Hospitalization and treatment under the compulsory medical insurance quota. More details after viewing the pictures.
- Aneurysm clipping
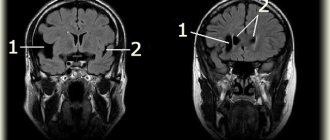
A cerebral aneurysm is a local protrusion of the arterial walls. The disease often occurs without symptoms. As the brain aneurysm grows, a significant thinning of the walls of the formation occurs, which can lead to its rupture and the development of hemorrhagic stroke.
Depending on the shape, a cerebral aneurysm can be spindle-shaped or saccular. The exact type of disease can only be determined during a comprehensive diagnosis. Saccular aneurysm is much more common.
General information about arterial aneurysms
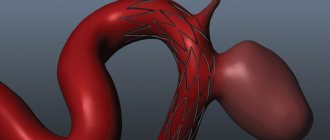
An aneurysm is a local expansion of a vessel with gradual thinning of its wall. The process is irreversible; over time, under the influence of blood flow pressure, the protrusion only increases and, one day, may rupture. This leads to internal arterial bleeding. Without timely medical attention, a ruptured aneurysm leads to death.
Other possible complications include: thrombosis, thromboembolism (when a blood clot breaks off and clogs other vessels), infection of the aneurysm.
Etiology
It is quite difficult to establish the exact cause due to which an aneurysm of the vessels of the eye is formed. Experts point to abnormal development of blood vessels. The defects involve a violation of the structure of the vessel; its wall is thin and cannot withstand pressure when stretched. Factors that can trigger the process include the following conditions:
- traumatic brain injury;
- damage to the ophthalmic artery;
- chronic increase in blood pressure;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- infectious diseases.
Classification of Aneurysms
, single- and multi-chamber aneurysms are distinguished
.
By form:
- saccular
ー local protrusion; - fusiform
ー dilation of an entire section of the artery.
Special type: dissecting aneurysm
. In this case, blood enters between the layers of the vessel wall, gradually pushing them apart.
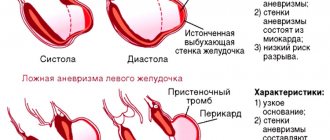
It is necessary to distinguish between true and pseudoaneurysms
. The latter represent a hematoma near the vessel, while its wall is in order.
Pediatric aneurysms
Vasodilation is congenital and appears at an early age. This is often forgotten, making diagnosis difficult. Parents should be aware of this danger and not let frequent complaints of pain in the stomach or head go to chance.
Aortic aneurysm
Depending on the location, the following types are distinguished:
- sinus of Valsalva;
- ascending part;
- arcs;
- descending part;
- abdominal section.
Cerebral aneurysms
Depending on the location, aneurysms are distinguished:
- internal carotid artery;
- anterior cerebral;
- midbrain;
- vertebrobasilar system.
Choosing a method to turn off an aneurysm
| Aneurysm occlusion with stent assistance |
The advantages of endovasal treatment are primarily important in patients in the acute period of hemorrhage, with aneurysms of the paraclinoid part of the ICA and the vertebrobasilar region. Until recently, the main factor determining the possibility of aneurysm occlusion using the endovascular method was considered to be the ratio of the size of the aneurysm body and its neck. It has been established that the larger the size of the aneurysm and the wider its neck, the greater the likelihood of distant recanalization after the initial total occlusion. To solve this problem, stent-assisted techniques have been developed. The essence of the stent-assisted technique in the treatment of aneurysms is to prevent displacement of the coils of the coils into the lumen of the supporting vessel. This is achieved as follows: in the first stage, a stent is installed in the vessel at the level of the aneurysm neck, and then a microcatheter is passed through the stent cell, through which microspirals are delivered. In recent years, a new category of intracranial stents has emerged, the so-called flow divert stents, which reduce blood flow in the aneurysm by directing the main blood flow through the supporting vessel. Thrombosis of the aneurysm after installation of such a stent occurs on average within 4 to 6 months after surgery. This technique is most effective for treating large and giant aneurysms. Currently, the Research Institute of Neurosurgery annually performs about 250 microsurgical and 150 endovascular operations on aneurysms in the “cold” period after SAH (21 days or more). The choice of surgical method depends, first of all, on the anatomical features of the aneurysm. The endovascular method is preferable for ICA aneurysms of the paraclinoid and infraclinoid location. For MCA bifurcation aneurysms and ACA-ASA aneurysms, direct interventions are more often performed, since the structural features of these aneurysms (predominantly wide neck, proximity of the ostia of second-order arteries, variations in the structure of the ACA, etc.) and the impossibility of using stents limit the use of the endovascular method. The decision on the method of operation is influenced by the age of the patient - in young patients direct operations, which are more radical, are preferable. Limitations for the endovascular method are pathological bends and severe atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries. If a stent-assisted operation is necessary, a history of bleeding of various etiologies should be taken into account, since stent installation requires long-term use of anticoagulants in the postoperative period. In some cases, microsurgical operations are performed as a second stage in cases where only partial occlusion of the aneurysm was achieved during endovascular intervention. The opposite situations are also possible - endovascular intervention after palliative direct surgery (strengthening the aneurysm with gauze, incomplete clipping). The results of microsurgical treatment of aneurysms in the cold period after SAH have remained quite good for many years. The risk of a new neurological deficit is slightly higher with microsurgical exclusion of the aneurysm, and the risk of death is higher with endovasal treatment.
