Causes of the condition
Cardiac asthma is the second name for acute failure of the pumping function of the left chambers of the heart. The occurrence of pathology may be associated with diseases of the cardiovascular and other systems; the main reasons are presented in the table.
| Cardiac (associated with left ventricular weakness) | Extracardiac (the appearance of disorders is caused by increased vascular permeability) |
|
|
The diagnosis of cardiac asthma is most often made at the prehospital stage of emergency care, which requires a differential approach to treatment depending on the underlying cause.
Reason
Cardiac asthma is a combination of other important cardiovascular diseases. All stinks are mainly associated with the increasing deficiency of the left sac. Most often, SA develops at the stage of decompensation of the following illnesses:
- Myocardial infarction.
- Mitral valve stenosis.
- Chronic cardiac aneurysm.
- Aortic defect.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Cardiosclerosis.
Such illnesses as acute nephritis and diffuse glomerulonephritis can also lead to cardiac asthma, and then to swelling of the lungs.
Main signs and symptoms
The pathogenesis of the development of symptoms of cardiac asthma is realized through:
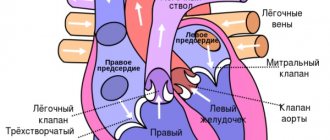
Decreased pumping function of the heart. Adequate blood flow to the left chambers and the absence of outflow contributes to the accumulation of fluid in the vessels of the lungs, with an increase in the volume in which the permeability of the wall increases. An increase in hemodynamic pressure “pushes” plasma into the intercellular space (interstitium) with further sweating into the alveolar cavities.- Increased permeability of the vascular wall against the background of other pathologies in which pulmonary edema can develop with preserved or minimally reduced cardiac function.
Swelling
Edema is a pathological accumulation of fluid in tissues that develops due to impaired lymphatic or venous outflow.
Features in acute heart failure:
- first, swelling of the neck area develops with difficulty breathing;
- swelling of the saphenous veins (jugular veins);
- swelling is cold, dense with a bluish tint;
- the liver increases in size (hepatomegaly).
- free fluid in the abdominal and chest cavity, pericardium.
The development of edema in cardiac asthma is associated with a decrease in the function of the right sections (due to impaired outflow along the pulmonary trunk), and stagnation of blood in the superior and inferior vena cava system.
Choking and coughing
The occurrence of symptoms from the respiratory system is caused by a decrease in the respiratory surface of the lungs due to the accumulation of fluid in the alveoli. Main features:
- dyspnea;
- suffocation;
- cough;
- hemoptysis.
The difference between the concepts of “shortness of breath” and “suffocation” lies in the severity and severity of symptoms.
Choking is an extreme form of breathing disorder, which is accompanied by a feeling of lack of air and fear of death.
Cough is one of the most common signs of pulmonary edema. Main symptom characteristics of cardiac asthma:
- constant (rarely in the form of attacks);
- sputum - mucous in moderate quantities, often mixed with blood (due to increased pressure in the chest cavity during coughing, bronchial arterioles rupture);
- secretion of foam (blood plasma contains a large amount of protein, which “foams” with sharp and fast air flows during coughing).
The appearance of cough in patients with cardiac asthma is caused by irritation of mechanical receptors in the bronchioles and the “need” to empty the lungs of fluid.
Dyspnea
Symptoms of cardiac asthma include shortness of breath as one of the key manifestations of the pathology, which is characterized by difficulty inhaling and exhaling, an increase in the frequency of respiratory movements and a feeling of lack of air.
Features of dyspnea of cardiac etiology:
- mixed type (as opposed to an attack of bronchial asthma, when exhalation is difficult);
- progression;
- patients take a forced orthopneic position - half-sitting with the lower limbs lowered and leaning on the shoulder girdle;
- the skin is pale, cold with sticky sweat.
X-ray examination of the chest organs with such symptoms is characterized by a picture of “wet lungs” with a diffuse decrease in the transparency of the fields, a blurred vascular pattern.
