Make an appointment by phone: +7 (343) 355-56-57
+7
- About the disease
- Cost of services
- Sign up
- About the disease
- Prices
- Sign up
A concussion is a form of traumatic brain injury. In which short-term memory loss may occur, brain dysfunction is reversible. Usually the cause is various traumatic situations. In case of injury, the protective fluid is not able to prevent the impact of brain tissue on the bone tissue of the skull. The injury requires hospitalization and consultation with a specialist.
Classification
Concussion is classified into three degrees:
1.
Mild degree.
The victim is conscious, and within half an hour after the injury there are typical complaints of headache, dizziness, nausea, and disorientation in space. After half an hour the condition returns to normal. 2.
Average.
Consciousness is preserved, short-term memory loss occurs, the symptoms are similar to mild, dizziness persists, there may be a headache, nausea, the victim is disoriented in space. 3.
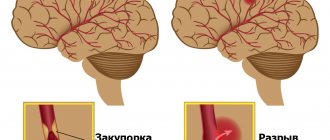
Severe degree. For her, loss of consciousness lasting a couple of minutes, maybe several hours, is accompanied by retrograde amnesia. Symptoms of headache, dizziness, nausea, disorientation in space can remain for two or three weeks, problems with sleep, and loss of appetite occur. Organic brain lesions lead to the appearance of vascular dementia. This is a secondary disease, that is, occurring against the background of some pathological process. The main reason is a previous ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.
Recommendations for the treatment of concussions
If hospitalization is not required, with the permission of a doctor, a mild concussion can be treated at home:
- Bed rest and rest are required, no work. Long sleep is very important.
- You cannot read, watch TV, play computer games or use gadgets.
- Under no circumstances should you play sports.
- You are allowed to listen to music, but not through headphones.
- You can use herbal sedative drops or herbal infusions.
- In your diet, you should give preference to dairy and plant products, limit salt intake - to prevent increased pressure, including intracranial pressure.
If the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner and all recommendations are followed, recovery will occur quickly and without complications.
Symptoms of a concussion
General symptoms:
The victim complains of memory loss, dizziness, tinnitus, double vision, intense headache, nausea leading to vomiting, and fatigue. There is sleep disturbance, daytime sleepiness, irritability, and emotional lability. After the injury, confused speech appears, short-term memory loss (retrograde, anterograde amnesia), increased sensitivity to light, noise, balance is disturbed, uncoordinated movements, smell and taste are lost.
Symptoms that may bother you for a longer period:
- intense headache, may be migraine;
- difficulties with reading, remembering, writing;
- absent-mindedness, difficulty concentrating;
- nausea, vomiting;
- drowsiness, weakness;
- dizziness.
General information
A concussion is a condition that occurs as a result of a mild traumatic brain injury. As a result of the concussion, interneuronal connections are temporarily disrupted. It occurs very often and ranks 1st among conditions associated with traumatic brain injuries. Despite the fact that the injury is considered relatively minor, it is extremely important after any traumatic brain injury to consult a doctor, conduct examinations and follow his instructions. After all, this condition requires obligatory observance of rest and following other doctor’s recommendations. The ICD-10 code for concussion is S06.0.
Treatment with folk remedies
To speed up the healing process, you can use some folk remedies.
- Infusion of mint, lemon balm and mistletoe. Take 1 tbsp. l. each of the herbs, pour into a thermos and pour 2 tbsp. boiling water Infuse overnight, drink half a glass 4 times a day.
- St. John's wort decoction. It is prepared from 2 tbsp. l. St. John's wort and 1 glass of water. The decoction should be brought to a boil, infused and drunk 100 g three times a day.
- Restoring infusion. Take 10 g of mint leaves, hop cones, buckthorn bark, lemon balm herb and 20 g of valerian root. Mix all ingredients, take 2 tbsp. l. means and fill it with 2 tbsp. boiling water Drink 100 g several times a day, be sure to take the infusion before bed.
- Soothing infusion. You need to take 2 tbsp. l. herbs mint, motherwort and lemon balm, pour 1 liter of boiling water and leave overnight. Drink half a glass three times a day.
- The infusion is soothing and restorative. It is necessary to take hop cones, buckthorn bark, lemon balm, valerian root, birch leaves, fireweed, and St. John's wort in equal proportions. Pour 3 tbsp. l. this collection with one liter of boiling water and leave for 2 hours. Drink half a glass 3 times a day.
- A remedy for insomnia. Mix 1 tbsp. l. mint herbs and 1 tsp. cinnamon. Pour boiling water (1 liter) and leave in a thermos for 2 hours. Drink 4 r. 100 g per day, also taken before bed.
- A mixture of honey and nuts. Chopped nuts should be mixed with honey in equal proportions and take 1 tbsp of this remedy. l. every day for six months.
- Bee pollen. It is recommended to take its granules - half a teaspoon per day for a month. Repeat after six months.
- It is recommended to sleep on a pillow with soothing herbs - mint, lemon balm, lovage, clover.
In children
A concussion in a child is a serious condition. If children experience the symptoms described above after being injured, they should immediately consult a doctor. In addition, as pediatrician Komarovsky and other experts note, parents should take into account that alarming symptoms can develop within 24 hours after the injury. Therefore, it is important to pay close attention to the baby’s condition.
You cannot use any treatment methods on your own. What to do and what treatment regimen to use is determined only by the doctor. Therapy is usually carried out in a hospital to monitor the child’s condition and prevent possible consequences. With the right approach to treatment, the child’s condition returns to normal in about 3 weeks.
