Causes of nausea when pressure changes
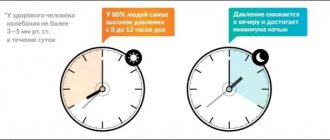
Nausea does not always indicate a serious health problem. The cause of the condition may be toxicosis in a pregnant woman, poisoning with low-quality products, motion sickness after traveling in transport, or anemia. But if the problem recurs regularly and is accompanied by an increase or decrease in blood pressure (blood pressure), it is worth undergoing an examination and understanding the root cause of the disorder. The diagnosis and treatment regimen for this condition depend on the pressure at which you feel sick.
Most often, experienced hypertensive patients experience nausea, accompanied by vomiting, headache and tinnitus. The more severe the stage of the disease, the more pronounced these symptoms are when blood pressure jumps. When blood circulation in the brain is impaired, the vomiting center is irritated, and an adult or child begins to feel sick and vomiting appears.
Nausea with high blood pressure is most often caused by the approach of a hypertensive crisis. The person begins to panic, this leads to the release of cortisol and adrenaline, which provoke the growth of cerebrospinal fluid. Against this background, intracranial pressure increases, and there is a risk of cerebral hemorrhage. The body tries to cope with the serious condition by increasing urination and vomiting begins.
Additional symptoms of the disorder include lethargy, redness of the face and neck, and numbness of the extremities. If high blood pressure develops into a stroke, then nausea is accompanied by slow speech, deviation of the tongue when protruding to the side, dizziness, and severe headache.
Both in case of a stroke and a hypertensive crisis, it is important to seek qualified medical help as quickly as possible
Nausea with low blood pressure may indicate physical or nervous exhaustion or meteosensitivity. The symptoms are caused by strict diets, lack of sleep, stress, and lack of vitamins and microelements in the diet. But things don't always turn out to be so harmless. A feeling of nausea with low blood pressure may be a manifestation of internal bleeding and pathologies of internal organs. This symptom is also characteristic of true hypotension.
Dizziness due to hypertension
Professor Olga Dmitrievna Ostroumova gave a lecture “Dizziness with arterial hypertension: is antihypertensive therapy sufficient?”
00:00
Drapkina Oksana Mikhailovna , executive director of the Internet Session, secretary of the interdepartmental council on therapy of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences:
— Now we are moving on to a new, very interesting section “Dizziness in the practice of a therapist.”
Section consisting of one lecturer and discussion. Professor Ostroumova Olga Dmitrievna. The lecture is called “Dizziness with arterial hypertension: is antihypertensive therapy sufficient?”
Olga Dmitrievna Ostroumova , professor:
— Good afternoon, dear colleagues.
We will talk to you about dizziness. Dizziness is at least one of the most common complaints that patients present (if not the most common complaint).
If you look at any manuals on internal medicine (and not only internal medicine), the description of the clinical picture of almost every disease will contain dizziness. It turns out that the number of diseases that cause dizziness runs into the thousands, if not tens of thousands.
But dizziness is not always correctly diagnosed. It is very difficult to treat it. This is the kind of complaint that almost always remains the last. Other complaints are already going away, but the patient keeps complaining and complaining about dizziness. It feels like this is a saving straw.
Issues of polypharmacy. In order to relieve dizziness, doctors use many medications off-label. In general, the problem, at first glance, is simple, but it turns out to be very complex.
The main problem is that what the patient understands by dizziness, what the doctor understands by dizziness and the formal definition of dizziness are completely different things.
In fact, the patient uses the word “dizziness” most often where it does not exist. He has “lightheadedness”, weakness, darkening of the eyes, and a faint state. The complex of sensations preceding fainting is called the beautiful word “lipothymia”. This is either a decrease in cerebral blood flow or a change in the direction of reducing its supply of oxygen and glucose.
This happens with orthostatic hypotension, with hypoglycemia and a number of diseases of the cardiovascular system (CVS): aortic stenosis, sick sinus syndrome, tachyatrythmia.
02:41
By dizziness, the patient very often understands instability, unsteadiness. When walking, he staggers and throws, especially when turning, changing the pace of walking, or when initiating walking. In particular, this happens with damage to the cerebellum, with peripheral neuropathy, and with a number of diseases of the spinal cord.
