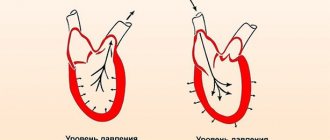
In general, the effect of low pressure on the heart is expressed in the inability of the blood transporting organ to fully perform its functions. As a result, hypotension occurs - one of the common pathological conditions of the cardiovascular system.
Low blood pressure can occur against the background of the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia, heart disease, stomach disease, as well as with large blood loss, the presence of a number of psychological painful conditions (depression, insomnia and others).
The International Center for Health Protection sees experienced cardiologists who can solve even complex problems. You can make an appointment by calling
The main manifestation of hypotension is a deterioration in the intensity of blood flow in peripheral blood vessels. As a result, the supply of oxygen and other useful components of the blood to the organs is disrupted.
In addition to pronounced clinical manifestations, this pathological condition is dangerous due to the development of various complications. It is especially important to monitor blood pressure in the case of diagnosing renal and cardiac pathologies. This circumstance may be a consequence of the development of a number of other pathological conditions. However, such predictions are only possible for special heart conditions.
What is arterial hypertension
Arterial hypertension is the most common disease of the cardiovascular system, associated with a persistent increase in systolic pressure to 140 or higher mmHg.
Art., and diastolic - up to 90 and above. Systolic pressure is the blood pressure in large vessels at the time of contraction of the left ventricle of the heart, and diastolic pressure is the pressure maintained by the tone of the vessel walls during relaxation of the ventricle.
High blood pressure syndrome is diagnosed based on three measurements taken in a quiet environment. The main condition is that the person does not take any medications that affect blood pressure the day before. To make a diagnosis, especially when examining older people, it is enough that only systolic pressure (also called “heart pressure”) is constantly elevated.
According to WHO, arterial hypertension is the most common cardiac disease in the world, affecting 30-45% of the population. The incidence rate is not affected by income, climate, or the general socio-economic situation of the country. The pathology is more often diagnosed in men; after 60 years, it is observed in 60% of people. WHO experts predict a further increase in the prevalence of arterial hypertension due to increasing life expectancy and the aging of the population in all countries. The number of people suffering from high blood pressure is projected to reach 1.5 billion by 2025.
The body's response to surges in blood pressure
The human circulatory system instantly reacts to changes in blood pressure. When blood pressure levels increase in the body, the following reactions occur:
- specific arterial receptors become active;
- through nerve impulses, they transmit the necessary signals to brain cells, resulting in an increase in the narrowed lumen of the vessel.
But if there are disturbances in the functioning of the regulatory mechanism, then the body becomes unable to independently stabilize blood pressure. The vessels can no longer dilate on their own. The result of such a deviation is the development of hypertension.
Classification
Arterial hypertension (AH) is classified according to various criteria:
- degree of pressure increase;
- severity of target organ damage, i.e. organs and systems most affected by high blood pressure;
- the cause of the appearance and development of pathology.
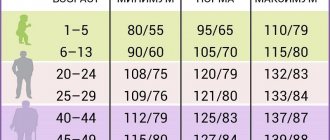
Classification according to blood pressure (BP) levels distinguishes several stages of arterial hypertension:
- A blood pressure not exceeding 120/80 mmHg is considered optimal. Art., but if blood pressure is within 139/89, this is considered normal;
- 1st degree of pathology - up to 159/99;
- 2nd degree - up to 179/109;
- 3rd degree (severe) - above 180/110.
Based on the reasons for the development of the disease, primary and secondary arterial hypertension are distinguished. Primary hypertension is also called essential hypertension or essential hypertension. Among all cases of hypertension, this type accounts for 95% of diagnosed cases. In secondary (symptomatic) hypertension, an increase in blood pressure is a consequence of pathology of other organs and systems of the body, for example, inflammatory kidney diseases, endocrine disorders, or problems with the central nervous system (CNS).
Dependence of blood pressure on atmospheric pressure.
«There is no bad weather. Every weather is a blessing..."
If a person is healthy, he does not feel the changes occurring in the atmosphere. There are many weather-sensitive people around; they feel weather changes, but without pathological symptoms. For some patients, this turns into weather dependence - their well-being changes depending on the weather outside the window.
