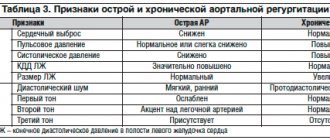
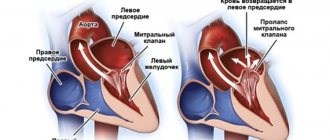
Among heart diseases, endocarditis is one of the most insidious. Under the influence of various infections (there are about 130 causative agents of this disease), the inner lining of the heart becomes inflamed. The danger is that the symptoms of infective endocarditis do not appear immediately, so patients do not always seek help in a timely manner. Also, the disease is not easy to diagnose, which is why treatment may be started later than expected. That is why cardiologists recommend regular examinations in medical centers equipped with modern equipment that has extensive research capabilities.
What is endocarditis
Symptoms of the disease occur in people of different ages, including children diagnosed with “congenital heart defects” (tetralogy of Fallot, single ventricle defects, etc.). It can be provoked by:
- mitral valve prolapse;
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;
- surgery on heart valves;
- cardiac septal defects;
- coronary heart disease (especially after surgery).
The disease is primarily infectious. Inflammation caused by microorganisms affects not only the endocardium itself - the internal tissues of the heart muscle - but also the heart valves and nearby vessels. Often the infection penetrates the liver, kidneys, and spleen.
Most often, pathology becomes a consequence of other diseases. The prerequisites for the occurrence of infective endocarditis is bacteriological infection of the body under various conditions. The infection also affects the heart when its valves are injured due to the installation of prostheses and pacemakers, on the surface of which microorganisms can develop. There are atherosclerotic forms caused by dystrophic changes in cardiac tissue, and rheumatic forms - due to rheumatism of the heart valves.
Treatment
Pathology therapy is carried out:
- Medication.
- Surgically.
Drug therapy is aimed at relieving signs of heart failure, arrhythmia and preventing complications.
Doctors prescribe the following drugs:
- Beta blockers. These drugs can reduce the manifestations of heart failure and arrhythmias.
- Diuretics. These drugs are prescribed to reduce the load on the heart muscle.
- Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents. These drugs help prevent thrombotic complications of the pathology.
- Antibiotics. These drugs help prevent the development of bacterial endocarditis.
If the disease is actively developing and threatens serious complications, surgical interventions are performed. One of the popular ones is heart valve replacement.
Indications for surgery are:
- severe chest pain;
- dyspnea;
- frequent fainting;
- chronic heart failure in a severe stage;
- endocarditis.
The intervention is quite complex and lengthy. After surgery, patients have to stay in the hospital for a long time (up to a month).
Today, open-heart interventions are being successfully replaced by minimally invasive ones. They are carried out through a mini-access without cutting the sternum. The intervention is endovascular. It is used in aortic valve replacement. The operation is performed by introducing a prosthesis through the femoral vein. Of course, doctors strive to minimize all consequences and risks. Nevertheless, preference (if possible) is almost always given to drug therapy.
Are you interested in prices for services in our clinic in Moscow? We adhere to a loyal pricing policy. Thanks to this, you do not overpay even for extensive examinations and long courses of therapy. The price of a consultation with a cardiologist is also relatively low. At the same time, you can always count on receiving comprehensive professional support even in advanced situations.
Classification and causes of endocarditis
In accordance with the causes and clinical manifestations, the disease is classified as follows.
Infectious (bacterial) endocarditis most often manifests itself in an acute form. Ulcers and polyps form on the heart valves or in the heart tissues, which lead to functional disorders.
The chronic or subacute form is usually caused by streptococci. The disease is manifested by ulceration and changes in the shape of the heart valves, the formation of blood clots in the vessels, followed by blockage. The consequences may be inflammation of the kidneys and heart attacks of other organs.
A non-infectious disease occurs against the background of a general weakening of the body, with various intoxications, and in older people with the development of marasmus. Among the forms are degenerative warty, abacterial, etc. Most often it manifests itself in the form of thrombotic deposits on valve tissue.
Rheumatic endocarditis , as the name suggests, occurs due to rheumatism. In this case, inflammation spreads to the heart valves and causes heart defects. There are 4 forms: diffuse, acute warty, recurrent warty, fibroplastic.
