For certain diseases, special exercises are an important treatment measure. Cardiac arrhythmia is no exception. Despite the fact that with this pathology a number of loads are contraindicated, proper gymnastics for cardiac arrhythmia can significantly alleviate the patient’s condition. Let's consider what it is and what it may include.
Exercises for cardiac arrhythmia: benefits
Anaerobic exercise helps maintain muscle tone and restores normal functioning of the heart muscle. Breathing exercises for cardiac arrhythmia are the basis for the treatment and prevention of attacks. It helps patients restore their breathing rhythm and normalize blood circulation.
For heart pathologies, exercises are prescribed to normalize the functioning of the entire cardiovascular system. However, in case of arrhythmia, the complex must be selected so as to prevent overvoltage. Exercises are selected taking into account all the characteristics of the disease and are done under the supervision of a specialist. It is important to strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations and not violate the sequence of exercises.
Gymnastics, which is indicated for arrhythmia, does not involve high loads. It helps improve blood circulation and heart rate, charges the body with vigor and energy.
Breathing exercises for cardiac arrhythmia
Breathing exercises are prescribed to patients to restore oxygen supply to the brain, normalize heart rate and prevent hypoxia.
The exercises are performed every day - in the morning before breakfast and at night.
The complex includes the following exercises:
- Warm up. Stand up and take a few small, quick breaths in and out. And at the same time, begin to slowly walk in place, taking each step as you inhale.
- The exercise is performed in a standing position. Lower your hands down, while inhaling sharply, quickly clench your palms into fists as far as you can, and while exhaling, unclench them. Make six turns with breaks of 25 seconds.
- Place your arms along your body, spread your legs shoulder-width apart. Exhale slowly while leaning forward and stretching your arms. As you exhale, straighten up and lower your arms. Do no more than 13 repetitions, then rest.
- Stand up, clench your two hands into a fist, place them on your waist. Unclench your fists and lower your arms while inhaling sharply. As you exhale, return to the starting position.
The number of breaths needs to be increased every day.
If you feel dizzy, stop exercising. You cannot overload the body. Start with a small number of repetitions and gradually increase it. Breathing exercises can be performed not only for arrhythmia, but also for prevention. They have a beneficial effect on the functioning of all organs and systems, helping to saturate them with oxygen.
Need for movement
This is how a person is designed - to be healthy, he must be physically active. Roughly, you can compare the body to a car - when buying a car, it is better to take an old one, but which drives regularly, than a new one, which has stood in the yard of the house for several years and has never started. Therefore, even if a person is sick, even if he has difficulty getting out of bed, he needs movement. The only question is in doses - the patient needs to recover and return to his former life, and not harm himself with excessive zeal.
Not only the functioning of the body depends on movement, but also mood, the ability to work mentally, movement also distracts from difficult thoughts about illness, thus the future life comes to the fore, and not thoughts about sad prospects. People with a diseased heart and blood vessels need aerobic exercises, that is, those that force them to move with free breathing, without static stress and temporary stoppage of lung function.
Loads should be every day and gradually increase. First, you can do exercises in a sitting position, walk slowly, then complicate the set of exercises. There is no point in rushing - with daily effort, a person can feel completely healthy after many months, and possibly several years. To determine the condition of the heart, a cardiologist conducts special tests, diagnostic studies with different types of loads and determines the pace of exercise. In rare cases, exercise is not allowed at all until the cardiac condition normalizes.
Buteyko gymnastics for cardiac arrhythmia
Dr. Buteyko’s gymnastics for arrhythmia are popular. It is based on training in proper breathing. Initially, the method was used to treat bronchial asthma, but over time it was discovered that it helps to effectively treat other diseases.
The essence of the exercises is to relax the diaphragm and reduce the depth of breathing. The complex includes the following exercises:
- Take a small breath through your nose so that your stomach and chest remain motionless. Hold your breath for five seconds, exhale smoothly and continuously. The exhalation should last for 4-5 seconds. There is a pause for the same amount of time. The exercise is performed ten times.
- Combining the diaphragm and chest breathing. Relax, inhale deeply (for 7.5 seconds), first filling the diaphragm with air, and then the chest. Then exhale slowly, starting with your lungs. Pause for five seconds, then repeat the exercise 10 times.
- During pauses, perform a relaxing nose massage.
