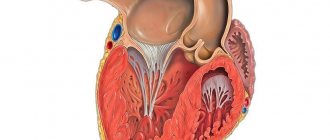
What is a chord: location and functions
For normal heart function, it is important that during ventricular systole the communication with the atria is completely blocked. This is ensured by two valves:
- right tricuspid;
- left (also called mitral) - bicuspid.
Fleshy trabeculae are attached to the valve flaps, as well as chordae tendineae (cords, heart strings) , formed by dense connective tissue and extending from the papillary muscles. Nature “invented” these structures in order to hold the valve flaps:
- when the cords contract, the valves open;
- at the moment of relaxation of the strings, the valves close tightly, creating a barrier to blood entering the atria.
Sometimes during intrauterine development additional, “extra” fibers are formed. They can be found on both the right and left, but in 90% of cases the left ventricle “suffers.” If such a string goes from the papillary muscles to the walls of the heart or sags freely, cardiologists call it a false chord of the left ventricle (LVF). If it is directed from one wall of the ventricle to another, then such a fiber is called an abnormal cord (ATLV).
The LVDC differs from the mitral valve support string:
- shorter length and thickness;
- structural organization.
A normal, typical fiber is characterized by one central core, in which up to 5 main blood vessels pass. The false chord of the left ventricle is formed by 2–3 rods, separated by connective tissue, inside of which there are microvasculature vessels.
You can also find the following formulation: “additional trabecula of the left ventricle.” Doctors often mean LVDC in this case, although, from an anatomical point of view, the trabecula is a separate structure that continues the cardiac string.
In the English-language medical literature, the term falshe-chordae is used - “false chord”. Some authors recommend replacing the literal translation with “ectopically attached notochord”, as it more accurately reflects the essence of the changes.
Truths and lies about false chords
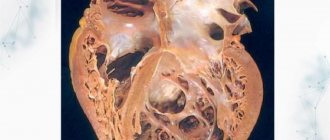
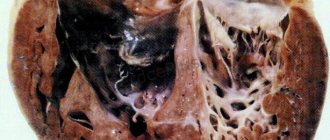
Quite often, when performing an ultrasound of the heart (Echocardiography), a false chord of the left ventricle of the heart is detected. Synonyms for this finding are: accessory chord, accessory chord, atypical chord of the left ventricle.
What is it? This is a connective tissue thread-like formation located in the cavity of the left ventricle of the heart and has no functional tasks in the heart, i.e. unnecessary and at the same time harmless formation of the heart. That is why it is classified in the group of so-called “minor heart anomalies” - i.e. such anomalies, which, of course, are present in the heart, but the prognosis of its life practically does not change, and in most cases do not require any treatment.
And, you will correctly note, since this chord is false, then it is probably real!
Of course have! These are the real chords located between the papillary muscles of the mitral valve and the mitral valve leaflets, and, like parachute lines, they hold the valve leaflets taut, ensuring its proper functioning.
Detection of false chords of the left ventricle of the heart is already possible during an ultrasound examination of the fetal heart. When performing echocardiography, false chords are detected in patients of all ages - from newborns to elderly patients. Some hereditary predisposition to this anomaly has been noted, incl. and in some families, in three generations, we detect false chords.
There have been statements that the presence of false chordae in the heart may be associated with other diseases and syndromes, but observations in recent years reject these assumptions.
And here, as always, at the most interesting place, when everything was so good and just had to end, let’s move on to the ambush.
The false chords, like the strings of a musical instrument, stretch and shorten during contractions of the heart, and with each contraction of the heart, a wave of blood expelled into the aorta hits them, like the fingers of a guitarist. And, lo and behold, this chord sounds! This means that in the presence of false chords, a heart murmur is heard. It’s in it, in that noise, that there’s an ambush!
Having heard heart murmurs, primitive-minded doctors diagnose the patient with “congenital or acquired heart disease,” dooming him to significant restrictions in life, employment, receiving unnecessary treatment, etc. I know of numerous cases where women with such “chordal” heart murmurs had their fates ruined, prohibiting them from becoming pregnant and giving birth, assuming they had a serious cardiac disease. And let’s not even talk about cases of bans on playing sports and enrolling in military schools!
The second point of this ambush is paradoxically the opposite of the previous paragraph. So, the diagnosis of a false chord has been established, and, accordingly, the fact of a “chordal” heart murmur has also been established. The patient, his parents and the whole family are glad that everything worked out and they can drink champagne. And time passes, diseases do not sleep, and attack daily and nightly, both patients without false chords and those with them. And then, God forbid, this patient with false chord fell ill with the flu, or scarlet fever, for example. Carditis (inflammation of the heart) develops, and a completely different, already pathological heart murmur appears. The patient feels bad, he goes to the clinic, but the attending physician, opening the patient’s outpatient card, sees a note that he has a “chordal murmur” and, accordingly, ignores the new auscultatory data. Adequate treatment is not prescribed, time passes, and the disease progresses to a severe, sometimes irreparable stage.
