RW blood test - what is it?
Blood test RW
- This is a serological test for the detection of antibodies to Treponema pallidum.
The methodology for conducting this study was proposed by August von Wasserman at the beginning of the 20th century, since then the analysis has been named after him - the Wasserman reaction
(RW).
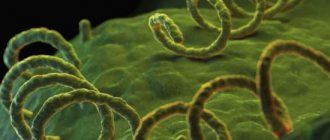
Treponema pallidum is the causative agent of syphilis.
Syphilis is a classic sexually transmitted disease. Transmitted primarily through sexual contact. You can also become infected through blood. There is a possibility of infection through household means, since Treponema pallidum can be contained in undried saliva and other body secretions.
During the course of the disease, primary, secondary and tertiary syphilis are distinguished.
Primary syphilis is characterized by the appearance of a specific ulcer (chancre) at the site of infection (this can be the genitals, oral or rectal mucosa). A little later, the nearest lymph nodes enlarge - inguinal when the genital organs are affected or submandibular when the oral mucosa is affected. The ulcer heals on its own 3-6 weeks after it appears.
Symptoms of secondary syphilis are observed 4-10 weeks after the onset of the ulcer. These include a pale rash all over the body (including the palms and soles), headache, general malaise, and fever (flu-like). Lymph nodes throughout the body enlarge. Then the symptoms disappear, returning from time to time.
Tertiary syphilis is characterized by damage to the nervous system, bones and internal organs. It occurs many years after infection in the absence of proper treatment for the disease.
Thus, a person with syphilis may have long periods during which there are no symptoms. Much depends on the state of the body's immune system. Sometimes, upon contact with an infection, the disease does not develop, but the person becomes a carrier of the infection (the so-called asymptomatic carrier).
In these situations, an RW blood test is the only way to detect the presence of the syphilis pathogen in the body. The analysis also makes it possible to determine how long the carriage of syphilis lasts.
What is RW
For many patients, doctors prescribe blood donation for RW. The analysis is mandatory, so it is prescribed to healthy patients who come to a medical facility with symptoms of an infectious disease or are admitted to a hospital for treatment. The shelf life of the results is no more than 30 days if the person has no signs of infection. This type of diagnosis has been used for more than a century since the famous German immunologist proposed it to detect syphilis.
- ACCP for rheumatoid arthritis: norm, analysis, interpretation
Modern doctors take blood for RW to identify an infection in a person, and this does not depend on the reason for the patient’s visit to the hospital. What is the Wasserman reaction? This is a rapid blood test in which material taken from the patient is tested with a special antigen. The RW test gives a positive result when nonspecific antibodies enter into a microreaction with lipids.
When is an RW blood test necessary?
The RW blood test is a standard procedure to confirm the absence of the syphilis pathogen in the body. It is necessary for everyone whose profession involves contact with people or food - doctors, cosmetologists, hairdressers, cooks, etc. An RW blood test is also one of the mandatory procedures during pregnancy. It is carried out upon registration and in the third trimester (at the 30th week).
An RW test can also be prescribed when symptoms appear that make one suspect the possibility of syphilis infection:
- rashes on the skin and mucous membranes of unknown origin;
- enlarged lymph nodes (primarily inguinal);
- ulcers on the mucous membrane and discharge from the genitals.
It is recommended to take an RW test if you have casual sexual contact. However, it must be borne in mind that the analysis will be indicative only 5-6 weeks after sexual intercourse. Before that, the analysis may be negative even if infection occurs.
When is a test for Treponema pallidum prescribed?
Syphilis is a disease caused by Treponema pallidum.
The microorganism belongs to bacteria.
It is distinguished by its ability to become chronic and affect not only the genital organs, but also any systems of the human body.
Not all people are tested for this pathology in everyday life.
However, doctors identify several categories of patients for whom examination is strongly recommended.
Among them:
- women planning a pregnancy or already carrying a child (the examination is aimed at early diagnosis of the disease, preventing the birth of a baby with congenital syphilis)
- patients in whom surgical intervention is planned in the near future to eliminate any other pathological conditions
- people who have been imprisoned in places of deprivation of liberty, even for short periods
- people who need to exclude all infectious diseases to make a correct diagnosis of a different nature
- applicants for a vacant position in a kindergarten, school, food production and other similar enterprises where the pathogen can be spread through contact and household contact
- blood donors who regularly donate their blood or its elements to blood banks to further help people
- people who are prone to drug addiction of any form (where there are drugs, there is often unprotected sex, which contributes to the spread of treponemes in the population)
In some cases, the study is recommended for preventive purposes.
