Description
Amyloidosis is a disease that is accompanied by disruption of protein metabolism and the functioning of the immune system.
The consequence of such disorders is amyloid - intercellular deposition of homogeneous protein masses in all organs of the body and its tissues without exception. As it progresses, it displaces and replaces healthy cells of the affected organ, thereby causing loss of physical inactivity, which often provokes the development of dystrophy. If amyloidosis is not treated, it can lead to multiple organ failure, which can lead to death. Medical scientists have found that amyloidosis affects almost 1% of the world's population. At the same time, secondary amyloidosis occurs several times more often than primary amyloidosis. This disease can be inherited. Such cases were observed among representatives of Armenian and Jewish nationality, as well as in Mediterranean countries.
There are 2 main forms of amyloidosis:
- systemic (tissues of most organs are affected);
- local (tissue damage in any one organ: kidneys, heart, skin, etc.)
Interesting fact: men suffer from amyloidosis twice as often as women.
Classification of amyloidosis
- Primary (idiopathic) amyloidosis. Its causes are not always known. The study revealed that amyloid fibrils are a consequence of immunoglobulin chains, which is called paramyloidosis. Symptoms of primary amyloidosis can be: myasthenia gravis, which leads to muscle atrophy;
- abdominal pain accompanied by diarrhea and dyspepsia;
- disorders of the genitourinary system and menopause;
- diseases of the visual organs (retinitis, periarteritis, etc.)
Prevention of amyloidosis
This terrible disease can be avoided by using special diets and a variety of nutritional supplements. The first thing you need to do is:
- reduce your intake of foods high in protein. This mainly applies to dishes of animal origin;
- increase the consumption of fish dishes, foods containing whole grains, as well as vegetables, fruits and nuts;
- Avoid dairy products, sugar and foods containing caffeine;
- eat more foods containing vitamin C. These are citrus fruits, cabbage, tomatoes, apples, gooseberries, baked potatoes and many other foods.
Treatment depends on the type of disease. If amyloidosis is primary, then following an anti-protein diet will lead to a good result. Chemotherapy and the use of colchicine can also give a positive result. Secondary amyloidosis involves the prescription of antibiotics, antiarrhythmic and diuretic drugs that act on a specific organ.
If medications do not help, surgery is prescribed. In this way, bone marrow, kidney or liver transplantation, heart transplantation and even implantation of a pacemaker can be performed.
Organ damage due to amyloidosis
- Kidney damage. A common and very dangerous disease. Symptoms of renal amyloidosis have 4 stages: latent, proteinuric, nephrotic and azotemic.
- Liver damage. The size of the organ increases, which can be determined by palpating the abdomen. Amyloid liver damage is manifested by liver enlargement, jaundice, and portal hypertension.
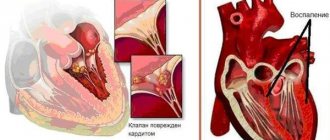
- Amyloidosis of the heart. Its manifestation is accompanied by arrhythmia, shortness of breath, fainting and cardiomyopathy. Amyloid deposits can be present both in the heart muscle and in its lining.
- Amyloidosis of the skin. Promotes disruption of blood supply in the vessels, which is expressed in dryness and peeling of the skin. A rash in the form of small red pimples may appear.
- Joint disease. In joint amyloidosis, the hands and feet are affected first, followed by the knees and elbows. Characterized by painful movements, tissue swelling, increased skin temperature in areas of inflammation.
- Muscle damage. Amyloidosis of these organs manifests itself in their weakness, increase in size and compaction. Accompanied by pain and the appearance of dense nodules. If the disease is neglected, the muscles are compressed, the blood supply is disrupted, resulting in their death.
- Disease of the nervous system. Amyloidosis of the central nervous system is characterized by the deposition of amyloid in the brain tissue; a direct consequence of this process is a violation of the patient’s mental abilities.
- Amyloidosis of the gastrointestinal tract. The absorption of nutrients and vitamins changes. This manifests itself in the form of diarrhea, sudden weight loss, fatigue, mental disorders, as well as hair loss and anemia.