- Perform 10 full breaths, first on one side of the nose, then on the other.
- After taking a full breath and drawing in your stomach, hold your breath for 7.5 seconds, then rest. Repeat the exercise 10 times.
- Take 12 breaths. The inhalation should last about two seconds. The exercise is performed for a minute.
- Then very rare level breathing is done.
These exercises help strengthen the cardiovascular system and prevent new heart diseases. But before starting the technique, you need to consult a doctor, since it has contraindications.
How to stop an attack of tachycardia
Special exercises and techniques can help stop an attack of tachycardia at its first signs.
- Take a deep breath and hold your breath, while trying to push the air down.
- Breathe deeply for 5-10 minutes: take a deep breath and exhale slowly (3 times longer).
- Press your fingers firmly on your eyeballs (until it hurts) for 10 seconds, then release. Continue this action for several minutes.
- Fill a basin with ice water and immerse your face in it for a few seconds. You can simply wash your face with cold water. The temperature change should cause your heart rate to drop.
- Sometimes a strong cough or artificially induced vomiting helps stop the attack.
If the condition does not improve and the pulse exceeds 120 beats per minute, immediately seek medical help.
Physical exercises for cardiac arrhythmia
Physical activity is an important treatment for arrhythmia. But it must be correct and moderate. In addition, regularity is important. In addition to special exercise therapy for arrhythmia, the following sports may be useful as prescribed by a doctor:
- Swimming. Helps maintain muscle tone.
- Walking in place.
- Walking outside.
- Slow running.
- A ride on the bicycle. Helps to engage a large number of muscle groups and restore the correct breathing rhythm.
In the first weeks after discharge from the hospital, the pace of simple walking should be no more than 100 steps per minute. To monitor this, you can use a special pedometer. Over time, the number of steps increases to 150 per minute.
You can start running after 2-3 months. At first, the distance should be no more than 300 meters. After a week it can be increased by another 100 meters. The pace should be slow.
Exercising for arrhythmia: exercise
Exercise for arrhythmia also plays an important role. Exercises are performed in the morning and evening. They help maintain normal functioning of the cardiovascular system and strengthen blood vessels, which is especially important for elderly patients.
Gymnastics for the heart for arrhythmia may include the following exercises:
- Pull-ups on toes. In this case, your feet should be positioned shoulder width apart. Control your breathing while doing this. The number of approaches is from 12, with breaks of 7-10 seconds between them.
- Arm curls. Performed while inhaling and exhaling, up to 14 times per approach. Breaks should be no more than five seconds.
- Turns. Place your feet shoulder-width apart and place your hands on your waist. It is done, like other exercises, while inhaling and exhaling. When turning, you can spread your arms to the sides.
For arrhythmia, squats can be useful, but it is important to do them extremely carefully, no more than ten times with a break of a minute. Squats on one leg are prohibited. Charging is completed in the usual step on the spot for 2-3 minutes.
LLC "MGBS"
Breathing and contractions of the heart muscle represent a single mechanism for maintaining the vital functions of the body. Therefore, by changing the duration of inhalations and exhalations, as well as pauses between them, you can train your heart. Breathing exercises do not require endurance, money or time; it is accessible to everyone and only requires systematic implementation.
The benefits of breathing exercises for the heart
If you observe a person who is under stress or experiencing an attack of heart pain, then rapid and shallow breathing will be noticed in everyone. Since our body works on the principle of feedback, slowing down and deepening breathing can have a healing effect on many organs. Even simple fixation on an even rhythm and awareness of the duration of the breathing cycle is used in meditative practices.
The positive effect of breathing exercises is manifested in this way:
- the blood and muscle fibers of the heart are saturated with oxygen;
- with deep breathing, the cavities of the heart are better filled with blood and are released from it during contraction;
- when holding your breath, an artificial oxygen deficiency is created, which dilates the cerebral and coronary vessels;
- the rhythm of contractions is normalized;
- the balance between the processes of excitation and inhibition in the cerebral cortex is restored.
Breathing exercises are effective for preventing congestion in the lungs. It is recommended in the early recovery period after a heart attack and cardiac surgery. Sometimes this is the only type of activity available to the patient.
We recommend reading the article about exercises for the heart. From it you will learn about physical activity and basic rules for training, useful exercises for the heart muscle.
