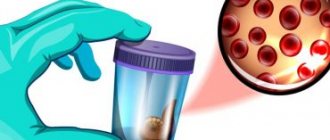
Saliva is a fluid in the body that performs important functions. After food enters the oral cavity, the process of digesting food begins with the help of enzymes found in saliva. It also moistens food to make it easier to swallow and taste the food. Saliva neutralizes alkali and acid, and also protects against various microbes.
Quite often, people turn to medical institutions asking why there is blood in their saliva. If everything is normal in the body, then there should be no blood. If it is, then it is necessary to find out the reasons and determine the correct treatment. It is important to understand that saliva with blood can be both a safe phenomenon and a sign of a dangerous pathology.
Bloody discharge can be classified according to daily volume: true hemoptysis (no more than 50 ml), light bleeding (no more than 100 ml), moderate (up to 500 ml), heavy (up to 1000 ml).
Coughing up blood: causes of illness in adults
In some cases, when the cough is strong, dry and hysterical, a small amount of scarlet blood in the sputum may be the result of damage to small superficial vessels in the bronchi, pharynx or trachea. This phenomenon is not dangerous if it is not accompanied by other alarming signs. However, if the cough does not subside, the symptoms increase, the volume of blood is significant, or the streaks do not disappear, this may be a sign of serious problems and illnessesSource: EarwoodJS, ThompsonTD. Hemoptysis: evaluation and management // Am Fam Physician. 2015 Feb 15;91(4):243-9..
When to go to the doctor?
Take your child to the doctor if your child's sore throat does not go away after breakfast.
Call an ambulance immediately if:
- the child has difficulty breathing;
- he cannot swallow;
- The infant is drooling unusually, which may indicate an inability to swallow saliva.
If an adult has pharyngitis, visit a doctor in the following cases:
- severe or prolonged (more than a week) sore throat;
- throat hurts often;
- difficulty breathing, swallowing, or opening your mouth;
- earache;
- joint pain;
- rash;
- fever above 38.3 for more than three days;
- blood in saliva or sputum;
- pain when turning the head;
- nodes and tumors in the neck;
- Hoarseness, hoarseness lasts more than two weeks.
What diseases are typical for hemoptysis?
The appearance of sputum with blood when coughing is called hemoptysis, it is possible with various diseases:
- COPD with severe bronchitis or emphysema;
- pneumonia (acute or exacerbation of chronic);
- tuberculous lesions of the lungs and bronchi;
- cancerous tumor in the lungs;
- injuries to the chest and lung tissue.
In addition, impurities of blood in coughed up mucus are possible with lesions of the nasopharynx (including nosebleeds) and the upper parts of the digestive tract.
If cough or hemoptysis appears, even without fever, it is important to consult a doctor. This is especially dangerous if symptoms such as fever, shortness of breath, severe weakness, pain in the body or limbs appear against the background of coughing up blood. You need to call an ambulance immediately. Such an attack may be a symptom of a serious illness. It is important to immediately determine the correct diagnosis and begin treatment. Source: K. Krenev, Ya Kabysh, O Yudin. Difficult patient or patient with hemoptysis // Sciences of Europe, 2021, No. 48, pp. 17-22.
Possible complications
Ignoring the symptoms of minor hemoptysis can lead to the development of massive bleeding.
It causes the airways to fill with blood, which blocks access to air. As a result, death from asphyxia (suffocation) may occur. Death is also possible with heavy blood loss, amounting to about 4–4.5% of the total body weight. If left untreated, the disease that caused hemoptysis continues to progress and cause complications. With cancer, metastases appear, with pneumonia and tuberculosis - fibrosis of the lung tissue, with bronchiectasis - bleeding, abscess, infarction and necrosis of the lung.
Diagnostic methods
Since coughing up blood can be a sign of a serious illness, it is important to make a diagnosis as quickly and accurately as possible. A complex of laboratory tests and necessarily radiography or CT, ultrasound or MRI are required to determine the source of bleeding, especially if it is severe enough. Sometimes blood may not come from the respiratory system, but from soft tissues, the pleural cavity or the esophagus.
