Arrhythmia in children
Medicine considers the concept of respiratory arrhythmia, and this is perhaps the only case of cardiac arrhythmia in a child when there is no reason to worry. In approximately thirty percent of the remaining cases, it is necessary to pay close attention to a child with arrhythmia and conduct a comprehensive examination of the body as early as possible in order to identify the cause of the rhythm disturbance.
Arrhythmias in children are divided into acquired and congenital, and in cases where a disturbance in the normal frequency or rhythm of heart contractions begins at an early age, say, in the presence of arrhythmia in a 7-year-old child, there is a high probability that an organic pathology is occurring. Based on clinical manifestations, the following types of cardiac arrhythmias in children are distinguished:
- Tachycardia;
- Bradycardia;
- Extrasystole;
- Sinus arrhythmia;
- Migrating source of rhythm;
- Paroxysmal tachycardia;
- Atrial fibrillation;
- Sick sinus syndrome.
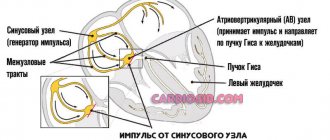
The reasons why arrhythmia occurs in children vary from psychogenic reactions to organic pathology. This includes infectious diseases, heart disease, endocrine pathology, and functional conditions as well. Each specific type of arrhythmia can be provoked by a number of reasons from those listed, various combinations of them, or may appear due to a single disturbance in the homeostasis of the body. Sinus tachycardia is an increase in heart rate of more than 160 beats per minute at rest in young children and 140 beats in older children, provided that other elements of the electrocardiogram are located in the normal sequence. This type of arrhythmia implies a normal mechanism of contraction of the heart muscle with shortening, but within normal limits, of all intervals between the elements of the ECG.
Sinus tachycardia can occur under conditions of psychoemotional stress or physical exertion, while acting as an adaptive mechanism of the body to changing environmental conditions. However, this arrhythmia in children can also occur against the background of organic heart pathology of various origins. Also, the heart rate may increase in response to an increase in body temperature, a decrease in blood pressure, significant blood loss, and a decrease in myocardial contractile function, which can be inflammatory, dystrophic, toxic or ischemic in nature.
In addition, the presence of concomitant diseases, such as thyrotoxicosis, vegetative-vascular dysfunction or a state of shock, increases the heart rate. Some medications increase heart rate, examples of which are methylxanthines, anticholinergics, sympathomimetics, arteriolar vasodilators, etc.
The opposite rhythm disorder to tachycardia is called bradycardia, and the heart rate decreases to less than 80 beats per minute in newborns and less than 70 beats per minute in older children. All electrocardiogram intervals are kept within normal limits, as in the case of tachyarrhythmia, but, unlike the latter, bradycardia is characterized by a prolongation of all elements of the contraction cycle of the heart muscle. Physiological bradycardia is typical for children whose heart muscle is trained, so if your child attends sports clubs or enjoys another hobby that trains his body in terms of physical endurance, there is nothing to fear.
However, there is often another reason for bradycardia, and it may be an increase in the influence of the vagus nerve, which often accompanies peptic ulcer disease; head injuries, increased intracranial pressure also lead to a decrease in heart rate; hypothyroidism, hypothermia and severe hypoxia can cause a decrease in heart rate. Among external interventions, the cause of bradycardia may be excessive administration of potassium preparations into the body, the use of beta-blockers, opioid analgesics, some tranquilizers and cardiac glycosides. Infectious lesions of the heart muscle (myocarditis), sick sinus syndrome are also causes of bradycardia.
Sinus arrhythmia in children
However, there is such a thing as sinus arrhythmia in children, also called respiratory arrhythmia, and if your child is diagnosed with such a rhythm disorder, you should not panic ahead of time. Sinus arrhythmia in children is normal if the differences in the duration of the RR intervals increase by more than 0.15 seconds. This means that the intervals between heartbeats are uneven, which may go unnoticed, but can also be felt as interruptions in the heart.
