In addition to vegetative-vascular dystonia, many people receive another mysterious diagnosis - neurocirculatory dystonia (NCD). This strange and incomprehensible “disease” is also marked with ICD 10 code. Sometimes all these words frighten the patient much more than everything that happens to him. And having received such a statement on his medical card, a person begins to panic, seriously believing that he is sick with something serious and incurable.
What is neurocirculatory dystonia of mixed type, code according to ICD 10? Is she as scary as she sounds? How to treat this frightening disease? These questions, of course, are of great concern to those who are faced with a similar problem. But don't worry. Everything is not as scary as it seems. Especially if you understand everything in detail.
general information
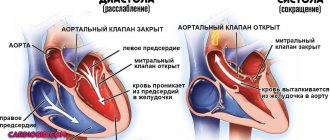
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is responsible for the unconscious regulation of the body. The movement of blood through the vessels, the digestion of food, the secretion of saliva - all these and many other processes occur automatically. The ANS itself is divided into two sections: sympathetic and parasympathetic. They are responsible for opposite processes and are in constant balance. Disturbances in this balance cause unpleasant symptoms, which form the clinical picture of NCD.
Adolescents and young women are more susceptible to the disease.
Causes
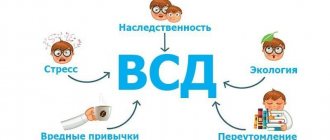
The list of causes of neurocirculatory dystonia is extensive. It includes:
- hormonal changes: puberty, pregnancy, menopause;
- acute and chronic stress;
- physical or mental fatigue;
- lack of sleep;
- bad habits: smoking, alcohol abuse;
- poor nutrition and excess body weight;
- change of climate and time zones;
- hereditary predisposition;
- drinking large amounts of coffee, energy drinks, and certain medications;
- infectious diseases;
- pathology of the endocrine glands;
- mental disorders;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- chronic pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, digestive or cardiovascular systems.
Make an appointment
Make an appointment with a cardiologist
If neurocirculatory dystonia reduces the quality of your life, or you do not know what diagnosis your ailments are associated with, we invite you to see the best cardiologists at the private Multidisciplinary Medical Center in Moscow. After diagnosis, an accurate diagnosis will be made, and this is the first step towards recovery.
You can make an appointment for a fee with a cardiologist by phone or using a convenient online form, checking the price and work schedule of our specialists on the clinic’s website.
Moscow, st. Krasnodarskaya, house. 52, bldg. 2
+7
We work on weekdays and weekends from 8.00 to 21.00
Symptoms
The symptoms of neurocirculatory dystonia are very diverse and form the basis for the classification of pathology. However, it is possible to identify a number of common features that are characteristic of most types of NDC:
- frequent mood changes;
- constant fatigue and drowsiness;
- lack of strength, weakness;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- increased sweating;
- weather sensitivity;
- anxiety;
- feeling of lack of air, etc.
An exacerbation of the disease can be triggered by any stressful situation: an excess of positive or negative emotions, lack of sleep, or even a simple change in time zones.
Neurocirculatory dystonia of mixed type, code according to ICD 10 - what is it?
Let's start with the strange ICD 10 code, what does it mean. In fact, ICD 10 is the International Classification of Diseases 10 Revision. Health authorities review the diseases existing in the world every 10 years. New, previously unknown diseases can be added to the registry, amendments and additions can be made.
This code only means that the World Health Organization, which conducted the 10th Review in Geneva in 1989, added the term neurocirculatory dystonia to the list of known health problems. But this diagnosis is not recognized as a specific disease. It belongs to a number of somatoform dysfunctions and neuropsychic disorders (neuroses). Do not rush to get scared, such neurotic disorders are completely reversible and respond well to therapy.
More about neurocirculatory dystonia
In fact, NDC is absolutely the same as VSD. It’s just that some doctors prefer to write “vegetative-vascular dystonia”, others prefer to use the term “neurocirculatory”.
The disorder is a disruption of the neuro-autonomic system, caused by various factors and accompanied by various physiological symptoms.