Vague sensations that are difficult for the patient to describe: a feeling of heaviness, intoxication, discomfort inside the head. The patient also uses the word “dizziness” very often. In such a situation, most often we will talk about psychogenic dizziness (depression, phobia, anxiety). But not only this, of course. These are the most common options.
The first moment when the patient utters this word, you must try very carefully, with leading questions, to understand what complex of sensations is bothering him. Is it really dizziness?
True dizziness is the illusion of movement of surrounding people or objects around a person. Or, conversely, a person around people or objects. This is understood as true dizziness.
Accordingly, all diagnostic search algorithms, which are described in various manuals and monographs, relate to true dizziness. Once again, as taught in propaedeutics. Very thorough history taking. Try to understand, I emphasize again, with leading questions, what kind of complex of sensations the patient has, whether this is really true dizziness.
Believe me, most likely it will not be true dizziness. Further, based on the complex of sensations, the diagnostic search will go in completely different directions, completely inconsistent with the algorithm for true dizziness.
Our task is to talk about true vertigo. If this is really dizziness, if we completely simplify it without harming the patient, then we distinguish between vestibular dizziness (true, which is associated with the vestibular apparatus) and non-vestibular, that is, beyond it.
Vestibular vertigo. Vestibular apparatus. What is it, what are the options. The first is peripheral (damage to the labyrinth). The second is intermediate (vestibular nerve, transmission of impulses from receptors to the brain). Finally, the central one is where impulses about the position of our body in space come (this is the central nervous system).
05:54
Arterial hypertension is almost the most common complaint of dizziness among patients. Moreover, both before the start of antihypertensive therapy and during it. Including with formal stabilization of blood pressure, when we reach target numbers. It seems that this complaint haunts both patients and doctors.
If you look at whether these are really interconnected things, it turns out that, most likely, according to available data, arterial hypertension itself is not the cause of dizziness. We need to look for other reasons. For now, examine not the disease, but the patient, then treat.
We have already agreed that dizziness is a strictly defined thing - the illusion of the movement of objects around a person or, conversely, a person around objects or other people. The most common cause of true present dizziness in patients with arterial hypertension coincides with that in the population.
Relatively speaking, since hypertension occurs often in older people (more than 80%), the most common cause of true dizziness that exists in the population is involuntarily transferred to this population of patients with hypertension. This is benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. We will return to it later.
The most common cause of non-systemic (non-vestibular) dizziness is psychogenic dizziness. We will not comment on this.
Much more often, it is not hypertension that leads to dizziness, but, on the contrary, an excessive decrease in pressure. I would say, not even so much in terms of numbers (although this also occurs, they reduced the millimeters of mercury too much), but rather would focus your attention on the excessively rapid decrease in blood pressure. Pace, pace and more pace. Even in a state of hypertensive crisis.
Of course, if there is concomitant diabetes mellitus, this is hypoglycemia, rhythm and conduction disturbances, which are partly associated with hypertension, if there is myocardial hypertrophy. But very often with concomitant cardiovascular diseases (CVD) in the patient.
Of course, orthostatic reactions. They generally occur with arterial hypertension. But much more often in elderly hypertensive patients and when arterial hypertension is combined with diabetes mellitus. They happen without treatment. One of the features of hypertension in the elderly is an increase in orthostatic reactions.
Some antihypertensive drugs cause orthostatic hypotension and collapse as side effects. These are β-blockers. We rarely use these drugs to treat hypertension. But now these drugs are gaining popularity among urologists. Very often we began to encounter this indirectly.
09:29
In my opinion, extremely indicative and one of the fundamental works is the work carried out under the guidance of Professor V. A. Parfenov. This is a professor at the Department of Nervous Diseases of the First Moscow Medical University. The department is headed by Academician Yakhno. He deals with this problem a lot.
A very interesting, carefully executed study. 60 hypertensive patients were taken with a complaint of dizziness. The vast majority of situations (80%, four out of five patients) – nothing was found in the patients at all during the most thorough examination. There are no somatic or neurological disorders.
Thus, the first assumption that needs to be confirmed is psychogenic dizziness (anxiety, depression, phobias, and so on).
