Since the last quarter of the twentieth century, cardiovascular diseases have steadily occupied a leading position among the most common diseases of mankind. They overtook all possible infectious diseases and even cancer. Cardiovascular diseases are such a widespread phenomenon that scientists, when talking about them, often use the term epidemic, emphasizing their prevalence.
But about a century ago, at the beginning of the twentieth century, they were extremely rare. But by the 50s of the last century, heart disease was already in 10th place in overall statistics. Today, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), they are in sad first place.
Hungry Heart
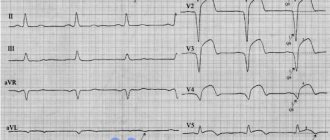
The heart, like any other organ, is supplied by blood vessels called coronary arteries. Narrowing of the coronary arteries leads to insufficient nutrition of the heart muscle, to oxygen “starvation,” which doctors call “ischemia.” Ischemia can occur when the heart requires more nutrients, such as during exercise. In this case, the patient experiences an attack of chest discomfort or angina. If blood flow through the coronary artery is suddenly blocked by a thrombus, then acute oxygen deficiency occurs and necrosis of part of the heart muscle, the so-called myocardial infarction, occurs.
Helpful information
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. To function well, the heart requires oxygen, which is supplied by the bloodstream.
What is ischemic, or coronary, heart disease?
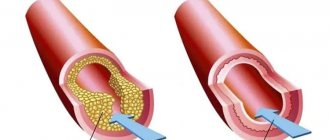
The basis of coronary heart disease is the gradual narrowing and blockage of the coronary arteries due to the deposition of fatty deposits called plaques on their walls. Plaques reduce the lumen of the artery, which leads to slow blood flow and insufficient nutrition of the heart muscle.
What is angina?
Angina pectoris is a signal that the heart muscle is receiving little oxygen and nutrients, which is expressed by the appearance of chest pain. Most often, angina develops during physical or emotional stress, which forces the heart to work more intensely. The pain may be accompanied by a feeling of tightness in the chest, heaviness, burning or squeezing behind the sternum. Typically, angina pectoris during exercise develops when the lumen of a large artery decreases by more than 50%. If the lumen is reduced by 90%, angina attacks can develop at rest. When less oxygen and nutrients enter the myocardial cell, metabolic disorders develop. This entire process of development of ischemia can be represented as an iceberg, the tip of which is the pain felt by a patient with angina pectoris, and the basis is metabolic disorders in the myocardial cell.
How long does angina pain last?
In most cases, the attack lasts no more than 5 minutes, but the duration can vary. Pain is usually relieved by taking nitroglycerin.
How is angina different from myocardial infarction?
In angina, blood flow to the heart muscle is partially reduced due to a temporary narrowing of the coronary artery. In a myocardial infarction, the blood supply to the heart muscle stops suddenly and completely due to a blockage in the coronary artery. As a result, the heart muscle dies. The presence of angina attacks significantly increases the risk of developing myocardial infarction.
In what cases should myocardial infarction be suspected?
Angina attacks become longer and more intense. Painful sensations persist regardless of movement and breathing. A feeling of fear, nausea, vomiting, sweating, a feeling of lack of air, and shortness of breath appear. No effect from taking nitroglycerin for 10 minutes.
Is angina treatable?
Yes. Your doctor will prescribe the drug that is most suitable for you, which will reduce the frequency of attacks and the intensity of pain. There are drugs that reduce or prevent the number of angina attacks by reducing myocardial oxygen demand or increasing its supply. These are beta blockers, nitrates, calcium antagonists. Currently, another group of drugs has appeared - myocardial cytoprotectors, which prevent ischemic cell damage and reduce the number of angina attacks, but through a different mechanism: influencing the “base of the iceberg” - metabolic processes directly in the myocardial cell. Remember that only a doctor will select the treatment you need in the required dose!
How should I change my lifestyle?
Follow a diet limiting the amount of salt consumed to 3g/s and fatty foods. Increased blood levels of cholesterol (C), triglycerides (TG), LDL cholesterol, this is the so-called “bad” cholesterol, contributes to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the coronary, cerebral, mesenteric arteries, as well as in tissues and internal organs (liver, pancreas) .
Cholesterol content in food (mg)
| Finished Products | Cholesterol in mg |
| Canned cod liver (100g) | 476 |
| Beef liver (100g) | 438 |
| Egg (yolk) | 202 |
| Chicken stomach (100g) | 212 |
| Shrimp (100g) | 150 |
| Fish caviar - pollock, red, black (100g) | 300 |
| Kidneys (100g) | 112 |
| Butter (50g) | 121 |
| Condensed milk (1 cup) | 2 |
| Sour cream 30% (1 teaspoon) | 5 |
| Fat cheese (25g) | 23 |
| Mayonnaise (1 teaspoon) | 5 |
| Chickens, white meat, wings, breast with skin (100g) | 80 |
| Boiled sausage (100g) | 60 |
| Milk 6%, fermented baked milk (1 glass) | 47 |
| Pork without fat (100g) | 88 |
Following the diet can lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels and promote weight loss. It is very important to quit smoking. Moderate exercise under the supervision of a doctor can strengthen the heart muscle and help the heart use oxygen more efficiently.