Nowadays, NCD and VSD are diagnosed in approximately 70% of the population of developed countries and cities. What is most interesting is that people living in the outback, surrounded by nature, silence, tranquility, practically do not experience such disorders. So we can safely say that neurocirculatory dystonia is a disease of big cities. Although, in fact, it is not a disease at all.
Dystonia affects people of all ages and even children. But the bulk falls on people aged 20 to 40 years. It is during this period that a person is most active and tries to achieve something in his life. And the difficulties he encounters cause various nervous disorders (neuroses).
Doctors divide neurocirculatory dystonia into 4 types:
- of the hypotensive type;
- by hypertensive type;
- by cardiotype;
- according to the mixed type.
In this article we consider the option of a mixed-type NDC - when “everything at once”. This type of dystonia occurs most often. It is the most difficult and unpleasant. If, for example, a patient with dystonia of the hypotensive type experiences chronic low blood pressure, loss of strength, and lethargy, then in people with NCD of the mixed type, blood pressure can jump a hundred times a day, and there is no stability in health - only one thing hurts , then something else.
Symptoms of mixed type NCD
The disorder is based on impaired functionality of the cardiovascular system, sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the nervous system. We can say that this is a global failure that occurred in the body, due to which all organs and systems began to work chaotically.
NCD gives so many symptoms and they are so varied that a person begins to suspect that he has the most terrible and incurable diseases.
As a rule, in 95% of cases, people with dystonia do not have any serious physiological diseases. But the insidiousness of VSD is that it is so similar to many diseases that large-scale diagnostics have to be done to exclude possible organic disorders and pathologies.
So, what symptoms occur with neurocirculatory dystonia of the mixed type, let us consider in more detail. After all, there are a lot of them.
Cardiovascular (cardiovascular) syndrome:
- Heart rhythm disturbances (tachycardia, arrhythmia).
- Pain in the heart area.
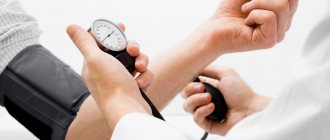
- Changes in blood pressure.
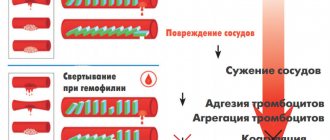
- Spasms of blood vessels and capillaries.
- Circulatory disorders.
Hyperventilation (respiratory) syndrome:
- Rapid breathing.
- Feeling of lack of air.
- Inability to take a full breath.
- Dizziness.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS):
- Frequent constipation or diarrhea (sometimes alternating).
- Bloating, flatulence.
- Spasms, pain in the intestines, stomach.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Loss of appetite.
- Difficulty swallowing food.
Psycho-emotional syndrome:
- Increased anxiety, fear, worry.
- Panic attacks.
- Irritability, aggression.
- Tearfulness.
- Apathy, depression.
- Sudden mood swings.
- Sexual dysfunction (decreased libido).
- Social phobia (may develop gradually).
- Agoraphobia (also develops gradually).
General symptoms:
- Sleep disorders (insomnia, difficulty falling asleep).
- Changes in body temperature.
- Hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating).
- Numbness of the limbs.
- Various pains in the body, muscles and organs.
- Headache.
- Decreased vision.
- Noise in ears.
- Frequent urination.
- Muscle twitching.
- Meteor dependence.
An impressive list, and it included only the most basic and common symptoms. But this is not all the tricks of the NDC. It all depends on the imagination of the victim, and what interesting and unique manifestations he can evoke in himself. Indeed, despite the physical signs, the main problem of dystonia lies in the psyche, in what is going on in a person’s head, in his inner world. The more the patient focuses on how he feels, the more pronounced and varied the symptoms.
NCD with its manifestations can significantly spoil the quality of life and even deprive a person of his ability to work. Fortunately, all this is reversible and you can get out of neurosis as quickly and easily as you fell into it. Of course, if you make efforts to “save” yourself.
Types of pathology
Depending on the prevailing symptoms, several types of NCD are distinguished.
- Cardiac. Symptoms related to the heart come to the fore. A person experiences stabbing or pressing pain in the chest, which is accompanied by an increased or decreased pulse, and a feeling of interruptions in the functioning of the heart. The pain syndrome often spreads to the left arm, completely simulating a serious pathology. At the height of an attack, a person often feels weak, dizzy, and afraid.
