Vegetative-vascular dystonia: to treat or not to treat?
The disease itself, as well as its symptoms, have been known for a long time.
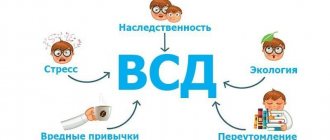
VSD in adolescents is successfully diagnosed, but an unambiguous method of treating the disease has not yet been found, since doctors have not yet been able to fully decipher the pathology itself. So far, doctors have more complete information only about the peripheral effects of neurological problems in the regulation of cardiac and vascular activity. However, it is still not clear how infections influence the onset and course of the disease.
At the moment, most experts are inclined to consider the main and most common cause of vegetative-vascular dystonia in adolescents to be stress.
The treatment method depends on the cause of the disease. Since stressful situations are considered the main ones, drug treatment for VSD is practically not carried out. Prevention measures and treatment are limited to reducing the number of stressful situations, improving the general emotional state and redistributing mental stress.
However, with exacerbation of vegetative-vascular dystonia, it is possible to use medications in therapeutic doses. Such methods stop attacks of vascular disorders and normalize the teenager’s condition.
The flexibility and adaptability of a teenager’s nervous system is one of the reasons why doctors look at the manifestation of symptoms of the disease without much alarm. In young children, the processes occur even faster and easier, therefore, the prognosis is usually favorable.
Prevention of vegetative-vascular dystonia in children and adolescents
Vegetative-vascular dystonia in adolescents and young children can be practically asymptomatic, especially if adults pay due attention to the prevention of VSD.
We are talking about leading a healthy lifestyle, playing sports at both an amateur and professional level, diet, as well as sleep and wakefulness. For better vascular condition, it is necessary to diversify your diet by adding more fiber and vitamins, as well as foods containing potassium and magnesium. But it is better to exclude fatty and fried foods or at least reduce their consumption to a minimum. The reason for avoiding thermally processed fats is the risk of developing atherosclerotic processes. Naturally, during this period it is best to increase the child’s time in the fresh air.
Symptoms
Manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia in children and adolescents are diverse and diverse; in fact, any symptoms of deterioration in general physical and psycho-emotional well-being can fit under this concept. In total, about 30 different syndromes have been described based on more than 150 complaints.
Basically, symptoms of VSD in children and adolescents include disorders of the central nervous system, cardiovascular system, respiratory system, and gastrointestinal tract. The most common signs were:
- increased fatigue;
- sleep disorders;
- dizziness;
- cardiopalmus;
- arrhythmia;
- changes in blood pressure;
- headache;
- diarrhea;
- feeling of lack of air;
- increased body temperature without signs of infection;
- change in pupil size;
- muscle and joint pain;
- chills;
- hand tremors;
- increased sweating;
- cold extremities;
- pain in the heart area.
In adolescence, in boys and girls, VSD often manifests itself as increased anxiety, unreasonable fears, and sudden changes in mood. In some cases, parents note excessive emotionality, violent expression of feelings, and sometimes unmotivated aggression and anger.
Changes in body temperature
As noted above, vegetative-vascular dystonia in adolescents has a huge list of different symptoms. However, an important indicator that the disturbances are not caused by more serious diseases requiring immediate medical attention can be the absence of fever.
The combination of several common symptoms of VSD and elevated temperature indicates the presence of an infection or a source of inflammation in the body. Naturally, only an experienced doctor can diagnose an infection and promptly begin treatment of an infectious disease. Therefore, at the first signs of an increase in temperature, you should seek medical help rather than try to relieve the symptoms on your own.
Classification of autonomic disorders
Depending on the intensity, origin, and nature of autonomic disorders, several subgroups of VSD are distinguished.
Depending on the cause, psychogenic, hereditary, infectious and dyshormonal forms of vegetative-vascular dystonia are distinguished; in some cases, children have a mixed type of VSD, which is characterized by a combination of several causes of symptoms.
According to the nature of the disorders, the syndrome is:
- sympathicotonic, when the disorder is expressed in restless, overly emotional and even aggressive behavior;
- vagotonic, which manifests itself in the form of chills, increased or decreased body temperature, dizziness, sensation of a foreign body in the throat;
- combined, when there is no clear predominance of certain symptoms.
There are also systemic, local and generalized forms of pathology according to the degree of prevalence of disorders. According to the severity of VSD disorders, there are mild, moderate and severe forms.
Methods of drug treatment of VSD in adolescents
The main way to relieve painful conditions associated with exacerbation of vegetative-vascular dystonia in adolescents and young children is to reduce stress levels and develop stress resistance as a method of resisting neuroses. Despite this, for more complex manifestations and symptoms such as regular headaches, fainting, sleep disorders, lack of appetite, tearfulness and irritability, decreased emotional background, the doctor may prescribe a course of the following medications:
- sedatives that calm the nervous system;
- antidepressants that improve the overall emotional state;
- complexes of vitamins and minerals that strengthen the body as a whole.
Treatment is carried out only under the supervision of a neurologist and only after an examination that can reveal abnormalities in the condition of the circulatory system.
With age, most symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia in adolescents go away on their own. However, one cannot rely only on this. By using the full range of preventive methods, you can reduce the need for treatment or make it more gentle, but you cannot completely eliminate the use of medications or follow general recommendations. General recommendations include:
- timely diagnosis and treatment of any infectious diseases;
- establishing and maintaining a daily routine;
- proper distribution of the load over a certain period of time to reduce fatigue;
- regular walks and outdoor activities;
- reducing time spent on a computer, tablet, phone;
- high-quality and regular massage - therapeutic and relaxing;
- monitoring intracranial pressure and the condition of the spine, including posture correction.