Heart pain and arrhythmia
Cardiac symptoms in acute circulatory failure most often arise due to a cardiac cause of the pathology.
Main manifestations:
rapid heartbeat (tachycardia);- pain behind the sternum, pressing in nature, lasting more than 20 minutes;
- a feeling of interruptions in the work of the heart (constant or paroxysms), sudden stops or extraordinary contractions;
- loss of consciousness (due to a sudden decrease in blood pressure, development of cardiogenic shock).
Diagnosis of rhythm disturbances and the choice of medications for relief are carried out based on the results of electrocardiography (ECG) recorded in 12 leads.
Pathogenesis
In a number of severe cardiological illnesses, insufficiency of the left ventricle is formed, which does not allow the weakened muscle of the ventricle to drain from the leg veins, causing a large blood loss. As a result, blood stagnation occurs in a small amount of blood circulation, and blood plasma leaks into the alveoli of the lungs. In especially important episodes, liquid accumulates in the bronchi. All this sounds characteristic of cardiac asthma, manifesting itself in the appearance of the buttocks, coughing and coughing.
The movement of the blood pressure in a small amount of blood flow provokes a reflex reaction, when the vessels in the alveoli are rushed. This organism tries to avoid further transudation of plasma into the tissues of the lungs. A similar compensatory reaction is known as the Kitaev reflex.
In fact, it is created more viciously, as the fragments create a stronger pressure in the leg veins, the stronger the reaction of the body in the form of Kitaev’s reflex. The more the arterioles are pressed, the greater the pressure on the veins of the lungs, which leads the blood to the left ventricle. Due to the weakness of the myocardium, a complete shortening and even worsening of the situation with a high pressure in a small amount of blood flow cannot be achieved.
The following officials can improve the health of the sick:
- Movements instead of liquid in the body (hyperhydration, complicating the process of removing liquid from the body).
- Increased blood flow on the surface of the small stake when occupying a horizontal position.
- Disorder of central regulation, which occurs more often during sleep.
- Physical or emotional attraction.
Cardiac asthma is accompanied by rapid heart rate and breathing, hypertension, and increased activity of the respiratory muscles. In addition, during the hour, breathing is required to observe the effect of forced inhalation, which in turn promotes the blood flow of the small vessels. In this case, central neuroregulation begins to break down, which gradually weakens the activity of the heart. As a result, cardiac activity becomes less effective, and the patient’s condition becomes even worse.
First aid to the patient: a short algorithm
Cardiac asthma is an indication for emergency transportation of the victim to a cardiology hospital or intensive care unit of a specialized center.
At the pre-medical stage it is necessary:
- call an emergency medical team (EMS);
- provide the patient with a free flow of oxygen (unfasten tight collars, open windows);
- give a semi-sitting position, lowering the lower limbs (for patients with low blood pressure - horizontal);
- if there is a history of coronary heart disease - Nitroglycerin or Isoket under the tongue;
- measure blood pressure; if the readings are low, apply venous tourniquets alternately to the arms and legs. It is forbidden to remove it abruptly - due to the risk of developing cardiogenic shock.
Timely (within the first 30 minutes) elementary methods of emergency care improve the prognosis for the patient: survival rate increases by 2 times.
The use of folk remedies to relieve cardiac asthma is strictly prohibited.
Upon arrival of the ambulance, the patient is provided with venous access (catheter) and painkillers are administered (Promedol, Morphine).
Emergency actions for pulmonary edema
Emergency care for cardiac asthma during hospitalization involves a set of measures that are aimed at increasing the pumping function of the heart and compensating for existing disorders (symptomatic therapy).