- NCD of hypotonic type. This type of dystonia is manifested by a periodic decrease in blood pressure. Insufficient oxygen supply to the brain leads to severe dizziness or even fainting. Against the background of low pressure, a spasm of the capillaries occurs, as a result of which the skin turns pale, the hands and feet become very cold. Lack of oxygen leads to a subjective feeling of stuffiness and shortness of breath.
- NCD of the hypertensive type. Manifests itself with periodic increases in blood pressure. During an attack, a person feels hot, his face turns red, and a severe headache appears. Vomiting often occurs during an attack. Often the trigger is a change in weather. Patients get tired quickly and experience mood swings.
- NDC of mixed type. This type of pathology is the least predictable. Blood pressure rises and falls, which is accompanied by corresponding symptoms. Often there are malfunctions in the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea, flatulence, vomiting), and kidneys (frequent urination). The person becomes emotionally unstable and has trouble sleeping at night.
Depending on the type of flow, the following types of NDC are distinguished:
- mild: symptoms of the disease appear extremely rarely, the person leads a normal lifestyle;
- moderate: manifests itself in single crises, the frequency of attacks affects daily life;
- severe: a person experiences symptoms of NCD almost constantly; against their background, vegetative crises regularly occur.
Neurocirculatory dystonia: what is it?
This condition is one of the most common reasons for visiting a cardiologist and neurologist.
At different ages, from a third to a half of all registered pathologies of the cardiovascular system are precisely neurocirculatory dystonia. It has been noted that most often it occurs in young and middle age, from adolescence to 45 years. There are also gender differences - in women the disease is registered much more often. Neurocirculatory dystonia in children most often develops in adolescence during puberty, when the body is rebuilt and all regulatory processes, including the functions of the cardiovascular system, undergo significant changes. Psycho-emotional stress, which often accompanies puberty, also plays an important role. Pathogenesis of neurocirculatory dystonia
The essence of neurocirculatory dystonia is a violation of control of the cardiovascular system by the nervous and endocrine systems. It is neurohumoral control that ensures homeostasis by maintaining balance in the sympathetic-adrenal, cholinergic, histamine-serotonin and other systems that regulate numerous vital processes of the human body. In case of failures in the complex regulatory system, which can be caused by a variety of influences, the interaction of the hypothalamic-pituitary system and peripheral endocrine glands is disrupted, the acid-base state of biological media, and all types of metabolism change. The myocardium is very sensitive to these changes, therefore it reacts with changes in contractile function, and vascular tone also changes. A stable response to the action of various factors is gradually formed - a symptom complex of neurocirculatory dystonia of a certain type, appearing in certain circumstances.
Types of neurocirculatory dystonia
The classification of neurocirculatory dystonia is based on the leading symptom of the disease. There are 4 main types:
- Neurocirculatory dystonia of the cardiac type (disturbance of the heart comes to the fore).
- Neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotonic type develops when the balance shifts towards the parasympathetic nervous system (vagotonia). The main symptom is a decrease in blood pressure (BP).
- Neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypertensive type is a predominance of the sympathetic nervous system (BP increases).
- Neurocirculatory dystonia of a mixed type (changes in blood pressure in one direction or another are combined with disturbances in the functioning of the heart).
In practical medicine, a classification of neurocirculatory dystonia according to severity is used. There are: mild, moderate and severe degrees.
Vegetative crisis
A vegetative crisis is a sudden failure in the functioning of the ANS. As a rule, it occurs in young patients. Depending on the symptoms, there are three types of crises:
- sympathoadrenal (panic attack): develops due to the release of stress hormones into the blood, as a result of which the patient’s blood pressure and pulse sharply increase, severe chills, anxiety, fear of death appear;
- vagoinsular: the opposite type of crisis, manifested by a drop in pressure and pulse, sweating and weakness; often accompanied by diarrhea;
- mixed: combines characteristics of both types.