This type of arrhythmia is called respiratory if the cycle fluctuations are associated with the phases of breathing. In this case, the child’s heart rate increases as he inhales and decreases as he exhales. Thus, if the cardiogram was taken from a child in a cold room, there is a high probability that sinus arrhythmia will be reflected on the ECG, because the child reflexively holds his breath from contact with cold surfaces or sensors. Such a condition should not be a cause for concern, because in conditions of intensive growth of a child’s body, the heart does not have time to adapt to the new, constantly changing conditions of blood circulation.
This means that a recorded episode of sinus arrhythmia in children at 6, 7, 8 years old is not a pathology. Another situation is when the doctor has ruled out the possibility of respiratory fluctuations in the heart rate, but sinus arrhythmia still occurs. The period of recovery after acute infectious diseases and the presence of concomitant diseases of the body that are not directly related to the cardiovascular system, but affect the heart rhythm, should also be excluded. If sinus arrhythmia persists, the cause most likely lies in the heart itself. It may be myocarditis, congenital heart disease, chronic rheumatic heart disease, heart tumor, vegetative-vascular dystonia, or a hereditary rhythm disorder.
Cardiac arrhythmia in a child: diagnosis and treatment
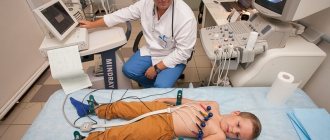
Diagnostics includes collecting a medical history, a set of urine and blood tests (both general and biochemical), ultrasound and x-ray of the heart. Auscultation (listening with a phonendoscope) and electrocardiogram (ECG) are very informative. These procedures will help determine whether there is cause for concern and whether more detailed examinations are required.
Treatment of arrhythmia mainly takes place at home. Hospital care is only necessary in more serious cases. Since we are not talking about an independent disease, but the result of an underlying one, therapy is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause.
Drug therapy consists of maintaining the balance of electrolytes in the heart muscle, improving its nutrition, and eliminating infections if they are identified during diagnosis. If examinations confirm the diagnosis of arrhythmia, do not give up. Today, medicine has come a long way in its strategy for treating heart disorders. Contact the Children's Medical Center "Human Health" for detailed consultation and diagnosis. The center's cardiologists successfully treat arrhythmia. They will help you defeat the disease and adjust your child’s lifestyle.
Moderate sinus arrhythmia in a child
Moderate sinus arrhythmia in a child is not dangerous if its cause is immaturity of nervous regulation, as is the case with respiratory arrhythmia. However, even trained children may experience seemingly causeless sinus arrhythmia, and in this case, a visit to a cardiologist is mandatory. Each case of arrhythmia in a child must be subjected to observation and strict control, because if sinus arrhythmia occurs without an obvious reason, especially if the child makes complaints, which will be discussed below, a comprehensive examination of the body is necessary.
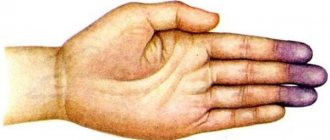
Regular observation by a cardiologist is the key to timely diagnosis of the transition of a moderate arrhythmia in a child into something more serious. Often respiratory arrhythmia is detected during a routine examination, but sometimes the child makes specific complaints. If the child’s age is too young for him to be able to formulate a complaint about poor health or pain, sufficiently observant parents themselves can notice changes in the child’s behavior if they look closely at the baby. When the heart stops working, the child may experience cyanosis (blue discoloration) or pale skin.
This is also accompanied by shortness of breath, which may manifest itself at a younger age as intermittent, “choking” crying. Such cases of arrhythmia can appear at any time of the day, and therefore the child is characterized not only by anxiety during the day, but also by sleep disturbance at night. The baby loses his appetite or continues to eat, but with great reluctance. Also, if you look closely, in some cases you can see the pulsation of large vessels. Older children may lose consciousness when a cardiac arrhythmia occurs or complain of dizziness. Also at this moment, the pressure may decrease, and some children feel the heart skip a beat or, conversely, make a strong push.