According to the protocol, in a hospital setting the following is carried out:
- oxygen therapy (depending on the patient’s condition: through a mask or in artificial ventilation mode);
- in the presence of hemoptysis with pink foamy sputum, use antifoam agents (Antifomsilan) using a special inhaler;
- diuretic therapy: Furosemide intravenous bolus 40 mg (Torasemide - 20 mg);
- vasodilators: intravenous Nitroglycerin – allowed when systolic blood pressure increases more than 110 mmHg;
- if there are signs of bronchial obstruction: Prednisolone, Theophylline;
- inotropic support (increasing the strength of heart contractions): Dopamine through a syringe injector at a dose of 3-5 mcg/kg/min, Dobutamine 2-20 mcg/kg/min;
- cardiac glycosides (if there is supraventricular paroxysmal tachycardia, atrial fibrillation on the ECG) - Digoxin.
Anticoagulant therapy is recommended for patients with acute coronary syndrome, atrial fibrillation, artificial valves, and deep vein thrombosis. Effective drugs are low molecular weight heparins (Enoxyparin, Fraxyarin, Deltaparin), which are administered subcutaneously at the rate of 0.1 ml per 10 kg of human weight.
Antiarrhythmic therapy is prescribed depending on the form of the disorder:
- ventricular fibrillation - electrical pulse therapy (up to 360 J), intravenously - 150-300 mg of Amiodarone, 1 mg of Adrenaline according to resuscitation recommendations;
- sinus or supraventricular tachycardia: Metoprolol;
- atrial fibrillation: Digoxin 0.125-0.25 mg intravenously, Amiodarone 150 mg, anticoagulant therapy is required;
- bradycardia (reduced heart rate): Atropine 0.25-0.5 ml, Isoprenaline 2-20 mcg/kg/min.
After relief of the acute disorder, the patient remains in the intensive care unit for 3 days, followed by transfer to a cardiology hospital to prevent possible relapses, rhythm disturbances and complications.
Diagnostics
Cardiac asthma in its clinical progression may be similar to low-grade asthma. For example, lack of breath and other signs of shortness of breath are also characteristic of bronchial asthma. Violent breathing and panic attacks often intensify during a hysterical attack. Other similar signs may be mistaken for SA for laryngeal stenosis or mediasthenic syndrome.
In making a correct diagnosis, we are first aided by the patient's history of illness. It is known that the patient had early history of hypertension or heart failure, so the development of cardiac asthma is highly likely. When the SA attacks, it is difficult to carry out diagnostics, the fragments in the first blood are to blame for the attack on the buttocks. However, doctors conduct a thorough objective examination of the pulse, evaluate the mucous membrane and skin, listen to the breath and heart tones.
An important diagnostic criterion that indicates the presence of cardiac asthma is the appearance of the first attacks in adulthood. Also, such patients almost always have another cardiac pathology.
With AS, the following changes may occur:
- The pulse is thread-like or weakly palpable.
- Tony's heart is muffled, you can hear the rhythm of a gallop.
- Arterial pressure on the kidney is indicated as movement, and then decreases.
- In the lungs, you may hear either wheezing or dry irritation.
To clarify the diagnosis, instrumental methods of investigation must be carried out. Firstly, electrocardiography, which shows characteristic signs of left ventricular insufficiency, arrhythmia or myocardial ischemia.
If possible, take a chest x-ray. The image will show signs of blood stagnation in a small amount of blood circulation: enlargement of the root of the legs, thickening of the leg muscles, and the contours of the heart may change.
Treatment: what pills to take to prevent complications
Secondary prevention of cardiac asthma involves preventing the progression of pathology and the development of undesirable consequences. Such patients are prescribed basic (basic) and symptomatic drug support depending on the primary disease:
antiplatelet therapy: Aspirin 75 mg/day – for life;- nitroglycerin 0.0005 mg - under the tongue when an angina attack occurs;
- in case of lipid imbalance – Atorvastatin 20 mg/day;
- angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (patients with arterial hypertension) – Lisinopril 10 mg/day;
- diuretic therapy: Spironaloctone 50 mg/day;
- patients with atrial fibrillation - indirect anticoagulants (Sinkumar, Warfarin), the dose of which is selected individually under the control of the state of the blood coagulation system.
Patients with impaired pumping function of the heart are monitored by a cardiologist, which means regular examinations, laboratory and instrumental studies, and periodic adjustment of drug doses.