Types of neurocirculatory dystonia
There are different classifications of this disease. Thus, according to etiological characteristics, dystonia is divided into:
- Essential
- the disease occurs due to a hereditary predisposition to it. - Psychogenic
– the factor that provoked the disease is severe stress, psychological trauma or a prolonged state of excessive emotional stress. Also included in this category is dystonia, which occurs as a result of hormonal imbalance in the body. - Infectious-toxic
- regulation of vascular tone is disrupted after severe poisoning or taking certain “heavy” drugs. - Professional
– resulting from prolonged physical activity.
Neurocirculatory dystonia develops in different ways; it can manifest itself in mild, moderate or severe form. It is important to divide patients with dystonia into hypotonic and hypertensive groups. Their manifestations of the disease will be different:
- Hypotonic neurocirculatory dystonia
- patients of the asthenic type, with cold extremities, pale skin and muscle weakness. - Hypertensive neurocirculatory dystonia
- patients with excess weight, frequent heart pain and headaches, increased blood pressure and increased heart rate.
Complications
NCD is not an independent disease, but it can cause the development of dangerous conditions. In severe dystonia and lack of adequate therapy, it can cause:
- myocardial infarction;
- ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- cholelithiasis and urolithiasis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- arterial hypertension that does not respond to classical treatment regimens.
Malfunctions of the ANS also affect the immune system. Resistance to infections with this pathology is significantly reduced.
Diagnostics
In the process of diagnosing neurocirculatory dystonia, especially of the mixed type, it is important for the doctor to exclude other causes of similar symptoms. The patient will undergo a thorough examination, including:
- collecting complaints and medical history, clarifying all details of the course of the disease;
- standard examination, including assessment of the functioning of the main body systems, including both sections of the ANS;
- general blood test to exclude inflammatory manifestations;
- general urinalysis to exclude renal pathologies;
- biochemical blood test, which necessarily includes a study of glucose and cholesterol levels, hormonal status, blood clotting and markers of autoimmune processes;
- ECG, ultrasound of the heart;
- daily monitoring of ECG and blood pressure;
- functional load tests (bicycle ergometry, treadmill) to assess the heart’s response to stress and determine the “safety margin”;
- chest x-ray, spirometry if necessary (if the patient complains of shortness of breath and a feeling of lack of air);
- rheoencephalography, Doppler ultrasound of the head and neck vessels: to assess the quality of blood supply to the brain and its structures;
- MRI of the head, x-ray of the sella turcica to visualize or exclude space-occupying formations;
- electroencephalography if one or another form of epilepsy is suspected.
During the examination, the patient also consults with a therapist, neurologist and cardiologist. If necessary, doctors of other specialties are involved: psychiatrist, endocrinologist, pulmonologist, gynecologist, nephrologist, etc.
Diagnosis of neurocirculatory dystonia
The diagnosis of neurocirculatory dystonia can be established based on complaints and examination data. Typically, patients present characteristic complaints and describe the symptoms of the disease quite vividly, especially if we are talking about a severe course of the disease with crises. At the same time, the symptoms of the disease are very nonspecific and can therefore be mistaken for manifestations of other conditions. Conversely, under the “mask” of neurocirculatory dystonia, serious pathologies that require extensive treatment can be hidden. For this reason, it is so important to conduct a thorough examination of a patient who complains of pain in the heart, changes in blood pressure and neurotic disorders.
An important criterion for suspecting neurocirculatory dystonia is the presence of several symptoms at once, the appearance of which is clearly related to the influence of external factors. The presence of symptoms for at least 2 months is taken into account. With dystonia, their intensity usually does not increase, although progression of the disease is possible.
During the examination, the doctor (therapist, cardiologist, neurologist) evaluates the pulse and respiration rate, their rhythm, and measures blood pressure. To determine the state of the autonomic nervous system, a skin dermographism test is performed. To do this, a blunt object is drawn across the surface of the skin (for example, the edge of a spatula or the blunt end of a ballpoint pen). After 10-20 seconds, a line appears, which can be red (appears earlier and lasts longer, rises above the surface of the skin) or white. Red dermographism is characteristic of the predominance of the parasympathetic system, white – of the sympathetic one.