And here is more information about exercises for arrhythmia.
Useful exercises to strengthen the myocardium
In diseases of the cardiovascular system, it is the loads that can increase the resistance of the myocardium to oxygen starvation that bring benefits. These include walking, running, swimming, dancing. Breathing exercises have a similar effect on the heart muscle. Methods for carrying it out may differ, but the most important rule is that the exercises must be performed at an individual, comfortable level.
First aid for arrhythmia
The method of restoring heart rhythm using breathing is based on the fact that a measured rhythm of inhalation and exhalation, which a person can control, normalizes the rhythm of contractions of the heart muscle. Therefore, any option with counting the duration of respiratory movements helps with arrhythmia.
To do this, you can inhale for 2 - 3 counts and exhale for 4 - 6 counts. In this case, you need to be in a sitting position with a straight back. It is recommended to gradually stretch your inhalations and exhalations, focusing on your sensations.
After mastering this exercise, the following type of pulmonary exercises is recommended to prevent attacks:
- Left hand behind back.
- The right hand is located near the face.
- Close your right nostril with your right thumb.
- Inhale through the left nostril.
- Close the left nostril with your ring finger and exhale through the right nostril.
After 8 - 10 breathing cycles, you need to change hands. The duration of the first lesson should not exceed 2 - 3 minutes, then you can slowly increase it. The duration of inhalations and exhalations is determined by comfortable sensations.
For cardiac aneurysm
The use of any load for training, even breathing, with an aortic or cerebral aneurysm, is possible only after consulting a doctor, since stress can provoke intense internal bleeding and death.
If there is a small and stable aneurysm or an operation has been performed to remove this vascular defect, then the doctor may allow you to do gymnastics, including breathing. In this case, any low-intensity and slow movements with simultaneous inhalation and exhalation are indicated:
- spread your arms to the sides - inhale, hug yourself by the shoulders with them - exhale;
- with the pelvis stationary, turn the chest to the right - inhale, return to the starting position - exhale;
- in a position lying on your back, inhale with your stomach for 2 counts, raising the abdominal wall; for 4 counts, exhale, drawing in your stomach.
Watch the video about doing exercises for the heart and their benefits:
After operation
From the second day, with an uncomplicated postoperative course, patients begin breathing exercises under the guidance of a doctor to prevent congestion in the lungs. To do this, it is recommended to spend 5-6 times a day for 5 minutes:
- exhale through closed lips (movements like when blowing out a candle);
- inflating balloons or rubber toys;
- exhaling air through a straw into a glass of water.
After 5-6 days it is allowed to sit on the bed and walk within the ward. At this time, breathing exercises are carried out in an expanded mode. Recommended:
- deep belly breathing with accentuated exhalation,
- smooth stretching of the exhalation length,
- inhale for 3 counts and exhale, and then 2 more short exhalations.
With tachycardia
To slow down your heart rate you need maximum relaxation. This can be achieved by changing the ratio of the duration of inhalation and exhalation, as well as by pausing after exhalation. In the first lessons, the ratio of these phases is 3:5:2.
Every day they are increased by 1 count, if discomfort appears, they are stopped until a stable result is obtained, and then you can continue to stretch each breathing movement. If at first it is difficult to breathe like this, then after 3-4 cycles they return to normal breathing; after its restoration, it is recommended to extend the lesson.
Tachycardia is an indication for breathing exercises
To improve blood vessels
To normalize vascular tone and increase performance, the following exercise is performed: after a normal (non-forced) inhalation, you need to exhale sharply and briefly, while drawing in your stomach as you exhale. This is followed by a passive inhalation and a sharp exhalation.
Do 10 cycles of the right nostril with the left one closed, change sides, also take 10 inhalations and exhalations, then with both nostrils 15 times.
General recommendations for performing breathing exercises
Such classes do not require special equipment or a special room, but this type of training also has rules:
- the room should be well ventilated, it is better to study near an open window;
- drafts must be avoided;
- the optimal option is nature, park, river bank;
- The recommended time is in the morning; if classes are held in the afternoon, at least 3 hours must pass;
- the clothes chosen are spacious, natural, without tight belts and collars;
- Most often they practice while sitting on a chair or on the floor with their legs crossed;
- the head does not fall back, the back is straight;
- the whole body is sure to relax.
