Medical editor: Strokina O.A. - therapist, functional diagnostics doctor. November, 2021.
Early ventricular repolarization syndrome (EVRS) is a medical concept that includes only ECG changes without characteristic external symptoms. It is believed that SRRS is a normal variant and does not pose a threat to the patient’s life.
However, recently this syndrome has become viewed with caution. It is quite widespread and occurs in 2-8% of cases in healthy people. The older a person gets, the less likely it is that he or she will have SRR; this is due to the emergence of other cardiac problems that are similar in electrocardiographic signs as they age.
Most often, early ventricular repolarization syndrome is diagnosed in young men who are actively involved in sports, in men who lead a sedentary lifestyle, and in people with dark skin (Africans, Asians and Hispanics).
Early ventricular repolarization syndrome - what is it? General information
Specific cardiac syndrome is found not only in patients with heart pathology, but also in absolutely healthy people. Early repolarization of the ventricles is called premature repolarization syndrome. Very often, WPW syndrome confused with premature repolarization, despite the fact that these are completely different pathologies.
Pathological changes on the ECG were considered normal for a long time, until a clear relationship with heart rhythm disturbances was revealed. The disease is asymptomatic, which greatly complicates timely diagnosis.
The syndrome of early (premature, accelerated) repolarization of the ventricles of the heart is characterized by specific changes in the electrocardiogram in the absence of obvious causes. ICD-10 code: I45.6
Possible manifestations and consequences for the body
As a rule, if repolarization is disrupted, nothing bothers a person. Therefore, in almost everyone, this syndrome is detected either during a preventive medical examination or during examination for another disease.
If symptoms appear, then only if a repolarization disorder occurs against the background of some kind of cardiac pathology. Then the patient may complain of heart pain, dizziness, rapid pulse, etc.
I am often asked whether impaired myocardial repolarization is dangerous, especially during pregnancy. No, but it may indicate the presence of cardiac disease.
As for SRRH, for a long time it was considered absolutely harmless, it was taken for an “accidental find”. However, many years of clinical studies have cast doubt on this.
It turned out that those people who had signs of SRR on the ECG have a very high risk of developing paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in the future (in a few years).
Pathogenesis
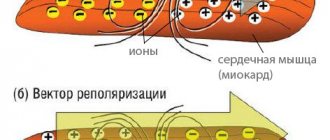
Contraction of the chambers of the heart occurs as a result of changes in the electrical charge in myocardial cells - cardiomyocytes . As a result, sodium, calcium and potassium ions move into the intercellular space and back. The process is carried out in alternating main phases:
- depolarization – contraction;
- repolarization is relaxation before a new contraction.
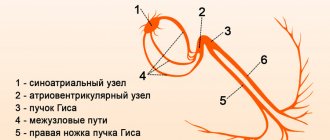
Early repolarization of the ventricles is formed as a result of improper conduction of the impulse through the conduction system of the heart from the atria to the ventricles. To transmit the electrical impulse, abnormal conduction pathways . The development of the phenomenon is due to an imbalance between repolarization and depolarization in the basal regions and apex of the heart. Characterized by a significant reduction in the period of myocardial relaxation. On the ECG, along with the SRRS, a disturbance of repolarization processes in the myocardium is often recorded, in particular, a violation of the repolarization of the lower wall of the left ventricle.
Clinical case
I recently observed a patient who came to me with complaints of difficulty breathing, which worsened when walking, climbing stairs, and at night.
He has been suffering from arterial hypertension for several years. I did not receive any treatment. During a general examination, an increased heart rate of up to 126 per minute and high blood pressure of up to 150/95 mmHg are noted. Art., swelling of the feet and lower thirds of the legs, enlargement and tenderness of the liver upon palpation. An ECG was performed. interpretation - sinus tachycardia, diffuse disturbances in the processes of repolarization of the left ventricular myocardium, signs of left ventricular hypertrophy. The patient was referred for echocardiography. Holter monitoring revealed no other pathological abnormalities. The result is hypertrophy and dilatation (expansion) of the left chambers of the heart, a decrease in the ejection fraction of the left ventricle - 55%. A clinical diagnosis was made: “Chronic heart failure stage IIB, functional class II according to NYHA. Background disease: Stage III hypertension, stage 2 arterial hypertension.” Treatment was prescribed: limiting salt intake to 3 g per day, Bisoprolol 5 mg once a day, Perindopril 10 mg once a day, Amlodipine 5 mg once a day.
Classification
In children and adults, early ventricular repolarization syndrome can have 2 development options:
- without damage to the cardiovascular system;
- with defeat.
According to the nature of the flow, they are distinguished:
- transitory form;
- permanent form.
Depending on the location of the ECG signs of SRGC, they are divided into 3 types.
- I characteristic signs are observed in a healthy person. ECG signs are recorded only in chest leads V1, V2. The likelihood of complications developing is extremely low.
- II ECG signs are recorded in the inferolateral and lower sections, leads V4-V6. The risk of complications is increased.
- III ECG changes are recorded in all leads. The risk of complications is the highest.
Diagnostics
Since this syndrome is an electrocardiographic phenomenon, it can only be established with a certain examination:
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the heart (echocardiography): stress echocardiography (for impaired ventricular contractility)
- resting echocardiography;
In addition, tests are carried out on a bicycle ergometer or treadmill: after physical activity, the heart rate increases, and the ECG signs of SIRS disappear.
A potassium test is used: after taking potassium chloride, panangin or rhythmocor at least 2 grams, the severity of ECG signs of repolarization syndrome increases.
A test with isoproterenol and atropine is not used due to severe side effects.
It is important to distinguish between SRR and myocardial infarction, pericarditis, Brugada syndrome. For this purpose, differential diagnosis is carried out.