A mandatory examination item is electrocardiography (ECG). It can detect various rhythm disturbances (depending on the type of disease), as well as a negative T wave in two or more leads. Most often, patients consult a doctor not during a crisis, but during a period of remission, that is, at the time of treatment, complaints may well be absent. In this case, for objective diagnosis, stress tests are carried out, the essence of which boils down to performing an ECG after any stress.
Types of ECG tests with stress:
- Hyperventilation test: the patient undergoes an ECG, then breathes deeply for 30-45 seconds, after which an electrocardiographic study is performed again. Sometimes the time of deep breathing is extended, focusing on the appearance of dizziness. With neurocirculatory dystonia after hyperventilation, the pulse increases 1.5-2 times, a negative T wave appears or its amplitude increases.
- Orthostatic test: the patient is given an ECG in a supine position, then he gets up and remains in an upright position for 10-15 minutes, after which a repeat ECG is recorded. The presence of neurocirculatory dystonia is indicated by the same changes as during the test with hyperventilation.
- Drug test: after performing an ECG, the patient is given one of the β-blockers or potassium chloride, and after 40-60 minutes, when the drug has taken effect, a repeat ECG is performed. A drug test allows you to differentiate neurodystonia and diseases accompanied by organic changes (coronary heart disease, cardiomyopathies, myocarditis). In case of organic pathology, after administration of the drug, a positive T wave appears on the ECG, and in case of dystonia, a negative wave appears.
Treatment of neurocirculatory dystonia
Treatment of NCD has several goals:
- reduction in the strength and frequency of attacks;
- eliminating specific symptoms that cause discomfort in the patient;
- stabilization of the nervous system, in general.
The doctor’s task is to correctly select not only medications from various groups, but also non-drug treatment methods: physiotherapy, exercise therapy, massage, psychotherapy, etc.
The choice of specific medications depends on the form and severity of the disease. The patient may be prescribed:
- sedatives to eliminate excessive anxiety (Persen, valerian-based drugs, etc.);
- sleeping pills for poor sleep quality (donormil, zolpidem);
- tranquilizers in the presence of severe crises that occur like a panic attack, as well as in the ineffectiveness of softer drugs (afobazole, phenibut, atarax, etc.);
- antidepressants for excessive apatite, lethargy, depression; improve heart function, reduce pain (paroxetine, sertraline);
- nootropic drugs to improve memory, concentration and general stimulation of the body (glycine, piracetam, pantogam);
- drugs to improve metabolism in the brain (Actovegin, Cerebrolysin);
- angioprotectors to restore full blood supply to the central nervous system (Cavinton, pentoxifylline);
- antihypertensive drugs from the group of adrenergic blockers for increased pulse and blood pressure (anaprilin, bisoprolol);
- hypertensive drugs for low blood pressure (caffeine, mezaton, preparations based on ginseng and lemongrass);
- antioxidants that help strengthen the body in general (succinic acid, mexidol);
- multivitamins, as well as preparations with a high content of B vitamins to improve nerve conduction (milgamma, neuromultivit).
The selection of a specific combination of drugs, their dosage and regimen of administration is carried out only by a doctor, depending on the clinical situation and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Non-drug treatments for NCD are used as an adjunct to medications. Their task is to strengthen the body and increase its resistance. The most popular are:
- physiotherapy: laser treatment, magnetic therapy, electro- or phonophoresis, electrosleep;
- massage of the cervical-collar area and general;
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- a variety of relaxing procedures: wraps, floating, applications, etc.;
- psychotherapy;
- Spa treatment.
It is important to remember that most of these techniques can only be used outside of an exacerbation.
Make an appointment
Symptoms of neurocirculatory dystonia
The clinical picture of neurocirculatory dystonia depends on the type of disease, but there are also general symptoms that are characteristic of all types. This is a neurosis-like condition, the signs of which are internal tension, tremors, sweating, anxiety, a feeling of lack of air or a feeling of “incomplete breathing”, “lump in the throat”, and in a chronic course - fatigue, irritability, sleep disturbance, decreased emotional tone and cognitive disorders , combined into the term “asthenic syndrome”. Against the background of this condition, symptoms of dysfunction of the cardiovascular system appear, which are different for each type of dystonia. The main difference between neurocirculatory dystonia and neurosis is the presence of disorders of the cardiovascular system.