Patients with cardiovascular diseases often do not tolerate any sudden temperature fluctuations, atmospheric pressure, wind, or heat. They feel discomfort, in some cases pathological symptoms appear (blood pressure increases or decreases, pain in the joints, heart pain, etc.). Those with high or low blood pressure are more likely to suffer.
What a weather-dependent person feels: Some patients very clearly sense weather changes in the form of a “barometer”. They can accurately predict what to expect from the weather in the coming days. When atmospheric pressure changes, the patient feels:
- The head hurts, powerlessness sets in, the heart hurts.
- Performance decreases sharply.
- Lethargy.
- Blood pressure rises or falls.
- Complete apathy.
- Joints and whole body hurt
- The stomach is bloated.
- Irritability appears.
The drop in temperature outside the window is especially poorly tolerated.
- There is an exacerbation of chronic diseases.
- Attention wanders.
- Sleep is disturbed (we are either sleepy all day or we experience insomnia).
Why does a person acquire weather dependence and how to deal with it:
- We have more and more problems in our lives that we cannot or do not know how to calmly solve. This means a constant negative load on the human nervous system. “All diseases come from nerves,” everyone has heard. Immune defense sharply decreases, our body weakens.
- There are a very large number of patients with hypertension, hypotension, and dystonia. Our blood vessels are not healthy.
- Poor nutrition, immobility or low mobility, ignoring walks in the fresh air, smoking, alcohol.
- Ecologically unfavorable place to live.
How to help yourself:
A person suffering from weather dependence already knows, immediately in the morning, that such a day has arrived.
- When he wakes up, he feels tired. In such cases, it is better not to get out of bed right away - you may feel dizzy.
- Stretch a little, roll onto your stomach.
- Then get on your knees, then on all fours.
- Very carefully tilt your head from side to side, forward, back.
- Rotate with your arms and hands.
- Get down to the floor.
- You can do abdominal exercises, but if you feel very unwell, it is better to postpone it.
- Vigorous rubbing of palms against each other effectively removes lethargy. Then apply hot palms to your eyelids. Repeat three times.
- The lethargy will definitely pass.
- If you feel unwell and do not want to move, turn on your favorite music and listen to it. Choose one that will lift your mood. Perhaps after a few minutes you will want to stand up, smile, do a few movements.
- A useful procedure in the morning is to massage the ears. There are many active areas of the body here. All organs wake up from their massage. Just rub your ears, knead them.
- Ventilate the premises more often, do not be afraid of the cold. There is no oxygen in the stuffiness - this is very harmful. You are constantly apathetic, lethargic and weak in a stuffy environment.
- Go to the kitchen and start your day with a glass of water at room temperature. By doing this you will help your stomach wash away from its walls the unnecessary things that have accumulated at night.
- Be sure to take a shower, preferably a contrast shower (changing hot and cold water).
- Have breakfast, without it the weakness will not go away. Green tea and coffee with milk will help with low blood pressure. If you have high blood pressure, it is better not to drink such drinks. Drink tea from linden or chamomile, rosehip.
- You can eat boiled eggs, oatmeal porridge, bran or grain bread with a small amount of butter (if there are no contraindications). You shouldn't eat heavily.
- Meteorological dependence and how hypertensive patients can deal with it:
- Take multivitamins as prescribed; there are very few of them in our products.
- Move more, it's not just words - it's incredibly good for your health.
- Never overeat, no matter how tasty the food is.
- Adjust your sleep (there should be a dark room, silence, a clean bed, the room is ventilated, you are calm).
- Fight stress. By nightfall they should be at zero.
- Control all chronic diseases and treat them on time.
- Hypertensive patients should have more potassium in their food (berries, fruits, herbs, vegetables, nuts, only fresh fish without frying).
- Less salt, smoked meats, white flour, fat. Less fatty, red meat.
- Replace eggs, fish, and nuts with protein.
- Drink hibiscus tea - it is incredibly beneficial. Tinctures of oregano, chamomile, thyme, and motherwort will help.
- Avoid coffee and tea on such days. The pressure will definitely rise.
- Be sure to take an increased dose of the drug for high blood pressure if it does not decrease.
- Try to avoid stressful work. Don't lie down, walk slowly. Low mobility is bad for your health – it will only get worse.
Follow the recommendations given to you and stay healthy.
