead to loss of consciousness or coma.