What to do, you ask in fear! You have completely confused us!
It's simple! Chordal cardiac murmur has a special, musical timbre, which an experienced cardiologist can clearly distinguish from pathological and other functional cardiac murmurs. Thus, already at the stage of simple examination and auscultation of the patient, such an experienced doctor is already able to correctly diagnose this minor cardiac anomaly, or suspect a serious illness in the presence of another cardiac murmur.
And if doubts arise about the diagnosis, he will always conduct an echocardiography on the patient - a reliable and accurate method of ultrasound examination of the heart, which can confidently detect both a trifling false chord and a serious heart disease. And remember: neither an ECG nor an x-ray can detect the left ventricular chord; these studies are carried out for other valid purposes!
And more about lies. Many Internet resources repeat the same thing about the bluish color and the disappointing prognosis of patients with false chordae. Be smarter, don’t allow yourself to be deceived, and if you have any complaints or doubts about health and heart issues in particular, contact specialists, preferably honest ones.
Health to everyone! R. Shukhnin.
In the photo: false (synonym: atypical, accessory) chords of the left ventricle of the heart in an infant and an adult.
Ultrasound of the heart, cardiac development abnormalities, false chord, heart murmur, echocardiography
Reasons for the development of the anomaly
The main etiological factor in the occurrence of such an anomaly as an additional chord in the heart of a child is genetic predisposition. The risk increases if the mother has cardiac pathology. But experts do not exclude other reasons for the development of small cardiac anomalies:
- consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- smoking;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- stress;
- excessive physical activity;
- malnutrition;
- environmental pollution;
- radiation.
An abnormality of connective tissue is closely related to its dysplasia. The formation of the fetal cardiovascular system ends by the eighth week of intrauterine development. Obstetricians and gynecologists know that the blood of the unborn child circulates independently already on the 26th day of pregnancy, heart valves are formed at the 6th week, therefore it is in the first trimester that a woman needs to be especially careful about adverse effects.
Diagnostics
{banner_banstat5}
The examination is carried out under the supervision of a cardiologist, and if necessary, a specialized surgeon is involved. It is extremely difficult to identify a violation without patient complaints, because there are no clues.
An approximate list of methods if a targeted assessment of cardiac structures and search for anomalies is carried out:
- Analysis of symptoms. You need to understand what worries the patient. If there are at least a few signs, the question becomes simpler.
- Anamnesis collection. Lifestyle, nutrition, professional activity, family history, current and previous diseases and conditions, other points. It is also important to link them to the clinical picture, if any. For example, the occurrence or intensification of pain after physical activity, eating, etc.
- Echocardiography. The main method for visualizing tissues of cardiac structures. Used for early diagnosis and is considered the first method of examination. But with a small lesion or complex localization, ECHO does not always provide enough information.
- In this case, they turn to MRI. This is the gold standard in visualization. Allows you to demonstrate in detail the condition of the muscular organ and identify all possible deviations. No contrast required.
- Electrocardiography. Used to identify functional disorders and arrhythmias. It also does not show any changes if we are talking about a small anomaly. When symptoms are present, objective features of extrasystole, tachycardia, and fibrillation are detected. Depending on the case.
Other methods do not provide sufficient information. That's why they are rarely prescribed.
Based on the results, doctors draw a conclusion regarding the nature of the process and develop a strategy for possible therapy.
But the situation is not so obvious. Just because everything is normal now does not mean that the situation will continue. Therefore, the diagnosis is made several months later, after dynamic observation.
Symptoms and indications for visiting a doctor
Pediatric cardiologists divide LVDC into those that are hemodynamically significant and those that do not affect health and quality of life. In the vast majority of cases, parents are unaware of the existing anomaly - the child develops absolutely normally.
The clinical picture of LVDC does not have specific signs. Sometimes, even in the neonatal period, a murmur is diagnosed - an acoustic phenomenon in the form of a whistle or creaking, which the doctor hears when listening to the heart. The cause of the noise is the sounds of turbulence as blood moves in the left ventricle or the vibration of an additional heart string.
The manifestation of LVAC is determined by its intracardiac topography and the period of a person’s life. During the so-called growth spurts, when there is an increased increase in body length, children have complaints about:
- excessive fatigue;
- unmotivated fatigue;
- pale skin;
- periodic increased heart rate;
- pain in the area of the projection of the apex of the heart;
- feeling of lack of air.
