Resuscitation is the restoration of body functions when they are significantly reduced with a high threat of death, as well as a return to life in case of sudden death. The goal of resuscitation is to prevent sudden death, stabilize vital functions, and, if possible, restore some of what is lost due to illness or injury.
Further treatment and recovery will take place in another, non-intensive care unit. The task of specialists in the intensive care unit (or ICU) is to prevent death from a person.
When is resuscitation required in oncology?
Resuscitation in oncology involves, if not returning a cancer patient to an absolutely normal life, then maintaining vital functions in a stable state.
In what cases is a patient taken to the intensive care unit? There are differences in the work of the oncology intensive care unit from the usual ones. In addition to typical cases of cardiopulmonary resuscitation after cardiac arrest or fatal rhythm disturbances, which also happens during a malignant process, a cancer patient is admitted to the intensive care unit:
- After extensive combined operations for common malignant processes, when the cancerous tumor and adjacent organs and tissues are removed as a single block.
- After thoracic interventions, when a change in the anatomical relationship in the chest cavity after removal of part or all of the lung with lymph nodes or a tumor conglomerate of the mediastinum directly affects the functioning of the heart.
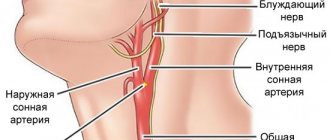
- After removing part or all of the stomach for cancer, because the malignant process causes a catastrophic metabolic disorder that at the end of the last century led to the death of one in four of those operated on, intervention in the abdominal cavity can lead to irritation of the vagus nerve, which partly determines the heart rhythm.
- With all interventions on the brain, due to the danger of swelling and compression of the medulla oblongata, where the regulatory centers of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems are located.
- In case of severe complications of stage 4 chemotherapy, for example, in case of critical thrombopenia with the risk of spontaneous bleeding, necrotic enteritis, and so on.
- For post-chemotherapy complications of grade 3 in patients with severe concomitant diseases, when their decompensation is possible.
- When using certain immunological anticancer drugs that cause severe allergic reactions, and during high-dose chemotherapy.
- To monitor the patient’s condition after some “non-standard” methods of administering chemotherapy.
- In case of decompensation of concomitant diseases, for example, hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic coma due to diabetes mellitus, ventricular fibrillation, and so on.
- In case of breathing problems as a result of extensive metastasis to the lungs, forced mechanical ventilation is required.
- After bleeding in any organ due to the disintegration of a malignant tumor.
It is impossible to list all the clinical situations when the functioning of organs and systems becomes so insufficient to support life that emergency and active intervention by professionals is required.
How does anesthesia work?
Any anesthesia, local or general (the latter is also called anesthesia), is a medicinal intervention in the body that helps to avoid pain stress. In response to a pain impulse from the injured area, pain awareness occurs in the cerebral cortex. To prevent this, you need to block the nerve endings. Local anesthesia stops the transmission of pain impulses in a certain area - the medicine passes through the cell membranes and disrupts the reactions in them. As a result, nerve impulses are blocked and the sensation of pain does not occur. Consciousness is preserved during local anesthesia, and the effect lasts on average one to two hours. Anesthesia, or general anesthesia, is an effective method when a large area of the body is undergoing intervention. In this state, the person sleeps soundly and is well relaxed: tension in the muscles and other tissues should not interfere with the surgeon’s work.
Oleg Karmanov notes that it is wrong to be afraid of damage from the anesthetic: enduring pain is much more dangerous. In many cases, the risk of losing your life from painful shock during surgery without anesthesia is very high. According to the doctor, modern anesthetics are well controlled. This means that as soon as the active substance is no longer introduced into the body, it quickly disintegrates and the patient wakes up. The only absolute contraindication is an allergy to the drugs used, and possible side effects are usually associated with the presence of additional substances in the solution: vasoconstrictors (vasoconstrictors), preservatives and stabilizers.
What do they do with a patient in intensive care?
They do everything that can stop the fatal decline in body functions, mainly these are multi-liter and many-hour droppers with various medications. In some situations, a subclavian catheter is installed, which allows not only to administer large volumes of fluid, but also to determine central venous pressure and take blood for analysis at any time. In some cases, for all manipulations, it is sufficient to place a catheter in the peripheral - ulnar vein.
In some cases, it is necessary to maintain adequate breathing with a ventilator, then a special tube is inserted into the trachea, and the patient is put into medicated sleep.
After operations on the gastrointestinal tract, a probe is installed through the nose, through which wound exudate and digestive juices produced in excess are removed.
After surgical interventions on the organs of the urinary system, a catheter can be installed in the urethra for better tissue restoration.