A detailed medical history is important - all health problems that preceded the appearance of the cough (smoking, injuries, colds, abdominal pain, etc.). They may indicate possible causes. If the source of bleeding is in the bronchi, an additional bronchoscopy may be prescribed. All diagnostic procedures are usually performed during hospitalization in a clinic.
How to quickly stop bleeding from gums
What to do if you need to quickly stop bleeding from your gums? For this purpose, you can use one of the following methods:
- Rinse your mouth with cold water or mint mouthwash. Decoctions of herbs - chamomile, oak bark, fir, calendula - help reduce the manifestations of unwanted symptoms.
- Apply a cotton swab soaked in chlorhexidine to the bleeding area. You need to press it tightly and wait until the bleeding stops.
- Glue a special protective homeopathic strip. You can buy it at the pharmacy.
No matter how long your gums bleed, you cannot put off a visit to the dentist. The problem will not go away on its own, but will only get worse.
Treatment
It is important to remember that hemoptysis is only a symptom. It is important to treat the underlying condition and make efforts to stop the bleeding. If these are inflammatory processes (pneumonia, bronchitis), a course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory therapy in combination with drugs to regulate blood clotting are indicated. Regular cleansing of the bronchi from bloody sputum (sanitation) is also indicated.
If this is a tuberculosis lesion, anti-tuberculosis therapy is necessary, including surgical interventions on the affected lesions (cavities). For injuries and abscesses, the solution to problems is surgery; for cancerous lesions, tactics are selected individually, depending on the stage. Source: Ittrich H, Bockhorn M, Klose H, Simon M. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Hemoptysis // The Diagnosis and Treatment of Hemoptysis.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2017 Jun 5;114(21):371-381. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2017.0371..
How to eliminate constant bleeding gums
To carry out successful treatment, it is important to find out why the gums are bleeding. You should not self-medicate, since the problem requires an integrated approach, which consists in eliminating the cause and restoring the health of the gums. Only a doctor can tell you how to treat a disease that causes bleeding. Different techniques may be needed.
Professional teeth cleaning
If dental plaque provokes complications in the form of bleeding, it is necessary to thoroughly clean your teeth. This does not mean ordinary hygiene procedures at home, but hardware cleaning in a dental office. The doctor uses ultrasound to crush the tartar, the particles of which are washed out with a mixture of water and air. You need to carry out a hygiene procedure twice a year. Unfortunately, not all patients comply with such recommendations.
Air Flow technology is used to remove soft deposits. In this case, finely dispersed soda is supplied along with water. After the procedure is completed, the teeth are polished, which further prevents the accumulation of plaque.
Such actions are sufficient for diagnosed gingivitis. The doctor will also tell you what to do to restore the mucous membrane. This may include rinsing or taking certain medications. Professional teeth cleaning is used if gingivitis has progressed to periodontitis. But this is only the beginning of treatment. Let's talk about ways to eliminate the disease further. If periodontal pockets have formed, you will need powerful ultrasound devices, such as Vector. In this case, the periodontist should deal with oral hygiene.
Rinse with solutions
Antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity can be carried out in the form of rinses based on the following agents:
- "Furacilina";
- "Rotokana";
- "Miramistina";
- "Chlorhexidine";
- alcohol solution "Chlorophyllipt".
Soda-saline solution also helps. You can add a few drops of iodine to it. It is better to use solutions through an irrigator - this increases their effectiveness. In case of bleeding, you need to use special toothpastes, including Parodontax, Lakalut, Colgate Total Pro. The compositions should not have a bleaching effect.
Drug therapy
To eliminate bleeding gums, the doctor may prescribe ointments and gels. They are applied to the problem area after rinsing the mouth. The following drugs are in demand in dental practice:
- "Metrogil Denta" - has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, often prescribed for stomatitis, after tooth extraction;
- “Asepta” is a propolis-based gel that quickly relieves inflammation;
- "Kamistad" is a drug available in two forms (for children and adults);
- "Elugel" is a strong antiseptic that effectively fights pathogenic environments.
For inflammatory processes, the doctor may prescribe medicinal bandages, antibiotics (in some cases), and a course of vitamins.