- Enlarged spleen. Amyloidosis of this organ leads to an increase in its size and the development of hypersplenism, which is characterized by anemia and leukopenia.
- Pulmonary amyloidosis. Occurs with pneumonia, pleurisy, cyst. Most often located on the walls of the blood vessels of the lungs and bronchi.
Treatment of amyloidosis can only be carried out with an accurate examination of the patient in a hospital setting.
Symptoms
Photo: prosimptomy.ru
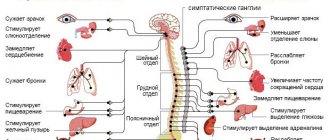
The signs of amyloidosis observed in people with this disease directly depend on the affected organ. In this regard, it is impossible to single out any specific group of symptoms and, depending on the amyloidosis of a particular organ, entire symptom complexes are distinguished. It should also be noted that primary generalized amyloidosis is characterized by a polymorphism of the clinical picture, since, along with the intestines, the heart, skin, kidneys, endocrine and nervous systems can be affected.
Often the first symptoms may be a prolonged elevated body temperature and a significantly increased ESR.
Kidney damage due to amyloidosis.
The most common location is renal amyloidosis. The symptoms of this pathology are very diverse and very dangerous without adequate treatment. The clinical picture of renal amyloidosis is manifested by some symptoms of chronic renal failure, namely:
- Quantitative changes in urine: oliguria (less than 500 ml of urine is excreted per day) and anuria (less than 50 ml over the same period) are observed.
- Disturbances in general health: the appearance of irritability, anxiety, weakness and increased fatigue.
- The appearance of edema - due to a decrease in the concentration of proteins, fluid moves into tissue structures, which leads to edema. With prolonged progression of the disease, fluid accumulates in the abdominal and thoracic cavities, as well as the pericardial cavity, leading to ascites, hydrothorax and hydropericardium.
- Due to damage to the kidney parenchyma, an increase in blood pressure occurs, arrhythmias and hypertrophy of the heart muscle appear.
- Violation of the mental and functional state - manifests itself as a result of the damaging effect of urea in non-functioning kidneys - leads to mental disturbances, insomnia, impaired memory and mental abilities.
- Anemia: due to damage to the kidneys by amyloidosis, the required amount of erythropoietin, which stimulates the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow, ceases to be produced.
Liver damage due to amyloidosis.
In generalized forms of the disease, so-called hepatic amyloidosis develops. Symptoms are caused by the deposition of amyloid in the liver tissue and, as a result, compression of hepatocytes (liver cells) and structures of the hepatic lobule (vein, artery, bile duct). When amyloid accumulates, the liver increases in size, and portal hypertension occurs as a result of compression of the blood vessels. Next, the pressure in the portal vein increases, the veins of the spleen, esophagus and other internal organs expand. All this is manifested by the appearance of ascites, bleeding from dilated veins of the esophagus (often), bloody stools (melena), and vomiting mixed with blood.
When amyloid compresses the biliary tract, jaundice occurs (as a result of the accumulation of bilirubin), which is accompanied by severe itching and yellowness of the sclera.
Intestinal damage due to amyloidosis.
One of the possible lesions is intestinal amyloidosis. Symptoms of this form are characterized by:
- Chronic diarrhea - constant, frequent and prolonged diarrhea - leads to exhaustion of the body, and the person begins to lose weight.
- Syndromes of exudative enteropathy and malabsorption are the most common symptom of intestinal amyloidosis - in this case, a huge amount of protein is lost, which migrates from the blood into the intestinal lumen, being excreted. Malabsorption syndrome is characterized by a rapidly progressive course. Due to the simultaneous exudation (release) of protein into the intestinal lumen, disturbances of protein metabolism predominate in the form of persistent hypoproteinemia (decrease in the amount of protein in the bloodstream) and edema. Hypoproteinemia in this case is very difficult to correct with replacement therapy.
- Intestinal obstruction - is formed as a result of local (local) deposition of amyloid and the development of a tumor-like formation, which, compressing the intestinal loops, leads to impaired evacuation of feces. This manifestation can lead to severe complications, including sepsis.