We recommend reading the article about physical activity for arrhythmia. From it you will learn about whether it is possible to play sports if you have an illness, acceptable options for physical activity, and the reasons for the development of arrhythmia after playing sports.
And here is more information about playing sports with bradycardia.
Breathing exercises can be used to restore normal functioning of the cardiovascular system. It is prescribed at any age and even with minimal training; it is recommended for bedridden patients and after heart surgery. It activates metabolic processes and trains the body's adaptive capabilities. The basic rules are comfortable performance and regularity of classes.
Doing exercises for the heart is useful both for healthy people and for those with organ disease. This can be minor physical activity, breathing exercises, to improve the health of the main muscle. It is advisable to conduct training daily.
In some cases, exercises for arrhythmias can help control rhythm disturbances. This can be physical exercise, breathing, Nordic walking and running. Complete treatment of arrhythmia without a set of exercises is extremely rarely carried out. What complex should be done?
You need to train your heart. However, not all physical activity for arrhythmia is permissible. What are the permissible loads for sinus and atrial fibrillation? Is it possible to play sports at all? If arrhythmia is detected in children, is sport taboo? Why does arrhythmia occur after exercise?
Options for how to strengthen the heart depend mainly on its condition. They also affect blood vessels and nerves. For example, in old age, exercise will support the heart muscle. After a heart attack, folk remedies can be prescribed for arrhythmia.
Physical inactivity develops in adults and children. The concept includes quite broad problems. If cardiovascular failure has developed, then returning to normal life is very problematic; the consequences in some cases are complete atrophy of organs. It is necessary to change your lifestyle.
For most patients, cardio training for the heart is simply necessary. Any cardiologist will confirm their benefits, and most strengthening exercises can be done at home. If your heart hurts after exercise, it means something is not being done correctly. Caution is required after surgery.
Respiratory arrhythmia in children, adolescents and adults is often detected on an ECG. The reasons may lie in an unhealthy lifestyle or excessive stress. Symptoms include breathing problems, cold extremities and others. Sinus readings on the ECG influence the choice of treatment.
Exercise therapy begins after a heart attack from the first days. The set of exercises gradually increases. To do this, doctors determine the degree of exercise therapy for which the patient is ready after myocardial infarction and stenting, if any.
If a cardiac aneurysm is detected, surgery may be the only chance for salvation, only with it the prognosis improves. It is generally possible to live without surgery, but only if the aneurysm, for example, of the left ventricle, is very small.
Exercise therapy for arrhythmia
Treatment of arrhythmia with physical exercises involves a whole complex of special gymnasts. The doctor must create an individual program based on the severity and extent of the disease, the nature of its course, and the recovery time that the body needs. The load on the body must be strictly dosed.
The exercises differ in the following ways:
- Anatomically. The complex can be developed for individual muscle groups.
- By independence. Exercises can be passive, prescribed for disorders of motor activity, as well as active, which the patient can perform independently.
To achieve results, exercises are performed to strengthen certain muscle groups. Over time, muscle tissue adapts to physical activity, and disturbances caused by arrhythmia are gradually corrected.
Exercise therapy is also prescribed for atrial fibrillation. However, you should not perform exercises on your own, as they may worsen the condition. Gymnastics should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Therapeutic exercise helps to increase the effectiveness of drug therapy many times over, restore normal motor activity, heart rate, and blood circulation. However, it is important that the exercises are appropriate to the patient's medical history.
What is atrial fibrillation
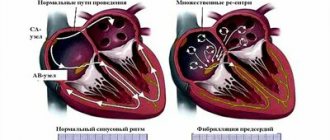
Atrial fibrillation is a heart disorder in which the electrical impulse is distributed unevenly throughout the heart. Because of this, the heart chambers work uncoordinatedly: instead of contractions, twitching or “flickering” occurs in the atrium, and the ventricles also contract in the wrong rhythm.
The picture on the left shows a normal heart rhythm, sinus. The electrical signal is generated in the sinus node and spreads evenly through the conduction system of the heart. The right shows how electrical impulses are generated randomly in different places and cause atrial fibrillation.
There are 3 forms of atrial fibrillation:
Paroxysmal or paroxysmal - manifests itself in short attacks that go away on their own within a few minutes or hours. Some people may have only one attack in their entire life, while others may have them several times a day. In this case, you need to consult a doctor to rule out pathology and other forms of the disease.
