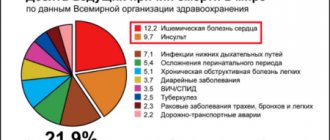
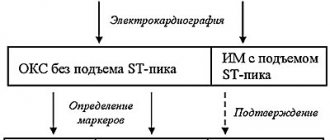
Diagnosis of angina is based primarily on typical symptoms – pain in the heart area. However, to confirm the diagnosis and choose the optimal treatment, your doctor may prescribe additional examinations.
When diagnosing angina, your doctor will listen to your heart to assess the rhythm of contractions, heart rate, and the presence of a heart murmur. The doctor will also examine you for concomitant diseases that may worsen the course of angina: he will measure your blood pressure (at the first visit, usually in both arms) for timely diagnosis of hypertension and refer you for a biochemical blood test. A test for glucose (sugar) will help rule out diabetes; a test for cholesterol and its fractions (LDL, HDL) will reveal elevated levels of blood fats, which contribute to the rapid progression of atherosclerosis.
To more accurately diagnose angina and determine the prevalence and severity of atherosclerotic vascular lesions, you may be referred for examinations:
|
Diagnosis of angina pectoris
An important task in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases is the differential diagnosis of angina pectoris. In most cases, angina pectoris is a symptom of coronary heart disease that develops as a result of cholesterol deposition on the inner walls of blood vessels, so the efforts of cardiologists should be aimed at diagnosing the latter.
If you feel discomfort and pain in the chest or left shoulder after heavy exercise or stress, immediately contact a cardiologist. Self-medication can worsen the course of the disease.
Remember, only a specialist using modern diagnostic tools can identify coronary heart disease, prescribe treatment and prevent a tragic outcome!
Diagnosis of coronary heart disease
The success of preventive and therapeutic measures depends on the timely detection of the disease and correct diagnosis.
Of course, the initial stage of diagnosing IHD is the collection and analysis of the patient’s complaints. This is followed by an examination, during which the cardiologist measures the patient’s blood pressure, visually assesses his condition (degree of swelling, skin tone, sweating, behavioral characteristics, etc.), listens to his heart with a stethoscope for murmurs, rhythm disturbances, etc.
Next, the specialist may prescribe the following tests and studies:
- clinical and biochemical blood tests;
- blood test for markers of myocardial infarction;
- electrocardiography (ECG);
- echocardiography (Echo-CG);
- ABPM;
- ECG with stress;
- coronary angiography (x-ray contrast examination of the coronary arteries).
1 Ultrasound of the heart for ischemic heart disease
2 Diagnostics of coronary artery disease in "MedicCity"
3 ABPM for ischemic heart disease
Interview and examination of the patient
An important role in the differential diagnosis of angina pectoris is played by questioning and examination of the patient. When compiling a medical history, the cardiologist studies all the symptoms that concern the patient, risk factors, for example, the presence of bad habits, obesity, etc., as well as possible genetic predisposition. During the examination, the doctor listens to heart sounds, looks for signs of damage to the main arteries, as well as signs of lipid metabolism disorders - one of the main causes of the formation of cholesterol plaques. Externally, they manifest themselves in the appearance of xanthoma and xanthelasma - skin neoplasms of a characteristic yellow color.
Holter monitoring
Daily, or Holter, monitoring is a continuous process of monitoring the patient’s heart throughout the day using a special recorder, the data from which is sent to the stationary equipment of the attending physician. This type of ECG allows you to diagnose unstable angina and angina in the absence of symptoms, helps evaluate previously prescribed treatment, records changes in the cardiogram during exercise, stress, sleep, etc. It can be either outpatient or inpatient, it depends on the purpose of the study and the patient’s well-being.
Features of the procedure
An ECG shows ischemia, angina, arrhythmia and other pathologies of the heart muscle in both adults and children. The study is carried out at rest, although studying changes in some indicators requires a small load. An ECG will also show heart failure. When carrying out the procedure in children, it should be taken into account that their normal values will differ from the established limits for adults.
To obtain accurate data from the results of an electrocardiogram, you should trust your heart to be checked by qualified specialists and have it done in specialized institutions. They are in every city. In the city of Bronnitsy, the Immunity MC conducts similar cardiological studies.
Cost and appointment
Load tests
Electrocardiography with physical activity (Stress ECG, Veloergometry) is a very useful method that helps diagnose angina pectoris. Also, do not forget about stress echocardiography, which allows you to clarify the diagnosis. Since angina pectoris manifests itself during physical activity, the method allows you to accurately determine the load threshold, the recovery period, and study the work of the heart after pain relief. Such diagnostics are carried out on a special bicycle ergometer and treadmill (treadmill). However, it is not suitable for everyone: stress tests are contraindicated in patients with acute angina.
Detectable diseases
This is what an electrocardiogram determines:
- Arrhythmia
- Myocardial infarction
- Myocardial dystrophy
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
- Ventricular hypertrophy
- Angina pectoris
- Tachycardia
- Bradycardia
- Cardiac aneurysm
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pericarditis
- Myocarditis
It is mandatory to do an ECG for patients over 40 years of age.
What is not visible on the cardiogram
No matter how perfect the diagnosis may seem, it does not show some pathological changes in the functioning of the heart muscle.
