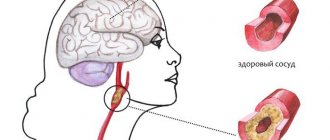
Unfortunately, a disorder such as stroke is very common. And if previously older people suffered from damage to the blood vessels of the brain, today young people also turn to specialists for help. In our information article we talk about the consequences of the disease, in particular about strabismus and how to restore vision.
In this article
- What is a stroke?
- Types of lesions
- What are the causes of stroke?
- What are the symptoms of a stroke?
- What are the consequences of a stroke related to the visual organs? How to recover? What will be the treatment?
- How to treat strabismus during a stroke?
- What does drug treatment include?
- Gymnastic exercises for the treatment of strabismus
- Surgery to treat strabismus after stroke
- Recommendations
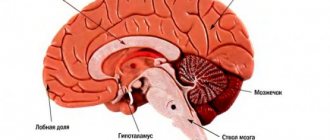
What is a stroke?
Experts call a stroke an acute disturbance of blood circulation in the brain, which entails focal damage. Unfortunately, every year the disease becomes younger and more common: people after thirty years of age often experience a stroke. It manifests itself as sudden weakness in the limbs and disturbance of consciousness, as well as facial asymmetry, impaired speech and vision, and other signs that we will discuss below. It is important to diagnose this disease in time and begin treatment. Will the body be able to fully recover? It is difficult to answer this question unambiguously, since it will depend on physiology and age, as well as a number of other factors. In any case, treatment is necessary to correct cardiac, respiratory and metabolic disorders and combat cerebral edema. Also, a person after a stroke needs specific pathogenetic, neuroprotective and symptomatic therapy that will prevent complications.
Types of lesions
Experts distinguish two types of stroke - ischemic and hemorrhagic. They are radically different from each other, as they have different mechanisms of action and principles of treatment. So, the first type can be called a cerebral infarction in another way. What happens at this moment? The work and patency of the cerebral arteries is disrupted, which leads to prolonged ischemia and changes in brain tissue in the area of the blood supply to the affected artery.
In turn, a hemorrhagic stroke is provoked by a pathological (atraumatic) rupture of a cerebral vessel with hemorrhage into the cerebral tissue. Neurologists summarize that ischemic stroke most often affects people after fifty years of age, while hemorrhagic stroke can also occur in the younger generation. For example, at the age of 40 years.
Forecast of microstroke
If the disease was diagnosed on time, no serious consequences are observed in patients after a mini-stroke. In young patients, the rehabilitation period can take only a few days; in older patients it usually takes up to a month. If a person begins to pay due attention to his health and follow the doctor’s recommendations, the prognosis is favorable, but if not, he should expect a recurrence of the attack, including an increased possibility of a stroke.
During the rehabilitation period, patients may experience the following disorders:
- Men at a young age experience memory loss, erectile dysfunction, frequent headaches, seizures, and mood swings.
- In women, the consequences usually affect the nervous system and are associated with frequent mood swings and even possible depression.
- In the elderly: difficulty in motor activity, decreased vision, epileptic attacks, decreased memory and mental activity, speech impairment, sclerosis.
If the patient does not receive timely treatment, the microstroke may return within two to three days, and 50% of patients subsequently develop an ischemic stroke. In this case, mortality increases from 10 to 40%.
What are the causes of stroke?
What is the cause of stroke? Given the statistics, there may be various reasons. For example, arterial hypertension or atherosclerosis. Plus, unhealthy diet, dyslipidemia, alcoholism, severe stress, etc. Heredity also plays an important role.
An ischemic stroke develops as a result of a disruption in the passage of blood through one of the blood vessels supplying the brain. For example, due to occlusion of the carotid arteries. The cause of a sharp deterioration in cerebral blood supply may be a minor vascular spasm or thromboembolism. In turn, the cause of the latter is often cardiac pathology. The occurrence of the second type of stroke, that is, hemorrhagic, may be associated with the presence of various vascular pathologies. For example, cerebral atherosclerosis, systemic vasculitis and collagenosis. Rarely, but there are still cases when this type of stroke directly depends on blood clotting or incorrect therapy with anticoagulants and fibrinolytics.
Diagnostics
Methods for diagnosing ocular stroke As a rule, diagnosis of the abnormality is carried out in a hospital. As soon as a person develops the first symptoms of pathology, he urgently needs to be examined by a neurologist. The doctor will evaluate the patient's reflexes, speech, vision and spatial orientation. If the suspicion of an ocular stroke is confirmed, a consultation with an ophthalmologist is scheduled.
