Cerebral ischemia is characterized by partial blockage and narrowing of blood vessels in the head, most often due to atherosclerotic deposits. Damaged vessels are not able to pass a normal volume of blood, so the brain tissue does not receive the required amount of oxygen and nutrients. Over time, a person notices memory loss, deterioration in performance, sleep problems against the background of chronic fatigue. These alarming symptoms should be a reason to visit a qualified physician. Otherwise, the patient may risk stroke, memory loss and disability.
How does cerebral ischemia occur?
Cerebral vascular ischemia is mainly an age-related phenomenon. The normal functioning of blood vessels ensures that all organs are supplied with a sufficient volume of blood. With age, the elasticity of the vascular walls deteriorates; they become overgrown with accumulations of cholesterol plaques. The greatest danger is caused by damage to large arteries.
The vessels of the head are especially sensitive to these deteriorations, because a fifth of all blood in the body passes through them. The human brain cannot function properly without a constant flow of oxygen and nutrients that the blood contains. A decrease in their volume invariably leads to the degradation of brain tissue, the death of neurons and the loss of some functions, often vital.
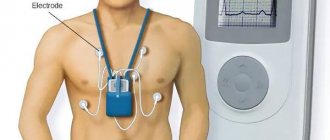
Ischemic processes in the brain can also be provoked by changes in the properties and composition of the blood (in particular, increased clotting) due to kidney disease, thyroid dysfunction, and metabolic disorders. Problems with the heart and toxic poisoning can also reduce the activity of blood flow in the vessels of the head. Now you can undergo a consultation and a set of preparatory examinations when registering for a course of enhanced external counterpulsation or shock wave therapy of the heart absolutely free of charge!
Promotion
Just until the end of autumn, undergo a free consultation and a set of preparatory examinations* when registering for a course of enhanced external counterpulsation or shock wave therapy of the heart.**
Send a request
* Check the details of the Promotion by phone. **Has contraindications; consultation with a doctor is required.
Enhanced external counterpulsation (EECP) Cardiac shock wave therapy (SWTS)
Hurry up to apply, the promotion period is limited.
Treatment of ischemic cerebral disease
Therapy for cerebral vascular ischemia consists of a conservative (medicinal) treatment method and a surgical one. The first method is aimed at improving vascular tone and blood pressure. The doctor will adjust the patient’s diet to eliminate the risk of the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and blood clots. But if they are already present, additional medications are prescribed in addition to the diet. In most cases, it is hypertension and atherosclerosis that are the root cause of the development of ischemia.
Drug treatment consists of the following:
- antihypertensive, reducing blood pressure in the vessels;
- lipid-lowering drugs (statins), which reduce cholesterol deposits;
- antiplatelet, blood thinning, preventing the formation of blood clots;
- nootropic, normalizing brain functioning;
- antioxidant, improving oxygen supply to tissues;
- anxiolytics and sedatives that reduce the manifestations of hyperexcitability.
Chronic ischemia requires more in-depth diagnosis, as well as radical treatment. Surgery is often necessary:
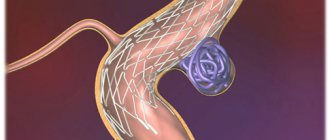
- stenting of the carotid arteries - expansion of the narrowing site using a metal tube;
- carotid endarterectomy - removal of plaque from the carotid arteries.
If the cause of chronic vascular disease is a blood clot or plaque, then during surgery they will be removed, which allows the patient to return normal vascular tissue, which will supply the brain with oxygen in full.
Neurologists advise not to overwork, get enough sleep and lead a healthy lifestyle, since discirculatory encephalopathy does not result in a quick recovery without following a diet and changing lifestyle.
Rehabilitation after surgery
Further rehabilitation measures consist of the following stages:
- Rehabilitation in a hospital setting during the patient’s hospitalization.
- Rehabilitation in a hospital department or in a sanatorium after the end of the acute period of illness.
- Outpatient clinic or home.
Causes of the disease
Atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension are two causes that account for the vast majority of cases of cerebral vascular ischemia. Cholesterol is especially actively deposited on the walls of blood vessels in people over 40 years of age. It is at this age that the risk of ischemic events increases. If the patient does not adjust his lifestyle, the growth of cholesterol deposits only progresses and leads to a deterioration in brain function.
