In the conditions of modern workload, the need to process the information flow, people are increasingly choosing a sedentary lifestyle, preferring to travel by transport, and as a result, diseases associated with physical inactivity are being discovered. In such conditions, every system suffers: neurology, gynecology, cardiology.
One of the serious consequences is stagnation of blood in the pelvis.
The very definition of “blood stagnation” means a violation of the natural outflow of blood from any area. Due to the location of a large number of organs in the pelvis, this disorder causes significant damage to the quality of life.
Pelvic organs:
- lower gastrointestinal tract, including the rectum;
- bladder;
- in women, reproductive organs: uterus, ovaries and vagina;
- in men: prostate gland and seminal vesicle.
All pelvic organs are secured by ligaments in their anatomical places and influence each other. The inflammatory process in one of them leads to inflammation in the others.
Causes of blood stagnation in the pelvis
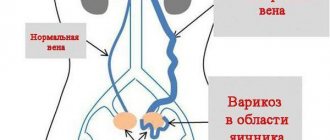
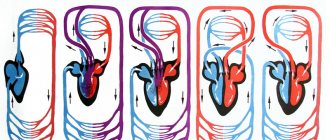
The blood supply to the pelvic organs is carried out through the large abdominal aorta, the outflow occurs through the venous network, which has a special structure - without valves. Arterial vessels for guaranteed blood supply to each organ have redundant branches.
The main reasons that lead to stagnation of blood in the pelvis:
- Physical inactivity. With a sedentary lifestyle, the amount of adipose tissue increases, flabby muscles compress the blood vessels;
- Tight or tight underwear that compresses blood vessels also impairs blood flow;
- Varicose veins are a violation of the elasticity of blood vessels, their deformation;
- Bad habits: alcohol, smoking lead to vasospasm, and this undoubtedly affects blood circulation;
- Unbalanced diet. The vascular tissues are constantly renewed and, obviously, for a healthy state you need proper replenishment of nutrients that will maintain the elasticity of the walls;
- Problems with the nervous system. Prolonged stress leads to vasospasm, and, accordingly, blood flow worsens;
- Prolapse of internal organs. This may be due to childbirth, heavy pregnancy, or heavy lifting. Displaced organs compress the vessels and impede outflow;
- In women, stagnation can be caused by structural features of the uterus, for example, a bend, a side effect of taking oral contraceptives, or abortion.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of calcium impregnation of blood clots is not completely clear. Phleboliths are the result of a slowdown in local blood flow, lymphatic drainage, and vascular dilatation. The onset of pathology is marginal intravascular thrombosis with endothelial defects, impaired coagulation and fibrinolysis. Then, fibrosis, mineralization as natural healing.
Passive precipitation of calcium crystals forms the core of stones; connective tissue fibers undergo secondary calcification. Each repetition of the pathological process provokes the growth of layers with the formation of phleboliths of the small pelvis or venous calculi. Phlebolithiasis is explained by a high concentration of phosphatase in the tissues around the bladder with deposition of the enzyme on the surface of the blood clot.
Phleboliths have an oval shape with the diameter of a vein and a multilayer membrane. According to the chemical composition, the stones contain calcium, magnesium, iron, which have high radiopacity. Therefore, shadows of phleboliths are the basis for x-ray diagnosis of the disease.
Symptoms
With stagnation, the negative effect accumulates. At the first stage, a person does not feel anything, but subsequently the condition worsens and the following symptoms appear:
- At the beginning, there are sensations of slight tingling and aching pain, which can worsen, for example, under stress;
- Feelings of heaviness in the abdomen, pressure;
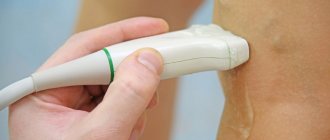
- Pain in the lower abdomen, many go for a pelvic ultrasound to find out where the inflammation is. The pain often radiates to the lower extremities, lower back, thigh, and genitals;
- Numbness of the lower extremities. Impaired blood supply to the pelvic organs leads to a deficiency of blood in the legs, and swelling may develop;
- Frequent urination and urinary incontinence.
Symptoms can occur individually or together. As a rule, deterioration of the condition is observed after physical activity and sexual intercourse.
Features of therapy
Phleboliths in the pelvis and stones in other locations do not require active treatment. Therapeutic correction is necessary when symptoms appear. For this purpose, the following methods are used in clinical phlebology:
- Sclerotherapy is the exclusion from the general blood flow of deformed veins with branches and malformations, with which phleboliths are in direct contact, by introducing into the vein a special sclerosant substance that glues the walls of the veins with subsequent death and desolation. Classic sclerotherapy and precision sclerotherapy are used under the control of visualization tools.
- Endovascular laser coagulation as monotherapy or in combination with vein sclerosis, surgery (for multiple stones).
- Phlebectomy in the classic version or after preoperative sclerotherapy to reduce the risk of uncontrolled bleeding.
- Selective removal of phleboliths - removal of stones from open access under the control of ultrasound, microscope or palpation. The technique alleviates symptoms, but, as a rule, is not performed independently: only in combination with other methods of correction.
In essence, conservative therapy is the correction of symptoms caused by phleboliths in the pelvis or other regions. In women, the symptoms of gynecological diseases predominate, so the entire arsenal of anti-inflammatory, absorbable, antibacterial therapy is used, which is correlated with the main gynecological pathology. In men, urological problems predominate, so treatment is focused on urethritis, prostatitis of various etiologies, and tumor processes.
Conservative treatment of phleboliths themselves involves taking the following medications:
- Anticoagulants (heparin-based) or antiplatelet agents: Ticlopidine, Iloprost.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, NSAIDs) to relieve pain and inflammation: Nise, Ibuklin, Voltaren, Nurofen, Ketorol.