Prepared by general practitioner of the Slonim Central District Hospital Levkevich D.I.
Reasons for development
The reasons for the development of arterial hypertension are still not completely clear. The main theory of its origin suggests that the cardiovascular system is affected by a violation of the regulatory activity of the higher parts of the central nervous system. Risk factors for developing pathology:
- Hereditary predisposition. The risk of developing hypertension is associated with the presence of heart problems in close relatives: previous heart attacks, early death, heart failure.
- Prolonged stress, uncomfortable working conditions, mental overstrain.
- Poor nutrition, excess salt in the diet. In combination with a genetic predisposition, salt consumption of more than 5 g per day significantly increases the risk of developing hypertension, since salt retains fluid in the body and causes vasospasm.
- Sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity.
- The presence of endocrine diseases in a person: diabetes mellitus, pathology of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
- Increased cholesterol levels in the blood. Because of this, the lumen of the arteries narrows and blood pressure on the walls of blood vessels increases.
- Overweight and obesity.
- Bad habits. Smoking constricts blood vessels and increases the activity of the central nervous system. Alcohol abuse increases the load on the kidneys.
- In women - hormonal changes in the body during menopause.
- Age and gender. After 60 years of age, arterial hypertension occurs in half of the population, but in men under 40 years of age the disease is diagnosed more often.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions, presence of hazardous industries in the region of residence.
- Lack of potassium and magnesium in the body, which are involved in many physical and chemical processes and affect the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels.
Important! Arterial hypertension is increasingly being diagnosed in young people under 30 years of age. This trend leads to an increase in mortality from cardiovascular diseases during reproductive age. It is necessary to regularly measure blood pressure and consult a doctor even if it is slightly but persistently elevated.
Secondary hypertension can develop as a result of taking certain medications.
Figure 1. How the vessels of people with arterial hypertension (hypertension) differ from the vessels of people without the disease. Source: CC0 Public Domain
Controllable factors for hypertension
The reasons leading to high blood pressure and which can be avoided are:
- obesity;
- bad habits (smoking and drinking alcohol);
- violation of the daily routine;
- insufficient sleep and rest;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- chronic stress;
- professional activities associated with nervous and mental overload;
- unhealthy diet (excess salt, fatty, smoked foods, unhealthy foods, etc.)
Attention!
Even in the absence of characteristic symptoms of high blood pressure (and a history of hypertensive crisis), it is necessary to have a tonometer at home to measure blood pressure. This is especially true for all persons over 40 years of age, regardless of gender and occupation.
Forms of arterial hypertension
Correct determination of the form of arterial hypertension plays a decisive role in preventing the development of dangerous complications and choosing the optimal therapeutic tactics. This is especially true for secondary hypertension as a consequence of dysfunction of some individual organs and systems of the body.
Nephrogenic parenchymal arterial hypertension
The most common cause of secondary arterial hypertension is kidney disease. Pressure may increase with pyelonephritis, nephropathies of various natures, tumors, tuberculosis of the kidneys and other renal pathologies.
This form of hypertension is more common in younger people. It is characterized by normal blood pressure at the initial stage of the disease. The development of the disease and severe tissue damage cause an increase in blood pressure against the background of chronic renal failure.
Nephrogenic renovascular arterial hypertension
The cause of renovascular hypertension is a violation of arterial renal blood flow, in most cases due to atherosclerosis of the renal arteries. A persistent increase in pressure develops when the lumen of the renal artery narrows by more than 70%. A characteristic sign of this form of hypertension is an increase in pressure to 160/100 mm Hg. Art. and higher.
The disease usually begins acutely, and the pressure cannot be reduced with antihypertensive drugs.
Ultrasound examination determines the asymmetry of the kidneys and disruption of the main blood flow. The disease often leads to myocardial infarction and stroke. In the absence of adequate therapy, only 30% of people are predicted to survive in the next 5 years.
Pheochromocytoma
This hypertension, which is caused by a hormonally active adrenal neoplasm, occurs in approximately 0.3% of symptomatic hypertension. The periodic release of adrenaline, dopamine and other hormones into the blood causes a sharp increase in blood pressure and often leads to a hypertensive crisis.
The diagnosis is made based on the results of hormonal tests and instrumental studies. Pheochromocytoma can only be treated surgically.
