Blood clotting disorders are a group of pathological conditions characterized by malfunctions in the hemostatic system. It consists of keeping blood in a liquid state, stopping bleeding in cases where the walls of blood vessels have been damaged, and also dissolving blood clots that have already fulfilled their function. The reasons may be different: as a rule, they arise due to a lack of one or several factors at once or the appearance of their inhibitors in the blood. They provoke a decrease in the ability of blood to clot and the development of serious and potentially life-threatening diseases.
The Department of Hematology at CELT offers diagnosis and treatment of blood clotting disorders in Moscow. We employ leading domestic hematologists, whose qualifications are sufficient to accurately diagnose and carry out effective treatment according to international standards. They are helped in this by a powerful diagnostic and treatment base and modern gentle techniques. You can find out the approximate prices for our services in the price list in the “Services and Prices” section of our website. We recommend checking the numbers with our information line operators.
1.What is hemophilia and its causes
Hemophilia
is a blood disorder in which the blood does not clot properly. Typically, this occurs because a person with hemophilia lacks a certain clotting factor. This means it can be difficult to stop bleeding. Moreover, this can apply to both ordinary bleeding from wounds and falls, and bleeding during some operations. It also happens that some people with hemophilia begin to bleed internally for no apparent reason.
There are two main types of hemophilia:
- Hemophilia A
is caused by the absence of active blood clotting factor VIII. According to statistics, approximately 1 in 5,000 male infants are born with type A hemophilia. Blood clotting factor VIII is a plasma protein. The greater the deficiency, the more severe the symptoms of hemophilia. - Hemophilia B
(Christmas disease) is caused by a lack of active blood clotting factor IX in the body. This form of hemophilia is less common and is diagnosed in about 1 in 30,000 male infants.
Hemophilia is usually inherited and almost always affects men. In very rare cases, a person can develop hemophilia without a family history. This is called acquired hemophilia, and it occurs in both men and women.
Causes of hemophilia
Hemophilia, both type A and B, occurs due to a defect in a pair of chromosomes that affects the presence of a certain blood clotting factor in the body and how it works. In the case of acquired hemophilia, the blood clotting factor stops working as it should because it begins to be attacked by antibodies that the body itself produces.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
What is diabetes mellitus? And what types is it?
Diabetes mellitus is a term that unites a group of diseases accompanied by an increase in glucose (sugar) in the blood. There are many different types of diabetes, but the main two are:
- Type 1, insulin-dependent
- it is also called “childhood” or “young people’s diabetes”, since it mainly affects children or young people; - Type 2, non-insulin dependent
- it is called “diabetes of the elderly”, since it is more common in older people. However, recently it has been diagnosed in young people and even children.
2. Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of hemophilia may include:
- Bleeding in a joint or muscle area that causes pain and swelling;
- Abnormal bleeding after wounds or surgery;
- Bruising;
- Frequent nosebleeds;
- Blood in the urine;
- Bleeding after dental surgery.
Some people with mild hemophilia may not experience all of these symptoms, especially as the person gets older. However, in infants it is usually possible to diagnose hemophilia based on some signs. So, signs of hemophilia in infancy may be an unusual reaction to the most common vaccination - intramuscular bleeding and serious bruising. Or, for example, bleeding that begins after cutting the umbilical cord and does not stop for a long time (but this happens very rarely).
Visit our Therapy page
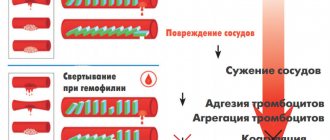
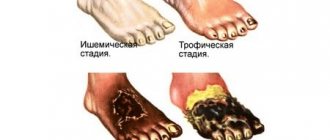
Bleeding disorder: symptoms
The clinical manifestations of the diseases listed above are similar, but appear in different combinations and with different intensities. Hemorrhagic syndrome is represented by the following:
- Hemorrhages into the skin and tissue;
- Bleeding of gums and other mucous membranes;
- Formation of bruises even with light blows and compressions;
- Systematic spontaneous nosebleeds;
- Intense menstruation in women;
- Prolonged bleeding even with minimal damage to small blood vessels;
- Bleeding into muscle and joint tissues, initiating necrosis.
