Such manifestations can occur several times a year, a month, a day, or even not stop; they can last seconds, minutes, several hours or days in a row. In this article we will consider, specifically, episodic interruptions in the functioning of the heart.
Of all the variety of arrhythmias, the most common cause of these sensations are:
- extrasystole (extraordinary contractions of the heart)
- short paroxysms of tachycardia (episodes of heart rate acceleration)
In addition to interruptions in the functioning of the heart during an attack, you can experience the following types of discomfort:
- shortness of breath
- nagging or burning pain in the chest
- dizziness
- feeling of lack of air
- feeling of fear
There are a great many options for extrasystoles. But their main division is supraventricular (less dangerous) and ventricular
By origin, extrasystole can be of organic or functional origin.
Why might an arrhythmia attack occur?
Rhythm disturbances appear due to changes in cardiomyocytes (the working mass of the heart muscle), the conduction system (cells that establish the order of contractions), or due to pathology of other systems and organs. The following reasons are identified:
- Physical overload . An untrained heart tries to provide blood to the suddenly working muscles of the limbs, which leads to natural tachycardia. In this case, it is very important to know your submaximal heart rate - a limit beyond which you should not go. At higher heart rates, the organ wastes energy irrationally, since the period of myocardial relaxation is critically reduced.
- Psychological stress . Under the influence of strong emotional experiences, biologically active substances are released that cause the heart muscle to contract faster. “Pressor amines” are mediators synthesized by the adrenal glands (Adrenaline, Norepinephrine, Epinephrine, Norepinephrine), which cause vasospasm, tachycardia, and increased body temperature. During the day, their concentrations change, just like a person's mood.
- Abuse of bad habits and stimulants (nicotine, alcohol, tea and coffee) significantly changes the heart rhythm. Different substances have different effects on contraction frequency. In any case, it is strongly recommended to avoid bad habits due to their not always predictable harm to the cardiovascular system. There are a large number of fatal arrhythmias, in which it is extremely difficult to provide effective assistance to the victim due to the lack of medical personnel nearby. The lion's share of them falls on the state of intoxication.
- Hypoxia is a decrease in oxygen content in the blood. Occurs during prolonged stay in closed, hot rooms, in large crowds of people, or in the presence of respiratory diseases.
- Taking medications - glycosides, antidepressants, sympathomimetics.
- True cardiac causes : exacerbation of existing heart pathologies (coronary disease, developmental defects, cardiomyopathies, arterial hypertension).
- Endocrine pathologies (thyroid dysfunction), diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Idiopathic arrhythmia - occurs in the absence of an obvious cause.
Resulting
Why does the heart, which for the time being had been beating a clear rhythm, suddenly begin to lose track of it? This could be due to many circumstances:
- congenital or acquired heart disease;
- arterial hypertension;
Article on the topicHalfway to a stroke? Dispelling the main myths about hypertension
- electrolyte imbalance (deficiency or excess of potassium, calcium, magnesium in the body);
- hormonal imbalances (therefore, in menopausal women, the risk of arrhythmia increases);
- taking certain medications (diuretics and sympathomimetics, for example);
- concomitant diseases (thyroid pathologies, in particular);
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol, drug addiction).
What to do and how to relieve symptoms?
If the condition is accompanied by fear of death, loss of consciousness, or the person’s condition worsens significantly, it is necessary to call an ambulance. Before her arrival, at the pre-hospital stage, you should adhere to the following algorithm:
- Determine the presence and nature of arrhythmia by palpating the pulse in the carotid or peripheral arteries.
- Eliminate the impact of the factor, which provoked the arrhythmia:
- hypoxia - take to fresh air, free from tight clothing;
- physical overload - ensure complete rest;
- psychological stress - organize an emotionally comfortable environment, give a calming medicine (valerian tincture - 40 drops);
- known illness - for example, to stop the angina attack that caused the arrhythmia with Nitroglycerin.
- Carry out drug correction of arrhythmia (performed by qualified specialists).
Clinically it is possible to detect:
- Atrial fibrillation (fibrillation) (chaotic excitation and contraction of the muscle fibers of this part of the heart causes irregular functioning of the ventricles). The main clinical symptom is the phenomenon of pulse deficiency. The heart rate (determined by placing the hand on the middle third of the left side of the chest) exceeds the frequency of oscillations of the walls of the arteries at the periphery (to count on the inside of the wrist, press 3-4 fingers against the radius 0.5 cm below the end of the eminence of the thumb). Atrial fibrillation requires drug correction (antiarrhythmic drugs, cardiac glycosides, calcium antagonists, beta blockers), prescribed by a specialist after taking an electrocardiogram. Emergency care for fibrillation at the pre-medical stage is to give the victim a sedative (Valocordin, valerian) and provide comfort. You can try the hallux valgus tests described below, but their effectiveness in this case is low.
