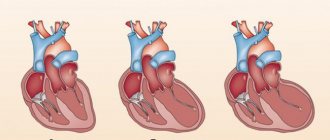
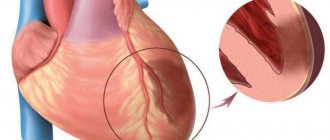
Among diseases that can suddenly worsen and lead to extremely negative consequences, myocardial infarction is especially dangerous. Treatment should be started as early as possible. At the initial stage, it may consist of first aid, and the rehabilitation stage can last for several months. The patient is provided with comprehensive care, including drug treatment, surgical and non-surgical methods, and rehabilitation therapy aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease. With a professionally designed recovery program, life after a heart attack can return to normal, subject to certain restrictions.
What are coronary stents and why are they needed?
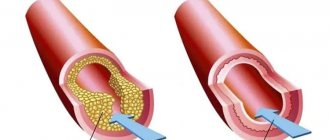
A coronary stent is a medical device that is a frame in the shape of a metal cylinder, installed in narrow places in the artery (with cholesterol deposits) to widen them, thereby ensuring normal blood flow.
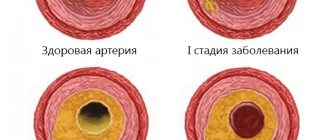
Stents can combat arterial stenosis that occurs due to the deposition of atherosclerotic plaques. Cholesterol is deposited on the walls of the arteries and narrows the lumen, thereby preventing blood flow. Poor blood flow causes oxygen starvation and lack of nutrients in the organs. One of several ways to relieve such bottlenecks in the arterial system is stenting. Installation of a stent is not always indicated for the patient, but only in some severe cases when there are no contraindications, but more on that later.
Application area
One of the common causes of the development of heart pathologies is a decrease in vascular elasticity and vasospasm. The arteries gradually lose their ability to expand, which leads to local disturbances in blood supply. Also, if the process is chronic, this contributes to the accumulation of cholesterol deposits on the vascular walls. Scientists all over the planet are actively working to develop an effective method to combat this disease. Coronary stenting is one of the existing ways to solve the problem.
Stenting is a procedure for integrating a special dilating device into a vessel. It is a tube with a mesh texture that can take the desired shape when implanted. The device acts as a frame. As a result, the narrow or spasmodic section of the artery should expand, and the blood flow should return to its previous state.
This treatment method belongs to endovascular surgical interventions and is considered minimally invasive. It is performed exclusively by experienced surgeons of the highest category.
Let's consider the stenting algorithm using the heart as an example. The catheter on which the element is fixed is passed through the femoral artery through the introducer. The conductor must be moved to the designated area where it is planned to install the expander. As soon as the catheter is inserted, the artificial frame is fixed, inflated under the action of the balloon, and normalizes blood supply to the heart muscle.
The operation involves local anesthesia. The average duration is relatively short, from 20 minutes to 3 hours. If necessary, the surgeon installs several devices at once.
Diet after myocardial infarction
Life after a heart attack involves following a diet with foods that do not put a strain on the vascular system. Nutrition after myocardial infarction should include easily digestible food, and it should be taken 5-6 times a day in small portions. The diet should include cereals, low-fat dairy products, juices, vegetables, and dried fruits.
The most strict diet is during the hospital period. It includes unsalted liquid porridges, vegetable soups made from ground products. In the future, nutrition will be normalized. Coffee, tobacco, and alcohol are strictly prohibited!
Indications
Installation of coronary stents may be indicated by a doctor in the following cases:
- complete blockage of the coronary artery during or after myocardial infarction;
- narrowing or complete blockage of the arteries with a high risk of heart failure;
- narrowing or complete blockage of blood vessels with a high risk of severe angina.
Stenting is done only in cases where there are no contraindications to the operation. In another case, bypass surgery is performed.
Myocardial infarction: rehabilitation and life after an attack
At the rehabilitation stage, it is important to gradually expand the patient’s activity. For this purpose, professional cardiology clinics and sanatoriums use modern programs aimed at preventing and treating muscle atrophy and pulmonary congestion. They include physical therapy and physiotherapy.
Life after a myocardial infarction does not end at all if the patient is offered a competent and effective rehabilitation program. In some cases, the patient will have to change his job if it involves physical or emotional stress.
Contraindications for surgery
- If intervention is required in an artery with a diameter of less than 3 mm.
- If the patient has a large number of cholesterol plaques, more than 1 centimeter in length.
- If the patient is allergic to iodine-containing drugs.
- If the patient has a large number of cholesterol plaques, more than 1 centimeter in length.
- If the patient has poor blood clotting.
- If the patient has a serious condition, accompanied by a drop in blood pressure, impaired consciousness, shock, liver, kidney or respiratory failure.