Gum curettage
For periodontitis with the formation of deep periodontal pockets, the following surgical techniques are used:
- Closed curettage. To carry out the procedure, the doctor uses a special instrument – a curette. With its help, the doctor cleans the roots of the teeth. The tool penetrates to a depth of 3 mm.
- Open curettage. The technique is used when the deposits are deeper. It involves the following actions: peeling of the gums, cleaning and antibacterial treatment, suturing.
The disease can be cured using an integrated approach. Therefore, it is important to follow all doctor’s recommendations even after the procedure.
Prevention
The main methods of preventing hemoptysis are preventing the pathologies that cause it. Quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, regular exercise, and timely treatment of colds are important.
Sources:
- Earwood JS, Thompson TD. Hemoptysis: evaluation and management // Am Fam Physician. 2015 Feb 15;91(4):243-9.
- Ittrich H, Bockhorn M, Klose H, Simon M. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Hemoptysis // The Diagnosis and Treatment of Hemoptysis.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2021 Jun 5;114(21):371-381. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2017.0371.
- K. Krenev, I am Kabysh, O Yudin. Difficult patient or patient with hemoptysis // Sciences of Europe, 2021, No. 48, pp. 17-22
Preventive measures
To avoid gum problems, you must follow a number of simple rules:
- Perform high-quality and correct hygiene procedures aimed at oral health. It is necessary to select care products that will not injure the mucous membrane. You should brush your teeth morning and evening. Use dental floss with caution. Instead, you can use an irrigator, which will help effectively remove food debris. Your toothbrush should be changed every three months.
- Balance your diet. The body must receive all the necessary vitamins and minerals. To strengthen teeth and gums, it is important to eat solid plant foods, such as apples and carrots.
- Give up bad habits, in particular smoking. Toothpicks should be used with caution.
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations at the dentist - at least twice a year. This will allow timely detection of oral diseases.
Paying close attention to your oral health will help you maintain a beautiful and healthy smile for many years.
Post-Covid syndrome: When they start coughing up blood, it will be too late
Under the flurry of reports about the new coronavirus, we seemed to have stopped getting sick from other diseases and seemed to have forgotten about them. But they never thought of forgetting about us. Doctors also remember, warning that those who have recovered from Covid sharply increase the likelihood of contracting pulmonary tuberculosis, that very “consumption” colorfully described in Russian literature back in the 19th century. Do you think that the ancient disease has long been defeated and forgotten? No matter how it is. The World Health Organization also predicts a new outbreak of tuberculosis in connection with the pandemic. But even without that, despite obvious progress in treatment, at least 1.5 million people die from tuberculosis every year in the world.
The causative agents of tuberculosis - a whole group of dangerous microbacteria, named after their discoverer "Koch bacilli" - have existed on the planet probably as long as man himself. Thousands of years ago, Indian laws prohibited taking wives from families suffering from tuberculosis.
Causes of blood taste in mouth
Changes in taste during pregnancy
Pregnant women are characterized by sharp hormonal changes, which cause an increased sense of smell, changes in taste preferences and sensations. As a result, a specific metallic taste, perceived as the taste of blood, occurs when eating fully cooked meat products, fish or even vegetable dishes. The symptom occurs periodically and often goes away on its own after some time.
Anemia
The main reasons for changes in taste are a drop in hemoglobin and coagulation disorders, leading to capillary fragility. The taste of blood in the mouth is especially common in young women if anemia develops during pregnancy. Its persistence throughout the day, combination with painful nausea, the urge to vomit, indicates concomitant pathology (coagulopathy, hypovitaminosis). In the absence of gestation, an anemic change in taste is observed with chronic bleeding, neoplasia, etc.
Gingivitis
Chronic inflammatory disease of the gums occurs in 20-30% of the adult population. Usually, the taste of blood appears after brushing your teeth with hard toothbrushes, which cause trauma to the mucous membranes and bleeding gums. When gingivitis worsens, an unpleasant taste in the mouth is felt at any time of the day for no apparent reason. The symptom is accompanied by redness and swelling of the gums, and the formation of difficult-to-remove plaque on the teeth.
