How to avoid a heart attack
To avoid a heart attack and its complications, it is worth knowing what risk factors contribute to the development of this pathology:
- Arterial hypertension. Normally, blood pressure should not exceed 130/80 mmHg. Art. Any deviation from these values contributes to damage to the heart, blood vessels, brain, kidneys and, as a result, the occurrence of a heart attack, ischemic heart disease or stroke.
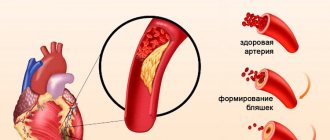
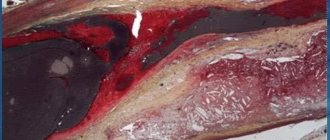
- High cholesterol levels. Prevention of heart attack in women and men includes controlling cholesterol levels. In a healthy person it should not exceed 5 mmol/l. If a person has a history of diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension and coronary heart disease, then this indicator should be less than 4.5 mmol/l. High cholesterol levels are one of the causes of the development of atherosclerosis, in which cholesterol plaques form in the vascular wall, narrowing the lumen of the vessel. If the resulting blood clot clogs a vessel, the blood flow in the vessels stops.
- Bad habits. Alcohol and tobacco abuse contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and several times increase the risk of coronary artery spasm and myocardial infarction.
- Heredity. The susceptibility to developing cardiovascular diseases increases significantly if close relatives have a history of diseases such as arterial hypertension, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction or stroke.
- Psycho-emotional overload. Constant stress increases the risk of developing coronary artery disease and other pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Clinicians have proven that the ability to withstand stress is the prevention of heart attacks in men and women, as well as somatic diseases.
- Physical inactivity. Low physical activity leads to detraining of the body, including the cardiovascular system. A rapid pulse and irregular heart rhythm at rest and with minor physical exertion can lead to coronary artery disease, and subsequently to a heart attack.
Primary and secondary prevention of myocardial infarction is aimed at eliminating risk factors that contribute to the risk of developing this pathology. If it is impossible to influence a factor such as heredity, then an annual medical examination, giving up bad habits and an active lifestyle are effective measures that can help you avoid myocardial infarction.
Only healthy lifestyle will not help
– You didn’t say anything about being overweight. Does it matter?
– It has, but not as much as is commonly believed. By the way, the cause of complications is not only high, but also too low weight. And hereditary hypercholesterolemia often occurs in slender people. Although, of course, high cholesterol and obesity often go hand in hand.
– What about bad habits – smoking and drinking alcohol? Is it true that if an elderly person has been smoking a lot for a long time, quitting abruptly is more dangerous than continuing?
– People who have had a heart attack should definitely stop smoking. It's hard, but necessary. No one has ever died from nicotine withdrawal, but many die from smoking. As for alcohol, it is not necessary to follow the “prohibition” law after a heart attack. It has been proven that 2 glasses of wine a day for men and 1 for women are not harmful. But, of course, you can’t abuse it.
How to avoid heart disease? Three exercises against heart attack Read more
– Is it possible to “run away” or “swim away” from a heart attack? What sport will help reduce your risk?
– Physical activity, especially aerobic exercise, is very important for the prevention of heart disease, but heart attacks cannot be prevented through sports alone, as the example of many runners and swimmers proves. It is preferable to walk at a moderate pace for at least 30 minutes at least 4 times a week.
Features of heart attack prevention
Measures to prevent myocardial infarction are divided into two groups: primary prevention and secondary.
1. Primary prevention. These preventive measures apply to people who have a history of various heart diseases, with the exception of a heart attack.
2. Secondary prevention. Patients who have previously had a heart attack “on their feet” should follow the recommendations of specialists. In this case, prevention is aimed at recovery and prevention of relapse.
Primary prevention
If a person develops muscle necrosis as a result of a heart attack, then he needs to follow the following recommendations:
- To refuse from bad habits. Alcohol and smoking are strictly contraindicated for people with diseases of the cardiovascular system. Quitting smoking leads to a 43% reduction in the risk of coronary heart disease and coronary death.
- Blood pressure control. High blood pressure is one of the reasons for the detachment of a cholesterol plaque clogging a vessel. Self-monitoring of blood pressure is extremely important for the prevention of heart disease. According to statistics, among all patients who suffered a myocardial infarction, only 57% knew what their blood pressure was.