- The patient has malignant tumors that cannot be treated.
If a patient is contraindicated for stenting, but still wants this operation, then in some cases he may insist on having it performed at his own risk.
Treatment and rehabilitation after myocardial infarction using shock wave therapy
One of the effective methods of treating coronary heart disease, allowing you to avoid a heart attack or restore the body after the disease. It is used in cases where traditional methods of coronary artery bypass grafting and stenting are contraindicated or do not produce any effect.
Specialized equipment uses an ultrasound scanner to focus acoustic waves onto the area of myocardial ischemia. With non-contact exposure, new vessels are formed, resulting in a bypass effect - the blood supply to the heart improves, the number of angina attacks decreases.
The method is attractive due to its absolute painlessness. During the procedure, blood pressure does not change and heart rhythm is not disturbed. No side effects were recorded. After a course of procedures, you will be able to increase physical and emotional stress, and reduce the amount of medications consumed.
On the topic “Shock wave therapy for coronary heart disease,” watch the recording of the program “About the Most Important Thing” on Russia 1 channel, which was filmed with the participation of our cardiologist Elena Pisanko. The filming contains a clear example of the procedure itself, which took place in our clinic.
Types and types of coronary stents
Stents differ from each other:
- Length. The size of the stents varies from 8 to 38 millimeters.
- Diameter. There are from 2.25 to 6 millimeters.
- By design. They differ in the shape of the elements from which they are created.
- Material. They are made from steel, cobalt-chrome, PLLA polymer and others.
- Coated. Stents are available without coating or with drug coating Sirolimus, biolimus and others.
- Method of disclosure. They can open either independently or with the help of a balloon on a catheter.
- By type of drug coating. The medications used are Sirolimus, everolimus, paclitaxel and others.
By lenght:
Stents are available: 8, 10, 13, 16, 18, 23, 28, 33, 38 mm.
By diameter:
Stents are available: 2.25, 2.5, 2.75, 3, 3.25, 3.5, 3.75, 4, 4.25, 4.5, 4.75, 5, 5.25, 5.5, 5.75, 6 mm.
By design:
- mesh (made of woven mesh);
- tubular (from a tube);
- wire (made of wire);
- ring (from separate rings).
According to the material from which the frame is made:
- stainless medical steel;
- cobalt-chrome alloy;
- alloy of platinum and chromium;
- polylactose acid (PLLA) polymer.
By type of coverage:
- Uncoated with bare metal.
- Drug-coated, which releases a drug that reduces the likelihood of future artery narrowing.
- With double coating - external and internal, to heal the artery itself and prevent the formation of blood clots.
- Coated with antibodies, attracting endothelial cells, reducing the risk of thrombosis.
- Dissolving, made from a material that dissolves and releases a drug coating that prevents the recurrence of stenosis.
By opening method:
- self-expanding;
- opened by a balloon.
By drug coverage:
- Sirolimus;
- Zotarolimus;
- Everolimus;
- Biolimus;
- Paclitaxel.
Depending on the manufacturer, stents may differ in their characteristics and price. In Russia, the production of stents is carried out in accordance with GOST R ISO 25539-2-2012.
Advantages and disadvantages of using stents
Stents are an outstanding invention that can save the lives of many patients. But it is not suitable for all patients suffering from stenosis. Like other medical instruments, stents have advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- Minimally invasive, to eliminate the problem you do not need to make large surgical incisions on the body, but only a small hole on the body into which a catheter with a stent is inserted. Fast healing. The patient can be discharged on the 3rd day.
- Use of local anesthesia during surgery. There is no need to put a person to sleep. High percentage of successful cure (90%).
Flaws:
- There is a possibility of secondary stenosis, the appearance of blood clots and heart attacks. Occurs in 10% of patients.
- Complexity of the operation. The installation of stents in the heart is performed only by highly qualified surgeons.
- Some drug-eluting stents are expensive.
- Not all patients can undergo stenting - there are contraindications.
Difference between stenting and bypass surgery
Both surgeries are performed to improve blood flow in areas where the arteries are narrowed due to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. The difference between these methods is in the way they solve the problem of stenosis.
The bypass method involves creating a section of artery that bypasses the problem area. Normal blood flow is ensured through this new area. A section of the saphenous vein of the femoral, radial or internal mammary vein is used as a shunt. Bypass surgery is performed under general anesthesia.
Stenting involves installing a stent in a narrow place in an artery and expanding it, thereby normalizing blood flow. In this case, a shunt is not used, but the problem area in the artery is simply restored. The stent is inserted into the artery using a catheter with a balloon through a small hole in the body. At the desired location, the stent is expanded using a balloon and the catheter is pulled out. The operation takes place under local anesthesia.