17% – diseases of the peripheral part of the vestibular apparatus (benign paroxysmal positional vertigo or vestibular neuronitis). We'll talk about it a little.
A most thorough examination revealed a tumor of the cerebellar angle in one patient, and migraine in one patient. One patient had AV block. He was given a pacemaker, after which the dizziness disappeared.
11:03
None of the patients showed a connection between dizziness and increased blood pressure.
Let’s just say a few words about this peripheral dizziness. True dizziness is a defeat of the labyrinth. Peripheral cause, vestibulatory apparatus.
There are also several reasons for dizziness. But we are internists, not specialists in ENT diseases and not neurologists. A few words about benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (the most common cause of dizziness, in the general population, or in a patient with arterial hypertension. After psychogenic).
How does this dizziness manifest itself? Survey, survey and survey again. I won’t tell you anything new since you completed the propaedeutics course. 50% of the success of a diagnosis is a correctly collected analysis and complaints.
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is a short, no more than a minute, attack of systemic vertigo that occurs only with a certain position of the head. Most often in a lying position.
A single attack or a series of attacks at the slightest movement of the head. When you interview, the patient paints approximately this picture for you. Despite the extreme lack of time, do not forget to ask leading questions.
There are no neurological or any other symptoms; with repeated provocation of attacks, their severity decreases.
The presence of freely moving particles in the semicircular canals is the most common cause of dizziness.
There are the simplest tests for diagnosing it, which every internist can master. Treatment consists of special exercises, the effectiveness of which is up to 90%. Usually, drug treatment is not even required.
How to be. Of course, the main treatment should be aimed at eliminating the causes that caused dizziness. Treatment of dizziness is a complex treatment. No matter how safe it may seem (when almost everyone has a symptom, it is involuntarily easy to relate to it), we know how difficult it is to treat. The drugs must be used as a complex.
13:59
We have the drug “Betahistine” - an analogue of histamine. Histamine receptors are found in different organs. I want to pay particular attention to the H3 receptors that have been found in the cerebral cortex of rats. Accordingly, high histamine levels cause negative feedback and decreased histamine release.
Histamine receptors are located not only in the central nervous system (CNS), but also in the vestibular apparatus. The vestibular nuclei are very rich in histamine receptors.
Histamine is a very effective remedy in the treatment of dizziness and Meniere's disease, for example. But it is administered intravenously. It has a number of side effects. I think you represent them perfectly. I won't repeat myself. It is obviously unrealistic to treat patients with dizziness with histamine.
The corresponding searches were underway. Betahistine was created. A major study has begun. The drug has been used for quite a long time.
How it affects different types of receptors. Basically, it acts on the third type of receptors (H3 receptors). A powerful antagonist. Doesn't work on H2 at all. On H1 it is a very weak agonist. This action can also be neglected.
This immediately results in a very good safety profile. Low incidence of side effects. It has no effect on other types of receptors (non-histamine).
The drug that I think you know, Betaserc, shows a complex mechanism of action. It improves regional blood flow in the inner ear area. Normalizes the excitation of peripheral receptors. Normalizes the process of excitation in the area of the vestibular nuclei of the brain stem. Quite a wide range of mechanisms of action.
16:10
Appropriate placebo-controlled studies were conducted, where it was shown that Betaserc was significantly different from placebo. It reduces the frequency of dizziness attacks. It also differs from placebo in reducing dizziness severity and duration.
I think that you all have your own experience with this drug. For the sake of order, we talked about how it differs from placebo. Patients of this kind are very susceptible to placebo effects. We have no doubt about the effectiveness of Betaserk.
Let me very briefly recall the indications: treatment and prevention of vestibular vertigo of various origins, as well as a syndrome including dizziness and headache, tinnitus, progressive hearing loss, nausea and vomiting, Meniere's disease and syndrome.
The only contraindication is hypersensitivity to any of the components of the drug.
Like the vast majority of drugs, Betaserc has a dose-dependent effect, including in the treatment of dizziness. The most effective dose is 48 mg/day.