Persistent or temporarily stable - attacks can last several days, weeks or months. Characterized by the inability to restore heart rhythm without drug treatment and therapy.
Chronic or permanent - occurs, as a rule, with prolonged atrial fibrillation. In this case, the heart rhythm is not restored with the help of treatment, but learning to maintain normal well-being of the body is a feasible and important task.
If an attack lasts longer than 48 hours, blood begins to stagnate in the upper parts of the heart: clots form and the risk of complications increases - blood clots and, subsequently, stroke. Therefore, seeking cardiac care for any manifestation of arrhythmia is a vital necessity.
What exercises are prohibited for arrhythmia?
Not all activity will be beneficial for arrhythmia. For example, strength exercises with weights are prohibited. They can have a negative effect on the heart muscle.
Isometric exercises are also not recommended. With intense work of muscle tissue, blood circulation improves, but there may be a lack of oxygen in the heart area.
The use of barbells, dumbbells, expanders, and strength training equipment is prohibited.
For arrhythmia, exercises that involve holding your breath and staying in one position for a long time are not recommended. It is recommended to refrain from yoga and exercises to pump up the abdominal muscles.
Strength training involves sudden movements during exercise, which can cause deterioration in well-being, dizziness, and heart pain. Any load for arrhythmia should be moderate and dosed.
Arrhythmia: symptoms, causes
Arrhythmia as a disease manifests itself in the deviation of the heartbeat rhythm from the norm to a greater extent (tachycardia) or to a smaller direction (bradycardia).
ATTENTION!
This disease can become one of the first signs of severe pathologies, which will further develop and worsen. In addition, arrhythmia can lead to problems and disruptions in the functioning of the heart, up to its temporary stop.
The main symptoms of arrhythmia are:
- constant weakness and fatigue;
- headaches and dizziness;
- attacks of pain, pressure in the chest area;
- feeling of strong heartbeat;
- sudden acceleration or deceleration of heart rate (attacks);
- the appearance of shortness of breath and increased breathing;
- fainting and unconscious states.
To begin treating arrhythmia, you should find out the causes of the pathology. These include:
- frequent stressful and nervous situations;
- prolonged or excessive use of medications and traditional medicine;
- severe intoxication (poisoning) of the body;
- presence of heart disease (in particular, coronary disease and heart failure);
- diabetes mellitus of any degree;
- abuse of smoking, alcohol, caffeine;
- problems and pathologies of the circulatory system;
- history of traumatic brain injury.
REFERENCE!
Most often, arrhythmia manifests itself during a stressful state of the body, which can be noticed by the acceleration (in most cases) or slowdown of the heartbeat.
If symptoms of the disease occur, you should undergo an examination and begin treatment. First of all, you need to do special physical exercises.
Contraindications
In some cases, physical exercises and breathing exercises are contraindicated for cardiac arrhythmia. These include the following:
- Excessive disturbance of heart rhythm. This often occurs after a heart attack. Tachycardia may occur, and atrial fibrillation may become chronic.
- Regular attacks of angina, which mainly occur during physical activity.
- Insufficient amount of blood passing through the vessels.
- Impaired blood circulation due to congenital and acquired heart defects.
- Second or third degree of heart failure.
- Certain diseases of the kidneys and liver, thyroid gland.
- Hypertension.
- Inflammation of the walls of blood vessels of the lower extremities, accompanied by thrombophlebitis.
- Cardiac or aortic aneurysm if there is a threat of rupture.
There are quite a few contraindications to gymnastics, which is why you should not perform it without a doctor’s prescription. The specialist must take into account all the points and prescribe the most suitable complex.
Physical activity is good for the whole body. Proper muscle function helps restore blood circulation, activate brain activity, and normalize heart function. Loads need to be increased gradually. And, of course, remember that it is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
We suggest watching a video with exercises for arrhythmia.
conclusions
Adequate physical activity is indicated for almost all patients with rhythm disturbances during the absence of an attack. The main thing is to select it together with a cardiologist during functional stress tests. The required level of energy expenditure is calculated using the formula depending on the maximum heart rate: the person’s age must be subtracted from two hundred and twenty. 75% of this value is a frequency that cannot be exceeded during training. A competent approach to physical education significantly improves the patient’s quality of life.