Both methods are now used in medicine. Each patient is better suited to a certain method of operation based on his diagnosis and condition. Stenting is a more advanced method of treating stenosis, but it may be contraindicated for some.
Symptoms of angina
- The main symptom of angina is pain behind the sternum, which is also felt by a person as strong compression, as if the heart is being squeezed from the inside. Such pain can radiate not only to the left side of the body (shoulder, arm, under the shoulder blade), neck, but even to the stomach (its upper part).
- During an attack, you may experience a fast or slow heart rate. It is the change in heart rate that can precede an attack and be a kind of first symptom;
- A person may also begin to sweat (cold, sticky sweat), feel dizzy, or feel nauseous.
- Anxiety and fear may appear.
- Duration of attack: from several minutes to 15-20 minutes.
Angina pectoris has so-called “provocateurs” - physical activity and stress. According to the level of physical activity that provokes an attack, angina pectoris is divided into functional classes: from functional class 1 (pain appears only with very intense muscular work) to functional class 4 (pain appears only with minimal exertion or even at rest) .
An important feature of angina pectoris: the attack goes away after the cessation of stress - physical, emotional - or after a person takes medication (Nitroglycerin).
Preparing for stenting
Before stenting, the patient is examined. They take basic tests, do echo and electrocardiography. Coronary angiography is performed by injecting contrast into the circulatory system and performing an X-ray examination. A map of the coronary arteries is obtained. The site of stent insertion is determined.
As a rule, to prepare for surgery, doctors may require:
- Avoid food and water 8 hours before surgery.
- Avoid taking blood thinning medications 3 days before stenting.
- Shave your groin and wash yourself.
- Eliminate or reduce the intake of glucose-lowering drugs 2 days before surgery.
Operation stages
- The operation is performed in an operating room equipped with an angiograph, which allows the doctor to observe the artery and the movement of the catheter on a monitor screen. The patient is placed on his back and sedated to keep him calm and relaxed.
- Doctors cover the patient with sterile linen and neutralize the stent insertion site.
- Local anesthesia is given.
- A thin wire is inserted into the artery through a needle, which acts as a conductor.
- An introducer is inserted along the guidewire, through which other instruments will be inserted into the artery and the wire is removed.
- Through the introducer, the doctor carefully inserts a thin catheter with a stent and a balloon.
- A contrast agent is injected into the coronary artery to accurately visualize the movement of the stent.
- The stent continues to be carefully moved to the desired location.
- The stent is expanded using a balloon on the catheter, thereby normalizing the diameter of the artery.
- After stent placement, the introducer and catheter are removed from the patient.
- A compressive bandage is applied to the catheter insertion site.
Is stenting possible during pregnancy?
Installation of stents is not recommended for pregnant women, as during the operation an X-ray is taken, which can be harmful during pregnancy. The operation can be stressful; the pregnant patient is given contrast, anesthesia and other drugs, which can also have a negative effect on the fetus. Some drugs may cause allergic reactions.
Surgery for pregnant women is prescribed only in extreme cases; the surgeon informs the patient in advance about the possible risks and consequences and performs the operation only with her consent.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
They are considered an important addition to physical rehabilitation methods and significantly speed up the process of restoring important vital signs. Most often it is recommended to do self-massage and breathing exercises. If the course of rehabilitation is favorable, gradual exercise with measured loads and time is allowed. These types include ordinary walking over longer distances, race walking, swimming, and cycling.
Complications
In some cases, complications may occur after stenting. The reason may be an incorrectly performed operation or the characteristics of the patient’s body, how it reacts to the installed stent.
- Thrombus formation at the site of stent placement is the most common complication. To reduce the likelihood of blood clots, the patient is given blood thinning medications.
- Bleeding with hematoma. Occurs due to the introduction during surgery of drugs that reduce blood clotting. Rarely seen.
- Infection of the incision site where the catheter is inserted.
- Allergy to radiopaque contrast agent or drug coating on the stent.
- Re-narrowing of an artery in another location, as plaques carried by blood from a previously problematic area can break off and block another area in the artery.
- Restenosis is the body’s reaction to the installed stent, expressed in excessive growth of the inner lining of the vessel in the area where normal lumen was restored.
- Heart attack during stenting.
There is a greater risk of complications in patients with chronic diseases such as diabetes, kidney disease and blood clotting disorders. To exclude a number of complications, the patient is thoroughly studied before the operation and adjustments are made to the treatment, regulating blood clotting with medication, and selecting a stent with the desired drug coating. Carefully monitoring the patient's condition after surgery.
Recovery period
During this period, a set of measures is formed for the patient that will help him recover faster and reduce the risk of complications and recurrence of the disease.
After the operation, the patient lies in bed for 1-3 days in the hospital. At this time, doctors closely monitor the patient. After this, the person is discharged home, where he must also be at emotional and physical rest and observe bed rest. He should not take a bath or shower or exert himself physically.