Exacerbation of vegetative-vascular dystonia in adolescents can cause temporary exemption from physical education, as well as a reason for registering with a neurologist. In addition, regular examination helps to identify VSD in adolescents during the “lull” period and promptly prescribe treatment for the vascular system.
How to recognize a predisposition to VSD in children
A child with autonomic dysfunction is restless, shows increased anxiety, and quickly gets tired of outdoor games and noise.
Frequent awakenings at night in children or drowsiness during the day, bloating, sweating, excessive thinness or obesity, skin rash after stress, can also be a manifestation of a tendency to dystonia.
Children with a hereditary predisposition to VSD often suffer from functional disorders of the heart, stomach, intestines, and gall bladder. This is not associated with changes in the organs themselves, but causes quite noticeable symptoms. The main effect in the treatment of children with functional disorders is provided by sedatives and amino acids.
Teenagers with a tendency to dystonia experience hormonal changes very rapidly. Emotions often affect their physical condition, they quickly become exhausted. At this age, functional disorders of the internal organs can become the basis for the development of the disease.
Principles of prevention of vegetative-vascular dystonia
- Measured rhythm of life. This means that the child needs a daily routine, but it is important not to burden his life with a large number of events. There is no need to follow a rigid schedule, but key events should be predictable.
- Sufficient emotional communication with loved ones . In the first years of life, the intellectual and physical development of the child depends on emotional communication with the mother. The quality of contact and parental involvement in communication is more important than the amount of time spent together. This lays the foundation for psychological and neurological health.
- Physical activity that is feasible for a child brings him pleasure. Stimulation of muscle fibers and receptors of the musculoskeletal system helps regulate the activity of the sympathetic and parasympathetic departments. Professional sports is not a measure to prevent VSD.
- Any activity that brings psychological relief . Active recreation, communication with friends, pursuit of interests.
- A sufficient amount of protein and fat in the diet of a child of any age helps maintain the health of the peripheral nervous system and improves its adaptive properties.
- From 12 years of age, Eltacin® . This is a drug made from the amino acids glycine, cystine and glutamic acid, it can be used for a long time and does not accumulate in the body. The pharmacological action of Eltacin® is based on improving cellular respiration and increasing the amount of endogenous glutathione, which is a strong antioxidant.
Diagnostics
Determining VSD is a serious multi-step process, since the syndrome is established by exclusion. The specialist should carry out a number of diagnostic measures and consider or reject other possible problems. Only after this a set of therapeutic actions is selected.
A neurologist conducts a preliminary examination of the baby and then refers the teenager or infant to other specialists. Such measures are necessary to exclude any other organic and psychopathic diseases.
Diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia is carried out in 3 stages:
- Anamnesis collection. Developmental features are clarified, and the presence of bad habits in the baby or adults during gestation is established. Hereditary factors, as well as prenatal development, are important factors in the development of the problem.
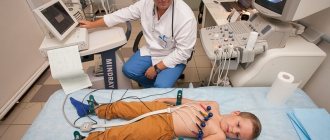
- Attention is focused on the functioning of the central nervous system. The child is prescribed additional hardware tests - EEG, ultrasound, ultrasound.
- Based on the data obtained, experts exclude the presence of possible pathologies characterized by similar discomfort.
In the absence of pathological physical and mental disorders, a diagnosis of VSD is established. Based on the severity of the condition and the symptomatic picture, comprehensive treatment measures are carried out. Therapy takes a long time - more than 1.5–2 months.
Diagnosis of VSD
The initial stage of the examination is the collection of a detailed medical history. The doctor needs to know almost everything about the little patient:
- age;
- features of intrauterine development, birth and the first years of life;
- past illnesses and surgeries;
- frequency of diseases per year;
- completed treatment;
- environmental situation in the place of residence.
The specialist needs to painstakingly collect all available information, including observations of parents, complaints of the child himself, and lifestyle features.
After collecting an anamnesis, a general examination is carried out, during which the doctor assesses the condition of the skin, mucous membranes of the nose and oral cavity, lymph nodes and other visible structures.
The next stage of diagnosis is laboratory and instrumental examination methods. Depending on the direction of symptoms and complaints, the following are performed:
- a set of laboratory tests of blood and urine;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI or CT;
- breath tests;
- allergy tests;
- EchoCG and ECG;
- electroencephalography;
- fluoroscopy.
Additionally, the attending physician can refer the child to a consultation with an ophthalmologist, surgeon, urologist, gynecologist, or otolaryngologist.
conclusions
The main reason for the development of dystonia is a violation of the autonomic system, which manifests itself in incoordination of the nervous, respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and urinary excretory systems. Often occurs against the background of endocrine, cardiovascular and neurological diseases. In children, VSD can be hereditary or caused by congenital pathology. Ignoring the first signs can provoke the development of a more serious psychosomatic illness. Therefore, if characteristic symptoms appear, you should contact a pediatrician or pediatric neurologist.
Prevention of VSD
General strengthening measures, timely vaccination, and prevention of potential risk factors will help prevent the occurrence of vegetative-vascular dystonia in childhood and adolescence. Experts recommend not overloading young children with excessive activities, and providing teenagers with comprehensive assistance in their studies and creativity.
It is important to closely monitor the child’s health, not to try untested or questionable methods in the child’s therapy, and not to give narrow-spectrum drugs as self-medication.
If you suspect VSD, contact a professional: our specialists will find the cause of autonomic disorders, select an individual treatment regimen and corrective techniques, taking into account all the characteristics of your child.