Other dental causes
A bloody taste in the mouth is detected in various pathological processes: medium and deep caries, pulpitis, periodontitis. The symptom can occur spontaneously, but is more often provoked by eating solid food and brushing teeth. A specific unpleasant taste of blood develops against the background of intense pain in the area of the diseased tooth. Odontogenic causes are dangerous due to their complications, so you need to visit a specialist as soon as possible.
ENT pathology
The taste of blood in the mouth often occurs with chronic rhinitis and sinusitis, in which atrophy of the mucous membrane occurs and scanty bleeding periodically begins. The bloody taste bothers you in the morning, when the blood that has accumulated overnight begins to flow down the back wall of the throat. The person experiences severe nausea and aversion to food. The discomfort disappears after rinsing your mouth and brushing your teeth.
Respiratory infections
Most often, the symptom occurs with influenza, for which a toxic effect on capillaries and spontaneous bleeding from the oral mucosa is pathognomonic. The taste occurs periodically in the first 2-3 days of infection, then disappears on its own. A similar clinical picture also develops in severe ARVI, pharyngitis and laryngitis.
Diseases of the gastroduodenal zone
GERD and gastritis are characterized by a taste of blood in the mouth after drinking alcohol, stress and heavy physical activity. In these diseases, the main reasons for the unusual taste are the formation of erosions in the mucous membrane of the digestive canal, which, under the influence of unfavorable factors, begin to bleed. Patients experience severe burning and pain in the chest, accompanied by an unpleasant sensation of blood in the mouth.
Cirrhosis
Fibrous liver damage provokes dilation of the esophageal veins and thinning of their walls, which is fraught with spontaneous bleeding. In the mouth of patients with cirrhosis, a strong taste of blood suddenly begins to be felt, and with massive bleeding, vomiting of dark red blood begins. The symptom occurs more often in men who abuse alcohol. If there is a suspected rupture of esophageal varicose veins, a person needs emergency medical care.
Cardiovascular disorders
The symptom is determined by hypertension, vasculitis, which is accompanied by thinning and fragility of the capillaries. A specific blood taste appears after physical activity or stress, leading to a rise in blood pressure and rupture of small blood vessels. During an attack of angina, accompanied by pain in the heart and shortness of breath, sometimes there is a feeling of an unpleasant taste of blood in the mouth.
Rare causes
- Diseases of the respiratory system
: bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, tuberculosis. - Poisoning with heavy metals
: lead, mercury, cadmium, etc. - Gastrointestinal pathology
: pancreatitis, cholecystitis, hepatitis. - Tumors
: malignant neoplasms of the oral mucosa and tongue, lung cancer.
What could be the reasons?
There are many reasons for coughing up blood. For example, traumatic damage to the trachea, pulmonary arteries or bronchi during tracheobronchoscopy. Various lung diseases can also be a source:
- Acute or chronic bronchitis
- Pneumonia
- Lung abscess
- Tuberculosis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Bronchiectasis
- Respiratory cystic fibrosis
- Lung cancer
Detailed description of the study
The study of the leukocyte formula includes determination of the total number of leukocytes, the absolute and relative content of promyelocytes, metamyelocytes, myelocytes, band neutrophils, segmented neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, lymphocytes, plasma cells. If blast cells are present in the blood smear, they are also indicated in this study. The study of the leukocyte formula is of great importance in the diagnosis of hematological, infectious, inflammatory diseases, as well as in assessing the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of the therapy. At the same time, changes in the leukocyte formula are not specific - they may have a similar nature in different diseases or, on the contrary, dissimilar changes may occur with the same pathology in different patients. The leukocyte formula has age-related characteristics, so its changes should be assessed from the perspective of the age norm (this is especially important when examining children).
The leukocyte formula determines the following types of leukocytes:
- Neutrophils protect the body from infections. Most often, the number of neutrophils increases in acute inflammatory and infectious diseases, tissue necrosis, and intoxication.
- Eosinophils are involved in the development of allergic reactions. Their number increases most often in allergic conditions and helminthic infestations, less often in tumors and some collagenoses.