- Antispasmodics: No-Shpa, Drotaverine, Spazmalgon.
To reduce congestion in the pelvis, an individual complex of exercise therapy and the use of a contrast shower are recommended. A special diet is required, excluding “heavy” foods that cause constipation, dyspepsia and filling the daily menu with fresh vegetables and fruits. The drinking regime should also be calculated - at least 1.5 liters of water per day.
If pathological inclusions are found in the inferior vena cava, surgery to implant a vena cava filter may be required.
In addition, varicose veins caused by phleboliths require the use of compression hosiery or elastic bandages. Underwear is selected according to size together with the attending physician. These can be special stockings, socks, tights.
Compression knitwear is of high quality and can normalize pressure in the vessels of the legs and pelvic veins. When using it, blood flows to the lower parts of the body evenly and measuredly. The density of knitwear is determined individually. The main thing is the absence of discomfort, since the patient will have to wear such underwear throughout the working day, during heavy physical activity: lifting weights, sports exercises, pregnancy.
Diseases that develop against the background of blood stagnation
As a result of prolonged stagnation, diseases develop that have to be treated with medication and, in some cases, surgery.
The following pathologies are observed in women:
- Adnexitis, inflammation of the appendages;
- Menstrual irregularities;
- Miscarriage;
- Infertility.
In men, the diseases are as follows:
- Prostatitis;
- Varicocele;
- Impotence.
One of the most common ailments is hemorrhoids, and almost everyone notices a deterioration in their emotional state.
What kind of pathology is this
Phlebolith are small particles of calcified blood clots that form in the veins. On X-rays they appear as white spots.
Often occur in the pelvic area and kidneys. They are also found in the maxillofacial areas, and with varicose veins.
Phleboliths are accompanied by severe damage to the veins. Unattached to the walls, they migrate to the nearest vessels.
Manifestations of pathology increase with the patient's age. They can be detected not only in older people, but also in infants. Since there are no obvious symptoms, the person is unaware of their presence.
Treatment
Treatment of diseases caused by blood stagnation is only a temporary measure. In any case, if there is a reason why the outflow is disrupted, then it must be eliminated; in order to receive recommendations, you need to schedule a visit to a therapist. It is very important to deal with the root problem; in most cases, diet and increased physical activity help, but this will have to be approached under the supervision of a doctor so as not to stimulate deterioration.
At the Heratsi Medical Center you can visit a therapist for free. It is also possible to invite a doctor to your home.
The cost of all services of the medical center can be viewed in the “Price” section or by calling the 24-hour hotline.
Watch a video with a simple exercise that will help get rid of blood stagnation in the pelvis:
Diagnostics
Since phleboliths do not have classical symptoms, their diagnosis is based on instrumental examination methods. The algorithm includes:
- History taking, physical examination.
- UAC, OAM, biochemistry.
- Analysis of plasma coagulability, prothrombin index. coagulogram.
- Fundus examination.
- Blood for hormones.
- Ultrasound scanning of veins, which makes it possible to assess the anatomical and hemodynamic features of the affected segments: phleboliths are defined as echogenic oval foci with a flickering artifact.
- Radiography reveals phleboliths in the projection of the small pelvis in the form of rounded shadows with many layers. An important diagnostic sign is the presence of radiotransparent).
- Computed tomography with contrast visualizes intravascular calcifications with multiple voids and branches.
- MRI of soft tissues visualizes the condition of nearby tissues and the degree of vascular damage (the “void flow” phenomenon).
- Biopsy with histological analysis of stones.
- Excretory urography.
- Sialography is a radiopaque or radionuclide study of the major salivary glands.
In order not to confuse phleboliths with stones of the kidneys, bladder, ovaries, prostate, you need to focus on their distinctive features:
- after filling the bladder, phleboliths do not change position;
- not associated with contrast enhancement of the kidneys or ureters;
- close to the pubis.
Discovery and description of phleboliths
Phleboliths in the pelvis - what is it? These are vein stones, which are calcifications of dried blood clots and look like beads of different diameters.
Phleboliths were first described and discovered by Albers-Schoenberg in 1905. The nature of their origin was described by pathologists Frenkel and Forsel. Phleboliths have a homogeneous and layered shadow with a dense center. Homogeneous phleboliths are formed during the sequential calcification of a blood clot. And layered - when fibrin threads join the calcification process.
Possible complications
Phlebostasis is the formation of multiple stones. In medical practice, phleboliths can cause a danger comparable to thrombosis. The risk of recurrence of occlusion increases.
With varicose veins, the likelihood of recurrent blood clots increases. If stones migrate and enter the portal vein, this is a dangerous complication. This can lead to pulmonary embolization, which has serious consequences.
Diet for phlebolitis
Nutrition for vascular diseases is aimed at strengthening the venous walls, normalizing blood flow and diluting it. Eating vegetables and fruits containing vitamins and quercetin, the routine helps thin the blood and improves the overall health of the immune and cardiovascular systems. Vegetables contain vitamins and microelements, fiber, which are beneficial for blood vessels, and can be consumed in any form. You should avoid vegetables that contain starchy substances and increase blood sugar levels. Fruits and berries, such as apples, cherries, cherries, rose hips, containing vitamin C and K, are very useful for poor blood clotting and as antioxidants. Frequent consumption of melons and watermelons, which contain very large amounts of liquid and sugars, should be avoided. Vegetable oils containing omega acids have a venotonic effect and contain vitamin E. The drinking regimen should consist of water and natural diluted juices.
It is not recommended to consume baked goods, confectionery products, fatty and fried foods, smoked foods, pickles and alcohol.