Signs of thrombohemorrhagic syndrome due to bleeding disorders:
- Hemorrhagic rash, bruises, hematomas;
- Intense bleeding from injection sites and wounds;
- Paleness of the skin, its coldness;
- Swelling of the gastrointestinal tract;
- A combination of necrotic foci and multiple hemorrhages.
3.Diagnostics and treatment
Diagnosis of hemophilia
If your doctor thinks you or your child may have a blood clotting problem, a blood test will be done. The tests will help check your body's clotting factor, the type of hemophilia, and the severity of the disease. The severity of the problem depends on how much clotting factor the body produces and how often and under what conditions bleeding occurs.
Depending on this, there are several types of hemophilia:
- Mild hemophilia
. The blood clotting factor level is at least 5% of normal. This type of disease is not always noticed, especially if the person has not had heavy bleeding after a major injury or surgery. - Moderate hemophilia
- the level of blood clotting factor is from 1% to 5% of normal. Bleeding usually begins after a fall, sprain, or severe muscle strain. - Severe hemophilia
is diagnosed when blood clotting factor levels are below 1% of normal. People with severe hemophilia often bleed up to several times a week, without any obvious reason.
If you have a family history of hemophilia and you are planning a pregnancy, ask your doctor about special tests that can show whether you are a carrier of the disease (only women can be carriers).
Treatment of hemophilia
Hemophilia can be treated by replacing missing clotting factors
. During this therapy, clotting factor concentrate is injected into a vein. This replacement therapy can prevent or treat bleeding.
You may need to take special medications to treat hemophilia. Sometimes such drugs are prescribed before a certain procedure, which may be accompanied by blood loss - surgery or, for example, dental treatment at the dentist. In some cases, it is also necessary to take pain medications to help manage pain due to joint damage.
By following all your doctor's recommendations for treating hemophilia, you will be able to lead a normal life with this disease. As a rule, modern clinics have the necessary resources to help patients with hemophilia.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
One of the first symptoms of diabetes is frequent urination
. Due to the fact that the child begins to go to the toilet frequently, gets up at night, becomes thirsty, and begins to drink more liquid. Parents usually notice that the child begins to drink a lot of water. Due to the fact that the sick child drinks and eats a lot, he begins to lose weight. Next, weakness and fatigue appear.
How is diagnosis carried out? Childhood diabetes is fairly easy to diagnose. We measure blood and urine glucose levels, as well as ketone levels.
4.What can be done at home for hemophilia?
To prevent bleeding and improve your well-being, patients with hemophilia can recommend the following:
- Ask your doctor about how to manage bleeding if you have hemophilia;
- Maintain a healthy weight. Additional stress on joints due to excess weight can cause bleeding in hemophilia;
- Choose forms of physical activity with caution. It is better to give preference to swimming and other sports that do not put unnecessary stress on the joints;
- Consult your doctor before taking any medications. And do not take aspirin, ibuprofen or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs because they affect blood clotting.
- Organize your living space to avoid injuries and accidents as much as possible.
Bleeding disorders: diagnosis
Diagnosis of diseases associated with blood clotting disorders by CELT hematologists involves comprehensive blood tests. They are necessary in order to find out the following parameters and factors:
- Blood clotting time;
- Speed of coagulation process;
- Activated clotting time;
- The rate of appearance of fibrin;
- The presence of a deficiency of plasma coagulation factors;
- Other.
In order to assess the condition of the spleen, intestines, liver, and brain, X-ray studies, ultrasound scanning and magnetic resonance imaging are performed.
Classification of disorders
There are three “branches” in the hemostasis system: coagulation - responsible for the formation of blood clots, anticoagulation - maintains the rheological properties of blood normal, and fibrinolytic - ensuring the dissolution of blood clots.
