A high pulse wave velocity in patients with COVID-19 may serve as a marker of a higher risk of death, a study by European scientists has shown. This indicator reflects the condition of the blood vessels. Pulse wave speed is usually higher in older people and hypertensive patients, plus it increases in a state of acute inflammation associated with coronavirus infection. It is likely that measuring this parameter in patients with COVID-19 may become an additional diagnostic measure that doctors will resort to in special cases, experts believe.
On the crest of a wave
Conspiracy strategy: coronavirus disguises its proteins as human ones
How does this affect the immune system's response?
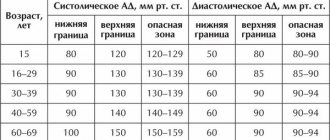
The high speed of pulse wave propagation through the arteries in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 may serve as a marker of a higher risk of death. This was shown by a study by a group of scientists from the UK and Italy. According to the work, the probability of death is considered increased when the pulse wave speed is above 13 m/s. It is believed that for young and middle-aged people the normal rate is 5.5–8 m/s. With age, the elasticity of the artery walls decreases and the speed of the pulse wave increases. Scientists used the indicator to predict the outcomes of coronavirus patients. The model also took into account the gender and comorbidities of patients. By taking into account the pulse wave speed, the accuracy of the forecast increased from 76.4 to 84.5%, the study indicated.
“The speed of the pulse wave is the speed at which increased pressure spreads in the vessels, caused by the ejection of blood from the heart during its contraction,” explained Vasily Stepnadze, an ultrasound diagnostics doctor at the SM Clinic. — An increase in this indicator, like high blood pressure or cholesterol levels, is a risk factor for cardiovascular complications.
A matter of the heart
Photo: IZVESTIA/Dmitry Korotaev
According to the specialist, the speed of the pulse wave depends on the elastic properties of the blood vessels. The stiffer their walls, the higher the indicator.
Fear and risk: 13% of Russians are genetically prone to severe COVID-19
Why are such people twice as likely to be on ventilators and have an increased likelihood of contracting coronavirus?
The study by European scientists involved 1,671 people. 737 of them were admitted to hospitals in Newcastle and Pisa with a diagnosis of COVID-19. 184 people died within 28 days of hospitalization. It turned out that the pulse wave speed in infected people was higher than in healthy people, on average by 1.89 m/s. For those who died from coronavirus, the rate was higher than for those who survived the disease, also by 1.89 m/s. According to scientists, an increase in pulse wave speed by 1 m/s increases the chances of death by 14%.
As experts noted, this indicator reflects the condition of blood vessels, which is influenced by age and blood pressure. And old age and hypertension are the main risk factors for COVID-19. According to the authors of the study, the speed of the pulse wave can be called a cumulative value that reflects the effect on the body of age, diseases of the cardiovascular system and disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels. In addition, pulse wave speed increases in a state of acute inflammation caused by coronavirus, the study showed.
Bad news
Almost all advanced programs and procedures are used in Kuban, including surgical treatment, up to heart transplantation
Photo: Evgeny Pereverzev, Kommersant / buy photo
Almost all advanced programs and procedures are used in Kuban, including surgical treatment, up to heart transplantation
Photo: Evgeny Pereverzev, Kommersant / buy photo
Mortality from CVD in Russia is growing every year, and the disease is becoming younger. It is noted that even young people aged 30-35 are experiencing problems with the cardiovascular system. Moreover, every next 10 years of a person’s life, starting from the age of 30, the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases doubles.
What and how to treat
In the Krasnodar region today, almost all advanced programs and procedures are used, including surgical treatment, up to heart transplantation.
“The region performs surgical correction of most congenital and acquired heart defects in adults and children, heart valve replacement, including minimally invasive, gentle procedures, while in children defects are detected at the stage of intrauterine screening,” says Elena Demyanovna, a cardiologist at the Zdrava clinic. Alexandrova.— In the region, surgical interventions on the vessels of the heart are performed through open (coronary artery bypass grafting) and intravascular (coronary angioplasty) approaches, including combined interventions. Operations are being carried out to radically treat cardiac arrhythmias.”
Harmonious work
The success of cardiologists in the Krasnodar region is facilitated by well-coordinated interaction with ambulance: if a patient with a heart attack is in a remote area, he is given thrombolysis at the stage of delivery to the cardiovascular center, so that upon arrival at the center he can immediately undergo angiography.
“The second part of the vascular program is medical examination and identification of patients at an early stage, when they have not yet reached a heart attack,” continues the chief cardiologist of the regional clinical hospital named after Ochapovsky. “This is also a huge job: the creation of offices and primary prevention departments in clinics of municipalities of the region . The medical prevention center with its network created in the districts is very helpful here.”