Loeffler's endocarditis is characterized by an increase in blood eosinophils and a decrease in the volume of the heart chambers due to fibrous changes in the endocardium and then the myocardium. There are three stages: acute (cell death within 5-6 weeks), thrombotic (formation of blood clots and atrophy of some tissues), fibrosis (sclerosis and thickening of the endocardium).
Rheumatism (acute rheumatic fever) - symptoms and treatment
The main, and in most cases, the only manifestation of rheumatism is heart damage caused by inflammation - rheumatic carditis (carditis). With rheumatic carditis, simultaneous damage to the myocardium and endocardium occurs. This is the main syndrome that determines the severity and outcome of the disease.
In the case of carditis, adult patients experience discomfort in the heart area, interruptions in heart rhythm, and rapid heartbeat. There may be mild shortness of breath on exertion [4][5][7]. In children, this pathology is more severe: the disease begins with palpitations, shortness of breath at rest and during exercise, and constant pain in the heart area [7]. However, according to the observations of most pediatricians, children rarely present subjective complaints. Only 4-5% of pediatric patients report discomfort in the heart area at the onset of the disease. But about 12% of patients complain of tiredness and tiredness, especially after school [2][10].
With ARF, it is possible to develop rheumatic arthritis , which affects the musculoskeletal system. This is the second most common clinical manifestation of ARF. The prevalence of rheumatic arthritis varies according to various sources from 60 to 100% [3]. Patients complain of pain in large joints, inability to move, and enlargement of joints [4]. Polyarthritis can occur alone or in combination with another syndrome, most often with carditis. A feature of the disease is rapid and complete reverse development with timely administration of antirheumatic therapy.
Rheumatic lesions of the nervous system occur mainly in children. It is worth noting such a disease as “minor chorea”, or rheumatic chorea (Sydenham’s chorea, St. Vitus’s dance). It is manifested by emotional instability and violent, erratic, involuntary movements (hyperkinesis) of the upper torso, upper limbs and facial muscles [1][2].
Rheumatic chorea occurs in 12-17% of children; girls aged 6 to 15 years are more often affected [11]. The onset is gradual: patients experience tearfulness, irritability, twitching of the muscles of the trunk, limbs, and face. They complain of unsteady gait and impaired handwriting. The duration of chorea is from 3 to 6 months. It usually ends with recovery, but in some patients an asthenic state (increased fatigue, mood instability, sleep disturbance), decreased muscle tone, and slurred speech persist for a long time [1][2].
Ring-shaped erythema is a rare but specific clinical manifestation of ARF. It appears during the period of greatest activity of the process in approximately 7-17% of children. Ring-shaped erythema is a non-pruritic, pale pink rash. It does not rise above the skin level and appears on the legs, stomach, neck, and inner surface of the arms. The elements of the rash look like a thin rim that disappears when pressed. The diameter of the elements ranges from a few millimeters to the width of a child’s palm.
Subcutaneous rheumatic nodules are also a rare sign of ARF. These are round, dense, painless formations, varying in size from 2 mm to 1-2 cm. They are formed in places of bony protrusions (along the spinous processes of the vertebrae, the edges of the shoulder blades) or along the tendons (usually in the ankle joints). Sometimes they appear as clusters consisting of several nodules. Often combined with severe carditis.
Additional clinical manifestations of ARF include abdominal syndrome (acute abdominal pain) and polyserositis - inflammation of the serous membranes of several body cavities (pleura, pericardium, peritoneum, etc.). These syndromes develop in children against the background of high inflammatory activity. Abdominal syndrome, caused by peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum), is manifested by acute diffuse pain in the abdomen, sometimes accompanied by nausea and vomiting, bloating, stool and gas retention.
pleurisy (inflammation of the serous membrane covering the surface of the lungs) may develop Pleurisy can be dry or exudative. Dry pleurisy is an inflammation of the pleural layers with the formation of fibrin on them. Exudative - inflammation accompanied by the accumulation of exudate of various types in the pleural cavity. With ARF, dry pleurisy is more often observed. Currently, this manifestation of ARF is rarely observed. It may be clinically asymptomatic or accompanied by pain during breathing, dry cough, and sometimes a pleural friction noise is heard [5][6][7].