- Gastrointestinal bleeding is a fairly common manifestation of intestinal amyloidosis, which is characterized by the development of various forms of anemia.
Damage to the nervous system due to amyloidosis.
The most common initial symptoms of primary amyloidosis from the nervous system include general weakness, fatigue and fairly rapid weight loss. In approximately 40% of cases, polyneuropathy develops with minimal involvement of internal organs, and in 15% of cases it may be the only manifestation of the disease. But in 60% of cases, primary systemic amyloidosis leads to polyneuropathy against the background of pronounced manifestations of amyloidosis of another localization (with existing amyloidosis of the heart, kidneys, intestines and others). The polyneuropathy is axonal in nature, involving predominantly thin myelinated (myelinated) and unmyelinated fibers, and clinically resembles diabetic polyneuropathy. First of all, sensory fibers that transmit pain and temperature sensitivity, as well as autonomic fibers, are affected.
The initial symptoms of polyneuropathy in amyloidosis of the nervous system are:
- Numbness
- Dysesthesia (sensitivity disturbances). In this case, sensitivity suffers more superficially than deep.
- Burning pain in hands and feet.
Damage to autonomic fibers and ganglia by amyloidosis is manifested by orthostatic hypotension, fixed pulse, erectile dysfunction, impaired skin trophism and decreased sweating.
At a later stage, muscle weakness and amyotrophy (impaired muscle function and nutrition) develop. At the same time, motor disorders are less pronounced in comparison with sensory ones.
Damage to muscle tissue due to amyloidosis.
The severity of movement disorders increases if amyloidosis affects muscle tissue directly, involving the proximal muscles of the limbs.
Amyloid myopathy manifests itself as more qualitative disorders, mainly in children, which is associated with weakness and fatigue of the already weakly expressed muscle layer, which arise as a result of their compaction and hypertrophy. If amyloid begins to be deposited in the muscles of the tongue, so-called macroglossia develops (enlargement of the tongue to an abnormally large size). Dysphagia (inability to swallow) and deepening of the voice may also occur. In some patients, respiratory failure occurs due to damage to the respiratory muscles by amyloidosis.
Skin lesions due to amyloidosis.
With primary amyloidosis, one can often note one or another skin rash: most often they are petechiae, purpura, nodules and plaques, but it is not possible to note any general criterion characteristic of cutaneous amyloidosis. In the nodular-plaque form of skin amyloidosis, a large number of plaques and nodes are observed, which are located mainly on the legs and ankles. A characteristic feature of this form of amyloidosis is the symmetrical arrangement of isolated nodules on both legs. This form occurs mainly in women.
During pregnancy
Pregnancy with amyloidosis is allowed only if the functional activity of the woman’s vital organs allows her to bear and give birth to a healthy child. Otherwise, pregnancy can cause death not only for the fetus, but also for the mother herself.
Certain local forms of amyloidosis do not prevent the onset and gestation of pregnancy. Childbirth can proceed without complications and result in the birth of a healthy baby when amyloid protein accumulates in only one specific organ or tissue (intestinal wall, muscle tissue). In the generalized form, the prognosis for the mother and fetus is determined by the reserves of the affected organ and the duration of the disease.
Diagnostics
Photo: pluska.sk
Modern methods for diagnosing amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is a disease that manifests itself as a pathology of protein metabolism and the performance of the immune system. Amyloid (protein-saccharide complex), which appears as a result of this disorder, can be deposited in the cells of any tissue of the body. As the disease progresses, it gradually replaces healthy cells, and the organ ceases to function. In severe forms of the pathology, multiple organ failure occurs (damage to 50% or more organs), leading to death.
The hereditary form of the disease is observed in the Mediterranean area, as well as in people of Jewish and Armenian nationality. Among men, this disease occurs twice as often.
The most common forms of the disease include nephropathic, in which deposits are observed in the kidneys, and systemic, in which amyloid deposits are found in many organs.
Amyloid deposited in different organs differs in structure. There are about 15 types in total, differing in structure and composition. They are based on two types:
- AA amyloid. Chronic inflammatory diseases cause high plasma levels of SAA protein and maintain them for a long period. When the protein is incompletely broken down, fibrillar AA amyloid is formed.