These include:
- Congenital heart defect
- Neoplasms
An ECG cannot diagnose cerebrovascular accidents (stroke). This pathology disrupts blood circulation in the brain, which can disrupt the functioning of other important organs. Carrying out a cardiogram in this situation will only determine the state of the heart muscle.
Pharmacological tests
Pharmacological tests are an alternative to stress tests and are recommended for patients who, for various reasons, cannot perform physical activity. The principle of their action is the introduction of special drugs, due to which the myocardial need for oxygen increases, thereby simulating activity. Depending on the drug, this need arises as a result of an increase in heart rate or redistribution of blood in favor of vessels not affected by atherosclerosis.
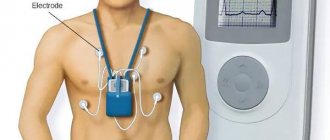
24-hour ECG monitoring (Holter)
Because stress tests may not be performed on all patients, your doctor may order 24-hour ECG (Holter) monitoring to detect ischemic changes. Just as with an ECG, small adhesive pads will be placed on your chest and electrodes will be attached to them. The ECG is recorded using a small portable device, which you will carry in a special bag over your shoulder for one or several days. You cannot take a shower or bath, or remove the electrodes yourself. If the electrode comes loose on its own, you must carefully return it to its place.
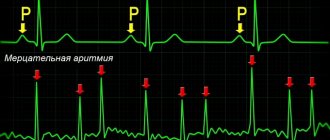
Registration of an ECG for a long time allows not only to record the heart rhythm and its disturbances, but also to “catch” ischemic changes during physical activity and stress (regardless of whether they are accompanied by pain or painless), as well as to record ECG changes characteristic of spasm of the coronary arteries in vasospastic form of angina).
To increase the information content of Holter monitoring in the diagnosis of angina, it is possible to discontinue medications (the same as before stress tests), perform physical activity to provoke painful attacks (climbing uphill, taking stairs, walking at a fast pace, etc.) and keeping a diary, in where you will record complaints and the time they occurred.
Save the Holter monitoring protocols with printed ECG fragments (as a rule, these fragments represent the identified pathological changes). Your doctor may be interested in this information not only immediately after recording the 24-hour ECG, but also several years after the study.
Thus, Holter is quite informative for diagnosing myocardial ischemia (including painless and vasospastic forms), and can also record disturbances in heart rhythm and conduction, and provide your doctor with additional information.
In the vast majority of cases, the cause of angina is atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries. Atherosclerotic plaques are distributed throughout all arteries of the body. For the initial diagnosis of atherosclerosis, ultrasound examination of large vessels located close to the skin can be performed. These are the arteries that supply blood to the brain and the arteries of the legs.
Diagnosis of angina pectoris at the Center for Pathology of the Circulatory Organs
Today, instrumental diagnostics play a valuable role in monitoring the state of the cardiovascular system. Coronary heart disease cannot be completely cured and requires the patient to pay increased attention to his own body. Monitoring the condition using modern medical equipment allows you to correctly adjust therapy, thereby prolonging the patient’s life.
The Center for Pathology of the Circulatory Organs conducts a full range of studies of the cardiovascular system . Our experienced cardiologists work with the latest medical equipment, which allows us to detect the disease in the early stages, as well as diagnose asymptomatic forms of angina.
Specializing in non-surgical methods for diagnosing and treating heart disease, our doctors quickly, painlessly and, most importantly, completely safely carry out any procedure, make an accurate diagnosis and return you to a healthy and fulfilling life!
Do not put off health problems; the key to success in the treatment of coronary artery disease is its timely diagnosis!
Multislice computed angiotomography (MSCT)
Unlike the carotid or femoral arteries, the coronary (coronary) arteries are extremely difficult to see using an ultrasound probe. When a doctor raises the question of the need for surgical treatment, the “gold” standard for diagnosing coronary atherosclerosis is coronary angiography, a surgical examination performed in the cath lab. Based on the results of CAG, surgeons can accurately determine not only the location and severity of atherosclerotic lesions, but also choose the method of operation. However, preliminary data on the vessels of the heart can be obtained using multislice computed tomography (MSCT). A special angio-program, which requires the introduction of an X-ray contrast agent into the body (intravenously), is capable of providing an image of the heart and blood vessels in three-dimensional format.
The study is carried out on an outpatient basis, painlessly, lasts about 10-30 minutes. During the study, the patient receives a dose of x-ray radiation and about 100 ml of x-ray contrast agent. To obtain a high-quality image, it is necessary that your heart rhythm is correct and quite rare (50-60 beats per minute, which is the lower limit of normal).
Thus, MSCT angiography is quite informative for obtaining preliminary data on the localization and severity of atherosclerotic lesions of the heart arteries, and in some cases, on the tactics of surgical treatment. However, MSCT results do not replace coronary angiography data, and this method is not recommended for routine examination of all patients with angina.
You have received information about the most commonly used methods for diagnosing angina pectoris and atherosclerosis as the main cause of angina pectoris.
Remember! These studies are carried out only when indicated, and the choice is made by your doctor based on your symptoms, the characteristics of your illness, the presence of concomitant diseases and the planned treatment strategy.