- Controlling sugar levels. Fragility of blood vessels is one of the reasons for the formation of cholesterol plaques. This feature is characteristic of people with diabetes. To prevent this process, a consultation with an endocrinologist, a comprehensive examination with subsequent therapy and medical supervision is required.
- Use of medications. Recurrence of myocardial infarction can be prevented with the help of antianginal drugs and anticoagulants. If there are risk factors, the doctor will prescribe therapy aimed at preventing the formation of blood clots, which are the main cause of heart attack.
- Active lifestyle. Physical inactivity provokes the development of many diseases, including pathologies of the cardiovascular system. People over 45 years old need to keep their blood vessels and heart in good shape. To do this, you should pay attention to aerobic exercise, which helps train and strengthen the heart muscle.
- Visit to a cardiologist. The prognosis for recovery from coronary artery disease and heart attack is unfavorable, so people with pathologies of the cardiovascular system are recommended to undergo a comprehensive examination twice a year, especially these recommendations apply to older people. Diagnostic measures include an electrocardiogram, ultrasound of the heart, and, if necessary, Holter monitoring.
- Fighting stress. Regular experiences and stress adversely affect the condition of the heart. For the most impressionable people, doctors recommend taking sedatives based on medicinal herbs.
- Balanced diet. Nutrition plays an important role in the prevention of heart disease, including myocardial infarction. After all, it is salty and fried foods that lead to overweight, obesity and diabetes. A good diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, fatty fish, seafood, and white meat (chicken, turkey, rabbit) will help you avoid heart pathologies. From your diet you should exclude fried, salty and spicy foods, smoked meats, fast food, carbonated drinks, red meat, baked goods, and fatty broths.
These measures are the prevention of coronary artery disease, stroke, myocardial infarction and its recurrence. If you follow the recommendations of cardiologists, you can prevent the development of this pathology by 80%.
Secondary prevention
This set of measures is recommended to prevent a recurrent heart attack. In this case, all the rules described above are recommended, only with some adjustments. This means that measures to prevent heart attack should be carried out after the illness and until the end of a person’s life. Secondary prevention is divided into two stages:
1. The first two years. The patient is gradually recovering and is under the supervision of the attending physician. He has seen an improvement in the condition of his heart muscle and emotional state. Blood circulation and metabolism are also normalized.
2. After two years. The body of a person who has had a heart attack recovers completely. Further prevention includes effective measures to prevent recurrence of the pathology. If a person experiences symptoms of heart disease, he should immediately consult a cardiologist: this will help prevent the development of serious complications. After full recovery, a person can find a job, but one should choose an activity that does not require physical exertion or stress.
Myocardial infarction is a serious disease that is quite difficult to cure completely. You can avoid its development if you adhere to the rules of prevention: give up bad habits, eat a balanced diet and, if necessary, take medications.
In addition to preventive measures, elderly people are recommended to undergo a full medical examination twice a year, lead a moderately active lifestyle, do not overwork, and maintain a daily routine.
Age increases risk
Elena Nechaenko, AIF Health: Roman Mikhailovich, are we talking specifically about the first year after a heart attack, because it is the most dangerous in terms of a recurrence of the disaster?
Roman Shakhnovich : Yes, that's true. But we must understand that the problem is not limited to one year. Although the risk decreases over time, it still does not reach zero. According to the Swedish Health Registry, 12% of recurrent heart attacks in patients occur over the next 4 years.
– Does a second heart attack proceed differently than the first?
– In terms of clinical manifestations, recurrent infarction is no different, but is characterized by a more severe course and poor prognosis. The risk of serious complications and death with each recurrent cardiac event is higher, so all heart attack treatment is aimed specifically at preventing recurrences.
Guess by group. Is it possible to predict the risk of heart attacks and strokes using blood? Read more
– Is the patient’s age the determining factor? It is known that Oleg Tabakov had his first and only heart attack at the age of 29. After this he lived a long, fruitful life. Does this mean that young people take less risks?