During the recovery period, drug treatment is prescribed for six months, designed to reduce the risk of re-stenosis, thrombosis and heart attack. And increase the length and quality of life.
During the recovery period, the doctor prescribes everything necessary to:
- Improve a person's physical abilities.
- Restore heart functionality.
- Slow down the process of ischemia.
- Bring laboratory parameters back to normal.
- Prevent possible complications after surgery.
- To form in the patient a correct lifestyle that ensures longevity.
- Provide psychological comfort.
Therapeutic exercises are a necessary element in the rehabilitation complex after myocardial infarction
Physical activity after myocardial infarction, along with a proper diet, is necessary for the full restoration of the functions and functioning of the heart and the body as a whole. In the absence of complications, the doctor creates an individual set of exercises for each patient. Therapeutic exercise is carried out even during bed rest - starting with movements of the hands and feet and ending with turns on different sides, moving to a sitting position. After discharge from the hospital, recommendations for rehabilitation and lifestyle after an attack necessarily include daily walking a certain distance.
Drug therapy
After stent installation, the patient is usually prescribed the following medications:
- Antiplatelet, reducing the risk of blood clots. (Aspirin, Aspicard, Aspinat, Trombogard, Acetylsalicylic acid, Clopidogrel, Detromb, Trombex and others. Prescribed by the doctor to each patient individually.)
- Statins, which lower cholesterol levels and reduce the likelihood of restenosis. (Simvastatin, Pravastatin, Pitavastatin, Lovastatin, Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin and others. Prescribed by the doctor to each patient individually.)
- Drugs that reduce the risk of heart attack.
The range of medications prescribed depends on the patient’s condition and health characteristics. It is necessary to strictly take in full all medications prescribed by the doctor for the period of treatment. After stenting surgery, it is strictly forbidden to self-medicate and take medications at your own discretion.
Lifestyle change
Atherosclerosis, as a rule, is caused by an incorrect lifestyle, and in order to fully recover after surgery and avoid arterial stenosis in the future, it is necessary to change your lifestyle to a healthy one.
The transition to a healthy lifestyle is:
- Do morning exercises, move and walk quietly for 30 minutes - 1 hour about 3-4 days a week.
- Completely eliminate active and passive smoking.
- You can safely enjoy swimming, skiing, use an exercise bike or treadmill evenly and measuredly for up to 6 hours a week.
- Avoid alcoholic drinks.
- Avoid fatty, fried and salty foods.
- Do not consume more than 4 grams of salt per day.
- Drink tea instead of coffee.
- Attend examinations by your attending physician.
- Eat more vegetables, fruits, fish, rye and bran bread.
The diet and exercise program is prepared by the attending physician. For successful recovery, you must fully adhere to the schedule he has drawn up.
All articles →
| Our company offers high-quality stents for coronary vessels. You can familiarize yourself with the entire range of manufactured medical equipment for cardiac surgery in the website catalog. We are pleased to present you a coronary stent at a price affordable for every consumer! | Go to catalog > |
Breathing exercises
In diseases of the cardiovascular system, breathing exercises play a special role. In terms of their physiological effects on the body and the cardiovascular system, they differ significantly from all other types of exercise and from any physical activity. If most exercises stimulate the cardiovascular and nervous systems to one degree or another, increasing the number of heart contractions, then breathing exercises, on the contrary, help calm cardiac and nervous activity and reduce shortness of breath.
You must carefully monitor deep and rhythmic breathing during exercise and alternate active physical exercises with special breathing exercises. Therefore, you should pay attention to correct, full (thoracic and abdominal), deep nasal breathing.
Exercises to develop nasal breathing:
- lightly stroke the nose from bottom to top, around the eyes and again to the bottom of the nose;
- tap your middle finger like a hammer on your nose, breathing freely;
- wrinkle your nose, fold it up;
- inflate the wings of the nose, then squeeze them, exhale;
- tap your nostrils with your middle fingers and exhale completely, lightly stroke your nose upward - inhale;
- kneading the base of the nose from the sides with rotational movements with your middle fingers, exhale completely, stroking your nose upward - inhale;
- tap your fingers on the right and left of the nose, then on the forehead and cheeks near the nose;
- rub the septum under your nose with your index finger, slightly lifting the tip of your nose;
- close the left nostril and exhale and inhale with the right, then the same with the left;
- sing a melody with your mouth closed to the sound “m”.
Repeat each of these techniques 7-8 times.
Do not hold your breath while performing breathing exercises. Often, holding your breath is accompanied by muscular effort and is called “straining.” If you hold your breath during physical activity, the face becomes purple, the peripheral veins and vessels of the eyeball fill with blood.