1. Neurocirculatory dystonia of the cardiac type is accompanied by cardialgia, interruptions in heart function, palpitations, and shortness of breath appears during physical activity. Pain in the heart can be stabbing, aching, short-term or long-lasting. Changes in blood pressure are not observed or they are insignificant. Upon examination, tachycardia is detected, including paroxysmal, respiratory arrhythmia; extrasystoles and changes in T wave voltage in both directions can be detected on the ECG.
2. Neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotonic type is characterized by a decrease in systolic blood pressure below 100 mm Hg, which is accompanied by symptoms of vascular insufficiency:
- chilliness of hands and feet;
- sweating;
- hypersalivation;
- dizziness up to loss of consciousness;
- weakness, fatigue, headaches.
3. Neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypertensive type is characterized by periodic rises in systolic blood pressure to 130-140/85-90 mm Hg. Art. against the background of general symptoms of dystonia. In some cases, an increase in blood pressure does not affect your well-being. If symptoms appear, they correspond to the picture of hypertensive heart disease (headaches, tachycardia, sensation of pulsation of the vessels of the head or neck), and peristalsis is weakened and the pupils dilate.
4. Neurocirculatory dystonia of mixed type combines cardialgia syndrome and a change in blood pressure in one direction or another, which is accompanied by the characteristic symptoms described above.
Depending on the severity of symptoms and the conditions of their occurrence, three degrees of severity of neurocirculatory dystonia are distinguished.
- In mild cases, symptoms are moderate and occur due to exposure to external factors. Mild neurocirculatory dystonia does not require treatment.
- With moderate severity, the symptoms are more pronounced, they significantly reduce performance and require treatment.
- Severe dystonia is characterized by persistent symptoms that significantly affect quality of life and require ongoing drug therapy, sometimes even in a hospital setting.
The course of neurocirculatory dystonia can be different. Most often, against the background of complete or incomplete remissions, vegetative crises occur, provoked by the influence of the listed reasons. Vegetative crises can be quite severe, lasting up to 2-3 hours and ending in involuntary urination or defecation.
Symptoms of crises also depend on the type of neurocirculatory dystonia.
- Sympathoadrenal crisis: severe headaches, increased blood pressure, heart pain, numbness and coldness of the extremities, pallor, tachycardia, general agitation. In some cases, there may be a rise in body temperature even to febrile levels.
- Vagoinsular crisis: decreased blood pressure and pulse rate, feeling of heat, heaviness in the head, lack of air, dizziness and weakness, nausea, increased intestinal motility, constriction of the pupils.
- Mixed crises: a combination of symptoms of both types of crisis or their alternation.
If you experience similar symptoms, consult your doctor
. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Prevention
Prevention of NCD is important not only for healthy people who are at risk, but also for those who are already closely confronted with this pathology. Changing your lifestyle, adjusting your diet and physical activity help strengthen the body and significantly reduce the risk of unpleasant symptoms. Doctors recommend adhering to the following rules:
- eliminate overtime, ensure daily proper rest;
- create the most peaceful atmosphere at home and at work;
- go to bed on time (duration of sleep at night is 8 hours or more);
- do not ignore walks in the fresh air;
- choose a suitable sport that will allow you to practice for your pleasure (swimming, walking, cycling, yoga, Pilates, etc.);
- adjust nutrition: the daily diet must meet the standards for caloric content, the ratio of dietary fat, the content of vitamins and microelements;
- minimize the consumption of food stimulants: tea, coffee, fatty foods, smoked foods, alcoholic drinks;
- drink at least 2 liters of clean water daily (other drinks do not count).
Compliance with these rules is useful for the prevention of not only neurocirculatory dystonia, but also many other diseases. The body always responds gratefully to care for it and begins to cope much better with inevitable stress and physical activity.
Causes of neurocirculatory dystonia
Today it is believed that there is a predisposition to the development of neurocirculatory dystonia, but for its formation it is necessary to be exposed to certain external factors, the list of which is very large.
- Acute and chronic infections, accompanied by intoxication and, as a consequence, disruption of neurohumoral balance.
- Hormonal changes that may be associated with puberty, pregnancy, the menstrual cycle, etc.