Infectious (bacterial) endocarditis
In the acute form, the symptoms of bacterial endocarditis develop quite quickly. Typically, the infection affects the lining of the heart valves, 2-10 mm ulcers appear on the tissues of the valves, and the valves themselves swell - platelets and fibrin accumulate, and aneurysms form. As a result, one of the large vessels may become blocked by a blood clot, and valve particles may come off. In some cases, septic infarction cannot be excluded.
If you do not seek qualified help in time and do not start treatment:
- heart failure develops;
- the structure of valves and leaflets is deformed;
- arrhythmic phenomena appear;
- hemodynamics are impaired.
Patients with subacute septic endocarditis are characterized by the same manifestations of pathology, but in this case, most often the tissues are affected by thrombotic formations, which sooner or later clog one of the most important vessels.
Endocarditis in children
In children, the most common bacterial type of this disease occurs. The pathology is expressed by damage to the mitral and aortic valves, and then spreads to the internal cardiac tissues:
- the child experiences acute toxicosis;
- endocardial tissue becomes inflamed;
- myocardial damage occurs;
- blood vessels may become clogged;
- blood flow is disrupted.
Infectious endocarditis in children usually develops at a faster rate; inflammation can spread to other internal organs and lead to liver and kidney failure. Therefore, in this case, it is necessary to seek professional cardiac help as soon as possible.
Symptoms of endocarditis
The disease is characterized by an asymptomatic course at an early stage, as well as a sudden exacerbation against the background of a relatively healthy state. Symptoms of endocarditis in adult patients usually appear 10-14 days after infection:
- fever with chills, profuse sweating;
- the temperature may rise for several days;
- signs of intoxication appear: headache, weakness, exhaustion;
- the skin may acquire a pale, yellowish tint;
- rashes may be observed on the mucous membranes, feet, and palms.
These signs indicate the presence of an infection in the body, so you should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment.
They are complemented by more characteristic symptoms of infective endocarditis in adults, which indicate the development of this particular disease:
- arthritic changes in joints;
- damage to the heart valves;
- thrombosis and blockage of large arteries;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- kidney infarction and other lesions;
- rapidly developing heart failure;
- pericarditis.
These symptoms of endocarditis are identified during diagnostic procedures.
Diagnostics
To identify pathology, a specialist:
- Evaluates patient complaints, studies anamnesis, paying special attention to past infectious diseases.
- Conducts a full inspection.
- Orders an ECG. This examination can detect arrhythmia.
- Prescribes echocardiography. This examination helps to detect defects, determine their type, as well as the presence of circulatory disorders and their severity.
Additionally, the cardiologist can refer the patient to a rheumatologist and cardiac surgeon. Comprehensive diagnostics allows you to quickly make an accurate diagnosis and begin therapy.
Important! Diagnosis is also carried out during therapy. Examinations make it possible to identify the causes of pathology, associated disorders, change the dosage of medications taken and solve other important problems.
Diagnosis of endocarditis
Qualified diagnosis of infective endocarditis is a whole complex of examinations. The patient is prescribed a cardiac screening program, which includes:
- various types of electrocardiogram (24-hour monitoring, stress echocardiography);
- Ultrasound of the heart and blood vessels;
- computer sphygmomanometry.
Modern diagnostic methods are also applicable: cardiac rhythmography, Dopplerography. Blood tests and cultures for sterility are required - one of the most important examinations for infective endocarditis.
Treatment of endocarditis
At an early stage, treatment of infective endocarditis consists of antibiotic therapy and cardiac support with medications. If septic endocarditis has already manifested itself as significant changes in the tissues of the heart (damage to the valves, aorta, myocardium), surgical intervention is possible.
- Antibacterial treatment for symptoms of endocarditis involves the use of modern antibiotics (benzylpenicillin, penicillins, amphotericin, etc.) administered intravenously.
- Passive immunization is carried out to neutralize bacteria in the body. For this purpose, special antitoxic serums (immunoglobulin, hyperimmune plasma) are most often used intravenously.
- Surgical intervention is performed in cases where it is necessary to remove foci of infection in the tissues of the heart and restore cardiac structures altered by the disease. The services of a cardiac surgeon are necessary if the patient has progressive heart failure, vascular thromboembolism, etc.