The following methods can be used in the diagnostic process:
- CT angiography (visualization of blood vessels).
These instrumental methods help identify the location and degree of occlusion, and also help determine the course of treatment. To detect malformations, vascular aneurysms and other pathologies, radiography is often also prescribed, and ultrasound and ECG can be used to identify the causes of eye stroke. Laboratory tests also play an equally important role in diagnosis: urine and blood tests help determine the concentration of glucose, as well as the presence of electrolytes and kidney metabolites.
What are the symptoms of a stroke?
Of course, the symptoms of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke are different, but they also have common signs. First of all, it is worth noting that the first type of disease develops more slowly than the second. At first, focal and general cerebral symptoms signal a stroke. In turn, the hemorrhagic type develops more rapidly, begins with general cerebral manifestations, against the background of which focal symptoms appear and progressively increase. In the case of subarachnoid hemorrhage, meningeal syndrome is typical.
Now about all the symptoms in more detail. By general cerebral pain we mean severe headaches, nausea, and often loss of consciousness. Focal signs depend on where in the brain the stroke occurs. If in the carotid artery, then there is a decrease or complete loss of muscle strength in the limbs of one side of the body. Homonymous hemianopsia is also possible, that is, loss of the same halves of the visual fields of both eyes. In some cases, photopsia (false appearance of light flashes, sparks, luminous lines) and visual hallucinations are noted. With a stroke in the vertebrobasilar area (it forms the right and left vertebral arteries that supply the cerebellum, trunk and occipital lobe of the brain), dizziness, diplopia, visual field defects, hearing impairment, oculomotor disorders, dysphagia (inflammation of the oral cavity, pharynx of the esophagus) are noted. Since without medical help it is impossible to understand where exactly the stroke occurred, one should rely on general cerebral signs. Once the diagnosis is made, surgical treatment is necessary.
How to treat strabismus during a stroke?
Since strabismus after a stroke is one of the most common problems, the question of how to cure strabismus after a stroke becomes the most pressing. To restore visual function after a stroke, there are several time-tested techniques. These include:
- drug therapy;
- therapeutic and preventive gymnastics for the eyes;
- operation.
What the treatment will be is decided by the ophthalmologist together with the neurologist, taking into account the type of disease, how the stroke progresses, the individual physiological characteristics of the patient and many other factors. In some cases, a comprehensive approach is used to achieve maximum recovery. Below we will talk about each method of treating strabismus after a stroke.
Prevention
Testing for cardiovascular disease is key to preventing ocular strokes. This may include regular cholesterol and blood pressure checks, as well as discussion of other risk factors for heart disease, such as family history, diet and lifestyle.
Heart disease risk factors play a role in the risk of ocular strokes. An article in the journal Eyes found that 64% of people had at least one new, undiagnosed risk factor for heart disease that was discovered after a stroke. The biggest factor for these people was high cholesterol.
In general, to maintain healthy blood vessels and prevent eye stroke, people should do the following:
- exercise regularly; The Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans recommend 2.5 hours per week.
- Eat a healthy diet including plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains and unsaturated fats.
- work with a nutritionist, as recommended for some people.
- avoid smoking or quit smoking
- work with your doctor to treat other conditions, such as diabetes.
What does drug treatment include?
Despite the great development of medicine, there are still no special drugs aimed specifically at restoring vision after a stroke, but there are drugs that can solve local problems. The effect of medications after a stroke is usually aimed at the following results:
- normalization of blood flow in the brain;
- regeneration of rheological properties of blood;
- elimination of metabolic disorders;
- reducing the volume of necrotic tissue;
- normalizing oxygen delivery to the brain and reducing the sensitivity of cells to its lack.
Using such an integrated approach, it is possible not only to minimize the number of necrotic neurons, but also to restore some sections that were slightly damaged. The ophthalmologist also recommends taking medications aimed at relieving tension and blockage of blood vessels, which will help regulate blood supply. But usually such drugs are used in the first few hours after a stroke in order to eliminate focal signs as soon as possible.
Vasoactive drugs are used to reduce the volume of necrotic tissue. If the patient has increased sensitivity of cells to hypoxia, then vitamin E is prescribed. It is a powerful antioxidant.