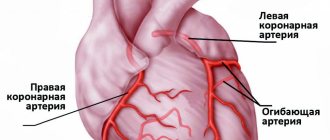
– As for our great artist, I don’t know for sure whether he had a heart attack or not, since in those years there were frequent cases of overdiagnosis - making a diagnosis without sufficient grounds. But the risk really depends on age, and linearly. The older the patient, the higher the risk of a recurrence of the disaster. The situation is especially dangerous in patients over 80 years of age. But the dependence on gender is much less pronounced. Women suffer from heart attacks less frequently until menopause, and then catch up with men. Concomitant diseases play a major role. These are primarily diabetes mellitus, uncontrolled arterial hypertension, severe clinically pronounced atherosclerosis, which is the basis of a heart attack. It is especially important how things are in the patient’s heart arteries. If the problem is with one artery, this is nothing, but if several arteries are covered with plaques at once, the situation is complicated. The size of myocardial infarction, initial complications, and features of the course of the disease are also important.
Clinical options for the development of myocardial infarction
The classic form of myocardial infarction is accompanied by a severe pain syndrome of a compressive, tearing, burning nature. The pain is most often localized behind the sternum, but can also radiate to the left arm, left shoulder, lower jaw, and interscapular area. As a rule, the pain lasts more than 20 minutes and is not relieved by nitroglycerin within 5 minutes.
Other symptoms of classic myocardial infarction:
- increased sweating;
- psychomotor agitation;
- feeling of fear of death.
There are also atypical options for the development of myocardial infarction:
- abdominal form. In this case, the patient experiences heartburn, nausea, vomiting, pain in the upper abdomen;
- arrhythmic form. Characteristic signs are heart rhythm disturbances, a feeling of interruptions in the heart;
- asthmatic form. The main symptoms are shortness of breath, suffocation;
- painless form. It is characterized by the absence of pain or the presence of mild pain that occurs at varying frequencies. This form especially often develops in patients with diabetes mellitus and in people who have already suffered a myocardial infarction in the past.
Why is the painless form dangerous? First of all, the development of sudden cardiac death. In addition, if in the acute period a myocardial infarction occurs without clear clinical symptoms, then in the future this can lead to the development of chronic heart failure.
The painless form of myocardial infarction can be recognized by other signs. For example, a person may experience shortness of breath, increased fatigue, and exercise intolerance.
Fate or prevention?
– There is an opinion that a high risk of heart attack is a fatal predetermination. And no matter what you do, there is no chance of escape. This is true?
- Of course not. Everything we talked about were effective methods of prevention. After a heart attack, people live actively for decades! The main thing is not to let the situation take its course. It is necessary to follow all recommendations of the cardiologist. Stick to your cholesterol goal by taking medications that have proven effectiveness, not dietary supplements or drugs advertised on TV. Regularly monitor your blood pressure and sugar levels, follow a diet, remain physically active, do not smoke, and do not abuse alcohol. If you approach prevention in a comprehensive and disciplined manner, you can significantly reduce your risks and avoid a heart attack.
First aid for myocardial infarction
In providing first aid, the principle of the “golden hour” is very important, from the moment the symptoms of the disease appear until the patient is admitted to the hospital. In critical situations, even more rapid action is required. The severity of the condition during a heart attack depends on how much the lumen of the vessel is blocked by a thrombus. If occlusion (complete obstruction) of a vessel occurs, a critical condition develops. The patient has 20–40 minutes left, after which necrosis of the cardiac tissue occurs.
It is very important not to wait for the pain to subside or for the work day to end. If symptoms characteristic of a heart attack appear, you should immediately take the necessary medications and call an ambulance.
Before doctors arrive, a person with coronary syndrome should be provided with first aid.
Correct algorithm of actions:
- Place the person in a semi-sitting position. For example, you can put the patient in bed and place pillows under his back. A semi-sitting position reduces the load on the heart.
- Provide the patient with complete physical and mental rest, try to calm him down. Physical and emotional stress increases myocardial ischemia and increases the need for oxygen in the heart muscle.
- Free your body from constrictive elements of clothing - remove your tie, belt, unbutton your shirt collar.
- Create an influx of fresh air - open a window or vent.
- Give the patient half a tablet of aspirin to chew. This will reduce the area of the heart attack and reduce the risk of death.
- If possible, you need to measure the person's blood pressure.
- If you have high blood pressure, be sure to give a drug for hypertension, as well as nitroglycerin. Nitroglycerin capsules are placed under the tongue and sprayed under the root of the tongue as a spray.