Primary aldosteronism
The disease is caused by excessive production of the hormone aldosterone in the kidneys - it is responsible for the retention of sodium ions in the body and the excretion of potassium ions. When the potassium-sodium balance is disturbed, excess potassium is formed in the cells. Because of this, fluid accumulates in the body and blood pressure increases.
Drug therapy for primary aldosteronism does not give the desired effect. Patients suffer from cramps, muscle weakness, and thirst. Pathology can lead to stroke, hypertensive crisis, and pulmonary edema.
Itsenko-Cushing's syndrome and disease
Cushing's syndrome and disease is a change in the hypothalamus, which results in excessive synthesis of glucocorticoid hormones by the adrenal cortex. One of the signs of the disease is obesity.
Blood pressure that is elevated due to hormonal imbalance is not reduced by taking blood pressure lowering medications. When the diagnosis is confirmed by CT and MRI of the adrenal glands, surgical or hormonal treatment is prescribed.
Coarctation of the aorta
One of the rare forms of arterial hypertension, the cause of which is difficulty in blood flow in the systemic circulation due to congenital narrowing of the aortic lumen.
Coarctation (narrowing) of the aorta is diagnosed immediately after the birth of a child or in early childhood. As a result of narrowing of the main blood vessel, blood flow deteriorates, which leads to systolic overload of the left ventricle of the heart. When measuring blood pressure, high readings are noted in the arms and normal or low readings in the legs.
If there is significant stenosis of the artery, surgical intervention is indicated.
Dosage forms of arterial hypertension
Some medications increase blood viscosity, retain salt and water in the body, cause vasospasm, and cause arterial hypertension.
These medications include cold drops with ephedrine derivatives, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, some hormonal contraceptives, antidepressants, and glucocorticoids.
Such drugs should be taken strictly as prescribed by a doctor and under his constant supervision.
Neurogenic arterial hypertension
The causes of arterial hypertension can be traumatic brain injury, encephalitis, and neoplasms in the brain. This type of hypertension is called neurogenic.
Characteristic signs: convulsions, headaches, tachycardia. Normalization of blood pressure is possible only after successful treatment of the underlying disease.
Possible consequences of vasoconstriction for the body
With the development of persistent hypertension, accompanied by a constant increase in blood pressure, the vascular system experiences continuous stress. Especially if a person, even knowing about his illness, does not take any measures to stabilize blood pressure.
As a result of excessive overstrain, the muscle and elastic vascular layer becomes thinner. Subsequently, the structure of the blood vessels completely changes, and they transform into thin, fragile tubes. This leads to the fact that the blood vessels can no longer give an adequate response to changes in pressure.
Prolonged vasoconstriction is fraught with the development of complications in vital organs
Chronic narrowing of the vascular lumen causes the development of the following dangerous consequences:
- hypertensive crisis, pre-infarction conditions;
- increased risk of complete blocking of the vascular lumen with cholesterol deposits (plaques);
- if platelets grow in the blood, the risk of blood clots increases, which can also completely block the vascular lumens;
- detachment of a blood clot - when separated from the wall of a vessel, the blood clot, due to significant narrowing of the vessel, is able to block its lumen;
- entry of a blood clot into the vessels of the brain - the condition causes the development of ischemic stroke and complete/partial paralysis).
The narrowing of the vascular lumens causes a decrease in human performance. As a result of poor blood supply, various serious diseases develop. The legs are especially often affected. Chronic vasoconstriction is indicated by the appearance of the following symptoms:
Prevention of arterial hypertension
- regular occurrence of a feeling of numbness in the arms and legs;
- weak pulsation of the arteries;
- increased dryness of the skin of the legs, as well as the appearance of a characteristic bluish tint, alternating with areas with a marble pattern;
- muscle pain, worse at night;
- formation of trophic ulcers on the legs.
When such symptoms appear, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- with a blood-thinning effect - Aspecard, Heparin, Warfarin;
- helping to increase the elasticity of blood vessels - Ascorutin, Sermion, Fezam; Venolek;
- cleansing blood vessels from cholesterol deposits - Rozart, Lovastatin, Fluvastatin.
Important! The choice of drug depends on the current symptoms, general condition of the circulatory system, and blood composition.
