Tests and diagnostics
To identify the true cause of changes in the myocardium, it is recommended to undergo a full examination, which includes:
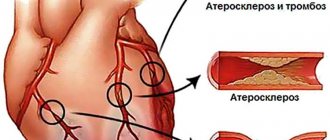
- General analysis and biochemical blood test. Based on the results, it will be possible to talk about the presence of an inflammatory process in the body, the functioning of the renal system and kidneys, and the level of cholesterol , which forms plaques in the coronary arteries.
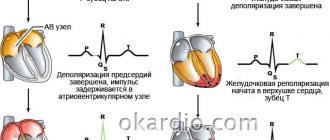
- ECG. Characteristic changes during the examination make it possible to determine further examination tactics. In some cases, it is recommended to perform an ECG with stress, or organize daily ECG monitoring.
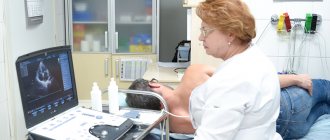
- EchoCG. Ultrasound examination of the heart allows you to assess the condition of the valve apparatus of the heart, identify areas of damage, and evaluate the pumping function of the heart.
- Myocardial scintigraphy. The radioisotope research method shows areas of accumulation of a special substance to identify areas of damage and determine their nature.
Changes in the myocardium on the ECG make it possible to determine further tactics for examining the patient to establish an accurate diagnosis and select the correct therapy.
Causes
Dystrophic changes in the myocardium
Such changes in the ECG are formed due to insufficient nutrition of cardiomyocytes, which inevitably leads to a decrease in the contractility of the left ventricle. Diffuse-dystrophic changes in the myocardium are observed with:
- pathologies of the endocrine system: diabetes mellitus , adrenal dysfunction, disorders of the thyroid gland;
- pathologies of the renal system and liver: excessive amounts of toxic metabolic products negatively affect the functioning of the heart;
- chronic diseases of infectious origin: changes can be observed with tuberculosis , influenza , malaria , etc.;
- chronic iron deficiency anemia : constant oxygen starvation affects the functioning of cardiomyocytes;
- with an unbalanced diet, with vitamin deficiency in the diet;
- with excessive nervous and physical overload;
- with fever and concomitant dehydration;
- in case of poisoning with alcohol, medications or chemical components.
Metabolic changes in the myocardium
What it is? Characteristic nonspecific changes on the ECG are formed as a result of disturbances in intracellular metabolic processes associated with potassium and sodium ions.
Metabolic changes are associated with dystrophy of the heart muscle and appear when:
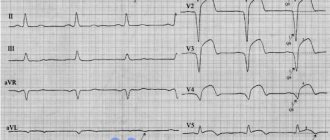
- ischemia , which is reflected on the cardiogram in the form of deviations of the T wave. Its polarity and shape changes in the leads corresponding to the damaged areas;
- myocardial infarction : the location of the ST segment changes on the ECG, which is located either above or below the isoline;
- death, necrosis of the myocardium, which is characterized by the appearance of an abnormal Q wave.
Scar changes
Areas of scar tissue form at the site of a former inflammatory process, necrosis, as a result of which normal, healthy cardiomyocytes lost their contractility and were replaced by connective tissue that does not have elasticity. Focal cicatricial changes on the ECG indicate a previous myocardial infarction .
- The lower wall of the left ventricle is characterized by changes in leads: II, III and a VF (indicates damage to the right, less often the left circumflex coronary artery).
- The anterior septal region is characterized by changes in leads: V1 and V2 (the left descending septal branch is damaged), or V2-V4 (the left descending coronary artery or its branches is involved).
- The anterior-lateral region is characterized by changes in leads: I, aVL, V4-V6 (the circumflex artery or the left descending artery is damaged).
- Anterior widespread infarction is characterized by changes in leads: I, aVL, V1-V6 (the left descending coronary branch is damaged).
Moderate inflammatory changes in the myocardium
Characteristic changes are observed in myocarditis, in which the voltage of the waves in all leads decreases and rhythm disturbances are recorded. Moderate left ventricular changes may occur after:
- typhus , diphtheria ;
- rheumatism , after streptococcal infection ( tonsillitis , tonsillitis , scarlet fever );
- infections caused by the Coxsackie virus, rubella , influenza , measles ;
- exacerbation of an autoimmune disease ( systemic lupus erythematosus , scleroderma ).
Brown myocardial atrophy
This is what a macropreparation is called during histological examination. Characteristic pathological changes in the myocardium are formed as a result of a long-term lack of blood supply, which is observed in debilitating diseases, cachexia , drug abuse, increased physical activity, and also in old age. lipofuscin, is deposited . Its granules are a product of impaired metabolism in cardiac muscle cells, weakened by insufficient nutrition and blood supply.
Treatment of early ventricular repolarization syndrome
Repolarization syndrome does not require specific treatment. The only thing that is offered to the patient is observation by a cardiologist.
However, a person with SRS should avoid alcohol consumption and intense physical activity to avoid triggering an attack of tachycardia.