Each intensive care patient is connected to a monitor that informs about the respiratory and heart rate, blood pressure and oxygen concentration in the blood at the current time. At certain intervals, blood is drawn for tests.
In addition to medical procedures and infusions, the patient is given hygienic measures - treatment of the skin and mucous membranes, the “toilet” of the wound is performed - dressing, and of course, timely emptying of the bladder and intestines is monitored.
The order of the Ministry of Health requires turning the patient over in bed every 2 hours to prevent ischemia of soft tissues as a result of their compression by body weight, which threatens the development of bedsores. Bedsores are dead tissue and not only a source of toxic decay products, but also a gateway to infection. Intensive care staff often do not have the time to regularly turn patients over, nor the strength to shift large immobilized bodies, so modern intensive care units must have special anti-decubitus beds or functional beds that facilitate patient care.
How to prepare for surgery under anesthesia and why it can be bad after it
Depending on the type of intervention, you need to undergo prescribed examinations - usually blood tests, an ECG, and sometimes, for example, an ultrasound of the lower extremities, to exclude the presence of blood clots - and also stop drinking alcohol and taking certain medications for a certain time before the operation. If the test results satisfy the doctor, he will confirm the planned operation. In this situation, drugs with a mild effect are used and recovery from anesthesia is usually painless. It is worth considering that during the operation processes such as changes in blood pressure may occur - but the work of the anesthesiologist does not stop after the patient is put under anesthesia; During the entire operation, the doctor monitors the depth of anesthesia and brain activity. The so-called neuroprotection is also used - protecting nerve cells with the help of certain medications.
Karmanov notes that unpleasant consequences after recovery from anesthesia—memory impairment, absent-mindedness, hallucinations—usually occur during emergency operations when you need to act very quickly, for example, after a large loss of blood as a result of a car accident. In these cases, drugs with a hypnotic, that is, hypnotic, effect are used, which can give such side effects. With special care, the doctor should also select drugs for pain relief for those who have cardiovascular diseases, problems with the respiratory system, kidney failure, hormonal disorders and diabetes.
Can relatives not be allowed into intensive care?
The public has achieved the official right to have relatives visit a patient in intensive care, but the Ministry of Health has not yet prepared standard all-Russian rules for admission to the department, so at present everything depends on the attitude of the administration of the medical institution to this issue.
Many employees of public hospitals speak out against visiting the intensive care unit, as if relatives “bring the infection” and interfere with work, this is partly true, especially since an unconscious patient does not need the presence of relatives. Relatives are afraid that without their vigilant supervision, the patient may do something wrong or even harm. This, of course, is not true: intensive care unit staff are extremely interested in the patient’s speedy recovery and transfer to another department.
In private clinics, relatives are allowed into the ICU, at the same time showing sympathy for the misfortune and demonstrating therapeutic activity in the fight for the life and health of the cancer patient.
On the verge of mysticism
Denis Nikolaevich! I recently read the most interesting novel by Evgeny Vodolazkin “The Aviator”. Not a fantasy novel. The realities of the early and late nineties of the last century. Its hero Innokenty went through hellish torture during the years of Stalinist repressions in a concentration camp. He ended up in a special laboratory where prisoners (instead of death) were frozen. It remained frozen for decades. We learned how to defrost. Innocent was also unfrozen... According to his passport, he is almost a hundred years old. But in essence he was born again. He is young, he is an advertising hero, he is in love and loved, he is waiting for the birth of a child. He is recognized as man of the year. It’s just that the past doesn’t let go. He remembers the horrors of the camp, remembers the executioners. The main thing, and this is noticed by the doctor who observes and knows Innocent, his wife notices, and he himself: not only is it becoming more and more difficult to walk, his memory is fading, his consciousness begins to become confused. And this is irreversible: the process of death of body cells is underway.
I understand that “Aviator” is the author’s brilliant fantasy. But freezing is not akin to a coma? Don't you always come out of a coma? And if they go out, does she leave any traces? Does the person fully recover? How long can you be in a coma? Why is the patient sometimes put into this state? Finally, what is coma? There is no insurance against it.
Denis Protsenko:
Let me start with the fact that coma and cryotechnology (that same freezing) are fundamentally different things. Therefore, as a doctor and specialist in the field of critical care medicine, I will talk about the present and more studied. Coma is a complex disorder of important body functions. This is a pathological condition in which there is no consciousness and the patient lies with his eyes closed, despite various external stimuli. He does not open his eyes when he hears pain or shouts. And this is one of the main signs of coma. With closed ones at any depth of unconsciousness, that is, coma.
So he still hears and feels pain? Doesn't he just open his eyes?