Acute circulatory disorder of the retinal vessels
With occlusion of the central retinal artery (OCAC), obstruction of the central retinal artery or its branches occurs, caused by thrombosis, embolism, or vascular spasm. Spasm manifests itself as vegetative-vascular disorders or organic changes in the vascular wall due to hypertension, atherosclerosis, etc., which is typical, in particular, for older people. In patients with ACAS, systemic diseases are distributed as follows: sclerotic lesions of the cardiovascular system - 35%, hypertension - 25%, heart defects - 8%, temporal arteritis - 3%. And in almost 25% of cases, the cause of CASC is never determined.
OCSA is a predominantly unilateral disease, without a clearly limited age category of patients (20 - 85 years). Men are more often affected by the disease.
Gymnastic exercises for the treatment of strabismus
This method is certainly one of the simplest, but quite effective. Especially when it comes to strabismus. However, you need to be patient, since eye gymnastics is not the fastest method of restoring vision. The ophthalmologist will tell you more about the exercises that are necessary after assessing the situation. It is worth noting that in most cases, gymnastics only relieves tension from the eyes, eliminates redness and burning, but cannot completely restore vision. It is recommended to train not only the visual organs, but also all parts of the body that have atrophied as a result of the stroke.
Surgery to treat strabismus after stroke
Often, for strabismus after a stroke, doctors resort to surgical intervention. It is important to understand that the operation will not eliminate the causes of strabismus and the consequences of a stroke, but will return the eyes to their natural position and reduce the risk of diplopia, that is, double objects, so that a person can normally perceive the world around him. At the moment, there are several types of elimination of strabismus after a stroke. But what type of operation the specialist chooses will depend on the type of strabismus and the general condition after the stroke.
Complications and consequences
Treatment is based on identifying the type of ocular stroke. If you feel the primary symptoms, you need to urgently contact an ophthalmologist, so that the doctor examines the eyeballs and fundus of the eye, prescribes an electronic analysis of blood vessels, and sends you to an appointment with a neurologist. Diagnostic results determine treatment methods for ocular stroke.
Therapy and consequences depend on the severity of the obstruction, as well as the time of progression of the pathology. In the early stages, treatment is effective and allows you to fully or maximally restore all impaired functions. In the later stages, laser surgery is actively used to treat ocular stroke, which helps to partially restore most visual functions.
There are times when problems still remain. Usually this is a distortion of objective perception, the appearance of blind spots, and loss of visual fields. The rehabilitation period consists of proper nutrition, taking vitamins and undergoing a course of therapeutic eye gymnastics under the supervision of an experienced trainer-doctor.
Visual impairment can become irreversible after a stroke, even leading to blindness, if timely assistance is not provided to the patient. This is the main and most dangerous complication of the disease. An equally serious consequence is retinal detachment and macular defects, which also leads to vision loss. The transition of the pathological process to the second eye and optic nerve atrophy occur less frequently.
When the retina lacks nutrition, the body begins to come up with workarounds. This is how new blood vessels form – neovascularization. This is not a healing process - the new vessels are too brittle and tortuous, and the risk of rupture is high. There are known cases of neovascularization of the optic nerve head and neovascular glaucoma.
Recommendations
Stroke is an extremely serious disease that leads to damage not only to the visual organs, but also to other organs. Therefore, immediate contact with specialists at the first signs of a stroke is of paramount importance. It is also important to note that an independent disease such as an eye stroke often occurs. In this case, a separate course of treatment is prescribed. The recovery period will directly depend on how quickly medical care was provided and, of course, on the degree of damage and the age of the patient. Today, strabismus after a stroke can be cured in various ways or using an integrated approach. What kind of therapy will be determined solely by the ophthalmologist.
Prevention
Prevention comes down to the treatment and prevention of affecting diseases. Regular visits to a therapist, vision and fundus examinations should be carried out at least once a year.
Precautionary measures:
- avoid eye strain, wear safety glasses when working with a computer and telephone;
- avoid smoking, drinking alcohol;
- dose physical and emotional stress;
- maintain a sleep-wake schedule;
- do not take any medications without first consulting your doctor;
- know and treat chronic and hereditary pathologies;
- take courses of vitamin complexes to improve immunity, especially in the spring and autumn.
Taking precautions and knowing the basic symptoms and methods of recognizing an eye stroke will help you avoid such a terrible condition. If this happens, react in time and correctly and maintain your health.