Mechanism of increased blood pressure
Blood pressure is regulated by a complex system of stimulation or inhibition of blood flow in the vessels. An increase in pressure occurs with an increase in the volume of cardiac blood output per minute and the resistance of the vascular bed. This physiological process is controlled by the hypothalamus and the vasomotor center located in the brain stem.
Three main reasons can lead to an increase in blood pressure:
- narrowing of the arterioles of the systemic circulation;
- a shift of blood masses towards the heart due to narrowing of the veins - this leads to an expansion of the heart cavity, an increase in tension in the heart muscles and an increase in the volume of blood ejection;
- increased cardiac activity based on a signal from the sympathetic nervous system.
Clinical and pathophysiological changes in target organs
Arterial hypertension negatively affects the functionality of many organs and systems of the body:
- Heart. Excessive efforts of the heart muscle to push excess blood volume through narrowed vessels leads to hypertrophy and impaired diastolic function of the left ventricle. Against the background of constant oxygen starvation, the heart stops contracting fully, resulting in the development of chronic heart failure. Due to the fact that the vessels remain in a narrowed state for a long time, the muscle wall is replaced with connective tissue. This can cause atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries.
- Brain. High blood pressure is the main cause of non-traumatic intracranial hemorrhage, ischemic stroke, hypertensive encephalopathy, cognitive impairment and dementia.
- Kidneys. Impaired kidney function can be both a cause and a consequence of arterial hypertension. Renal failure as a result of constantly elevated blood pressure manifests itself in the form of pathological leakage of protein through the renal filter (microalbuminoria) and a decrease in the excretory function of the kidneys.
- Due to constant narrowing, the vessels of the fundus of the eye impede the blood supply to the tissues of the eye, and they experience oxygen starvation.
According to the severity of target organ damage, there are 3 stages of hypertension:
- at stage I, laboratory and instrumental studies do not show any changes in target organs;
- at stage II, the results of blood tests or studies of the heart and blood vessels using ECG, ultrasound and other diagnostic methods show the presence of at least one sign of damage. Among them: increased creatinine levels in the blood, left ventricular hypertrophy, the presence of cholesterol plaques, etc.;
- at stage III, clinical signs of target organ diseases appear: stroke, heart attack, angina pectoris, aortic aneurysm, heart or kidney failure, visual impairment and others.
Clinical picture
The course of arterial hypertension depends on the stage of the disease, the level of pressure increase and the target organs involved.
At the initial stage, the disease may be asymptomatic and detected only during routine blood pressure measurements.
As the pathology develops, complaints of headache, heaviness in the back of the head, tinnitus, rapid heartbeat, sleep problems, and decreased performance appear.
Photo: wavebreakmedia / freepik.com
Persistent increase in pressure above 140/90 mm Hg. Art. may cause:
- constant shortness of breath, even with minimal physical effort;
- pain in the heart area;
- increased sweating, numbness of the limbs;
- edema and severe puffiness of the face.
Spasm of the ocular vessels is manifested by small hemorrhages in the retina, loss of clarity of vision, and flickering of spots before the eyes.
Each of these symptoms requires immediate consultation with a cardiologist.
Make an appointment
Very often, patients find out about their arterial hypertension by accident, during a medical examination or simply out of curiosity by “measuring” their blood pressure while visiting a “hypertensive” patient... Often, nothing bothers such people, not even a headache. And this is the danger, because without feeling an increase in blood pressure, it is impossible to “spread a straw” - to protect yourself from terrible complications: stroke and myocardial infarction. Therefore, every self-respecting person who cares about his health, his performance and the well-being of loved ones should periodically measure his blood pressure. If you don’t yet know your blood pressure “numbers,” then the information in this article is for you. If you are “hypertensive,” then perhaps this information will help you live a full life.