Denis Protsenko:
Yes. This is, if you like, an axiom: a person in a coma always lies with his eyes closed. But much depends on the depth of the coma and its classification. There are several such classifications. The reason for the development of coma is also important. Most often, coma occurs as a result of acute cerebrovascular accident. And in young people, the cause is often traumatic brain injury or poisoning.
How long can a person be in a coma?
Denis Protsenko:
From a few minutes to decades. There are such isolated observations, even descriptions in specialized literature.
Do you mean and to whom General Anatoly Aleksandrovich Romanov, who was wounded in 1995? He has been in a coma for a quarter of a century.
Denis Protsenko:
Not quite in a coma! As far as I understand his medical history, Anatoly Alexandrovich began to emerge from his coma after two weeks. He began to open his eyes. However, coming out of a coma also goes through certain stages. Unfortunately, his recovery stalled at a very early stage and he is still in a vegetative state. He opens his eyes. But he has no other signs of higher nervous activity.
A person can be in a coma from a few minutes to decades
Does he have the so-called “locked-in man” syndrome? This is when a person lies motionless, but his gaze is fixed on external stimuli.
Denis Protsenko:
Indeed, the “locked-in person” syndrome is one of the phases of recovery from a coma. But as far as I monitor media data about General Romanov, he never reached this phase.
In addition to the “man locked up” phase, there is also a phase that you call the phase of gross psychoorganic disorders...
Denis Protsenko:
This is not what I call. This is a generally accepted classification. And it consists of a combination of three characteristics: sloppiness, gluttony and hypersexuality. It is believed that coma is a protective reaction of the body when the brain does not want to remember negative information when it wants to rest. That is why most patients who survived a coma and recovered consciousness do not remember this period. Unlike the hero of the novel Vodolazkin, with whom we began our conversation.
But since we remembered it, let’s continue. For those who are in a coma, for those who survived it, do some body cells die off? First of all, the brain?
Denis Protsenko:
It depends on the cause of the coma. If the cause was damage to the brain substance (trauma, cerebral hemorrhage), then the brain cells die. And in a coma, which is a consequence of poisoning, brain cells are restored.
Why are some patients put into a coma? And how is this done?
Denis Protsenko:
This is done with the help of medications. At one time they tried to treat mental illness this way. Now this has actually been abandoned.
But you can often hear from doctors that the patient was put into an artificial coma...
Denis Protsenko:
We use the term “induced coma” to explain to relatives of patients one of the methods for treating cerebral edema, which is essentially a deep, drug-induced sleep.
How long can it last? Does the brain and other organs of the body suffer?
Denis Protsenko:
This method of treatment is carried out only in an intensive care unit. The patient is under close supervision of medical personnel and special monitors. This guarantees a combination of effectiveness and safety of this treatment approach.
What about diabetic, hepatic coma?
Denis Protsenko:
The cause of coma may be metabolic disorders. And these disorders occur both in diabetes and liver diseases. Manifestations of the same coma are the same closed eyes and other clinical signs.
— Can a person who has survived a coma recover completely?
Denis Protsenko:
I will answer as a person who survived a coma 20 years ago as a result of a car accident: it did not stop me from giving you this interview today.
When can relatives not be allowed into intensive care?
Relatives are not allowed in if there is a threat to the health of an intensive care patient, that is, with signs of an infectious disease, including a runny nose. The ICU patient is weak and it is extremely difficult for his body to resist infection.
Children are not allowed and there are enough reasons for that. Firstly, a child with an infection does not realize that he is not healthy, especially since his activity decreases little even at high temperatures, so parents may not notice the onset of the disease. Secondly, he may touch tubes and medical devices with his hands, run or move awkwardly, disrupting the operation of equipment and disturbing personnel. Thirdly, children take death lightly, but the shock of what they see in the hospital will disrupt the child’s psychological comfort for a long time.
When performing medical manipulations and procedures, relatives are also not needed, it is unpleasant for them to see it, and the staff feels psychological pressure.
The presence of several relatives in the intensive care unit is excessive; one or two close people for a short time is quite enough to maintain the spirit of a cancer patient; do not forget that it is hard for him, he gets tired very quickly. Sitting all night long is not good for anyone, healthy people are exhausted, and the patient is simply not aware of round-the-clock vigil at the bedside.
What is sedation and why is it needed?
Sedation is the intravenous administration of non-narcotic hypnotics that induce shallow sleep. It is used for various types of endoscopy, for colonoscopy, but most often in the dentist’s office. When a person is dozing, light contact with him is possible: vital reflexes and body functions are preserved and the patient responds to the doctor’s requests, for example, to turn his head or “bite a piece of paper.” Sedation is accompanied by local anesthesia to numb the work area itself.
