What is blood pressure?
Blood pressure, or blood pressure, is the force with which blood presses from the inside onto the walls of blood vessels. Due to the fact that in nature there is also atmospheric pressure, which exerts its influence on all living organisms and objects, blood pressure is the amount by which blood pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure.
Each heartbeat sets the blood in motion, creating upper pressure (systolic) and lower pressure, which is measured at the moment the heart muscle relaxes, that is, in the intervals between beats. This pressure is called diastolic.
Upper pressure shows the force with which the heart, at the moment of compression, pushes blood out of the left ventricle. At this point the highest indicator is noted. As the force of the push is distributed throughout the circulatory system, the pressure loses its original value and a lower value is noted at the entry point into the heart.
At the moment when the heart relaxes after a beat and its valve closes, blood fills the small vessels and capillaries. Pressure may increase during this period due to the response of the arteries to the blood flow. Generally, the higher the systolic pressure, the more resistance the artery walls have. This means that when the upper pressure is high, the lower pressure often increases.
Types of hypotension
Reduced diastolic blood pressure (hypotension) is divided into several types:
- Orthostatic hypotension. This diagnosis can be made to an elderly person, since this condition is provoked by age-related changes in the body. A decrease in diastolic pressure can be observed during sudden movements - lifting or bending, when blood quickly flows into the limbs. However, with an immediate decrease in pressure, the heart continues to work at the same rhythm, despite the presence of weakness, loss of balance, or even fainting.
- Vegetovascular hypotension. It is observed more often in adolescents, when the nervous and cardiovascular systems are not yet fully formed, and the brain receives incorrect commands. If a command was given to increase the pressure, it decreases.
- Postprandial hypotension. This type of hypotension is manifested by a decrease in blood pressure after eating. The heart does not accelerate as the blood moves downward, there is no vasoconstriction, and the patient feels a sharp rush to the legs.
If diastolic pressure is reduced, but a high pulse is recorded, this condition is considered potentially dangerous. It indicates that the heart pumps blood with effort, and its passage through the capillaries occurs with difficulty.
Lower pressure 90 - is this normal?
Every person should have a blood pressure monitor in their first aid kit. If there is no one in the family who could manually inflate the cuff with a bulb and determine the pressure parameters by the movement of the arrow, you can buy an automatic device. It is not much more expensive, and in addition to pressure, it also counts the pulse and can determine signs of arrhythmia. Feeling unwell for no apparent reason should be a reason to measure your blood pressure.
The optimal indicators are considered to be a pair of systolic and diastolic pressures of 120/70 Hg, but even if these numbers rise to 130/80 Hg, this will be considered normal. Values of 140/90 Hg and above are considered elevated. With these values, the doctor can already diagnose arterial hypertension and prescribe a course of treatment.
A lower pressure of 90 units indicates the onset of hypertension. Such values can also appear at a young age, so not only older people need to monitor their blood pressure. Young people have a higher tendency to identify chronic pathologies, which are often accompanied by associated complications.
Why?
- heredity;
- unhealthy diet: eating foods high in fat (french fries, hamburgers, bacon, chips, ice cream, etc.);
- highly salted foods cause increased diastolic pressure; obesity;
- drinking alcohol (especially red wine, cognac, vodka) sharply increases DD;
- nicotine constricts blood vessels, which increases DD;
- the main reason for a sudden increase in DD is stress;
- sweetened soft drinks.
Increased lower pressure: causes
Lower blood pressure readings are often affected by emotional overload, stress, and excessive physical activity. If you have heart disease, it is important to avoid such situations. In addition, alcohol and salt can change the values. These two products have pronounced activity regarding the condition of blood vessels. Do not forget about smoking - this is an important factor that impedes the passage of oxygen through the bloodstream, reduces the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels and, as a result, makes them unable to respond to changes in external and internal factors.
Other reasons that increase lower blood pressure may be:
- adrenal dysfunction;
- pyelonephritis;
- renal failure;
- polycystic disease;
- amyloidosis;
- disorders of the thyroid gland, manifested by excessive or insufficient amounts of hormones produced.
- obesity;
- musculoskeletal problems;
- disturbances in the functioning of the heart.
An increase in lower pressure causes the kidneys to produce more renin - a special biological substance that, in the process of complex chemical reactions, activates the production of elements that have a vasoconstrictor effect. As a result, the heart is stimulated and blood pressure increases, which further aggravates the situation.
This situation can lead to chronic glomerulonephritis and kidney abnormalities. Normal blood flow is disrupted, the myocardium loses its ability to relax, the walls begin to be damaged, and their ability to stretch and contract in response to changes in temperature and other physical indicators decreases.
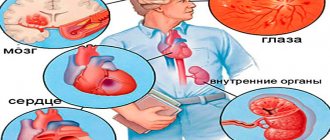
The absence of measures taken to normalize blood pressure will sooner or later lead to thromboembolism and impairment of cognitive reactions.
