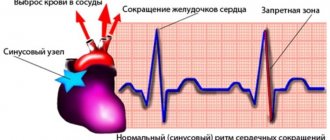
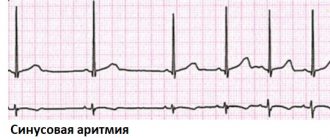
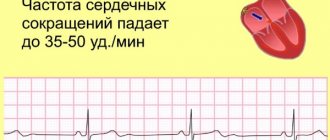
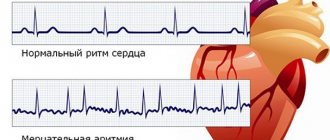
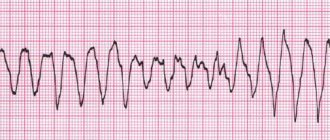
Types of arrhythmia in children
Taking into account the characteristics of heart rhythm deviations, childhood arrhythmia is divided into four key types:
- Tachycardia. Accompanied by increased rhythm. The heart rate normally increases with physical activity, elevated temperature, and stress. But if such a condition does not depend on external factors, it is considered a pathology. Tachycardia indicates a malfunction of the heart muscle and leads to its rapid wear.
- Bradycardia. Characterized by a rhythm that is too slow. The contraction frequency decreases to 30-50 beats per minute. Pathological bradycardia may not interfere with circulation and cause no symptoms. But if the rhythm drops below 40 beats per minute, the baby experiences fainting, chronic weakness and dizziness.
- Extrasystole. It is distinguished by the presence of contractions outside the rhythm. It occurs when an extraordinary impulse appears between normal heart contractions - an extrasystole. Extrasystoles can be multiple or single, appear according to a certain rhythm or randomly. Rare single extrasystoles are not dangerous and do not require treatment. However, with frequent group extraordinary impulses, diagnosis and treatment of the pathology is necessary.
- Atrial fibrillation . Random rapid contraction of different parts of the atria, which causes an acceleration of the pulse. This type of arrhythmia occurs most often in childhood. The pathology is quite dangerous and, if left untreated, causes heart failure.
Pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation
The possibility of the existence of three main mechanisms of atrial fibrillation has been experimentally and clinically proven: circulation (re-entry) of a wave of electrical excitation throughout the atrial myocardium (Th. Lewis, 1921), frequent formation of impulses in several ectopic atrial foci and early or delayed depolarization emanating from the main potential actions (Engelman, 1884; D. Scherf, 1948) [9]. The first of the three listed mechanisms is the most well studied.
There are a large number of experimental observations showing that the circulation of excitation around anatomical openings, pathological obstacles, and scar tissue can cause atrial fibrillation. With fibrosis or stretching of the atrial tissue, electrical fragmentation of areas of the atrial myocardium occurs, which contributes to the formation of a stable circulation of pathological excitation [10]. M. Janse suggests that atrial overstretch that occurs during atrial fibrillation, in turn, leads to a change in the state of membrane potassium channels involved in the repolarization process, which increases the duration of the refractory period and the action potential. Therefore, long-standing atrial fibrillation usually recurs after restoration of sinus rhythm. In the implementation of a specific electrophysiological mechanism of abnormal excitation of the atria during atrial fibrillation, a certain role belongs to changes in the neurovegetative regulation of heart rhythm. The likelihood of atrial fibrillation increases linearly with increasing frequency of vagal stimulation of the heart [11]. In these cases, acetylcholine blocks slow calcium channels [12], which leads to a decrease in the effective refractory period and an increase in conduction velocity through the atrial myocardium. In an animal experiment, stimulation of the vagus caused an increase in the flicker frequency.
Recently, attention has been paid to the theory of early apoptosis (programmed cell death) of atrial tissue cells. Apoptosis is a physiological cell death when genetically incompetent and old cells are quickly removed without subsequent inflammation, which ultimately contributes to the preservation of normal tissue structure. Early death of cardiomyocytes leads to the occurrence of arrhythmogenic disorders [13]. Hormonal imbalance plays a certain role in the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation. The most studied effect of thyroid hormones on the myocardium is the uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation and tissue respiration. As a result, the content of ATP and other energy substrates decreases, the number of adrenergic receptors and their sensitivity increases, the concentration of potassium ions decreases and the content of sodium ions increases, which leads to a decrease in the threshold excitability of the myocardium in various parts of the atrial tissue [14]. Of great importance in the occurrence and maintenance of atrial fibrillation is the disruption of the functional activity of the sinus node (sick sinus syndrome) and the activation of additional pathways (Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome) [9].
Symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia in a child
The symptoms of heart rhythm disturbances have different specifics and differ in children of different age groups.
Arrhythmia in a newborn baby can manifest itself through:
- pale, bluish skin;
- baby anxiety for no apparent reason;
- refusal to eat, breastfeed, or bottle;
- shortness of breath;
- slight or no weight gain;
- problems sleeping, crying.
Arrhythmia in a child aged 6 years and older very often has no symptoms. In such cases, pathology is detected during a routine medical examination. Only sometimes do children exhibit characteristic symptoms of the disease:
- excessive fatigue;
- poor body response to physical activity;
- causeless fainting, dizziness;
- pale skin;
- apathy or increased excitability;
- poor appetite;
- pain in the heart area.
When should you see a doctor?
Any diseases in the heart area are dealt with by a pediatric cardiologist. He should be visited as soon as parents notice something in their baby’s condition that worries them, for example, blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle, frequent fainting and other symptoms. You should not hesitate to consult if the child complains of burning, pain or pressure in the sternum.
It is important to seek help right at the very beginning, because any illness is easier and faster to cure in the initial stages of its development.
Much depends on the doctor’s level of qualification: he must specialize in children, have extensive work experience and have progressive views on treatment methods, that is, be aware of all the discoveries in the world of cardiology and pediatrics.
These are the specialists who work in the pediatric department of JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic), located in the center of Moscow at 2nd Tverskoy Lane, 10, a five-minute walk from the Mayakovskaya metro station. In the immediate vicinity there are also metro stations “Tverskaya”, “Novoslobodskaya”, “Chekhovskaya”.
You can register your child for a consultation with a specialist by calling +7 or using the feedback form. Here you can find out information of interest about the cost of admission and the level of qualifications of all specialists.
Causes of arrhythmia in children
Children's nervous, autonomic and immune systems have not yet entered a stable stage of maturity. It takes years before the sinus node, which is responsible for normal rhythm, begins to generate the correct electrical impulses for the rhythmic contraction of the heart chambers. Only in adolescents the heart begins to beat at the same rhythm as in adults - 60-80 beats per minute.
The most common causes of cardiac arrhythmia in children are:
- heart defects and anomalies (congenital or acquired);
- inflammatory cardiopathologies (myocarditis, endocarditis, etc.);
- severe course of infectious or viral diseases and their complications (angina, hepatitis, diphtheria, intoxication, pneumonia, typhoid fever);
- arterial hypertension;
- failures of nervous regulation of rhythm (vegetative-vascular dystonia);
- mitral valve prolapse;
- pathologies of the central nervous system;
- malignant diseases of the brain;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- anemia;
- hereditary diseases;
- difficult course of labor, prematurity;
- rapid development of the child’s body, in which the cardiovascular system does not keep pace with the growth of bone and muscle structures Source: Skudarnov E.V., Baranova N.V., Antropov D.A., Dorokhov N.A. Structure and etiological factors of cardiac arrhythmias in newborns Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics No. 3, 2021, p. 183.
Etiology
Sinus arrhythmia occurs in healthy people and is considered normal if it is not accompanied by clinical manifestations. A child may experience this after overeating or during sleep; as a consequence of physical overexertion - in athletes after training.
Pathological reasons:
- Cardiac – trophic disorders and inflammation affecting the pacemaker (myocardial dystrophy, congenital heart anomalies, myocarditis of various etiologies, circulatory failure).
- Extracardiac – bronchopulmonary and endocrine pathologies, negative effects of certain medications, micronutrient deficiency.
- Combined – if cardiac causes are combined with other factors.
I propose to discuss the causes of arrhythmia in adolescents. Child endocrinologists figuratively call metamorphoses of the body during puberty a “hormonal explosion,” and psychologists and neurologists working with teenagers note the lability of their nervous system.