- AL amyloid. Proteins of this type appear during the cleavage of amyloidoblasts (degenerated plasma cells). They are abnormal immunoglobulin compounds.
- The appearance of other types of amyloid is determined by the form of amyloidosis.
Types of disease
Amyloidosis occurs both independently and as a concomitant disease. Diagnosis of amyloidosis distinguishes several types:
Primary or idiopathic. With this type of deposits, deposits are found in all internal organs. It is impossible to determine the exact cause of the appearance. Multiple abnormalities are observed in the cells of the immune system with the accumulation of AL-amyloid in the skin, tissues of the muscular, nervous and cardiovascular systems. Its cause may be plasmacytoma (myeloma), a malignant tumor pathology.
Symptoms of primary amyloidosis:
- Myasthenia gravis with subsequent muscle atrophy;
- Dyspepsia and diarrhea;
- Pathology of the genitourinary and reproductive system;
- Damage to the organs of vision.
Secondary
It is a complication of any inflammatory disease. The reason for its appearance may be:
- Chronic infectious diseases: pyelonephritis, tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, malaria, syphilis or leprosy (leprosy);
- Chronic purulent diseases: osteomyelitis, purulent ulcers and wounds;
- Ulcerative colitis – inflammation of the colon;
- Tumor lesions of the hematopoietic organs: leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis, etc.;
- Rheumatological pathology: various arthritis, etc.
Secondary amyloidosis forms in the internal organs. There is a disruption in the functioning of organs with the greatest deposition of amyloid - in the area of the kidneys, spleen, liver or lymph nodes. Subsequently, the damage spreads to other organs, followed by death.
Hereditary
This form is formed due to genetic abnormalities in the cells of the immune system, leading to the appearance of amyloidoblasts. A similar pathology is diagnosed in some national groups or in a certain geographical area. Hereditary forms include:
- Periodic disease - familial Mediterranean fever;
- Familial nephropathic or English amyloidosis;
- Hereditary neuropathic amyloidosis - Portuguese, American or Finnish;
- Hereditary cardiopathic or Danish amyloidosis.
Senile
A systematic approach allows us to identify this pathology in people over 80 years of age. It includes:
- Cerebral or cerebral amyloidosis. Diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease;
- Amyloidosis of the heart. Affects the heart muscle. Deposits also form in the lungs, liver and pancreas.
Tumor
In this case, amyloidosis develops locally in organs with a pronounced malignant process. It is caused by medullary thyroid cancer or pancreatic islet tumor.
Hemodialysis
During hemodialysis prescribed to patients with renal failure, the level of B 2 -microglobulin in the blood gradually increases. This protein, when interacting with nucleoproteins, settles in the kidney tissues.
Diagnosis of amyloidosis
To diagnose amyloidosis, the patient is prescribed a number of different tests. This includes a general blood and urine test, blood biochemistry, ultrasound of internal organs, biopsy and genetic research.
General blood analysis
Determines abnormalities specific to amyloidosis. In the final stages of the disease, this study helps to identify the damaged organ.
General urine analysis
Diagnosis of renal amyloidosis shows the likelihood of developing inflammatory processes in the kidneys.
In case of kidney pathology, the following is detected:
- Proteinuria – protein content in urine over 3 g/l;
- Hematuria – detection of red blood cells in the urine;
- Leukocyturia – the presence of leukocytes in the urine;
- Cylindruria - the content in the urine of casts formed during amyloidosis from proteins, kidney epithelial cells, leukocytes and erythrocytes;
- Decreased urine density.
Blood chemistry
It makes it possible to assess the general condition of the body and determine the cause of amyloidosis. This analysis determines:
- Proteins of the general phase of inflammation, produced by the liver or certain leukocytes during the inflammatory process. Particular attention should be paid to the amount of fibrinogen.
- Liver tests indicate the condition of this organ.
- Increased cholesterol levels are a sign of nephrotic syndrome.
- A decrease in protein levels indicates nephrotic syndrome or liver failure.