The drug is very good for the speed of onset of effect. Maybe not completely until the dizziness completely disappears, but it is noticeable. Almost 80% (that's four out of five patients) feel either a complete disappearance of dizziness (depending on the severity) or a decrease in the severity and frequency of attacks. Almost everyone else feels the effect on the second or third day. It is extremely rare that the effect develops during the first week. Basically, the drug works on the first day or in the first days.
Recently a new dosage has appeared - 24 mg. Taken twice a day. There is no need to take the daily dose. The lower the frequency of administration, the better the patient’s adherence to therapy. Accordingly, the effectiveness of treatment is higher. There are economic benefits.
We weren’t lazy, we did the math. It turned out that the new dosage of 24 mg is 13% more economical than the dosage of 16 mg. In the old dosage of 8 mg, almost 50%.
The age-old and very difficult question: brand or generic. We will not go deeper into this painful topic. You understand that price should not come at the expense of quality.
In pharmacoeconomic studies there is such an indicator as “price-effectiveness” (the ratio of quality and price). Do we really gain something by paying less money? Or it will turn out to be “money down the drain.”
There was such a pharmacoeconomic study of a number of generics of the drug Betaserc. In short, the drugs Betaver, Vestibo, and so on have significant differences in clinical effectiveness.
Thus, in pharmacoeconomic terms, the drug “Betaserc” wins. It has proven to be most effective in relieving dizziness. There was better tolerance. Costs also indicate that among the three drugs studied, the original drug Betaserc turned out to be the most cost-effective due to its effectiveness. But, unfortunately, this is a very common reason.
This is what I wanted to discuss with you within the allotted time frame. I wish you to feel dizzy only from success.
20:29
How to get rid of a symptom of hypertension?
It is important to remember that a sharp decrease in pressure in such a situation can only worsen a person’s condition. What to do and how to help the patient before the doctors arrive? The set of medications that can be taken for hypertension and nausea consists of several types of medications. These include:
Headache with low blood pressure
- diuretics prescribed by a doctor;
- medications to lower blood pressure that the patient takes regularly;
- antiemetics;
- antispasmodics to eliminate spasms;
- painkillers that you can take for headaches.
If you feel nauseous and have a headache with high blood pressure, you need to provide the patient with rest. The person should take a relaxed position (half-sitting) and try to minimize any movements. A good solution would be a cold compress on the head and warming the feet with warm water. This increases the flow of blood to the legs from the head, and the pressure decreases slightly.
We must not forget about the flow of fresh air into the room. To do this, you can open the window slightly, turn on the fan or air conditioner. The clothes that tighten the chest and neck are unbuttoned. If your blood pressure is high, your readings should be measured every 15 minutes, and if the condition does not improve, take another dose of an antihypertensive drug.
Advice! Aromatherapy can be an additional help for nausea that accompanies high blood pressure. Wormwood or peppermint oil is good for calming, reducing the gag reflex and helping to reduce blood pressure.
How should a hypotensive person act?
The condition of low blood pressure and nausea can be caused by several reasons. For example, people who react sharply to changes in weather outside the window may suffer from the disorder. Taking certain medications can also cause a drop in blood pressure, nausea and vomiting. Heatstroke or sunstroke often cause discomfort in the stomach due to low blood pressure, severe weakness and increased heart rate. Such conditions do not pose a threat to life and pass rather quickly.
If the pressure drops sharply in a person who does not suffer from hypotension, then the cerebral blood supply decreases, which leads to disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus and provokes vomiting. Nausea with pressure below normal may indicate problems in the functioning of internal organs and requires mandatory examination. It is especially important to consult a doctor if this condition occurs repeatedly.
Hypotonic patients who suffer from low blood pressure regularly report nausea and vomiting against the background of a throbbing headache. This is due to changes in cerebral circulation characteristic of hypotension.
Other provocateurs of the condition include parasitic infections, radiation exposure, food poisoning, chemical poisoning, etc.
Whatever the reasons, the person should be helped. To do this you need:
- Place the patient horizontally. The legs should be higher than the head to ensure blood flow to the back of the head. If this is not possible, the person is seated with his head lowered between his legs.
- A great way to reduce nausea and stabilize blood pressure is to drink a cup of hot sweet tea.