According to anesthesiologist Yuri Timonin, propofol does not cause side effects, and the substance itself has a short-term effect and is quickly eliminated from the body. The big advantage of sedation is that it allows you to increase the treatment time to 3.5–4 hours, without stress for the patient, with easy awakening and no unpleasant consequences after it. Doctors recommend this method for arterial hypertension and angina pectoris, as well as for those who are afraid of dentists to the point of losing consciousness.
How should a relative behave in intensive care?
- You must be in clean clothes, a medical gown, clean hands, shoe covers on your feet, and a mask on your face.
- Perfume odors are irritating, since in a serious condition the sense of smell changes; you should not perfume yourself on this day.
- Phone beeps must be turned off, or better yet, all gadgets must be turned off. Maintaining silence is mandatory; loud sounds disturb staff and cause stress in patients.
- Without the permission of the staff, you cannot perform any actions with the patient: turn over, sit up, put on your feet, take you to the toilet, change clothes, and so on.
- You cannot feed - the patient receives a specific and, as a rule, very strict diet or is generally on intravenous nutrition.
- You should not give medications, homemade decoctions, pharmacy tinctures, dietary supplements and nutritional supplements previously prescribed for chronic diseases. Biological supplements may not be compatible with the medications the patient is receiving. Everything must be agreed with the attending physician.
A sick person and a patient in the intensive care unit are two very different things; some cannot recognize their loved one, his appearance changes so much. Not only because of the tubes and wires, but the tissues swell, the eyes become sunken, and the unconscious state changes facial features. Many are shocked by what they see; one must be prepared for an unpleasant experience or not enter the intensive care unit.
In the Euroonko intensive care unit they always help patients and support the spirit of relatives. We know what needs to be done and when, you can be confident in us. We do not guarantee immortality, but we help to live without suffering.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Bibliography
- Clinical recommendations. Anesthesiology and resuscitation / ed. Zabolotskikh I.B., Shifmana E.M. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2016.
- Moroz V.V., Bobrinskaya I.G., Vasiliev V.Yu. and others/Cardiopulmonary resuscitation// M.: FNKTs RR, MGMSU, NIIOR, 2017.
- Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 15, 2012 N 915n “On approval of the Procedure for providing medical care to the population in the field of oncology”
- Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated July 4, 2017 No. 379n “On amendments to the Procedure for providing medical care to the population in the field of oncology, approved by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 15, 2012 No. 915n”
Epidural anesthesia: pros and cons
Thanks to epidural anesthesia, when an anesthetic is injected into the space along the spinal canal, contractions become less painful and labor is noticeably calmer - while the woman is conscious. With a good dose calculation, sensitivity disappears almost only in the pelvic area, but sensations in the legs and the ability to move them remain. This anesthesia is also called walking epidural, although in fact you won’t be able to walk - your legs will be weak, and sensors or catheters on different parts of the body will not allow you to go far. The psychological aspect is also important: when you know in advance that it won’t hurt, it’s much easier to relax and not worry.
According to Oleg Karmanov, with epidural anesthesia already performed, it is faster and easier to proceed to an emergency caesarean section, if necessary: you will not have to waste time on pain relief. But you can’t always rely on epidural anesthesia; at a certain stage of labor it is already too late to perform it. The method has a number of contraindications, including intervertebral hernia and serious circulatory and coagulation disorders. Dangerous complications of epidural anesthesia are extremely rare.
Degrees of coma
To simplify differentiation, doctors distinguish the following degrees of coma during strokes:
- 1st degree . It is determined by lethargy or loss of consciousness with preservation of reflexes. This is mild damage to brain cells during a stroke and slight depression of the functions of the nervous system. At the same time, skin reflexes are weakened and muscle tone is increased;
- 2nd degree . It is diagnosed by the patient falling into deep sleep, lack of response to external stimuli, skin reflexes and pain;
- 3rd degree . It is caused by extensive hemorrhage and is determined by the absence of many reflexes, consciousness, and the reaction of the pupils to light;
- 4th degree . It is not comparable to life, as it is characterized by the absence of spontaneous breathing, a sharp decrease in pressure and hypothermia. All reflexes are absent. A patient in this stage of coma has virtually no chance of returning to normal life.
Main consequences of the condition
There are several outcomes that can result from coma after a stroke. Firstly, the patient will return from a dangerous condition with (in rare cases, complete) restoration of vital functions. Secondly, death as a result of brain death, which can occur due to severe hypoxia.
Thirdly, a way out of the situation without restoration of functions, with preservation of paralysis and paresis, as well as with impaired memory and intelligence. Fourthly, the transition to a vegetative state with the preservation of limited reactions to stimuli, while the person cannot speak or think.
Proven fact: full restoration of health is possible only in 10% of cases.