Diagnostic methods
To determine the nature and extent of disorders, methods such as CT and MRI are used. During a diagnostic CT study, abnormalities are detected - areas of hemorrhage, damage to parenchyma (nervous tissue), fractures of the bone structures of the skull. Computed tomography is considered the most informative method for identifying indications for emergency surgery.
Other advantages of CT: the ability to examine patients in a state of psychomotor agitation, and quick results. Neuroimaging is mandatory for patients:
- Children under 16 years of age.
- Patients with signs of intoxication.
- Patients with a blurred, erased clinical picture.
- Patients taking anticoagulants on an ongoing basis (as part of a program for the treatment of chronic vascular pathologies).
With a mild concussion, changes in the structure of the brain matter are detected in 15% of cases. If, during the initial examination of the patient, neurological symptoms of a focal type are observed, morphological changes in the nervous tissue are detected with a frequency of 50% of cases.
An MRI study is more sensitive to detecting axonal damage of a diffuse type, changes in the structure of the parenchyma, and hematomas of subdural (under the dura mater) localization. MRI reveals hemorrhagic disorders that are associated with axonal damage.
How to help the victim?
The first step is to call an ambulance, even if the person refuses, claiming that he is already better. Delay often leads to subsequent difficulties in carrying out diagnostic measures.
But giving any painkillers or other medications before the doctors arrive is strictly prohibited. In the best of circumstances, pharmacological agents will only blur the overall clinical picture. But in a more serious scenario, they will only harm a weakened body.
While others are waiting for specialists to arrive, the patient will need to provide:
- cold;
- hunger;
- peace.
It is better to start with the last point, which provides for mandatory bed rest in the safest possible environment. Moreover, it is extremely important not just to send a person to sit without unnecessary movements, but to move him to a horizontal position, limiting his mobility.
Recommends applying cold to the head. A heating pad with ice water, pre-wrapped in a towel, is best suited for these purposes. If you don’t have ice on hand, a simple cold compress made from a rag will do. Exposure time is up to 5 minutes.
It is also important to ensure that the victim’s head is slightly higher than the body itself. Open a window to allow fresh air to enter.
When, during the initial examination, it turns out that the patient is unconscious, the first task of those around him is to bring him to his senses. Having shifted the person to his side, it is worth going for ammonia. A cotton swab is moistened with the solution and then brought to the patient’s nose.
If a person constantly falls into an unconscious state, then it is better to leave him to continue lying on his right side, bending his left arm and leg 90 degrees. The head should be directed towards the floor. This will ensure complete intake of air into the lungs, as well as prevent tongue retraction or suffocation due to uncontrolled release of vomit.
You should not give the patient any alcoholic drinks “for courage,” as this will only increase the already significant load on the cardiovascular system, increase blood pressure, and increase cerebral edema. In cases where outpatient therapy is indicated, the person is not allowed to return to their usual pace of life.
During treatment, you will have to give up any physical activity, and also not watch TV or strain your eyes when working with a computer. If you follow such a simple rehabilitation program, you will be able to recover in approximately 2-4 weeks.
In some cases, for final confirmation of recovery, it is necessary to undergo auxiliary instrumental diagnostics. This can be either computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
Pathogenesis
Normally, the human brain is located in the cerebrospinal fluid. When you shake your head sharply, a hydraulic shock occurs, triggered by a pressure difference in the cerebrospinal fluid. Sometimes the brain can hit the inside of the skull.
With injuries and contusions, a concussion of the entire brain tissue occurs. At the very beginning, there is a diffuse dysfunction of the brain ( fainting ). After a couple of minutes or hours, the severity of general phenomena decreases, and only signs of focal disorders remain in a certain area of the brain.
Symptoms of trauma develop due to the development of functional disconnection of the brain stem and hemispheres. When a shock occurs, some of the physical and chemical properties of neurons change, which can lead to changes in the spatial organization of protein molecules. It is also likely that there is a temporary disconnection of signals between the synapses of neuron cells and parts of the brain. A synapse transmits nerve impulses between cells. This is the site of contact between neurons or between a neuron and the effector cell that receives the signal. And if the relationship is temporarily disconnected, functional disorders develop. During a concussion, the entire substance of the brain is affected pathologically.
Causes of a concussion
Regardless of how the bruises were received, they end with the brain hitting the inner walls of the skull. The result is not long in coming, expressed in swelling of varying intensity. It is the swelling that causes the leading symptoms of a concussion to appear.
An external mechanical influence due to increased pressure on the head can provoke such a phenomenon. This definition even includes everyday hits against lockers or during a game of football. Sometimes this pathology is a consequence of a sharp fall or sudden braking of a vehicle.
In ordinary life, most often the victims of the condition are children of approximately school age who do not control their strength during various outdoor games, as well as elderly people who suffer from unsteady gait and often fall.
If you use the diagram of the main signs of a concussion, you can diagnose it for almost any person. The sooner medical care is provided to the victim, the faster he will complete his rehabilitation course. Even with consistently positive dynamics, recovery will take about a week. Reducing these periods threatens the development of complications.
It is impossible to predict how serious the consequences of ignoring an injury may be. It is believed that in the absence of timely medical care, patients in the future will not be able to quickly cope with even the simplest tasks. Such inhibition can be observed for months.
Also, untreated patients have an increased risk of developing:
- alcohol addiction;
- Parkinson's disease;
- sudden death.
To prevent a sad outcome, it is worth learning to recognize threatening symptoms and provide quality first-aid care.