An electrocardiographic examination can reveal the presence of extrasystoles, conduction disturbances, and signs of left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy. If the occurrence of a minor cardiac anomaly is caused by connective tissue dysplasia syndrome, LVDC is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- asthenic physique;
- low body mass index;
- joint hypermobility;
- history of dislocations;
- deformation of the chest bones;
- poor posture;
- structural changes in internal organs.
Symptoms of LVDC often appear during adolescence. Parents may attribute the teenager’s complaints to the difficulties of the school curriculum, overwork with tutors, overload in the sports section, and prolonged sitting at the computer.
Symptoms
Note that the diagnosis of MARS in cardiology in a newborn child is practically absent, since there are no clinical signs. More often, such anomalies make themselves felt at an older age. This can happen during the active development of the baby or after any illness. Symptoms for minor anomalies of heart development in children are as follows:
- frequent tingling in the heart;
- regular heart pain;
- the presence of sensations that the rhythm of the heartbeat is lost;
- fast fatiguability;
- frequent weakness;
- dizziness;
- changes in blood pressure parameters.
Diagnostics: how to determine LVHL
When the doctor tells you that your baby has a heart murmur, there is no reason to panic. The condition does not require emergency resuscitation measures or intensive treatment. The main diagnostic method is ultrasound examination. It will help clarify the location and number of additional strands. There are the following types of LVDC:
- according to location in the ventricle - apical, middle, basal;
- in relation to the axis of the heart - diagonal, longitudinal, transverse;
- by number - singular and plural.
If echocardiography has revealed an additional chord in the cavity of the left ventricle in a child of any age, I advise parents to undergo the following examinations:
- A general blood test is not important in terms of diagnosing LVHL, but it will reveal anemia or an existing inflammatory process in the body, which can aggravate the condition of a child with a minor cardiac anomaly.
- Electrocardiography. It is advisable to conduct Holter monitoring, which will exclude arrhythmia with greater diagnostic accuracy.
- ECG tests with physical activity will show how well the child’s heart “copes” with its function.
- Consultations with specialized specialists (orthopedist, endocrinologist, otolaryngologist).
I always explain to parents of infants that sometimes the abnormal chord can lengthen and “grow” into the valve, so during subsequent ultrasounds the doctor does not detect LVDC. In such cases, they say that the baby has “outgrown” this pathology.
What is an anomaly
First you need to figure out: what is an abnormal chord of the left ventricle?
This name refers to an anatomical feature of the structure of this organ, in which the chords (the so-called fibrous muscle connecting the opposite walls of the left ventricle) have an incorrect location. Of all the types of abnormalities found in the heart, this is the most common.
Irregular chords vary in number: both single (they account for 62%) and multiple (they account for 38%).
Sign up for a consultation
An abnormally located chord in the cavity of the left ventricle is not a disease; as a rule, it does not threaten the body in any way and does not interfere with blood flow. But, in some cases, it can cause disturbances and interruptions in heart rhythms.
Such a phenomenon as an abnormal chord of the left ventricle of the heart is often genetic in nature and is often transmitted to the child from the mother, who is not even aware of such a phenomenon in her body.
The following can lead to an abnormal phenomenon occurring in the womb during the development of a small organism:
- smoking during pregnancy (this is the most dangerous factor);
- bad ecology;
- weak immunity of women;
- improper (unbalanced) nutrition;
- frequent stress, emotional overstrain;
- infection to the fetus.
Interesting! It has been noted that this anomaly is characteristic of people with a thin body structure.
In adults, abnormally located chordae are found much less frequently than in children. This is because over time they may disappear as an anomaly. For example, stretch out or shift, fuse with the surface of the heart muscle. This phenomenon is understandable: in a newborn, the left ventricle of the myocardium has the shape of an ellipse, and with the growth and development of the body it becomes more like a ball.
There are cases when, against the background of advanced heart diseases and defects, drug or alcohol addiction, an abnormal chord appears.
call me back
Doctor's advice: how often to do echocardiography with false chord
For a standard check-up for a minor cardiac anomaly, it is enough to undergo an echocardiography once a year. The examination is scheduled unscheduled if:
- the patient has complaints, including those not directly related to cardiology;
- you notice that the child is growing rapidly;
- there was a sharp weight loss;
- a chronic disease has been diagnosed, such as asthma, gastritis, nephritis;
- the child goes to kindergarten, school, university;
- there is a question about the sports section;
- stress occurred: an exam, the loss of one of the family members, conflict in the children's team and at home;
- pregnancy is planned or determined.