Treatment in Italy
Russian Medical Server / Treatment in Italy / Center for the treatment of rare diseases in Milan / Rheumatic endocarditis - treatment in Italy
Endocarditis is inflammation of the endocardium. Endocarditis usually occurs as a manifestation of a general disease; Most often, by origin, rheumatic and septic endocarditis are distinguished; in addition, endocarditis can be syphilitic, tuberculous, traumatic, with myocardial infarction and other etiologies.
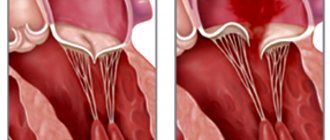
Most often, endocarditis affects the heart valves, less often the parietal endocardium of the heart cavities. Anatomical changes in the endocardium depend on the form of endocarditis. In rheumatic endocarditis, the endothelium of the heart valves is affected, followed by the imposition of thrombotic masses on them and the proliferation of granulation tissue. Wart-like formations appear on the heart valves (warty endocarditis). Septic endocarditis is characterized by ulcerative damage to the heart valves (ulcerative endocarditis) and the formation of blood clots on the damaged endocardium; Destruction of the heart valve is often observed. After any form of endocarditis, persistent changes in the structure of the heart valve may remain, disrupting its function, i.e., heart disease develops.
It should be noted that patients initially experience swelling of collagen fibers followed by a proliferative reaction. In the early stages, the surface of the valve begins to change. At the points of contact of the valves, platelets and fibrin begin to accumulate and settle, which leads to the appearance of growths (warts). The valve tissue under the growths is swollen. The tricuspid valve leaflets are subject to rheumatoid changes half as often as those of the mitral valve. Subsequently, the valves become scarred, wrinkled and deformed, and thickening or fusion of the walls is observed. This leads to the development of heart disease.
As a result of rheumatic endocarditis, valve insufficiency or stenosis may develop. Insufficiency is the incomplete closure of the valve leaflets, and stenosis is the narrowing of its opening. The most common complication is mitral valve insufficiency of the heart muscle.
Most often, rheumatic endocarditis develops between the ages of six and sixteen years, but recently there has been a decrease in the incidence in children. There are no specific features of the disease in children and adults; it progresses in exactly the same way.
According to the foci of occurrence, rheumatic endocarditis can be:
- valve;
- parietal;
- chordial.
The valve is considered the most common.
Treatment of rheumatic endocarditis is carried out by all known methods and includes taking medications and following doctor’s orders. If heart failure continues to develop, surgical intervention is performed.
The medical treatment of endocarditis involves the use of antibiotics, which are aimed at the complete destruction of beta-hemolytic streptococcus. As we have already mentioned, it is he who causes rheumatic changes in the heart. An intramuscular injection of benzylpenicillin is prescribed. It must be done four times a day for ten days.
After this, treatment with glucocorticosteroid drugs is prescribed. It is aimed at relieving inflammation of the heart muscle. Prednisolone tablets of 20 mg per day are used, you need to drink them one at a time after your morning meal. The main purpose of the patient taking these drugs is to prevent the development of heart disease.
Surgical intervention is performed only in case of unfavorable development of the disease and if the patient’s condition allows. Indications:
- formation and accumulation of pus in the endocardial area;
- heart failure continues to worsen;
- massive growths on the valve flaps;
The operation is performed by opening the chest and connecting the patient to a heart-lung machine. The heart surgeon cleans the valves and removes the affected areas. If necessary, a decision is made to replace severely damaged valves with artificial ones, but this is a separate operation.
The main complication of rheumatic endocarditis may be a heart defect. Valve insufficiency or stenosis is a rather serious ailment leading to the replacement of the valve with a mechanical one. The most common complication is mitral valve insufficiency of the heart muscle.
About 25% of patients who have had rheumatic endocarditis do not have valve defects, this is especially true in adulthood. In patients who have had this disease, the chance of developing infective endocarditis significantly increases, especially in the absence of prevention.
! Despite the fact that many of the diseases described in this section are considered incurable, the Center for the Treatment of Rare Diseases in Milan is constantly looking for new methods. Thanks to gene therapy, it has been possible to achieve outstanding results and completely cure some rare syndromes.
Contact a consultant on the website or leave a request - this way you can find out what methods Italian doctors offer. Perhaps this disease has already been treated in Milan.