Disorders of the blood coagulation system occur in one of two directions:
- In the direction of hypocoagulation - decreased coagulation properties (thrombocytopenia, von Willebrand and Wergolf diseases, hemophilia).
- Or its increase - hypercoagulation (thrombophilia, DIC and APS syndrome).
According to the mechanism of development, disorders of the vascular-platelet unit and failures in coagulation hemostasis are distinguished.
When to see a doctor
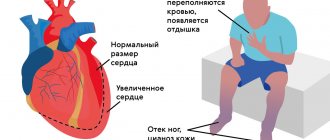
Many parents are interested in what to do if their child has thick blood. There is only one answer: if signs of such a pathological condition appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. This is especially important if the child is very young, since he cannot say that he is feeling unwell. If there are symptoms characteristic of increased blood viscosity, parents should make an appointment with a pediatric cardiologist with their child.
JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) in the center of Moscow employs specialists with extensive experience. They have completed internships in well-known foreign clinics. You can contact a specialist regardless of the child’s age. Our cardiologists work with both newborns and older children.
What is the prognosis for treatment?
With proper and well-chosen treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
There are different types of insulin. Many children use insulin pump therapy. But it is important to know that much here depends not on the treatment, but on how the child and his parents perceive the diagnosis and how they treat it. They will have to learn a lot. The first thing is to streamline your diet
and lifestyle. Please note that the diet does not change completely, it just becomes correct. And this is not just eating chips, chocolates and sandwiches.
Secondly, in childhood diabetes mellitus, blood glucose control
. Children do this often: optimally 6–8 times a day. There are now many different means to control blood glucose. First of all, these are glucometers, when for each measurement of glucose in the blood the child needs to prick his finger. But now there are systems where a sensor is placed in children for two weeks (for example, in the shoulder area). And with a special device (scanner) you can determine blood glucose every minute by bringing this scanner to the sensor. And then you don’t need to prick your fingers 6–8 times a day.
Is a full life possible, and why will you have to give up forever? And our children live full lives
. Participate in various competitions and competitions. I would say, on the contrary, they are smarter and more capable than children without diabetes. Probably because they had to grow up earlier. Learn to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right, and maintain a proper daily routine. They count bread units (this is the amount of carbohydrates) in order to correctly inject themselves with the required dose of insulin.
However, children with diabetes and their parents should be aware that they will be faced with the difficult question of choosing a profession. The fact is that some professions are contraindicated for diabetes:
- with heavy physical activity (miners);
- with significant neuropsychological stress (air traffic controllers, transport drivers);
- with irregular working hours, at night, with an unfavorable microclimate, with contact with toxic substances (chemical production).
Causes of thick blood in a child
The main factor behind blood thickening is a lack of water in the body, in other words, dehydration. It can occur in various pathological conditions. The reasons for thick blood in a child are as follows:
- diseases of the spleen or liver;
- severe and prolonged vomiting or diarrhea;
- burn disease;
- renal failure;
- indoor air is too dry;
- improper use of certain medications;
- vitamin deficiency (particularly affected by a lack of vitamins B and C).
Thick blood in a newborn baby is normal in the first 12 hours after birth. At this time, blood counts differ significantly from those typical for one-year-old children. This reaction is an adaptation of the body to a new environment.
Pathological blood viscosity can occur against the background of diseases:
- congenital heart disease;
- parasitic infections;
- obstructive diseases of the respiratory system;
- erythremia;
- leukemia;
- acute inflammatory diseases;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- injuries of various types.
What complications can occur with thick blood?
If a child’s thick blood persists for a long time, it is dangerous for the development of serious complications. If the viscosity is too high, the blood will move through the vessels too slowly. As a result, the oxygen concentration in it will decrease, which will lead to hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of tissues and organs. If there is a lack of oxygen, they will not be able to function normally.
Thick blood also increases the risk of thrombosis, in which cells simply stick together, thereby clogging the lumen of blood vessels. Such a condition sooner or later leads to a heart attack, stroke or tissue necrosis of organs experiencing hypoxia.