The second most common cause is chronic heart failure. If the heart does not produce enough blood, this automatically disrupts the nutrition of the brain. Also, symptoms of ischemia often appear in patients with various types of arrhythmia, since disruption of blood flow dynamics negatively affects the blood supply to the brain.
Other reasons include:
- hereditary angiopathy;
- kidney disease;
- blood diseases;
- diabetes;
- metabolic disorders;
- endocrine diseases;
- systemic vasculitis.
Deformations and abnormalities of the blood vessels of the neck, aorta and other large arteries can cause deterioration in blood flow to the brain. These can be either purely vascular diseases (for example, aneurysms), or damage, compression of blood vessels by neighboring tissues and structures (vertebrae with osteochondrosis, tumors).
Symptoms of gangrene
The symptoms of gangrene are extremely specific and cannot be confused with manifestations of other diseases and disorders.
Dry gangrene, which is most characteristic of vascular etiology, is not life-threatening. The affected tissues do not disintegrate, but become mummified - they dry out, losing fluid. Toxic substances are released in moderate quantities, and the body manages to inactivate them. The focus of necrotic lesion is clearly organic and distinguishable. Wet gangrene is characterized by intense and aggressive coverage of tissue structures, very rapid progression, and infection of the systemic bloodstream by poisons released during necrosis. This condition often becomes a consequence of an infectious process and poses a direct threat to the patient’s life.
Common symptoms of gangrene of the hands or feet:
- A sharp and severe attack of pain in the affected limb;
- Fading of the cover and its subsequent coloring in a marble shade;
- Reduction (in the dry form) or increase (in the wet form) of the limb in size;
- Complete loss of sensitivity in the affected tissues;
- Dyeing fabrics dirty gray (when wet) or blue-black (when dry);
- The appearance of a persistent putrid odor (in the wet form) / clear limitation of dead tissue (in the dry form).
The difference lies in the general well-being of the patient. With the wet form of gangrene, it rapidly worsens - symptoms of extensive intoxication appear, the pulse weakens, and chills are observed. With dry gangrene, such symptoms do not occur. The affected limb often detaches on its own.
Symptoms of cerebral ischemia
The disease is quite insidious and in the early stages it can manifest itself with symptoms that a person barely pays attention to or does not associate them with brain activity. For example, loss of attention, sudden mood swings, sleep disturbances (insomnia or, conversely, drowsiness). Most often, these signs are attributed to work fatigue.
However, later the symptoms become obvious and disrupt the usual rhythm of a person’s life.
- Dizziness, nausea.
- Headaches of varying severity.
- Forgetfulness.
- Feeling of coldness in the feet and palms.
- Numbness of the limbs.
If action is not taken at this stage to eliminate the symptoms using medicine, the disease will progress rapidly. Further signs can no longer be ignored.
- Temporary loss of vision (partial or complete).
- Problems with speech (incoherence, slurring).
- Headaches to the point of vomiting.
- Insomnia.
- Memory losses.
- Movement disorders when walking.
- Disorientation in time and space.
The situation becomes extremely dangerous, since with these symptoms the patient is only one step away from a stroke.
Principles of treatment
Treatment of leg swelling due to heart failure is based on eliminating the main cause - the disease itself. Of course, curing such a disease is quite difficult. But control is quite possible. In order not to aggravate the patient’s condition, it is important not to allow the disease to progress. In the first stages of the disease, rest, foot massage, and the use of cold compresses help well. Subsequently, more radical methods are required.
To relieve swelling in heart failure, cardiologists use medications - diuretics. They cause frequent urination, which leads to a decrease in fluid in the body. Both chemicals and natural remedies can be used as diuretics. Chemical diuretics include:
- Furosemide,
- Bumetanide,
- Piretanide.
Natural urinary products include:
- A decoction of fresh birch buds.
- Decoction of cherry stalks.
- A decoction of cornflower, dandelion and parsley flowers.
In addition to decoctions, it is recommended to eat as many fruits and vegetables as possible, which help remove water from the body. Raw cabbage, baked potatoes, cucumbers and pumpkin - all these products should be in the patient’s regular diet. Once or twice a week it is recommended to carry out fasting days, during which you should consume apples and cottage cheese.
If your legs swell due to heart failure, it is recommended to take glycosides. These are plant-based drugs that affect the entire human body. These medications help remove more water, thin the blood, and normalize blood circulation.
