Vegetovascular dystonia (abbreviated as VSD), along with scoliosis and flat feet, is consistently among the Top diseases with which conscripts try to achieve exemption from conscription.
At the same time, some manage to be released from military service with this diagnosis, while others are happily recognized by the military registration and enlistment office as fit and taken into the army. The situation around this disease is ambiguous; conscripts often do not understand what they can count on at the military registration and enlistment office, having been diagnosed with VSD. So a detailed article on the topic of dystonia has been asking for a long time.
Complex form of VSD
The decision to serve in the army is made by a special military medical commission. She also issues a conclusion - whether the conscript is fit or submits a petition for release. The basis for this is the presence of specific diseases. For example, neurosis and army are compatible concepts, since the illness is not serious. The VSD is not on the 2016 list, so they can take it into service.
The nuance is that the neurotic syndrome itself consists of dozens of concomitant diseases (hypertensive and vegetative manifestations, etc.). Vegetative-vascular dystonia disrupts the functioning of many organs, as well as the nervous, circulatory and digestive systems. Severe symptoms of diseases complicate the course of the syndrome and lead to complications that contribute to the emergence of specific diseases.
Reviews
Dear readers, was this article helpful? What do you think about the diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia and military service? Leave feedback in the comments! Your opinion is important to us!
Andrey
“With vegetative-vascular dystonia, getting category “B” is unrealistic. It’s faster to serve than to prove the severity of the disease.”
Oleg
“I have had VSD since I was a teenager. Frequent headaches and weakness. I went through all kinds of examinations, no pathologies were found. They write in conclusion - healthy. In the army I often felt unwell, but I served.”
Military medical examination
Generally, conscripts are released from service due to cardiac or circulatory problems. The diagnosis and category of the disease are indicated in the conclusion. Are people with mixed military forces accepted into the army?
Yes, but if some of the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia are in the acute stage, then they are classified as a separate pathology (for example, astheno, hypertension). And if the disease is among the grounds for exemption from service, the military medical commission issues an appropriate conclusion.
Do they take into the army with VSD? Any disturbances in the functioning of the body are recorded by military doctors. If deviations from the norm are detected, written notes are taken. Then the doctor sends the conscript for examination. If the diagnosis is not on the list, the conscript will be recruited.
Vegetovascular dystonia general concepts
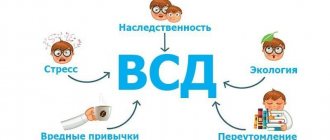
VSD is a polyetiological syndrome, which is characterized by dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. The term VSD is outdated; in the International Classification of Diseases it is indicated as somatoform autonomic dysfunction of the nervous system - code F 45.3 [4]. Autonomic disorders are secondary, occurring against the background of mental, somatic diseases, with organic damage to the central nervous system, due to hormonal imbalance in adolescence, etc. In some cases, vegetative-vascular dystonia is an integral part of other, more complex diseases:
- hypertension, hypotension;
- cardiac ischemia;
- endocrine disorders, thyroid diseases.
VSD, as a secondary symptom, manifests itself in mental, nervous, and depressive disorders. The true cause of the pathology is unknown. Presumably – abnormal intrauterine development.
Factors influencing the occurrence of pathological processes:
- physical, emotional fatigue;
- frequent or prolonged stressful situations;
- chronic infection in the body - caries, tonsillitis;
- injuries;
- diseases of the endocrine and nervous system;
- intoxication;
- bad habits – alcohol, smoking;
- violation of sleep and rest patterns;
- unfavorable working conditions, excessive noise;
- poor nutrition.
Symptoms are of two types - general malaise, complaints about the functions of a particular organ. The psychological painful state is combined with physical discomfort. The main symptoms of VSD:
- increased sweating;
- trembling of limbs;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- chronic fatigue;
- lack of energy;
- increased heart rate, arrhythmia;
- dyspnea;
- redness, pallor of the skin;
- feeling hot or chills;
- slight increase in temperature;
- fatigue;
- bloating;
- nausea;
- fainting;
- belching;
- vomit;
- bowel dysfunction;
- apathy;
- weather sensitivity;
- hiccups;
- rapid breathing;
- impaired urination - difficult, frequent;
- joint pain.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is often associated with low, high blood pressure, and heart pathologies. Depending on the characteristics of the symptoms and clinical picture, VSD is classified into mixed type, hypertensive, hypotonic, cardiac.