Arterial hypertension is generally considered to be an increase in resting blood pressure in the brachial artery of 140/90 mmHg. Art. and higher. Blood pressure can also increase in healthy people during periods of intense physical activity or psycho-emotional stress (stress). Most often, such a compensatory increase in blood pressure is proportional to the increase in heart rate.
rules for measuring blood pressure should be followed to ensure that the result is as reliable as possible:
- Avoid drinking coffee and strong tea for 1 hour before measurement;
- do not smoke for 30 minutes before measurement;
- discontinue nasal and eye drops for this period;
- measure blood pressure at rest, after a 5-minute rest, while sitting; if the measurement procedure was preceded by significant physical or emotional stress, the rest period should be extended to 15–30 minutes;
- You can use an automatic or semi-automatic tonometer, with a cuff placed on the shoulder (devices with the cuff placed on the wrist show less reliable results than traditional ones);
- The tonometer needle must be at the zero mark before starting the measurement;
- the tonometer cuff should be at the level of the heart, approximately at the level of the 4th intercostal space, its lower edge 2 cm above the elbow;
The technique for measuring blood pressure is as follows: place the phonendoscope membrane in the elbow area, inflate the air in the cuff to 20 mm Hg. Art. above the vanishing point of the pulse, then reduce the pressure in the cuff using the valve by approximately 2 mmHg. Art. per second, note the pressure value at which the first sound appears - this corresponds to systolic (“upper”) blood pressure. The pressure value at which the sounds (pulse) disappear corresponds to diastolic (“lower”) blood pressure.
If, however, your blood pressure turns out to be elevated, you should consult a doctor. Often arterial hypertension accompanies certain diseases (kidneys, thyroid glands, endocrine organs, etc.), and is only their symptom. Treatment of the underlying disease, in this case, will help fight hypertension. However, most often arterial hypertension is hereditary in nature, and is therefore called hypertension. Ask your relatives if there were any “hypertensive patients” in the family, or cases of death from stroke or heart attack? Be sure to tell your doctor about this.
What symptoms should alert you to hypertension?
First of all, it is a headache, localized mainly in the occipital region, dizziness, decreased performance, “flickering spots” before the eyes. Long-term arterial hypertension adversely affects human organs, primarily the heart, brain and kidneys. If you have had arterial hypertension for many years and at high blood pressure levels you feel well, the risk of cardiovascular complications (stroke and myocardial infarction) is still unusually high!
A severe manifestation of arterial hypertension is a hypertensive crisis.
A hypertensive crisis is a sharp rise in blood pressure. There are two types of crisis. The first type is manifested by a sharp headache, redness of the skin, palpitations, trembling, chills; the second – nausea, vomiting, visual disturbances, convulsions, drowsiness. A hypertensive crisis is dangerous due to serious complications. At high blood pressure, ruptures of small arteries of the brain can occur (hemorrhagic cerebral stroke develops), or a sharp narrowing of the blood vessels of the heart (myocardial infarction develops) or brain (ischemic cerebral stroke develops). Therefore, at the first signs of a hypertensive crisis, it is necessary to take actions to lower blood pressure recommended by your attending physician and call an ambulance.
Provoking factors for a sharp increase in blood pressure, and sometimes a crisis, can be:
- neuropsychic or physical overload;
- weather changes, magnetic storms;
- heavy smoking;
- abrupt withdrawal of certain medications that lower blood pressure;
- large meals, especially salty ones at night;
- consumption of food and drinks containing substances that increase blood pressure (alcohol, coffee, chocolate, cheese, caviar).
There are several known predisposing factors that contribute to the development of arterial hypertension. Fighting them can help lower blood pressure and reduce the dose of medications, which you will agree is beneficial, given the prices of medications in our country. So what are these factors?
The first factor is excess salt consumption ! Even if it seems to you that you are consuming a small amount of salt, remove the salt shaker from the table, try not to add salt to your food, limit saltiness, and especially smoked foods. The amount of table salt consumed should not exceed 1 teaspoon per day. Just one reduction in salt in the diet can reduce mean arterial pressure by 10 mmHg. Art. To reduce the negative impact of salt on the body, it is necessary to increase the consumption of foods rich in potassium (dried apricots, raisins, baked potatoes in their jackets, tomatoes, legumes). In addition, it has a beneficial effect on the tone of the cardiovascular system.