Symptoms
With a physiological decrease in lower pressure, patients do not experience a deterioration in their well-being. If the problem is caused by pathology, then oxygen starvation gradually develops. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- weakness and dizziness;
- colored spots before the eyes;
- pallor;
- fainting state.
Patients with chronic arterial hypotension constantly feel fatigue, drowsiness, and a desire to rest. A person with low blood pressure experiences increased sweating and may experience headaches. Low blood pressure makes it difficult to concentrate on work or study and makes a person emotionally unstable. Women with chronic hypotension may experience menstrual irregularities, and men have reduced potency.
In severe forms of arterial hypotension, patients experience vegetative crises. They are accompanied by a decrease in temperature, sweating, difficulty breathing, chest pain, nausea and vomiting, slow pulse, and loss of consciousness.
How to lower lower blood pressure
To normalize blood pressure, you must first understand the reasons that increase it. For example, with adrenal or thyroid dysfunction, the cause is improper hormone production. When they are in excess, the lower blood pressure rises sharply. A person with one kidney in such an acute condition can die.
If jumps in lower pressure occur due to the accumulation of fluid in the body, it is important to establish the water-ion balance. In some people, it is disrupted due to poor nutrition, overeating, and abuse of salty and fatty foods. For others, fluid stagnation is caused by an imbalance of hormones. In the first case, you can return your lower blood pressure to normal by restoring your diet, daily physical activity, and excluding large amounts of salty, smoked, and fried foods. In a situation with the influence of hormonal levels, it is necessary to receive a course of treatment from an endocrinologist.
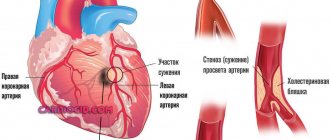
When lower pressure increases, the synthesis of renin is disrupted, which should normalize the force of action on the walls of blood vessels. But due to atherosclerosis, the pressure cannot be reduced - even with high elasticity of the walls, the lumen remains narrow due to overgrown atherosclerotic plaques. In such a situation, first of all, it is necessary to reduce the level of bad cholesterol in the blood and monitor its levels.
Treatment
Many people know how to treat diastolic blood pressure (high), but low blood pressure is much less common, so people are not aware of how to increase it. This technique consists of several methods of therapy: nonspecific and medicinal. They differ in the method of treatment.
Nonspecific therapy
Such treatment makes it possible to enhance the effect of drug therapy and protect the body from circumstances that provoke low blood pressure. Such recommendations are well suited for healthy people as a preventive measure against low blood pressure.
- Sleep well. The daily sleep requirement is at least 8 hours.
- During work, take short breaks (15 minutes), every 2-3 hours.
- Do morning exercises outside and walk. Every day a person should be in the fresh air for at least 2-3 hours.
- Strengthen vascular walls and train their elasticity using a contrast shower: gradually reducing the water temperature from hot to cold. In this way, both high and low diastolic pressure can be slightly corrected.
- Massage, knead and rub the body, especially the calf muscle tissue, areas of the hands and feet.
- Avoid hot baths, baths, saunas, and exposure to sunlight without a hat or headscarf.
- Cycling, rollerblading, skating, and light jogging more often.
- Drink strong teas and coffee drinks. For low blood pressure, ginger tea is recommended, purchased in a store or prepared independently from ginger root, grated on a fine grater. However, you should not regularly stabilize intravascular parameters using this method, because you can disrupt the natural self-regulatory abilities of the body.
If you devote enough time to the lifestyle described above, but the diastolic values of the tonometer are still low, you will need to resort to drug treatment.
Medicines
This therapy does not tolerate self-prescription. Before purchasing medications, you need to consult with a specialist who will determine the exact causes and indicate the path to treatment of the disease. If you postpone a visit to the doctor, you will have to get rid of not only intravascular abnormalities, but also diseases of the internal organs. The following medications are usually applicable:
- Herbal products: ginseng, eleutherococcus, lemongrass. They create a tonic and stimulating effect on the human body. They have contraindications for use, so medical consultation will be necessary, regardless of the origin of the drugs.
- With reduced tonometer values, combined with asthenia, manifested in the form of apathy and weakness, Pantogam, Paricetam, Phenibut, which belong to the nootropic group, are used. They improve metabolic processes occurring within a person, stimulate the central nervous system and activate energy processes.
- Multivitamins tone the human body, replenish the vitamin balance in the body, as a result of which the patient becomes resilient to nervous and physical stress.
The methods described above are best used in combination: nonspecific therapy together with medication (for serious deviations). If a person only occasionally experiences attacks of hypotension, then preventive measures alone can be used. But you should still consult a doctor to rule out the disease in a latent form.