In this age period, arrhythmia is detected most often:
- It is in adolescents that autonomic dysfunctions are usually diagnosed, accompanied by disruption of the interaction of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems;
- we must not forget about coronary disease, which, unfortunately, has become “younger” over the past decades;
- wanting to appear older, a teenager is easily influenced by his peers, he may secretly try alcoholic drinks or drugs, or pick up a cigarette;
- young people tend to neglect sleep and rest, and sit for long hours at the computer.
Even if your child has no complaints, try to find time to have a confidential conversation about committing to a healthy lifestyle. As surprising as it may sound, taking care of our body is ingrained in us in childhood and is “inherited” from our parents.
How dangerous is the disease?
In most cases, cardiac arrhythmia in a child has a favorable prognosis and is benign. However, for any form of the disease, it is extremely important to monitor the baby’s health, regularly conduct preventive examinations and, according to the doctor’s decision, undergo treatment.
In the absence of competent and timely treatment, the pathology can cause serious complications in the future. The long course of the disease has a detrimental effect on the functioning of the heart and leads to dangerous consequences.
Arrhythmia can cause heart failure and cardiomyopathy, which carry the risk of early disability and even death. Increases the risk of developing arterial hypotension and myocardial ischemia. A prolonged attack of tachycardia can provoke cardiogenic shock or acute heart failure with pulmonary edema.
In addition, the long-term chronic course of the pathology significantly worsens the child’s well-being. The quality of life is gradually decreasing, and constant fatigue and apathy only increase over the years Source: Dubovaya A.V. Modern approaches to assessing the quality of life of children with arrhythmias Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics, 2016; 61:5, pp. 75-81.
Diagnostics
Doctors identify several acute time periods when the possibility of developing pathology becomes especially acute. Often, arrhythmia in a child develops in infancy, at 4-5 years, at 7-8 years, at 11-12 years and in adolescence. Growth spurts occur during these age intervals. Therefore, carrying out preventive diagnostics and cardiac examination at this time is of particular importance, even if the symptoms of the disease do not manifest themselves.
Only a pediatric cardiologist or arrhythmologist can identify the deviation and establish a diagnosis. Initially, you should consult with a specialized specialist who:
- will study the medical history of a small patient;
- will conduct a full examination, palpation, percussion and auscultation;
- will prescribe the necessary laboratory and instrumental diagnostics.
To identify the disease and record the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes:
- Electrocardiography (ECG) is a method of studying the heart that allows you to record the electrical activity of the heart. With its help, the doctor identifies rhythm deviations and determines the frequency of muscle contraction.
- Daily ECG monitoring is a study of cardiac activity that takes place throughout the day. Compared to ECG, this method is more accurate. Allows you to record the dynamics of the rhythm during different periods of the child’s life: activity and sleep.
- Stress tests – analysis of heart activity during physical activity of varying intensity. Prescribed for suspected cardiac arrhythmia in a child 3 years of age or older.
The diagnostic results allow the cardiologist to diagnose the disease. Additionally, the doctor can prescribe procedures that will help identify the causes of the pathology:
- Echocardiography (EchoCG) is the study of the heart using ultrasound. With its help, you can detect the organic prerequisites for the development of arrhythmia: defects, neoplasms, etc.
- Electroencephalography (EEG) is the study of the electrical activity of the brain. It is prescribed if there is a suspicion of a connection between the pathology and abnormalities in the functioning of the brain.
- Radiography is a study using x-rays. Allows you to detect the preconditions for arrhythmia that are not directly related to the work of the heart: diseases of large vessels, pathologies of the spine, etc.
How should the doctor and parents act?
Parents often came to me with complaints that the pediatrician questioned them for a very long time, prescribed numerous examinations, and then said that there was no need to treat sinus arrhythmia in a child or teenager. How so? After all, the child has a heart condition. I absolutely agree with the attending physician on this issue.
Survey plan
Sinus arrhythmia does not require special therapy. In some cases, we focus on eliminating its cause - we treat the underlying disease. But this pathology sometimes “masks” other disorders. It's important not to miss them.
The examination plan for a child with sinus arrhythmia includes:
- A thorough collection by the doctor of anamnesis of life and illness. Don't be surprised if some of the specialist's questions seem strange to you. It is necessary to clarify genetic predisposition, risk factors, and the presence of concomitant pathological processes.