- Medications that increase blood pressure should be prescribed by a doctor. But there are drugs that are most popular among hypotensive patients. These are “Caffeine”, “Dopamine”, “Dihydroergotamine”. If you have a headache and nausea with low blood pressure, the Citramon tablet will help.
With low blood pressure, a 15-minute massage of the fossa located above the upper lip will help.
Uncomplicated hypertensive crisis
Hypertension occurs so often that it has already become something commonplace and familiar, which people brush off: just think, my blood pressure has risen, I’ll take the usual pill, lie down and it will go away. However, everything is not as simple as it seems.
Emergency
Like many chronic diseases, hypertension is fraught with emergency conditions, namely crises. A crisis is an increase in blood pressure (BP) above normal values
, accompanied by clinical symptoms and requiring immediate
controlled
reduction.
“Above the usual values” is important. There is an opinion that hypotensive people cannot have hypertensive crises, but this is not so. When blood pressure increases from the usual 90/60 to 130/80 (which is considered normal according to the generally accepted classification), a person may experience a real crisis.
Nausea at normal blood pressure
Your blood pressure is normal, but you start feeling nauseous regularly? There may be several reasons why you feel sick. They are:
- sudden change in body position;
- stressful situations;
- atmospheric pressure difference;
- staying in a stuffy room or transport.
This condition, if not regular, is not dangerous. However, if attacks become frequent and are combined with loss of consciousness, you need to make an appointment with a neurologist. Among the possible diagnoses in which nausea appears against the background of normal blood pressure may be the following diseases:
- disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- arthritis;
- spasm of cerebral vessels;
- diabetes;
- brain tumor;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- anemia;
- diet or fasting.
Important! Only a doctor can make a conclusion about the cause of the disorder and draw up a treatment regimen with medications and physical procedures. Self-medication is unacceptable. It can cause a number of disorders and worsen the patient’s condition.
Why do you feel sick when you have high blood pressure?
Nausea with hypertension is a consequence of a malfunction of the entire body. To a greater extent, this symptom is associated with dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system.
As the tonometer numbers increase, cerebral circulation disturbances are observed. In this case, the parts of the brain responsible for the gag reflex are stimulated. Constriction of blood vessels, an increase in blood pressure on the arterial walls leads to a malfunction of the sympathetic nervous system. With high blood pressure, the frequency of myocardial contractions increases. With tachycardia, a person often experiences nausea. Vomiting occurs due to increased intracranial pressure.
In addition to nausea, a number of other unpleasant symptoms occur with hypertension:
- headache;
- numbness of the limbs;
- redness of the epidermis of the face;
- weakness;
- chest pain.
If blood pressure rises frequently and is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, then you should consult a doctor. The doctor will conduct an examination, prescribe an examination, and find out what caused the pressure surges and poor health.
In the last stages of hypertension, nausea can be caused by renal failure and intoxication of the body.
Prevention measures
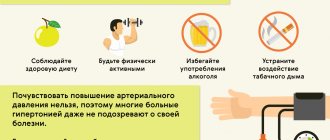
You can avoid nausea with pressure only by following a number of rules that help normalize blood pressure. Moreover, the recommendations for hypotensive and hypertensive patients are similar. You need to do the following:
- Give up bad habits - when nicotine and alcohol enter the body, the risk of developing disorders of the cardiovascular system increases.
- Lead an acceptable active lifestyle - regularly engage in sports, the intensity of which depends on the initial diagnosis. For example, a hypotensive patient can run in the nearest park and visit the gym, while for an elderly hypertensive patient, the optimal exercise would be morning exercises or swimming.
- Minimize stress. Of course, it is impossible to completely eliminate unpleasant situations from life, but it is possible to reduce their number to a minimum and not neglect the sedatives recommended by your doctor.
- Adjust your diet. An excess of fried, spicy, salty foods affects not only your figure, but also your overall well-being. Having mastered the rules of balanced nutrition, you can strengthen your body, stabilize your blood pressure and forget about bouts of nausea.
The answer to the question of whether nausea can occur at low, high and normal blood pressure is relevant for many. And it is important to pay attention to this symptom and not let it take its course. It is quite possible that the attack of vomiting is provoked by a serious disorder, which can only be identified after a comprehensive examination.