- Stress and other psycho-emotional stress.
- Many diseases of internal organs that disrupt homeostasis.
- Endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, pathology of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands).
- Diseases of the nervous system, head injuries.
- General fatigue.
- Bad habits (alcohol, smoking).
- Drinking large amounts of caffeine.
- Chronic intoxication as a result of any harmful substances entering the body (often happens at work).
- Staying in stuffy rooms, in the heat, especially in direct sunlight.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
Doctors at the Energy of Health clinic do not downplay the significance of the symptoms of NCD. We guarantee each patient a thorough examination, including all the necessary samples and tests, as well as selection of the most gentle, but at the same time effective treatment. At your service:
- drawing up a medication correction regimen in accordance with the characteristics of the course of the disease (not only the complex of symptoms, form and stage of the disease are taken into account, but also the emotional background, chronic diseases, hormonal status, characteristics of the patient’s work, etc.);
- restorative procedures: physiotherapy, massage;
- selection of physical exercises to perform in the gym with an instructor and at home;
- acupuncture;
- help from a psychotherapist and psychiatrist;
- selection of a resort for treatment in a sanatorium, collection of necessary documents;
- detailed recommendations for correcting lifestyle, nutrition, and physical activity.
We will help keep the disease under control and will always come to the rescue in case of exacerbation.
Causes of neurocirculatory dystonia of mixed type (ICD code 10)
Modern traditional medicine, despite its rapid development, still cannot say for sure what is the cause of VSD and NCD in such a huge number of people these days.
But this disease was known in ancient times. Hippocrates, who lived in the 5th century BC, called this illness “a disease of the soul,” and he was absolutely right.
Doctors believe that the cause of the development of NCD may be:
- Past infectious diseases.
- Chronic diseases.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Disturbances of the endocrine system.
- Systematic physical overwork of the body.
- Interaction with harmful substances at work (poisoning).
- Frequent stress.
- Suffered psychological traumas, shocks.
- Lack of sleep.
- Hereditary factor.
They are partly right. But psychotherapists, psychologists, psychiatrists and many healers are sure that all nervous disorders and neuroses happen for only one reason - internal imbalance. Even if we agree that VSD appeared after a hormonal imbalance or a serious infectious disease, what caused them? After all, physiological diseases also have a psychosomatic cause. And the same hormonal imbalance often happens after stress and strong experiences. And the infection often sticks to us due to the decline of immunity, which has also decreased due to stress. Therefore, the root of dystonia is precisely the psycho-emotional state of a person.
Neuroses arise because various conflicts occur within the individual, there are unresolved problems, experienced shocks, fears, tensions, negative thoughts, and the like.
Advantages of the clinic
The Health Energy Clinic uses an integrated approach to solving any patient’s medical problems. We offer the most complete range of services, including:
- consultations with narrow specialists, including obtaining the opinion of a foreign doctor remotely;
- all types of tests and diagnostic procedures;
- modern treatment regimens compiled on an individual basis;
- issuance of certificates and conclusions.
A healthy person can choose one of the comprehensive check-up diagnostic programs to identify hidden pathologies.
Neurocirculatory dystonia is a disease that is not recognized by all doctors, but its symptoms do not disappear. Don’t let disruptions in the nervous system ruin your life, sign up for diagnostics and treatment at the Energy of Health neurology clinic.
Diagnosis of NCD by mixed type
Although the causes of VSD lie in a person’s head, physical health should not be neglected. If there are signs of dystonia, it is recommended to make a primary diagnosis, which includes:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Blood chemistry.
- Ultrasound of vital organs.
- ECG.
- Rheoencephalography.
It is necessary to consult a neurologist, endocrinologist, cardiologist, gynecologist (for women), and urologist. Other specialists and studies are assigned as needed.
The main problem of modern doctors is that they do not consider the disease as a single whole of soul and body. Each specialist begins to treat a person exclusively in his own field, which ultimately leads to the prescription of a bunch of useless medications and a lot of wasted nerves and money. Therefore, when identifying NCD, it is recommended to immediately find a competent psychotherapist who can help the patient look at his body as a single system, and at his illness as a single problem, and find the underlying causes of the “failure.”