The second factor is excess body weight ! Nowadays it is common to say that you need to love yourself for who you are. Let's rephrase: love yourself and maintain your health. The desire to lose weight should not be an end in itself. To find out if you are overweight, you need to calculate your body mass index using the formula: Weight (kg) : height (m)2 (evaluate your result using Table 2). Normalizing weight helps lower blood pressure, reduces the risk of cardiovascular complications (heart attack and stroke) and the risk of death. The basic principle: the calorie content of food must correspond to the body's energy expenditure. This means that the energy we receive from food should be exactly as much as we can spend. Consumption of foods rich in calories (sugar, chocolate, fat, etc.), especially if you are not engaged in physical labor, can lead to obesity, cholesterol deposition in the walls of blood vessels, and, as a consequence, to atherosclerosis of the arteries and hypertension. Keep in mind that for men aged 40–60 years, whose work does not involve significant physical activity, the number of calories consumed from food per day should not exceed 2000–2400 kcal, and for women, respectively, 1600–2000 kcal. What foods are the most high in calories? Fatty meats, especially fatty beef, offal, cocoa, chocolate, cakes, caviar, lard, baked goods, alcoholic beverages. Agree, you can do without these products. What is recommended to eat? Salt-free, preferably with bran, bread, soups cooked in vegetable broth, lean meats and fish (preferably steamed), about a kilogram of vegetables and fruits per day, dishes and side dishes from cereals and pasta, low-fat dairy products, vegetable oils, low-fat sausage, vinaigrettes, salads dressed with sour cream or olive oil. Agree, the choice of recommended products is quite wide. If you like sausage, choose low-fat varieties, if you like milk or cottage cheese, then choose low-fat products, limit white bread, butter (it is known that the ban on the use of butter in catering establishments in one of the Scandinavian countries helped reduce mortality from myocardial infarction, So let's learn from the experience of others!). The calorie content of some products is indicated in Table 3.
The third factor is physical inactivity ! Reduced physical activity leads to low fitness of the cardiovascular system, decreased resistance to stress, excess body weight, and, ultimately, increased blood pressure. You can start by walking; go up to your floor without an elevator if you live in an apartment building. Do morning hygienic exercises, health-improving physical education (walking, swimming, cycling, skiing), play outdoor games (volleyball, tennis). Physical activity has the ability to “thin” the blood and reduce the level of “sugar” in the blood, thus preventing the development of myocardial infarction, cerebral stroke and diabetes. If you decide to start physical training, be sure to consult with your doctor so that he can rule out some contraindications for you and prescribe an exercise regimen that is suitable for you in terms of intensity. There are some general rules for physical exercise: regularity, optimal intensity, stages. Indeed, exercise should be regular, 3 – 5 times a week. The intensity of the load should be controlled using the pulse. This means that initially during physical activity your heart rate should not exceed 50% of the maximum allowable for your age (i.e. 220 minus your age). Then you can gradually increase the intensity of the load until you reach 60%.
The fourth factor is smoking ! The harm of smoking is undeniable! No one will probably argue about the dangers of smoking. However, some facts may be unknown to you. Tobacco smoke contains carcinogens and nicotine. Nicotine has a thrombus-forming effect (promotes the formation of blood clots in the blood vessels of the heart and brain), atherosclerotic effect (promotes damage to the vascular wall and the deposition of cholesterol in it), and increases blood pressure. There are no “light” cigarettes! After all, you can’t talk about “light” poison? If you smoke, you need to quit this bad habit.
What should you be prepared for if you decide to quit smoking? Within 2 weeks to a month, the following withdrawal symptoms may occur: a strong desire to smoke, excitability, anxiety, difficulty concentrating, irritability, worsening mood, feelings of anger, depression, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, tremor (small tremors in the hands), sweating , improved appetite, weight gain, increased cough, feeling of chest congestion, muscle pain, dizziness. Currently, methods of substitution care for smokers are widely used. There are chewing gums and patches containing nicotine, and reflexology is used.
The fifth factor is stress ! It is known that patients with hypertension have low resistance to stress. This contributes to the development of the disease and threatens complications. To overcome stress, use a few tips below:
- Strive for the highest goal available and do not fight over trifles;
- Treat others as you would like them to treat you;
- Don't try to do everything at once;
- Don't forget about rest. Monotonous work tires, changing activities helps maintain strength and health;
- Appreciate the joy of true simplicity of life, avoiding everything superficial, ostentatious, deliberate. This will earn you the favor and love of others;
- Try to see the bright side of events and people;
- If you need to undertake a depressing and unpleasant task (conversation), do not put it off until “later”;
- Before you do anything in a conflict situation, weigh your strengths and the appropriateness of your actions;
- Try to see your “pluses”, even if you fail in any business (or conversation);
- Set real and important goals in any business. Reward yourself for achieving your goal.