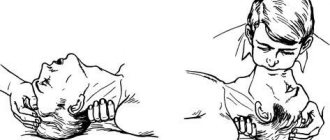
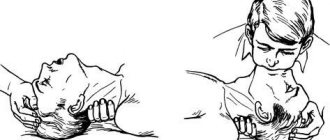
- Ventricular fibrillation (chaotic excitation and contraction of myocardial fibers). It is manifested by asystole - the absence of heartbeat and pulse in the peripheral (radial) and central (common carotid artery - located in the upper half of the neck, you need to slide your fingers from the Adam's apple up and to the sides) vessels. First aid: resuscitation measures . Before the ambulance arrives, you should press on the middle part of the sternum with straight, clasped hands at a frequency of 2 times per second. If you don't have the skills, you don't need to take breaths . Emergency assistance consists of defibrillation.
- Paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia (rhythmic heart contractions with a frequency of 140-220 per minute). The attack suddenly begins and ends. Symptoms include the sudden onset of a strong heartbeat, a feeling of pulsation in the head and neck, and tightness in the chest. Abrupt cessation gives the illusion of cardiac arrest. Treated with Lidocaine and Amiodarone.
- Paroxysmal sinus tachycardia (attack of heartbeat with a frequency of 150-240 beats per minute). Accompanied by sweating, dry mouth, dizziness, pain in the pit of the stomach. You can help with arrhythmia at home by performing vagal tests (their essence is the reflex activation of the vagus nerve, which causes bradycardia):
- squatting on your toes with tension in your abdominal muscles;
- massage of the carotid sinus (at the angle of the lower jaw);
- pressing on the root of the tongue (stimulating the gag reflex);
- imitation of a coughing attack;
- muscle tension at the height of a deep breath.
Diagnostics
Even if cardiac arrest is a rare episode, it is a reason to consult a cardiologist. Percussion can determine the expansion of the borders of the heart. During auscultation, muffled heart sounds and the presence of functional or organic noises are heard. To find out the cause of the symptoms, the doctor needs to obtain data from instrumental and laboratory research methods. Typically used:
- ECG.
During blockades, the ECG reveals a prolongation of the PQ interval and periodic loss of the QRS complex. Extrasystole is manifested by an extraordinary ventricular complex, after which a complete or incomplete compensatory pause occurs. Additionally, 24-hour Holter monitoring is prescribed. - EchoCG.
Ultrasound examination is necessary to find organic cardiac pathology that could cause freezing. Sonography can detect thickening of the heart wall, anatomical abnormalities, and a decrease in ejection fraction. Dopplerography is indicated to assess blood flow in the great vessels. - Biochemical tests.
Given the high prevalence of coronary artery disease, it is necessary to examine the blood lipid profile. The content of cholesterol and atherogenic LDL often increases. To exclude rheumatism and myocarditis, acute-phase blood parameters are determined - CRP, sialic acids. - Myocardial markers.
If cardiac arrest is accompanied by a serious condition of the patient and a sharp increase in symptoms, it is necessary to exclude a heart attack. For this purpose, the blood is examined for the level of troponin, myoglobin, AST and CPK enzymes. A slight increase indicates unstable angina, higher concentrations indicate myocardial necrosis. - Additional research.
If organic pathology is suspected, an MRI of the heart is performed. To identify signs of left ventricular heart failure, chest radiography is used. When cardiac arrest progresses to acute coronary syndrome, coronary angiography is performed.
Prevention of complications
Rhythm disturbances are dangerous due to the possibility of blood clots forming and breaking off. The most unfavorable in this regard is atrial fibrillation.
To avoid thromboembolic complications, the following drugs are used:
- Anticoagulants (reduce blood clotting):
- with a direct mechanism of action (heparin and heparinoids);
- with indirect (hydroxycoumarin and phenylindanedione derivatives).
- Antiplatelet agents (reduce the ability of platelets to stick together):
- acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin), Clofibrate, Anturan, Dipyridamole.
The drug regimen is selected by the attending physician based on the number of risk factors present in the patient.
Section materials
October 12, 12:02
In Russia, newborns will be tested for 36 diseases from 2022
October 11, 10:47
Severe risk group. How Covid is hitting older people
September 27, 12:13
All teenagers with hepatitis C were cured in St. Petersburg
September 24, 16:45
Governor Alexander Beglov extended coronavirus restrictions
September 23, 12:38
In St. Petersburg, doctors explained why pregnant women should get vaccinated against COVID
conclusions
Paroxysm of arrhythmia occurs with the active use of compensatory capabilities.