Of course, each of the listed complaints in itself seems to be a reason for a visit to the doctor, and if there is a combination of several of them, most likely the child suffers from something more serious than mild sinus arrhythmia. First of all, after the examination, the child will be sent for electrocardiography, and then two scenarios are possible: the baby can continue to be monitored on an outpatient basis or be sent to hospitalization. In case of hospitalization, tests include a clinical blood and urine test, an ultrasound examination of the heart, an echocardiogram, and a chest x-ray. In general, each diagnostic case is individual, and further tactics are determined by the attending physician.
Preventive measures
As already mentioned, arrhythmia can occur both at a young age and in adolescence. Based on this, methods of prevention are determined. First of all, it is necessary to promptly treat the disease that causes irregular heart function. It is important for teenagers to stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages. You should avoid stressful situations, and also run and jump less.
Traditional preventive methods include following a diet (the predominance of plant foods and low-fat foods), moderate physical activity, and frequent walks in the fresh air. The child will feel better if he is in a calm emotional state; rest during the daytime will not hurt; night sleep should be at least 8 hours.
Treatment of arrhythmia in children
Treatment of arrhythmia in children is carried out only after a thorough examination of the body and determination of the cause of its occurrence. Sinus tachycardia is treated in cases where the patient cannot easily tolerate the state of accelerated heart rate or further maintenance of such a rhythm will infringe on the body’s needs for oxygenated blood. If tachycardia is psychogenic in nature, auto-training or psychological assistance is possible. It is recommended to give up stimulants, strong coffee, tea, and spicy foods, as well as review the medications the child is taking.
The same thing - medications - must be carefully studied again, paying special attention to the list of side effects, and for bradyarrhythmia. In this case, it is also necessary to study the acid-base state of the child’s body, the volume of circulating fluid, as well as determine blood pressure. Treatment of sinus arrhythmia in children is not carried out if it is respiratory in nature and does not bring inconvenience to the child’s life. In opposite cases, contacting a pediatric cardiologist cannot be delayed, which has a positive side: everyone knows that early diagnosis is the direction in which modern medicine is moving. In addition, as mentioned above, arrhythmia in a child can be caused by concomitant diseases, the treatment of which in half of the cases gives a positive result without the need to act directly on the heart.
However, for timely, and more importantly, correct treatment, correct diagnosis is necessary, and in Moscow you will not find doctors more competent in this narrow specialty than the doctors working at the Svyatoslav Fedorov Children's Medical Center. Doctors here provide assistance every day and will take care of your child as if it were their own child. A friendly, open, pleasant atmosphere on the one hand and many years of experience in the relevant field on the other will make treatment for your child a comfortable and serious process at the same time. You will receive a diagnosis of the child’s objective condition, a careful analysis of each of the symptoms, strict implementation of the necessary diagnostic procedures and strict adherence to treatment protocols.
Regardless of how you are treated depending on the decision of the cardiologist - outpatient or inpatient, you can count on maintaining quality standards of care. The introduction of the latest examination technologies and maintaining experience with standard methods, modern diagnostic equipment, properly selected rational treatment, optimal timing of therapy and preventive examinations in the future - this and more is happily offered by the Svyatoslav Fedorov Children's Medical Center. By making the right choice in a medical facility for the treatment of your child, you ensure many years of health and a fulfilling life for your baby.
With prices for services of the medical center named after. Fedorov, check out the “Prices” page
What to do?
Arrhythmia is diagnosed only after an ECG examination, after which you need to visit a cardiologist. He will direct you to undergo all the necessary studies and tests. In most cases, if there are no additional deviations from the norm, treatment of arrhythmia in children is limited to maintaining a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition and regular cardiogram readings.
If we are talking about non-respiratory arrhythmia, then therapy is selected in such a way that it affects the root cause of the painful condition. Conservative drug therapy has the following directions:
- normalization of electrolyte balance;
- improving the metabolism of heart muscle cells;
- use of antiarrhythmic drugs.
Specific medications are used to achieve each goal. In particularly difficult situations, minimally invasive surgical treatment is indicated for children.
There is a positive effect from the following methods of influence:
- acupuncture, when special needles affect particularly sensitive points of the human body;
- physiotherapy – carried out through electricity, magnetic field and heat;
- psychological therapy.