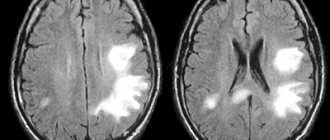
Diagnosis of cerebral vascular ischemia
The most important examination method for these symptoms is ultrasound of cerebral vessels. The “gold standard” is duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries, which effectively detects disturbances in the functionality and structure of blood vessels.
An objective picture of the disease is also presented by ultrasound transcranial Dopplerography of cerebral vessels. The study shows the speed of blood flow, the degree of damage to the vascular walls, etc.
These examinations are carried out by the Center for Pathology of the Circulatory Organs of the CBCP. For this purpose, the latest expert-class equipment is used.
Degrees of cerebral vascular ischemia
In medicine, it is customary to classify this pathology into three degrees. The most difficult is cerebral ischemia of the 3rd degree.
1st degree . Characterized by mild disorders of attention and intellectual activity. Most often, patients cope with complex tasks, but it takes them longer. There are no obvious limitations in life activity or coordination disorders yet, but minor signs of the disorder are already noticeable:
- shuffling gait;
- pain and numbness in the hands after physical activity;
- irritability;
- frequent weakness.
2nd degree . In some cases, the patient has little control over his actions. When performing work tasks, he often needs help and hints, which negatively affects his professional activities. The person may also lose some life skills. Increasingly, he is tormented by general ailments with the characteristic symptoms described above.
3rd degree . Pronounced neurological disorders appear in the form of Parkinson's disease, urinary incontinence, and problems with coordination. The patient may lose the ability to move independently, as he has poor control of his legs and loses the ability to navigate in space. There are disturbances in thinking, memory, and speech. In the absence of medical care, a patient with grade 3 ischemia will face complete personality collapse, ischemic stroke, and cerebral hemorrhage.
Chronic cerebral ischemia
Symptoms of chronic cerebral ischemia develop gradually, but with noticeable manifestations. They are often associated with cardiac dysfunction, angina pectoris, arrhythmia, diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis of peripheral arteries, and other diseases.
Most often, cerebral ischemia becomes chronic in cases of 2nd degree disease. This type of disease is characterized by long-term development without any complications. However, this does not mean that the disease does not progress. Usually, deterioration in health occurs unexpectedly. And any nervous or physical stress can provoke it.
Chronic ischemia does not require mandatory hospitalization.
Treatment of cerebral vascular ischemia
The patient is prescribed complex treatment, which includes:
- massage and physiotherapeutic procedures to improve blood circulation;
- hypoxic therapy to saturate tissues with oxygen;
- drug therapy to normalize blood pressure and restore blood circulation;
- surgical intervention to remove atherosclerotic plaques from blood vessels.
Treatment of chronic cerebral ischemia is combined with therapy for other organs and systems.
Prognosis and prevention
The consequences of cerebral vascular ischemia can be minimized if you consult a qualified doctor in a timely manner. This should be done when symptoms of the 1st degree of complexity appear. At this stage, preventive actions are sufficient:
- maintaining physical activity;
- nutrition correction;
- abstaining from nervous stress.
Even with symptoms of the 2nd degree of severity, the prognosis is positive, provided the patient follows all the doctor’s prescriptions. Seeking help at the 3rd stage of the disease is in most cases ineffective.
Consequences of untimely treatment of cerebral ischemia in the elderly
If you do not consult a doctor in time, an elderly person with chronic ischemia will show unpleasant signs of the disease: memory and performance deteriorate, and fatigue quickly appears. Night sleep becomes interrupted, insomnia appears, and during the day, on the contrary, you want to sleep.
Nausea and vomiting may occur, migraines begin to overcome, and you often feel dizzy.
The healing process is influenced by many factors, primarily age. The older the patient, the more disappointing the prognosis may be. Next comes the general physical condition of the patient, the presence of bad habits and other chronic diseases.
Statistics provide information on the survival rate of elderly patients within a year after treatment. The figure is 75%.
The chronic form of cerebral vascular ischemia is not life-threatening. The acute stage of the disease is much more dangerous.
In this case, urgent medical attention is required, otherwise ischemic attacks or acute oxygen starvation may occur.
An exacerbation is manifested by loss of sensitivity in certain parts of the body, even partial paralysis, and deterioration of vision in one eye. Timely medical intervention within 24 hours will relieve all symptoms.