Risk factors for developing aneurysms
The development of aneurysms is predisposed by the loss of elasticity and strength of the vessel wall. Weakness of the vascular wall may be due to congenital characteristics or the influence of external factors. The main reasons for the development of the disease:
- atherosclerosis - formation of cholesterol plaques;
- inflammation of the aortic wall (occurs with traumatic injury, syphilis, fungal infection);
- autoimmune diseases;
- congenital pathologies of connective tissue (cystic fibrosis, Marfan syndrome);
- trauma during diagnostic and therapeutic procedures (coronary angiography, heart surgery).
Symptoms of aneurysms
Often aneurysms do not manifest themselves for many years. A person does not suspect that he has a “time bomb” inside him that can explode at any moment. Often symptoms are ignored until they become more severe. The main manifestations of an aortic aneurysm:
- pain in the chest and abdomen of a diffuse nature without a specific localization;
- pressing pain in the heart area caused by compression of the coronary vessels;
- attacks of shortness of breath and dizziness;
- superior vena cava syndrome (when it is compressed) includes cyanosis, swelling of the face, neck, and arms;
- signs of compression of the esophagus (impaired swallowing), trachea and bronchi (difficulty breathing, frequent pneumonia), rotary laryngeal nerves (hoarseness), vagus nerve (decreased heart rate);
- nausea, vomiting, feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- palpable pulsating formation in the upper abdomen.
Cerebral aneurysms occur without typical symptoms. A person can only be bothered by frequent headaches.
Symptoms
At the initial stages, the pathology may not manifest itself in any way. We are talking about the so-called asymptomatic aneurysm. As it increases, a characteristic neurological picture appears:
- headache;
- loss of sensation in the lower extremities;
- violation of fine motor skills, diction;
- numbness of the face, weakening of the facial muscles, loss of control over facial expressions.
Impaired cerebral circulation changes character and behavior. The person becomes restless and emotionally unstable.
When an aneurysm ruptures, a severe headache occurs, which is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, and pallor. The patient experiences convulsions and develops photophobia. Due to impaired cerebral circulation, a person loses orientation and falls into an unconscious state. If there are signs of aneurysm rupture, you should urgently call an ambulance and take the victim to the neurological department.
Diagnosis of aneurysms
In some cases, pathology can be suspected when examined by a doctor. Next, a series of studies are prescribed to find the problem and assess its scale:
- chest x-ray;
- Ultrasound of the heart, Dopplerography of the thoracic and abdominal aorta, neurosonography;
- CT scan;
- angiography ー X-ray examination with preliminary introduction of a contrast agent into the vessel.
Prognosis and prevention of aneurysms
Without treatment, the prognosis for patients with aortic and cerebral aneurysms is unfavorable, as there is a high risk of rupture or thrombotic complications. If the operation is detected and carried out in a timely manner, the prognosis is much more optimistic.
To prevent complications, it is recommended that people at risk undergo an annual scheduled examination by a general practitioner, cardiologist, or neurologist. It is also important to lead a healthy lifestyle, because high cholesterol, smoking, and physical inactivity contribute to the development of this disease.
Prevention of aneurysms in children
In order to diagnose pathology in a timely manner and prevent the development of complications in children, it is worth paying close attention to possible warning signs:
- frequent complaints of headaches, chest and abdominal pain;
- cyanosis of the lips, nasolabial triangle, fingertips;
- nausea, vomiting, frequent belching, refusal to eat.
Take your child to the doctor regularly during the first years of life. If there is a burdened family history (one of the relatives previously had aneurysms), the child was born premature, with heart defects, or other congenital pathologies, neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain), ultrasound of the heart is recommended.
What is the cost of the operation
Due to the fact that clipping an aneurysm is a very complex and dangerous operation, it is not performed in all major cities of Russia. Thus, clinics with appropriate personnel and technical equipment exist in Moscow, Tyumen, Ufa, Kirov, Volgograd, Krasnodar and some other regional centers.
Regarding the cost of the operation, it should be noted that a planned intervention can be performed according to a quota allocated from the funds of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, but for this the patient must contact the regional department of the Ministry of Health and provide all documents confirming the need for the intervention.
In the event that the patient does not intend to wait several weeks or months, he can be operated on in any city at his own discretion, but at his own expense. The cost of operations depends on many factors and ranges from 12 thousand rubles to 180 thousand rubles for endoscopic surgery and from 22 thousand rubles to 170 thousand rubles for clipping an aneurysm.
aneurysm before/after surgery
Diagnosis and treatment of arterial aneurysms in Medical
When should you see a doctor?
You should contact a cardiologist or cardiovascular surgeon if:
- the attending physician suspects an aneurysm;
- during an examination for another reason, a pathological dilatation of the artery was discovered;
- there are characteristic symptoms.
There are two tactics for managing patients: dynamic observation (for small sizes, asymptomatic course, minimal risk of complications), surgical treatment.
Observation is carried out under x-ray control. To reduce the risk of possible complications, antihypertensive and anticoagulant therapy and cholesterol reduction are carried out.
Forecast for life
The prognosis of the disease depends on the location of the vascular protrusion and its size. The initial condition of the patient also has a huge impact. The mortality rate in case of rupture of a cerebral aneurysm exceeds 30-50%. Surviving patients sometimes retain the consequences of the condition in the form of movement restrictions, cognitive impairment and a significant decrease in quality of life. Mortality after recurrent hemorrhage exceeds 70%.
Therefore, it is so important to carry out surgical treatment in time, turning to a qualified neurosurgeon. The operation is postponed only if there are certain medical indications.
Successful neurosurgical operations are carried out at the Burdenko Research Institute. Patients with signs of an aneurysm or suspected aneurysm are admitted here. At the Institute of Neurosurgery, it is possible to carry out comprehensive diagnostics using the latest technology and further treatment of identified diseases.