Diseases incompatible with service
Do they take into the army with vegetative vascular dystonia? There are a number of diseases that are listed for exemption from service. Some of the most common and common ones are:
- vascular pathologies that lead to circulatory disorders;
- vascular dystonia of the hypertensive type;
- left ventricular dysfunction;
- heart failure;
- astheno, accompanied by severe complications;
- neurocirculatory asthenia.
This is not the entire list of diseases. You can begin to undergo examination before the medical examination if the conscript experiences frequent fainting, a poor cardiogram, etc.
If neurocirculatory dystonia is detected, a delay will require additional symptoms (sudden surges in pressure, decreased ability to work), and the army may not be available.
Are they recruited into the army with vegetative-vascular dystonia?
When deciding on the suitability of a conscript, the medical board is guided by the Schedule of Diseases for Conscripts . In Art. Section 24 of this document describes vascular diseases of the brain and spinal cord. According to this standard, fitness categories “B” and “B-4” can be assigned.
To count on category “B”, there must be monthly attacks confirmed by medical documents, which are accompanied by fainting. Otherwise, category “B” for dystonia is quite justified.
As for the diagnosis of neurocirculatory dystonia, this issue is described in Article 47 of the Schedule of Diseases. It also provides for documented visits to the doctor.
The conditions for obtaining category “B” or “D” for VSD depend on the type and severity of the vegetative-vascular disorder.
What categories exist for exemption from the army?
The grounds on which a conscript is released from service are divided into several categories. After a complete medical examination, a final diagnosis is made. Then the conscript turns to the military commissar. He makes the final decision whether or not to join the service. There are three categories of exemption:
- “B” - in peacetime, the conscript is removed from service, but is enlisted in the reserves;
- “G” - the potential serviceman is given a temporary deferment (for example, if astheno is detected);
- “D” - the conscript is not at all suitable for the army.
The deferment is given only for 6 months or no more than a year. This period is intended to treat the disease (for example, getting rid of panic attacks). If astheno is detected, the issue is resolved individually. After the deferment, the conscript is required to undergo a medical examination again. Exemption is given only if there are categories other than “G”. In all other cases, people with VSD are taken into the army.
How to document a diagnosis
Suspicion of any disease is based on the patient’s complaints, but to confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a full examination.
The following symptoms must be present:
- cardialgia;
- respiratory manifestations - shortness of breath, nervous cough, etc.;
- tachycardia;
- asthenic syndrome;
- psycho-emotional disorders;
- fluctuations in blood pressure;
- cardiac arrhythmia.
Examination methods:
- ECG monitoring
- blood pressure measurement
- Ultrasound of the heart, large vessels
- stress tests to determine the adequacy of the cardiovascular system’s response to physical activity
- study of external respiration functions (spirometry);
- gastroscopy;
- radiography of the OGK;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- laboratory tests of blood, urine, feces;
- study of the functional state of the brain (electroencephalography).
The diagnosis is established after a thorough, comprehensive examination, excluding other pathologies of the blood vessels, heart, stomach, intestines, etc.
In addition, in order to prove the severity of the disease, each time you feel unwell, you must seek help from specialists, make sure that symptoms, treatment, fainting, and other important points are recorded in the card.
Are the army and the VSD compatible?
Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia rarely lead to a delay or exclusion from military service. However, in VSD there are extensive signs of many diseases, so the conclusion is made after a full examination. Most of the symptoms will not interfere with military service, but it can act as a cure. For example:
- Poor physical shape can be corrected by exercise and exercise. In addition, the conscript is often in the fresh air.