In some cases, radiofrequency ablation of an additional beam is performed in an invasive way (a catheter is brought to the site of the beam and destroys it).
Sometimes energotropic therapy (B vitamins, carnitine, phosphorus and magnesium preparations, Mexidol, Kudesan), antiarrhythmic drugs (amiodarone) are used.
Important! The patient should retain all previous ECGs, which is required to exclude the diagnosis of myocardial infarction if heart pain occurs.
Dystrophic disorders
These changes in the myocardium of the left ventricle are provoked by a lack of nutrients, without which the heart muscle will not function normally. In medicine, this condition is referred to as cardiac dystrophy, and it appears due to the following factors:
- disruptions in the functioning of the kidneys and liver, because these organs are responsible for metabolic processes;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- shocks affecting the central nervous system;
- serious loads;
- low hemoglobin level;
- infectious pathologies of a chronic nature;
- intoxication;
- unhealthy diet, causing vitamin deficiency;
- frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- long-term use of drugs.
- Features of the ECG during myocardial infarction - the procedure and signs of the disease
Often this condition is detected in adolescents during exams, when they are mentally overstrained. But in young children, changes in the myocardium are considered normal, and all because metabolic processes are not yet perfect. Also, older people may suffer from such changes, because metabolic processes in their bodies slow down.
Description of the pathology
Changes in the myocardium of the left ventricle can provoke various diseases or metabolic disorders in the heart muscle.
Moderate cardiac dysfunction can be diffuse or focal. The first type is characterized by failure of the myocytes of the left ventricle, as a result of which they contract incorrectly. That is, the electrical impulse is carried out incorrectly through these cells. The second type is focal changes. In this case, scars form on the wall of the left ventricle. They consist of connective tissue that is not capable of conducting electrical impulses.
Moderate metabolic disorders can return to normal on their own, but if such disruptions occur frequently, the myocardium cannot recover.
Thus, changes can transform into irreversible ones. As the situation worsens, they can provoke cardiac pathologies.
When there is a discrepancy between energy consumption and its entry into the myocardium, the consequence will be degenerative changes. But even dystrophy does not always manifest itself, and if there are symptoms, it is often increased fatigue, which is not always paid attention to.
Left ventricular hypertrophy is a condition that the body activates to compensate for the blood flow process. This happens especially often if there is mitral valve insufficiency. Hypertrophy affects the condition of the walls of the left ventricle; they lose elasticity. This also applies to the septum between the ventricles.
With hypertrophy, thickening of the walls also occurs. It is not always uniform; it can occur according to a focal principle, that is, only in a certain area of a given cavity. And myocardial dystrophy leads to the fact that the wall of the left ventricle becomes significantly thinner, and the chamber cavity stretches.
Pathogenesis
Changes in the ECG are not a disease, but only a manifestation of some pathological processes occurring in the myocardium. With shifts in the biochemical activity in the heart cells, their contractility changes, which is reflected in the cardiogram when recording the conduction of impulses. Cardiomyocyte function can be impaired during inflammatory processes, for example, with myocarditis . Taking certain medications also affects the functioning of the heart muscle.
Long-term diabetes mellitus can gradually lead to atherosclerosis . Not only large vessels are affected, but also the coronary arteries that supply the myocardium. With inflammatory pathology in the gastrointestinal tract, the absorption of nutrients is impaired, which also negatively affects metabolic processes in cardiomyocytes.
Diffuse changes
What are “diffuse-type changes in the left ventricular myocardium”? This type is the most common. In this case, not only the left ventricle is affected, but also the entire myocardium, since diffuse changes are characterized by uniform damage.
Diffuse disorders appear both in moderate pathological processes and in acute situations, such as myocardial infarction. In the latter case, there are changes in the structure of tissues and disruption of metabolic processes. Diffuse changes are an accumulation of myocytes in the left ventricle, which, under the influence of certain factors, have changed and do not conduct impulses.
With diffuse disorders of the left ventricular myocardium, swelling of the legs, tachycardia, and even fluid accumulation in the lungs are added to the general symptoms.
Diffuse changes in the myocardium of the left ventricle can provoke a deterioration in the circulatory process, myocardial hypoxia and the appearance of necrotic foci. The most dangerous consequence of these disorders is myocardial infarction.
Is there a danger with changes in the myocardium?
Moderate changes in the myocardium are a fairly common pathology that gradually affects healthy cells of the heart muscle. Doctors say that this leads to the development and progression of heart failure. Let's consider whether it is worth showing concern when diagnosing such a pathology, what it is: moderate disturbances in the myocardium.
Such changes may not always be dangerous. Especially if it does not manifest itself with pronounced symptoms. Often pathology is discovered during a regular medical examination. If a person does not feel any problems with the functioning of the heart, then most likely there is no need to show concern. The reason for a visit to a cardiologist should be:
- pain in the heart area;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- dyspnea;
- high or low blood pressure;
- weakness, drowsiness.