- An increase in urea and creatinine levels is an indicator of renal dysfunction in amyloidosis.
Ultrasonography
This method makes it possible to determine the structure and structure of the tissues of internal organs, the degree and distribution of pathological processes.
Diagnosis of amyloidosis using ultrasound shows:
- Hardening and change in the size of the kidneys;
- Presence of cysts in the kidneys;
- Compaction and enlargement of the spleen and liver, accompanied by pathology of blood flow;
- Hypertrophy of the heart muscle;
- The presence of amyloid deposits in the walls of the main blood vessels;
- An increase in the volume of fluid in various cavities of the body - ascites, hydropericardium or hydrothorax.
Biopsy
Removal of a small part of tissue for examination using special methods. Its use makes it possible to diagnose amyloidosis in 90% of cases. Tissue from muscles, internal organs, and mucous membranes is taken for examination.
Genetic research
It is carried out if there is a possibility of developing hereditary amyloidosis. The patient's genetic material is taken for research and checked for the presence of genetic abnormalities in some chromosomes. If a pathology is detected, it is recommended that all blood relatives of the patient undergo examination to identify this disease in them.
Classification of renal amyloidosis
Systematization of the disease is based on parameters such as etiology and pathogenesis. Based on them, five of its forms are distinguished.
| Form | Characteristics |
| Congenital | AL amyloidosis, the development of which was provoked by the appearance and accumulation of light chains of immunoglobulins in the body tissues. The etiology of the disease still remains unclear, as well as the mechanism of its development. |
| Acquired | AA amyloidosis is secondary, caused by a number of chronic inflammatory processes in which the liver begins to intensively produce the acute phase protein alpha globulin. |
| Family | AF amyloidosis (or "Mediterranean fever") is hereditary. Residents of the Mediterranean (Greeks, Arabs, Armenians) suffer from it. The disease is based on a genetic defect that causes a disruption in the production of fibrillar proteins. |
| Senile | ASC1 amyloidosis develops in elderly patients due to impaired metabolism of serum prealbumin. According to medical statistics, the disease affects about 80% of patients over 80 years of age. |
| Local tumor-like | AE amyloidosis can be triggered by neoplasms of the endocrine system, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and senile dementia of the Alzheimer's type. |
Treatment
Photo: sodrugestvo.info
The goal of treating amyloidosis, regardless of the type and characteristics of the course of the disease, is to reduce the concentration of special precursor proteins, which subsequently turn into amyloid and are deposited in tissues. In addition, the most important task is to stabilize or restore the functions of internal organs, prevent the development of organ failure and increase the life expectancy of patients.
Symptomatic measures for amyloidosis are aimed at eliminating existing disorders: edema, arrhythmia, hypotension, heart failure, etc. Treatment of amyloidosis is mainly conservative. With the development of complications or a critical decrease in the functions of vital organs, surgical interventions are performed.
Treatment regimens vary depending on the type of disease:
- AA amyloidosis . Anti-inflammatory therapy is recommended in combination with surgical techniques for the development of local purulent processes.
- AL amyloidosis . It is necessary to suppress the clone of plasma cells that secrete special subunits of immunoglobulins (light chains). Stopping the synthesis of such compounds and their accumulation in tissues helps remove excess amyloid and stop the progression of the pathology.
- ATTR amyloidosis . For a long time, the only effective treatment for this type of disease was considered to be a liver transplant that secretes unchanged transthyretin. In recent years, in the early stages of the disease, therapy with a drug from the group of selective transthyretin stabilizers has been used with sufficient success.
Drug therapy
In the secondary form of the disease, pathogenetic therapy is required, aimed at eliminating or alleviating the course of the underlying disease. The list of medications, doses and duration of courses are determined individually, taking into account the nature and severity of the causative pathology. AA amyloidosis requires long-term, sometimes lifelong, basic therapy, which is supplemented with antibacterial drugs when complications develop.
High-dose chemotherapy is indicated for patients with AL amyloidosis. Achievement of remission is assessed based on laboratory parameters. Taking into account the existing symptoms in any form of amyloidosis, medications are used to eliminate disturbances in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, correct blood pressure and intestinal motility, and combat pain.