What can I expect in the future?
A healthy lifestyle and regularly taking medications prescribed by your doctor will help you live a longer, more active and fulfilling life.
The following tips will help you live a fulfilling life.
Follow all recommendations of your doctor;
Follow step by step to a healthy lifestyle;
Control your weight;
Have a clear understanding of the situations that cause angina attacks;
Keep a diary of self-monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate, and angina attacks.
Cardiologist Lador T.V.
Print Email
Two faces of a terrible disease
Often in the specialized literature two different terms are used - “angina pectoris” and “myocardial infarction”. Angina pectoris and myocardial infarction are two manifestations of one disease - coronary heart disease (CHD). At the same time, many patients who have had a heart attack are well aware of the symptoms of angina pectoris and, conversely, patients suffering from angina pectoris have ever suffered a myocardial infarction. The danger of myocardial infarction is that it often strikes suddenly - in about half of the cases, myocardial infarction occurs without any obvious harbingers of impending disaster.
Why is angina pectoris dangerous? Transition to myocardial infarction.
An angina attack usually goes away within 2 to 10 minutes.
after the first dose of a nitrate drug.
If an attack lasts more than 20–30 minutes
, it runs the risk of developing into
a myocardial infarction .
necrosis (death) of cells in one or more areas of the heart muscle occurs
Why does necrosis occur in the heart muscle?
Myocardial infarction is the result of severe oxygen starvation of the heart, when blood flow to the heart is reduced to a very low, dangerous level.
In such cases, the body uses compensatory mechanisms: additional small arteries send blood to the heart. But compensatory mechanisms cannot always cope with their task. For example, during a prolonged attack of angina.
In such a situation, first irreversible damage occurs, and then the death of those areas of the heart muscle that do not receive sufficient oxygen.
When the clock counts...
Angioplasty and stenting of arteries
- Cost: 100,000 - 250,000 rubles.
- Duration: 40 minutes
- Hospitalization: 1-2 days in hospital
More details
A fair question: can it effectively treat myocardial infarction? After all, its consequence is the necrosis of part of the heart muscle. If, during a developing heart attack, the cause of its occurrence is eliminated, that is, the patency of the clogged artery of the heart is restored, then the negative consequences of a heart attack can be significantly reduced.
The most accessible method of treating a heart attack is the administration of drugs that dissolve the clot. Such treatment can begin as soon as the doctor diagnoses a heart attack. But it is most effective only in the first hours from the onset of the disease. Later, the clot becomes more resistant to the drugs. In addition, after 6 hours from the onset of a heart attack, most of the cells in the affected area die and it is pointless to use drugs that are not sufficiently effective by this time. Another approach is mechanical removal of the obstruction in the coronary artery. To do this, using a special thin catheter, under X-ray control, the thrombus is recanalized and the lumen of the narrowed artery is expanded with a special balloon. This treatment method is called coronary angioplasty. Angioplasty is more effective than drug treatment late after a heart attack, with relatively “old” thrombosis.
Bypass pipeline
If blood flow cannot be restored using such a minimally traumatic method as coronary angioplasty, then they resort to open surgery - coronary artery bypass surgery. In this case, veins or arteries taken from other parts of the body are brought from the aorta, the main blood supply, to the arteries of the heart, so as to bypass (bypass) the area of narrowing or blockage. Similar methods can be used in the treatment of angina pectoris. Moreover, in developed countries they are already widely used. The advantage of surgical methods over medication is that they quickly and completely eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
Light at the end of the vessel
We can say that there is a certain category of people in whom the presence of atherosclerosis is very likely. In the vast majority of cases, narrowing of the coronary arteries occurs due to the development of deposits on the walls of the vessel - atherosclerotic plaques - narrowing its lumen. Increased blood cholesterol levels, a hereditary predisposition to cardiovascular diseases, excess weight, smoking, hypertension, diabetes mellitus are risk factors for atherosclerosis.
Prevention of angina
The best method of preventing disease is prevention. If you have at least one of the listed risk factors, except for heredity, which, unfortunately, cannot be influenced, it is advisable to exclude them.
- If you have physical inactivity
(sedentary lifestyle), include in your daily schedule
physical activity
that is suitable for you (for example, fitness, running, Nordic walking or regular walking for at least 30-60 minutes a day). It is not the severity of the physical activity that is important, but the involvement of a large number of muscle groups in the body. - Replace a high-calorie diet
based on eating fatty foods that contain a lot of cholesterol
with a balanced diet
that includes plenty of vegetables and fruits. Limit your salt and sugar intake. Instead of fried foods, choose steamed, boiled or baked foods. - The presence of excess weight
, as a rule, is a consequence of physical inactivity and a diet containing not only a lot of fat, but also a lot of fast carbohydrates.