Single LVDC is not considered a pathology. Experts consider them as an anatomical feature of a person. The presence of an additional chord is not a contraindication to attending physical education classes. Young men with abnormal cords can be drafted into the army if they do not have complications or concomitant pathologies. It is only important to clearly tell the child about his condition and warn him that he needs to be attentive to his health.
A minor anomaly of cardiac development is manifested by symptoms of autonomic dysfunction:
- pain in the heart area;
- emotional lability;
- fatigue;
- signs of astheno-neurotic syndrome;
- a characteristic heart murmur is heard.
Their manifestations can become more pronounced as the child grows, leading to various complications, for example, heart rhythm disturbances and the formation of additional pathways in the heart. This leads to poor exercise tolerance and a tendency to faint. Such children are at risk for developing infective endocarditis - complications after acute respiratory infections and tonsillitis in the form of an inflammatory process of heart tissue.
Prevention of the development of complications is a timely visit to a doctor in cases of the appearance of the listed complaints and the implementation of prescribed diagnostic measures.
Children are prescribed an ECG (to determine possible arrhythmias) and echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart). This method allows you to visualize the heart and large vessels, clarify the presence of cardiac abnormalities and determine whether there are disturbances in its functioning.
Make an appointment with a pediatric cardiologist and examination by phone +7(495)150-60-03
Services and prices
Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a pediatric cardiologist
2,200 rub.
Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with a pediatric cardiologist
2,100 rub.
Electrocardiogram at rest
600 rub.
Electrocardiogram with functional tests
1,000 rub.
Echocardiography with Doppler analysis (in PW, CW mode) and color two-dimensional Doppler mapping for children under one year old
RUB 3,800
Echocardiography with Doppler analysis (in PW, CW mode) and color two-dimensional Doppler mapping for children from 1 year to 7 years
3,700 rub.
Echocardiography with Doppler analysis (in PW, CW mode) and color two-dimensional Doppler mapping for children over 7 years old
3,600 rub.
What complications can occur with a false chord?
The prognosis for single abnormal chords is favorable. Complications are rare, but multiple transverse and diagonal chordae can act as a trigger for the development of diastolic dysfunction of the heart, increasing the risk of thrombus formation, bacterial endocarditis, and can also be combined with other congenital anomalies.
Sometimes LVHL can cause:
- extrasystoles;
- paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia;
- WPW syndrome;
- atrial fibrillation;
- TELA;
- thrombotic lesions of veins;
- ischemic stroke;
- cardiac arrest.
These disorders are observed in adulthood, but a teenager with LVDC should be informed about them. An unfavorable prognosis is characteristic only of non-compact left ventricular myocardium syndrome (LVSM), which is characterized by the presence of numerous additional trabeculae and chordae, combined with changes in the structure of the heart muscle.
Despite these complications, statistics claim: repeated clinical observations have not revealed a relationship between the presence of additional strands in the left ventricle and the risk of cardiovascular mortality.
Diagnosis and treatment
If a pediatrician detects murmurs when listening to the work of the myocardium, then you should definitely visit a cardiologist and undergo a diagnostic examination, including:
- taking an electrocardiogram (with its help it will be possible to identify whether there are disturbances in the functioning of the myocardium);
- ultrasonography.
It is very important that if the examination shows the presence of an abnormally attached chord of the left ventricle, you need to periodically visit a cardiologist, because this phenomenon creates noise, due to which it is possible to untimely pay attention to the appearance of serious diseases associated with the work of the myocardium.
Regarding the chord itself, it should immediately be noted that its abnormal location in the left ventricle does not require specific treatment, much less such as surgery. But there are a number of rules that must be strictly followed by those who have this phenomenon.
Treatment
As a rule, single LVDC without clinical manifestations do not require treatment. Medicines are prescribed for the development of complications and concomitant heart pathologies. Symptomatic therapy - antiarrhythmic drugs and substances that correct hemodynamics: diuretics, antihypertensives, antioxidants, potassium and magnesium preparations.
Surgical treatment methods (local cryodestruction and excision of left ventricular ventricle) are rarely used: if an abnormal cord causes arrhythmia that threatens the patient’s life.
Lifestyle recommendations:
- give up fast food and sugary carbonated drinks;
- spend at least an hour a day in the fresh air;
- do not sit too long at the computer;
- find time in your personal schedule for physical exercise;
- learn to cope with stress;
- get vaccinated against influenza and other infectious diseases in a timely manner;
It is imperative to discuss the issue of “bad habits” with your teenager. It is important that the young person consciously considers it unacceptable for himself to take a sip of a low-alcohol drink or inhale cigarette smoke.
Pregnancy is not contraindicated for women with LVDC. It does not pose a threat to health, passes without negative consequences for mother and child, you just need to notify the doctor about the existing additional chord.