Surgery
In case of life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, a pacemaker is required. With the development of local purulent processes against the background of AA amyloidosis, opening and drainage of abscesses in soft tissues, lungs, and joints is indicated. For ATTR amyloidosis, liver transplantation is performed. The technique is especially effective in people under 50 years of age with no complications from the cardiovascular system.
Since systemic amyloidosis often affects the kidneys with the development of renal failure, a number of patients require transplantation of this organ. Surgery is recommended in the absence of gross changes in the heart and gastrointestinal tract. The five-year survival rate after transplantation is about 65%, which is comparable to the rates for patients with chronic renal failure due to other diseases. A third of recipients of a transplanted kidney also subsequently develop amyloidosis, but transplant rejection as a result of amyloid deposition occurs in only 2-3% of cases.
Renal replacement therapy
Chronic renal failure is one of the leading causes of death in patients with systemic amyloidosis. Taking into account this circumstance, in case of serious impairment of kidney function, methods of extracorporeal blood purification become highly important. According to experts, the preferred option is peritoneal dialysis, which carries a lower risk of pressure drop during the procedure. Life expectancy for hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis is the same as for people with other kidney diseases. Good or satisfactory clinical and laboratory results of renal replacement therapy are observed in 60% of cases.
Procedures and operations
Transplantation of a donor organ is the only possible way to save the life of a patient with organ failure that has developed against the background of amyloidosis. It is important to understand that transplantation is only a symptomatic treatment method that is not able to eliminate the true cause and slow down the progression of amyloidosis. Even after transplantation, recurrence of the disease is possible.
What can be transplanted for amyloidosis:
- heart;
- kidney;
- skin;
- liver tissue.
A donor organ can be obtained either from a living donor or from a person who has been diagnosed with brain death, but at the same time retains the functional activity of the internal organs. To date, an artificial heart has been developed, which is presented in the form of a fully mechanized device that pumps blood in the human body. After transplantation, lifelong use of immunosuppressants is prescribed, which helps prevent rejection of the “foreign” tissue or organ.
Medicines
Photo: medvestnik.ru
The drug therapy regimen is drawn up taking into account the type of systemic amyloidosis:
- AA amyloidosis . Basic therapy for rheumatoid arthritis and seronegative polyarthritis is carried out with agents with cytotoxic, immunomodulatory, immunosuppressive, anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative effects. Treatment measures are continued regardless of the presence or absence of clinical signs of inflammation, focusing on the level of C-reactive protein in the blood. For severe gout and periodic illness, medications from the homomorphinan group are used. If ineffective, interleukin-1 inhibitors are used. Patients with suppurative processes are prescribed medications with antibacterial action.
- AL amyloidosis . Unlike multiple myeloma, with this form of amyloidosis, attempts are made to completely suppress the activity of the plasma cell clone. This aspect, combined with the rapid progression of the disease, necessitates early initiation of treatment and the use of high doses of fast-acting anticancer drugs. High-dose therapy is not indicated for patients over 70 years of age who have signs of amyloid damage to 2 or more systems, as well as patients with cardiac amyloidosis, gastrointestinal bleeding and a history of orthostatic hypotension.
Patients with ATTR amyloidosis and polyneuropathy require lifelong treatment with a selective transthyretin stabilizer. As part of the symptomatic treatment of all forms of amyloidosis, it is necessary to take into account contraindications to the use of calcium antagonists and cardiac glycosides, which have the ability to accumulate in amyloid deposits. ACE inhibitors and beta blockers are used with caution.
For congestive heart failure, diuretics are effective; for orthostatic hypotension, glucocorticosteroids and mineralocorticosteroids are effective. Somatostatin preparations are used to normalize intestinal function, and antidepressants and anticonvulsants are used to reduce the severity of pain in polyneuropathy.
Folk remedies
Amyloidosis is a serious disease that requires the use of official medicine. Folk remedies are ineffective and can harm the body. Patients with this diagnosis are advised to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and not self-medicate to prevent the condition from worsening.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
SEARCH FOR TREATMENT AROUND THE WORLD WITH YELLMED