- There is simply no room left for obsessive thoughts and neurotic syndrome. This is facilitated by constant employment and a military team that successfully fights depression.
- The conscript becomes not only stronger physically, but also mentally, and panic attacks disappear. He develops a sense of purpose. Composure and many other positive qualities.
Military service may be prohibited for a conscript with panic attacks. If the illness is serious, then it is necessary to obtain an exemption from military duty. For example, with VSD of the hypertensive type.
When is a conscript considered eligible?
In situations where the medical commission does not consider a conscript with VSD unsuitable for the army, he is assigned categories B2 or BZ, which indicate some restrictions in serving. These young men cannot be enlisted in the Air Force or border troops, but are quite suitable for military service in the navy, in the Ministry of Internal Affairs, chemical units, and in the management and maintenance of anti-aircraft missile systems.
It is noted that the army helps to overcome the manifestations of VSD in cases where disorders of the autonomic nervous system are exclusively functional in nature. A healthy, regular diet, physical activity, and a clear work and rest schedule help increase the body’s adaptive-resistant capabilities.
If after two to three months of service the symptoms continue to bother or intensify, the conscript is sent to the medical unit for hospitalization.
General advice to a conscript soldier diagnosed with VSD:
- notify doctors at the place of duty about the presence of pathology;
- in case of deterioration, submit a report to the commander (company, battalion, unit);
- Do not try to overcome panic attacks, insomnia, long periods of low mood, or headaches on your own.
Military personnel are subject to commission if:
- breathing disorders;
- persistent increase in blood pressure;
- bradycardia (low heart rate);
- migraines;
- fainting.
What to do if the required category was not given?
Since VSD is considered simply a neurotic syndrome that combines the symptoms of many diseases, liberation based on fragments of the manifestation of pathology is not given. It happens that doctors do not make a diagnosis, believing that the disease has not yet manifested itself, and the symptoms are quite distant.
Then the conscript has to go to serve. Having been diagnosed with VSD, he needs to take care of his health independently. If even slight signs of illness appear, you need to consult a doctor.
Frequent checks are very important, since living conditions have changed significantly from free life. NPD of the hypertensive type may appear. It is unlikely that the conscript will be among the “black sheep”. Even healthy and strong guys often take three months to adapt.
Vegetative vascular dystonia is not a death sentence. If it occurs against the background of a serious illness, you will have to forget about military service, but when VSD manifests itself as isolated symptoms, this is not scary. It is also necessary to take into account the fact that military service not only changes the daily routine, it contributes to the acquisition of excellent physical shape.
- What is depersonalization and how to treat it
- What is the reason for tachycardia after eating?
- How dangerous is vegetative-vascular dystonia?
- How to treat VSD of the hypertensive type
What should recruits be like according to medical criteria?
Military service is a serious test for young guys, both psychologically and physically. To meet the standards in daily exercises, a soldier needs a healthy heart, respiratory system, endurance of the whole body as a whole and a stable psyche in order to entrust the recruit with weapons and the lives of other people.
Do they accept guys with a mild degree of any pathology into the army? They take it, but with a note in the personal file about the existing deviation, for example, changes in visual function, excess weight, minor problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Representatives of the military commission believe that in the army the recruit will have conditions that will not negatively affect his well-being. Diet and sleep patterns, plenty of fresh air and physical activity under the supervision of professionals are a good alternative to a sedentary and questionable lifestyle in civilian life.
Deterioration of well-being during VSD at work
Very often there are situations when, before conscription into the army, VSD had a mild form, and already in the service its manifestations became more noticeable. There are well-reasoned explanations for this: first of all, excessive physical activity, little time for rest, and mental stress. All of the above factors can provoke an exacerbation of this disease. In case of severe illness, the army doctor is obliged to send the soldier to the hospital. If the treatment turns out to be ineffective, the fighter may be discharged. A serviceman is sent home when, against the background of vegetative-vascular dystonia, pathologies such as migraine, severe arrhythmia, neuroses, hypotension, disturbances in the respiratory system and much more appear.