What depends on us
Risk factors for the development of CVD are divided into three groups: fatal, avoidable and social. We cannot influence the first ones: gender (men are more susceptible to cardiovascular diseases than women), age (over 55 years for men, over 65 years for women), early menopause in women (up to 40-45 years), family history predisposition. As for the second ones, they can be eliminated. “Increased levels of blood pressure, cholesterol, homocysteine, impaired carbohydrate metabolism, excess weight, sedentary lifestyle, stress, smoking and alcohol consumption contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, endothelial dysfunction and, as a consequence, myocardial ischemia - these factors are among those that we we can successfully influence,” explains cardiologist at the “Be Healthy” clinic, candidate of medical sciences Maria Valeryevna Aristova. As for social risk factors, they are theoretically conquerable, but only through collective efforts: these are urbanization, industrialization and economic backwardness of the population.
When is it time to go to the doctor?
There are signs that require immediate consultation with a cardiologist. These are compressive pain in the chest, a long recovery period after habitual exercises, arrhythmia, high blood pressure, shortness of breath, and attacks of severe weakness.
“In addition, it is worth discussing with a cardiologist the range of individual modifiable factors,” says City Clinic cardiologist Elena Leonidovna Shukhardina. “For example, do you need to constantly take pills if you have high blood pressure? Is it possible to change physical activity and lose weight? Do you really need to drink a lot of water or aspirin? Is it worth following the example of friends who are taking a cholesterol drug brought from a trip abroad, or can you do without pills altogether? All such questions can be answered by being examined by a cardiologist.”
The advisability of early contact with a doctor speaks for itself: with primary prevention, the risk of fatal complications is reduced by 75-85%.
What to do
Prevention of CVD can be primary or secondary. Secondary, called medicinal, is carried out differentially with groups of patients with confirmed cardiovascular diseases. Its main goal is to prevent relapses of diseases and the development of complications in people with existing risk factors, reduce morbidity and mortality from these diseases, and improve the quality of life of patients.
Primary prevention is exactly what those who are still healthy need. It is aimed at people at risk in whom clinical manifestations of the disease have not yet been observed, and consists of observing a work and rest schedule, increasing physical activity, giving up alcohol and smoking, and a balanced diet.
Dangerous
A risk factor for the development of CVD may be a breathing disorder such as OSA - obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. The first sign of this condition is snoring. OSA can become one of the main causes of heart attack, stroke, and arterial hypertension. “To identify this condition, a number of diagnostic procedures are used,” explains Vasily Evgenievich Myazin, a somnologist at the TS Clinic, a functional diagnostician of the highest category. “These are questionnaires, respiratory monitoring, and sleep endoscopy. The examination allows you to determine the cause of snoring and the severity of the collapse of the upper respiratory tract during medicated sleep. After the examination, I explain to the patient all the nuances of his condition and determine further tactics for his treatment. If the condition is uncomplicated, or if there is a slight deterioration in night breathing, a few simple measures are usually sufficient.”
There is only one center for the diagnosis and treatment of sleep disorders in Krasnodar; it operates on the basis of the TS Clinic.
Men need to monitor the state of their cardiovascular system from the age of 30
Photo: Alexander Chizhenok, Kommersant
Men need to monitor the state of their cardiovascular system from the age of 30
Photo: Alexander Chizhenok, Kommersant
Good news
In Kuban, mortality from diseases of the circulatory system is decreasing. According to statistics available to Scientific Research Institute-KKB No. 1, the coordinator of the implementation of the federal project “Combating Cardiovascular Diseases” throughout the region, 492 out of one hundred thousand people die in the region per year, which is 3% below the target set by the national project. Hospital mortality from myocardial infarction has decreased, and good results have been achieved in terms of reducing deaths from acute cerebrovascular accidents.
Who needs diagnostics
Everyone and always - that is, regularly.
Today, cardiologists have at their disposal effective methods of clinical, instrumental and laboratory diagnostics that allow them to identify risk factors and act on them in a timely manner. “It is imperative to examine glucose, creatinine, lipid spectrum, transaminases, uric acid in the blood once a year, perform an ECG (and for those involved in fitness and cardio training - an ECG with stress, 24-hour heart rate monitoring), and occasionally measure blood pressure in the morning after waking up , advises City Clinic specialist, cardiologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences Elena Leonidovna Shukhardina.
“The mandatory minimum is annual blood tests, including cholesterol and glucose levels, blood pressure monitoring, as well as an ECG,” says cardiologist at the WMT High Technology Clinic Elizaveta Andreevna Nemtsova. “Based on the results, doctors can prescribe more extensive examinations: ECG with physical activity, 24-hour ECG and/or blood pressure monitoring, transesophageal cardiac stimulation, ultrasound examinations of the vessels of the neck or extremities (to look for atherosclerotic plaques), heart (to assess valve function and heart function) or referral to a cardiovascular center for such diagnostics , such as computed tomography of the coronary (heart) vessels or coronary angiography.”