What is normal blood pressure?
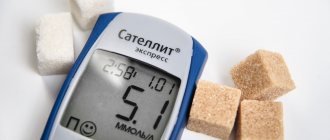
When measuring blood pressure, we focus on the reference 120/80 mmHg. Art. However, these figures are not indicative, since for each person they depend on age, degree of physical activity, dietary habits and even the weather. What does pressure 100/80 mean and should I be afraid of developing hypotension in this case?
Before diagnosing yourself with “hypertension” or “hypotension”, you must take into account that each organism is individual. Moreover, blood pressure readings can change throughout the day. The norm also depends on age. A young man actively involved in sports has a blood pressure of 100/80 mm Hg. Art. with a pulse of 80 there should be no concern. If the pulse is 100 beats per minute, this indicates tachycardia.
With age, blood pressure begins to rise, which is associated with wear and tear of blood vessels and other changes in the body. For example, for a 60-year-old man, low blood pressure with a pulse of 85 or higher is low and indicates problems in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
In addition to systolic and diastolic pressure indicators, the doctor pays attention to the pulse difference. If it falls within the range from 20 to 50 mm Hg. Art., this is considered normal. That is, with figures of 100/80 mm Hg. Art. It is impossible to talk about pathology without the presence of other symptoms.
Low blood pressure is considered to be a blood pressure of 90/60 mm Hg. Art. and below. If such numbers are constant, we can talk about chronic arterial hypotension. Temporary fluctuations in pressure downward are called a hypotonic state. To determine the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an examination, which includes daily monitoring of blood pressure and pulse rate.
Treatment recommendations
First of all, it is necessary to normalize your lifestyle. You should do gymnastics daily, preferably in the fresh air. Evening walking, swimming, cycling, and light jogging are excellent options for low blood pressure. You should stop drinking alcohol and smoking and normalize your sleep. And it is also important to correct the diet: give up fried, smoked and fatty foods, include a large amount of vegetables and fruits, grains in the menu.
The prescription of medications depends on the type of hypotension. In the primary form of the pathology, anticholinergics are used, which have a sedative and antispasmodic effect. In order to increase the heart rate (according to indications) and increase the return of blood to the heart, sympathomimetics are prescribed.
And they also use preparations based on herbal and other natural ingredients (tincture of aralia, ginseng, zamanikha, camphor, Pantocrine, Saparal). In the treatment of symptomatic hypotension, attention should be paid to the treatment of the underlying disease that caused the decrease in blood pressure. To regulate blood pressure numbers, it is important to take vitamins:
- Thiamine.
- Riboflavin.
- Niacin.
- Pantothenic acid.
- Pyridoxine.
- Folic acid.
- Cyanocobalamin.
- Ascorbic acid.
- Calciferol.
Important! Hardening helps well, which can be used to prevent a hypotonic state.
Reasons for decreased blood pressure
In the event that the readings are 100/80 mm Hg. A hypertensive person sees the art on the tonometer screen, this may indicate errors in the treatment of hypertension. For example, about the incorrect dosage of antihypertensive drugs. This may also indicate a violation of cardiac activity, which can be identified after examination.
Important! Blood pressure often decreases during the 1st trimester of pregnancy. During this period, the expectant mother’s body produces progesterone, a hormone that causes fluctuations in blood vessels. In the second trimester, the situation stabilizes and blood pressure approaches the levels that the woman had before pregnancy.
Other causes of low blood pressure include some diseases:
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia, in which low blood pressure becomes the norm for a person. Most often, tall people with asthenic physique face this problem.
- Diseases of the endocrine system, such as hypothyroidism and disorders of the adrenal glands.
- A number of chronic diseases, the list of which includes tuberculosis, tonsillitis and others.
The time of day also affects blood pressure. The values reach their maximum at 18–19 hours; the tonometer shows the minimum numbers at night.
Weather-dependent people who react painfully to the vagaries of the weather often suffer from attacks of hypotension.
A decrease in blood pressure may also indicate internal bleeding. But in this case it falls below 100/80. The heart rate also slows down sharply. A pressure of 100 over 80 is not a serious pathology. If the condition is accompanied by a deterioration in well-being, indicating hypotension, treatment is prescribed to normalize the pressure.
Feeling good with blood pressure 100/60
If the pressure drops sharply, the patient complains of headache, dizziness, pulsation in the back of the head, rapid heartbeat (at a pressure of 100 to 60, the pulse can reach 100 beats/min). Cold sweat, severe weakness appear, trembling in the limbs may occur, and body temperature decreases. The result of a critical drop in indicators is a fainting state requiring emergency assistance.
With chronic hypotension, the patient complains of daily weakness, fatigue, emotional lability, depression, and shortness of breath. With a chronic type of pathology, people get used to attributing their poor health to all sorts of factors, but not to a drop in pressure. The problem is associated with changes in weather conditions, fatigue at work, stress, overeating or, conversely, diet abuse.
Symptoms of hypotension
The development of hypotension is indicated not only by the numbers on the tonometer, but also by additional symptoms, including the following:
100 over 70 - is this normal pressure?
- lethargy, drowsiness, fatigue;
- decreased performance, accompanied by deterioration of memory and ability to concentrate;
- headaches and dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- nausea;
- increased heart rate and shortness of breath during exercise;
- decreased body temperature, coldness in the extremities;
- spots before the eyes;
- muscle weakness;
- sensitivity to light, temperature changes, loud sounds, irritability;
- problems related to the functioning of the digestive tract;
- deterioration of sexual function.
These symptoms do not always indicate the development of hypotension. They may be signs of other disorders in the functioning of internal organs and systems. The diagnosis is made after a comprehensive examination, which includes examination and questioning of the patient’s complaints, laboratory tests, monitoring of blood pressure throughout the day, etc.