Causes
The true reasons have not been fully studied. There are only hypotheses for the occurrence of early repolarization:
- Genetic predisposition. Mutation of genes that are responsible for balancing the processes of the entry of certain ions into the cell and their release out.
- Disruption of the processes of contraction and relaxation of individual areas of the myocardium, which is characteristic of type I Brugada syndrome .
- Changes in cardiomyocyte action potentials. The process is associated with the mechanism for the release of potassium ions from cells. This also includes increased susceptibility to a heart attack during ischemia .
According to statistics, accelerated repolarization syndrome is typical for 3-10% of healthy people of all ages. Most often, changes are recorded in young people aged 30 years, in people leading a healthy lifestyle and in athletes.
Nonspecific factors influencing the development of early ventricular repolarization syndrome:
- congenital form of hyperlipidemia , which provokes the development of atherosclerotic changes ;
- long-term use of certain medications, or overdose (for example, beta-agonists);
- connective tissue dysplasia , which is characterized by additional chordae in the ventricular cavity;
- high blood cholesterol
- electrolyte imbalance;
- neuroendocrine changes;
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;
- heart defects : congenital, acquired;
- disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system;
- hypothermia of the body;
- excessive physical activity.
Description of the cardiac cycle
The contraction of the heart is caused by electrical impulses that are conducted to each cell of the myocardium (heart muscle). After receiving such an impulse, each cardiomyocyte goes through a stage of contraction and relaxation, which constitute the cardiac cycle. However, behind each of these stages there is a complex mechanism for the flow of calcium, potassium and chloride ions out of and into the cell. The electrical changes in the membranes of cardiomyocytes that underlie contraction are called depolarization, and those that underlie relaxation are called repolarization.
Click on photo to enlarge
Symptoms
Clinical symptoms are observed only in the form of the disease that is accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system:
- loss of consciousness, fainting ;
- rhythm disturbances ( tachyarrhythmia , extrasystole , ventricular fibrillation );
- vagotonic, hyperamphotonic, tachycardial, dystrophic are formed under the influence of humoral factors on the hypothalamic-pituitary system;
- systolic and diastolic dysfunction of the heart caused by its hemodynamic disorders ( pulmonary edema , hypertensive crisis , shortness of breath , cardiogenic shock ).
Tests and diagnostics
The main changes are recorded precisely on the electrocardiogram. Some patients simultaneously experience clinical symptoms of cardiovascular diseases, but most often patients feel absolutely healthy and do not notice any changes.
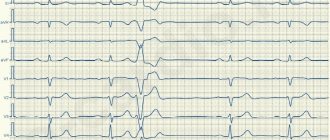
Early ventricular reoplarization syndrome on ECG:
- elevation of the ST segment above the isoline;
- the convexity when raising the ST segment is directed downwards;
- an increase in the R wave with a parallel decrease in the S wave or its complete disappearance;
- point J is located above the isoline, at the level of the descending knee of the R wave;
- expansion of the QRS complex on the ECG;
- a “notch” is recorded on the descending limb of the R wave.
Signs of SRS
There are no characteristic clinical signs of early ventricular repolarization syndrome. There are only specific changes on the ECG:
- ST segment and T wave changes;
- in a number of branches, the ST segment rises above the isoline by 1-2-3 mm;
- often ST segment elevation begins after the notch;
- the ST segment has a rounded shape and directly passes into a tall positive T-wave;
- the convexity of the ST segment is directed downwards;
- The base of the T wave is wide.
Early ventricular repolarization syndrome in children
The reasons for the development of early repolarization syndrome in children can be very different:
- lack of sleep and irregular daily routine;
- excessive emotional stress;
- physical overload;
- constant anxiety, stress or nervous fatigue;
- isolation, lack of healthy emotional contact with parents;
- hypothermia;
- poor quality and unbalanced nutrition.
A similar syndrome can be recorded on an ECG in any child who reacts too emotionally to the assessment of his knowledge at school, takes current events to heart, and is overloaded in extracurricular activities. Lack of proper rest and intensive training in sports clubs can negatively affect the child’s well-being.
Forecast. What is the danger of early ventricular repolarization syndrome?
Modern cardiologists work to prevent and prevent the development of pathology, which can lead to death. That is why patients with early ventricular repolarization syndrome should be regularly monitored by a cardiologist to monitor the dynamics of the ECG and to identify hidden symptoms of other pathologies. It is not the syndrome itself that is dangerous, but the consequences it can lead to in the absence of proper treatment of the causative disease.
Persons who play sports are recommended to undergo examination at specialized physical education clinics, assessing their condition before and after intensive training, as well as before competitions.
There is no clear data on the transition of SRGC to a serious pathology. The risk of death increases significantly with alcoholism , abuse of fatty foods and smoking. A timely and complete competent examination will help to identify or exclude the true cause and avoid problems in the future.
Treatment and proper observation
There is data on the use of so-called “energotropic” drugs (Carnitine, Kudesan), which normalize metabolic processes in the myocardium. However, repolarization disorders themselves usually do not require treatment.
I prefer to pay more attention to the conditions and pathologies that caused the disorders, and if they are identified, direct therapeutic measures (medicinal and non-medicinal) to eliminate them.
In the absence of any illnesses, it is necessary to regularly see a doctor in the future. At least once a year, undergo a minimum cardiological examination - face-to-face examination, ECG, Holter monitoring.
In case of long-term course of SRR, to prevent the occurrence of arrhythmias, I use magnesium preparations, less often - antiarrhythmic drugs (Amiodarone).
If life-threatening arrhythmias occur, radiofrequency ablation may be necessary.