This happens with physical or emotional overload, exacerbation of the disease. You can relieve an attack of arrhythmia at home by ensuring complete rest, sometimes using light sedatives. For sinus tachycardia, vagal tests will be effective, while ventricular fibrillation requires resuscitation measures. The diagnosis of arrhythmia is confirmed by an electrocardiogram.
Disruption of blood flow can lead to the formation of a clot in the heart cavity (detected by ultrasound), its rupture and thromboembolic complications. For prevention, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents (Warfarin, Xarelto, Dabigatran) are used as continuous medications.
You don't want peace
Many are sure that any increased heartbeat can be considered an arrhythmia. This is wrong. A rapid pulse is also possible with a completely healthy heart - for example, the heart rate always increases during emotional or physical stress. Therefore, to diagnose arrhythmia, you need to contact a cardiologist. In addition, home blood pressure monitors equipped with an arrhythmia indicator can help identify this pathology.
If a person has not yet been diagnosed, but suddenly he feels any unusual sensations or anxiety anywhere in the body, the first thing to do is count the pulse. In case of interruptions, rare or frequent heart rhythm, which is accompanied by any discomfort, you need to call an ambulance. At the hospital, an electrocardiogram will be taken to document heart rhythm disturbances, and the doctor will assess the risks of complications.
Heartfelt enemies. What to do to protect yourself from a heart attack? More details
Important
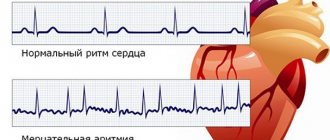
Atrial fibrillation is the most dangerous type of heart rhythm disorder.
It is fraught not only with the unpleasant sensations of heart failure, shortness of breath and pain in the chest, but also with dangerous stagnation of blood, as a result of which clots - thrombi - form in the vessels of the heart. By attaching to the vascular wall, they clog the bloodstream, preventing normal blood flow. But the worst thing happens when this clot breaks away from the walls of the blood vessels and, together with the blood flow through the ventricles of the heart, enters the aorta, and then into the brain. A cardioembolic stroke occurs, the devastating consequences of which cause large-scale brain damage.
How do arrhythmias manifest?
Different types of arrhythmias have their own manifestations. Only extrasystoles can be asymptomatic. With tachycardia, a person complains of rapid heartbeat, discomfort or chest pain, dizziness, sudden general weakness and fatigue, and shortness of breath. Also, with this pathology, blood pressure often decreases, which can cause a person to faint.
Some of these symptoms can also manifest themselves with bradycardia, in particular: dizziness, weakness, chest pain, fainting and fainting conditions. Also, with a decrease in the number of heart contractions, difficulty breathing, short-term visual disturbances, deterioration in concentration and memory, and episodes of confused thinking are observed. They arise due to the fact that the brain experiences oxygen starvation as a result of bradycardia.
The main sign of paroxysmal rhythm disturbance is a sharp deterioration in the condition. The duration of the attack is from two to three minutes to several days. During a paroxysm, a person feels a frequent and strong heartbeat, complains of general weakness, dizziness, tinnitus, sweating, nausea and flatulence.
Atrial fibrillation is accompanied by unreasonable fear (panic attack), and is also manifested by irregular heartbeat, intense sweating, shortness of breath, and severe general weakness. He even reaches the point of fainting. Different arrhythmias are similar in their symptoms. Therefore, making an accurate diagnosis is only possible in a medical institution.
Causes of cardiac arrhythmia in men or women
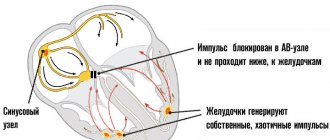
There are two common ways in which arrhythmias develop, which can be determined in a particular patient. There may be problems with the initiation of the electrical signal: either the sinus node is firing abnormally, or there is a competing impulse elsewhere in the heart. The second option is problems with the conduction of electrical impulses: connections from the atria to the ventricles are difficult (this is often called heart block).
People with heart disease are especially likely to develop arrhythmias, because heart disease, damage can prevent signals from the atria from reaching the ventricles, or certain areas of the heart may not fire normally.
High blood pressure and an overactive thyroid gland also increase the likelihood of arrhythmias. Alcohol can also cause atrial and ventricular arrhythmias. Some medications, such as decongestants and many prescription drugs, can make the heart susceptible to arrhythmias and should be used with caution in people with heart disease.
There are also hereditary and congenital (present from birth) types of arrhythmia, often resulting in a weak or delayed signal reaching the ventricles. The ventricles can emit their own signal, but it is often less than 40 beats per minute instead of the usual 60-90 beats characteristic of the sinus node. Source: "New Arrhythmia Theory" Clarifies Causes of Arrhythmia. Ermoshkin V.I. Educational bulletin “Consciousness”, 2015. p. 22-30.