Important! If blood pressure decreases regularly, this indicates hypotension, which requires regular monitoring of the condition. Unlike hypertension, the disease does not pose any obvious health risks, but can significantly worsen the quality of life.
Correction of indicators and first aid
To increase the pressure, you must follow the following algorithm:
- Call a team of medical workers.
- Lie on a horizontal surface with the leg end raised or lay the victim down in this way.
- Open a window or direct a fan to provide fresh air.
- Drink sweet warm tea or give the victim something to drink. You can add 10 drops of tincture of eleutherococcus, ginseng or Rhodiola rosea.
- Rub your whiskey with lemon essential oil.
Methods for correcting the condition
If you feel good with low blood pressure, there is no reason to worry. If you feel dizzy and have a headache, other symptoms of hypotension appear, and your pulse is 90 or higher, you should take measures to improve your well-being. To do this you need:
- take a comfortable position and relax, since an attack of hypotension can be triggered by nervous overstrain;
- do not make sudden movements, drink caffeine-containing drinks or alcohol in large doses in the hope that the condition will stabilize;
- take 20 drops of Volocordin diluted with water, valerian or motherwort tincture;
- relieve headaches with Citromon tablets that slightly increase blood pressure.
After 15 minutes, pressure and pulsation will return to normal. After stabilizing your condition, you should consult a doctor who will answer the question of why your blood pressure has dropped in your case, and will be able to prescribe a treatment regimen and give recommendations regarding physical activity and the optimal daily routine.
Blood pressure levels can depend on chronic diseases, age and even the weather. If a decrease in pressure brings discomfort and disrupts the usual rhythm of life, it is worth contacting specialists who can identify and eliminate the causes of the disorder.
Possible complications
Outside of therapy or with an insufficiently high-quality regimen, the following consequences may occur:
- Heart failure. As a result of a drop in output, blood stagnation and a decrease in myocardial contractility.
- Stroke. Acute malnutrition of cerebral structures. Potentially fatal condition.
- Heart attack. Necrosis of the muscle layer. Leads to deficiency, dysfunction and lifelong disability. The possibility of death always looms on the horizon.
- Cardiogenic shock. Carries the greatest danger. Even with timely assistance, no one guarantees the patient’s life. Statistics show that death occurs within 3-4 years, which happens less in almost 100% of people. The cause is a repeated episode of cardiac arrest or massive heart attack.
- Vascular dementia. As a result of constant disruption of nutrition of cerebral structures. Forms a clinical picture similar to that of Alzheimer's disease.
The general decrease in quality of life is a “bonus”. All conditions are associated with premature death.
Preventing such an outcome is one of the goals of treatment. It is solved in parallel with etiotropic and symptomatic effects.
Consequences and prognosis
Against the background of a constant decrease in blood pressure, the organs and tissues of the body do not receive the oxygen they need in full. In this case, the brain cells suffer the most. Hypoxia (oxygen starvation) causes the development of cognitive disorders: a person’s memory decreases, concentration and coordination are impaired. In old age, senile dementia develops.
Complications of hypotension may include:
- injuries sustained after fainting;
- visual impairment;
- heart, kidney failure;
- ischemic stroke;
- neurological pathologies;
- depressive states.
Predicting the outcome of the disease is quite difficult. It all depends on the effectiveness of blood pressure level correction.
Primary hypotension is difficult to treat. Blood pressure can be normalized in approximately 70% of all diagnosed cases. But this condition does not pose a particular threat to human life. A decrease in pressure to the level of 90/60 can occur for various reasons. And if the condition is accompanied by poor health, then the person needs to consult a doctor.
How does a constant decrease in SBP affect the patient's life prognosis?
The prognosis for low upper pressure is determined by the cause of hypotension. In the absence of serious concomitant cardiac pathology, kidney disease, or endocrine disorders, the prognosis is relatively favorable.
If low SBP is detected before the age of 25 years, there is a high probability of normalizing blood pressure using lifestyle correction. At older ages, patients are recommended to undergo a more thorough examination by a cardiologist, therapist and neurologist, drug therapy and physiotherapy.
Reasons why the upper figure may decrease
In the modern rhythm of life, factors such as stress, insufficient rest during intense workload, psycho-emotional experiences, and untimely treatment of underlying diseases lead to a decrease in blood pressure.
Other causes of low upper blood pressure are listed below:
Vegetative-vascular dystonia of the hypotonic type.- Pregnancy period, especially the first trimester, and in patients with severe toxicosis.
- Hormonal disorders, diabetes, hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency.
- Consequences of injuries to the head, neck, spine.
- Physical fatigue, especially among professional athletes.
- Congenital or acquired cardiac pathology, valve defects, incorrect selection of medications for hypertension.
- Neurosis, depressive disorder, chronic fatigue syndrome.
- Frequent changes in time zones and climate.
- Sudden change of weather.
- Dehydration, fatigue, consequences of infectious diseases, injuries, operations, blood loss.
Reduced systolic with normal diastolic: why does this happen?
Upper pressure decreases as cardiac contractility decreases. This can happen when:
- damage to the heart and large vessels due to atherosclerosis, rheumatism;
- decreased vascular tone;
- heart failure;
- dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system;
increased secretion of the hormone acetylcholine and decreased adrenaline;- taking sedatives that slow your heart rate.
However, it should be remembered that it is almost impossible to distinguish low systolic pressure from high diastolic pressure on your own. A single measurement of blood pressure at home is not enough to make a correct diagnosis. Cardiologists, therapists and neurologists focus patients’ attention on the need for examination by a specialist. Within the walls of a medical institution, special instrumental diagnostics are carried out to detect low SBP.