- Basophils are involved in allergic and inflammatory reactions. Their number increases with any allergic diseases, some blood diseases, hypothyroidism, etc.
- Lymphocytes are the main cells of the immune system, providing an adequate immune response to the body when exposed to foreign agents. The content of lymphocytes in the blood increases with infectious mononucleosis, many other viral infections, as well as with diseases of the lymphatic system and blood.
- Monocytes, cells that provide phagocytosis, i.e. “devouring” foreign microorganisms. Monocytosis - an increase in the number of monocytes - is characteristic of many infections: tuberculosis, infectious mononucleosis, sepsis. It occurs in blood diseases and collagenoses.
- Plasmocytes, cells of lymphoid tissue that produce immunoglobulins. Normally absent in peripheral blood, they appear there during viral infections, plasmacytoma, malignant tumors, and autoimmune diseases.
The study on calculating the leukocyte formula in the Hemotest Laboratory is carried out on automatic hematology analyzers, which use modern technology of flow cytometry and conductometry. The analyzer evaluates 10,000 cells in one sample, determining size, structural, cytochemical and other characteristics. After this, mandatory microscopy of a stained blood smear is performed to determine the morphological characteristics of leukocyte cells. When pathology is detected in the cytoplasm or nucleus of cells, this information must be indicated in the notes to the analysis. For microscopy of the leukocyte formula, Romanovsky staining is used. When calculating the leukocyte formula, laboratory keyboard counters are used. In a smear, 100 leukocyte cells are counted, followed by the percentage and absolute number of cells, based on the total number of leukocytes. Considering that the automatic and manual counting methods have different errors and reproducibility, automatic cell counting is more diagnostic. During microscopy, immature forms of granulocytes are differentiated into promyelocytes, myelocytes and metamyelocytes, band neutrophils, plasma cells are indicated and, if detected, lymphocytes of varying degrees of maturity are noted, a significant variation in the size of cells of the lymphoid series; polymorphism of lymphocyte nuclei; marginal basophilia and vacuolization of the cytoplasm of lymphocytes, uneven contour of the nucleus and cytoplasm. In visual differential counting, there are three main sources of error: uneven distribution of cells in the preparation, failure to recognize cells, and the presence of errors in repeated analyzes. This method is difficult to standardize and eliminate the “human” factor of analytical errors. The advantage of this analysis is the visual assessment of the morphology of leukocyte cells by the clinical physician.
Venous blood is considered the best material for laboratory research:
- To ensure the quality of the test result, it is necessary to donate venous blood (unless the child has special indications for taking capillary blood). When blood is taken from a finger, the blood cells are deformed, and some of the red blood cells are destroyed, forming microscopic clots in the test tubes. In this case, it is impossible to conduct research; in this case, repeated collection of biomaterial is required.
- In venous blood, blood cells are not destroyed, microscopic clots are formed much less frequently. That is why capillary blood is used only in children in isolated cases.
- Thanks to modern technologies, the procedure for collecting venous blood is painless and safe even for small children, since completely closed disposable BD vacuum systems are used, which eliminate infection and meet all international standards.
- Taking blood from a vein takes a few seconds.
Dental diseases
The most common cause of the taste of blood in the mouth remains dental diseases and lip lesions. Diseases are easily recognized by reddish-colored saliva, inflamed oral mucosa, and the presence of ulcers and erosions.
The main dental problems that cause the taste of blood in the mouth are:
- gingivitis - inflammation of the gums;
- stomatitis - damage to the mucous membranes;
- cheilitis - lip injuries;
- periodontitis is inflammation of the periodontal tissues.
Classification of hemoptysis
Hemoptysis is a fairly common symptom that occurs in people. It can be classified into the following groups:
- true hemoptysis - when blood is released in a volume of up to 50 ml in the form of streaks;
- minor pulmonary hemorrhage - when the volume reaches one hundred milliliters. Blood may appear in a foamy state;
- moderate pulmonary hemorrhage – when the volume reaches 500 ml;
- major bleeding - when the volume of fluid is more than five hundred milliliters.
It is worth noting that the volume is calculated per day, and not at one time.