- Electrocardiographic examination. It is important to carry it out at least three times - when the patient is lying down, standing, and then after physical activity.
- Stress tests. These include bicycle ergometry and treadmill. Thanks to them, it is possible to determine how the work of the heart changes during physical activity, as well as to identify hidden rhythm disturbances.
- Medicinal electrocardiographic tests. The action of certain drugs (in pediatric practice, atropine or a combination of potassium chloride and Obzidan is usually used) causes a decrease in the number of heart contractions, which confirms autonomic dysfunction.
- Holter monitoring. Your son or daughter lives with a portable device that records an ECG for at least a day. The examination will allow you to determine the circadian index - the ratio of the average number of heart beats during the day to the same indicator at night. From the age of two, 1.24 – 1.45 are considered normal values. If the index is less than 1.2, this indicates a decrease in vagosympathetic regulation, and if it increases more than 1.5, this indicates an increase in the tone of the vagus nerve. This coefficient is important for the differential diagnosis of sinus arrhythmia.
- Electroencephalography allows you to link changes in the number of heart beats with the bioelectrical activity of the brain.
- Echocardiographic examination diagnoses structural causes of sinus arrhythmia.
Perhaps the doctor will refer the patient for a biochemical blood test, echocardiography, radiography of the cervical spine, or rheoencephalography.
Sometimes viruses are a provoking factor in the development of sinus arrhythmia. Scientists have proven that herpes activates myocardial degeneration. Testing to detect the herpes virus may be required. Our main task is to clarify the cause of sinus arrhythmia and exclude other changes in heart rhythm.
Treatment of cardiac arrhythmia in children
After completing the examination, the doctor examines the results of diagnostic procedures and makes a diagnosis. Only after this, the specialist develops an individual treatment plan, taking into account the type and degree of development of the disease, its duration, the presence or absence of concomitant pathologies, the cause of the development of arrhythmia, the age and general health of the patient, as well as many other factors.
Complex treatment of arrhythmia in children involves taking drugs with a different spectrum of action: vascular, neurometabolic, antiarrhythmic. Antioxidants and cell membrane stabilizers are also used. The doctor determines the type of medication, dosage and duration of use individually.
In addition to drug therapy, preventive measures are also prescribed. Parents receive recommendations that will help speed up recovery and stabilize the child’s cardiovascular system:
- reduction of stress, emotional changes;
- healthy sleep and daytime rest;
- proper diet, which excludes fatty foods;
- normalization and maintenance of healthy body weight;
- monitoring cholesterol and blood glucose levels;
- regular preventive examination Source: Balykova L.A., Nazarova I.S., Tishina A.N. Treatment of cardiac arrhythmias in children Practical Medicine No. 5 (53), September 2011, pp. 30-37. .
Treatment of children's ari
Our medical centers provide comprehensive diagnostics and treatment of cardiovascular pathologies in young patients. By contacting SM-Clinic, you can be sure that:
- the child will be treated by qualified cardiologists;
- if necessary, related specialists will be involved in the therapeutic process, who will provide an integrated approach;
- the baby will be examined in a modern diagnostic center with advanced equipment that provides highly accurate results and eliminates the possibility of receiving erroneous data;
- consultations and other procedures will take place at a clearly appointed time, without queues or tedious waiting.
Sign up for a consultation by phone or fill out the feedback form, and we will contact you to confirm your appointment.
Sources:
- Balykova L.A., Nazarova I.S., Tishina A.N. Treatment of cardiac arrhythmias in children. Practical Medicine No. 5 (53), September 2011, pp. 30-37.
- Pavlova N.P., Maksimtseva E.A., Artemova N.M. Arrhythmias in children. Cardiovascular therapy and prevention No. 18, 2021, pp. 118-119
- Dubovaya A.V. Modern approaches to assessing the quality of life of children with arrhythmias. Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics, 2016; 61:5, pp. 75-81
- Skudarnov E.V., Baranova N.V., Antropov D.A., Dorokhov N.A. Structure and etiological factors of cardiac arrhythmias in newborns. Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics No. 3, 2021, p. 183