For example, you should not refuse analysis if a person is inclined to have a wild sex life.
After contact with an unfamiliar partner, if he was not protected by a condom, biological material is also required to be provided to ensure there is no infection.
In most cases, testing for syphilis performs a screening function.
This means that the initial assessment of the results allows us to identify patients who only have a possibility of the existence of a microorganism in the body.
In the future, a more detailed examination of patients at risk is carried out.
After which the final diagnosis is established.
Interpretation of RW blood test results
The result of the RW blood test may be:
Wasserman reaction
- negative. This means that antibodies to the causative agent of syphilis have not been detected. In most cases, such a result indicates that there is no Treponema pallidum in the body. However, with primary and tertiary syphilis, there may be cases of negative test results. Therefore, to be sure that you are not a carrier of the disease, the test must be taken several times.
- doubtful (about);
- weakly positive (“++”);
- strongly positive (“+++”).
A questionable and weakly positive reaction is also possible in the absence of syphilis infection. Thus, in 1.5% of pregnant women an erroneous weakly positive reaction is detected. A false positive RW result can be observed after vaccination, as well as with tuberculosis, diabetes, cancer, pneumonia, and viral hepatitis.
If there is a possibility of a false positive result, the test should be repeated.
False positive reaction
The result of the study is based on the production of antibodies by the human immune system. The analysis should show their presence in the patient's blood serum. A positive reaction indicates that the body is affected by an infection. However, RW analysis often produces unreliable data. This is called a false positive reaction. Reasons may include:
- oncological diseases;
- pregnancy;
- the patient had syphilis less than 12 months ago;
- viral hepatitis;
- alcoholism;
- diabetes;
- drug addiction;
- neglect of the rules of preparation for analysis;
- poor quality of research.
RW during pregnancy
All women who are preparing to become mothers are prescribed RW analysis to detect congenital syphilis and as a standard method for detecting various infections. However, the pregnancy period is different in that women's hormonal levels change dramatically, which can cause a false positive result. To make an accurate diagnosis, a series of repeated tests are performed.
In inflammatory processes
These Wasserman reactions are not used by modern doctors as a single marker for identifying syphilis, because this method is characterized by false negative and false positive results. For example, during inflammation, the body actively fights the disease and produces antibodies, which are detected by RW analysis. To more accurately detect syphilis, the patient is prescribed a treponemal RPHA test.
What to do if the RW result is positive?
If a positive RW result is obtained upon repeated analysis, the presence of the syphilis pathogen in the body is considered confirmed. In this case, it is necessary to urgently begin treatment.
Syphilis is highly treatable, especially in the early stages. The persistence of the pathogen in the body threatens the transition of the disease to the active stage and the development of manifestations of secondary and tertiary syphilis. The presence of Treponema pallidum in the body of a pregnant woman threatens not only her health, but also the health of the child: infection of the fetus, as a rule, leads to serious developmental disorders. Death is also possible.
Where can I get an RW test in Moscow?
If you need to do an RW blood test in Moscow, contact Family Doctor JSC. At Family Doctor you can get tested for RW on weekends and holidays.
It is possible to donate blood for RW at any of our clinics. Obstetricians-gynecologists, dermatovenerologists and urologists of the “Family Doctor” are always ready to advise you on the results of the analysis and, if necessary, prescribe an effective course of treatment.
Sign up for diagnostics Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Indications for analysis
Medical workers, employees of cosmetology and dermatology offices, and food workers are required to donate blood for RV. Other indications for a specific test are:
- pregnancy planning;
- preparation for operations;
- unprotected sex (especially with a new partner);
- suspicion of sexually transmitted infections;
- blood or sperm donation;
- the appearance of an incomprehensible rash on the mucous membranes and skin, discharge from the genitals, disruption of the menstrual cycle in women;
- visible enlargement of lymph nodes (especially in the groin area).