To cope with extra pounds, daily physical activity
(you don’t have to go to the gym right away, you can start with walking) and
switching to a balanced diet
. It is important to limit the consumption of fatty foods, flour and sweets, and instead choose vegetables, fruits, honey, nuts, and dried fruits in small quantities! - If there is an increased level of cholesterol
in the blood plasma,
diabetes mellitus
or
arterial hypertension
it is important
to consult a doctor
so that a specialist can help you choose the appropriate treatment and give individual dietary recommendations. - It is advisable to quit smoking
, because it can provoke not only angina, but also other, no less dangerous diseases.
Bypass surgery, angioplasty or medications
Which method is better - coronary bypass surgery, coronary angioplasty or drug treatment? Each of these methods has its own indications. Sometimes it is necessary to use different treatment methods at different stages. Of course, drug prevention and therapy are necessary in almost all cases. Coronary angioplasty can also be used successfully in most patients. Briefly, treatment methods for ischemic heart disease can be grouped as follows:
- Medicines . Some of them are necessary to reduce blood cholesterol or high blood pressure. Other medications help people with angina avoid attacks during exercise. Some drugs prevent heart rhythm disturbances that often accompany coronary artery disease. A number of drugs are necessary for the prevention of heart failure after myocardial infarction;
- Thrombolytic therapy . This type of treatment is used to eliminate a blood clot in acute myocardial infarction, when blood flow is obstructed by a blood clot. Thrombolytic agents dissolve clots and restore patency of the coronary artery. Thrombolytic therapy is often combined with angioplasty;
- Angioplasty is a method of expanding the internal lumen of blood vessels using a special balloon. In this case, through a small puncture, the doctor inserts a thin tube (catheter) and brings it to the narrowed area of the vessel, monitoring the process using x-rays. The balloon, expanding under pressure, pushes apart and flattens atherosclerotic plaques, creating conditions for normal blood flow. In some cases, after this, a metal frame is installed - a stent, which, being implanted into the wall of the artery, does not allow it to narrow again.
- Bypass operation . During bypass surgery, a new blood supply is created that bypasses the blocked section of the artery. Shunts are usually created from the patient's own vein or artery, for example from the patient's leg. Bypass surgery is usually performed surgically, although more gentle, non-surgical bypass methods have recently been developed.
All these techniques have been successfully used for many years by doctors at the Center’s Cardiovascular Surgery Department. In this case, proprietary developments are used, including a unique vascular stent developed by the head of the department Z.A. Kavteladze and his employees and now produced by WILLIAM COOK (USA).
What to do if you have an angina attack?
- First of all, you need to try to pull yourself together and calm down
. Sometimes attacks of angina pectoris cause feelings of fear and panic in patients, which leads to an additional release of adrenaline into the blood, an even greater increase in heart rate, and as a result the attack intensifies. It turns out to be a vicious circle. - It is important to take a comfortable sitting or reclining position
. You cannot walk, stand or continue physical activity because... this may make the attack worse. You need complete rest until the pain symptoms go away. - Take the nitrate preparation under the tongue
.
Nitrate drugs dilate blood vessels and thereby stop an attack of angina. This could be, for example, nitroglycerin in tablets or spray form. - If, after taking a nitrate drug, the chest pain does not subside, it is recommended to take a second dose of the drug
(in total, up to 3 doses of the drug are allowed to be taken at intervals of 5 minutes).
If the medicine does not work, the pain does not subside for more than 10 minutes and even intensifies, you must urgently call an ambulance
!
Provocative diagnosis
If a person has several risk factors for ischemic heart disease, further examination is necessary to find out whether the person is experiencing ischemia or not. To do this, various so-called “provocative tests” are carried out, for example, tests with physical activity. By comparing the parameters of the heart at rest and under heavy loads, a conclusion is made about the need for further examination. At the next stage, a study of the heart vessels is usually performed - coronary angiography. Provocative tests, drug tests, and coronary angiography are included in the extensive arsenal of diagnostic methods of our clinic’s specialists. Based on the results of coronary angiography, the doctor chooses treatment tactics. After such a comprehensive examination, you can quite accurately predict the risk of a heart attack and take the necessary measures to prevent it.
Causes of angina pectoris.
Angina pectoris does not occur out of nowhere; most often there is a situation due to which the heart muscle begins to experience a greater need for oxygen. These situations include:
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- high blood pressure, hypertensive crisis;
- heart defects;
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- smoking;
- frequent drinking of alcohol;
- hereditary predisposition.
Remember that an unhealthy lifestyle is as serious a reason for increasing the risk of angina as serious blood pressure and heart problems. Human health is a single system, and to preserve it it is necessary to take a responsible approach to all aspects of life.