Only a doctor can prescribe drug treatment Remember that at the initial stage of development of hypertension, you can lower blood pressure without medications, reducing the effect of those negative factors discussed above. But if it is impossible to do without medications, then medications are prescribed individually to each patient. It is likely that the medications your neighbor is taking are absolutely contraindicated for you. Therefore, do not self-medicate! Only a qualified doctor, using extensive specialized knowledge of chemistry and pharmacology, can prescribe you the medicine and in the dosage that will help you. It is important to know that you must take medications prescribed by your doctor constantly and in the dose that is recommended. The doctor can prescribe several medications, each, in this case, has its own point of application in the body (kidneys, heart and brain), protecting not only from surges in blood pressure, but also from complications of hypertension, prolonging your life. All drugs prescribed by a cardiologist must undergo numerous tests, their effect and safety have been established in international studies. The doctor always evaluates the ratio of the benefits of prescribing the drug to the likelihood of possible side effects.
Remember that your interest in achieving treatment results is an important factor that will help you and your attending physician cope with arterial hypertension!
Arterial hypertension in pregnant women
According to statistics, arterial hypertension is diagnosed in 5-8% of pregnant women. There are two types of hypertension:
- chronic - the woman had the disease before pregnancy and worsened after conception;
- gestational - formed in the second half of pregnancy.
The main reasons for persistent high blood pressure in pregnant women:
- weight gain;
- acceleration of metabolic processes;
- increased intra-abdominal pressure and blood volume;
- changes in hormonal levels.
Without timely treatment, hypertension during pregnancy can lead to serious complications: gestosis (preeclampsia, eclampsia), fetoplacental insufficiency, premature birth, placental abruption and others.
If arterial hypertension is detected, a pregnant woman should be under constant medical supervision.
Hypertensive crisis
A sharp sudden rise in blood pressure is one of the most common manifestations of arterial hypertension, this is a hypertensive crisis.
This condition can occur under the influence of stress, sudden changes in climate or weather conditions, or physical stress.
A hypertensive crisis is accompanied by nervous overexcitation or, conversely, lethargy, severe headache, nausea, and blurred vision.
The result of a crisis can be an acute cerebrovascular accident, myocardial infarction or other acute vascular disorder.
Physiological causes of low blood pressure
For an adult, blood pressure less than 95/65 mm is considered excessively low. But there are categories of people who feel comfortable with such indicators, and when the numbers increase to the ideal 120/80, they experience obvious signs of hypertension: headaches, arrhythmia and severe stress. At first glance, this is a paradox, but doctors recognize the existence of individual physiological norms that differ from the average.
- Slightly reduced blood pressure, for example, is typical for residents of high mountain regions, professional runners, and young women of fragile asthenic build. It is called compensatory. Usually this condition is not causing concern and does not lead to any health consequences.
- In some cases, vascular tone indicators decrease briefly with sudden changes in body position. These are orthostatic changes, also related to the norm. May be accompanied by momentary dizziness.
- Postprandial hypotension occurs after overeating. This is also a normal reaction of the body sending a large volume of blood to the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, the appearance of weakness or drowsiness is possible.
Physiological fluctuations in blood pressure are typical for people during air travel, sudden deterioration of weather, and exposure to various radiations. Indicators return to normal when the situation stabilizes.
Treatment of high blood pressure
Source: World Cancer Research Fund
Folk remedies
At the moment, there is no evidence of the effectiveness of folk remedies for the treatment of arterial hypertension. Refusing to visit a doctor with symptoms of hypertension and hoping to stabilize the condition with the help of folk remedies can lead to irreversible consequences and the development of serious complications.
Any folk remedy can only be an addition to the main treatment and must be approved by a cardiologist.
Drug treatment
Photo: lazy_bear / freepik.com
The drug treatment regimen is determined by a cardiologist after a comprehensive examination and determination of the causes of arterial hypertension. The choice of technique is made taking into account the gender, age of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases and the goals set.
The drug complex may include diuretics, sedatives, drugs that suppress vasomotor activity and some others, depending on the condition of the target organs.