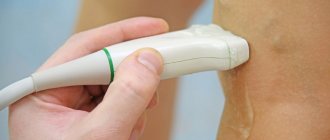
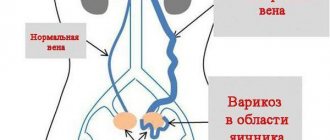
Varicose veins are an increase in the size of veins. Any superficial vein can become varicose, but the veins in the legs are most often affected. In an upright position (standing and walking), the pressure in the veins of the lower body increases.
For some, varicose veins and spider veins are simply a cosmetic problem, but for many people, varicose veins can cause heaviness and swelling in the lower extremities. Sometimes varicose veins lead to more serious problems - trophic ulcers.
Treatment may include both measures to prevent the development of chronic venous insufficiency and surgical procedures to remove veins (various techniques).
Read more about the treatment of varicose veins.
Causes of varicose veins
First of all, this is heredity: weak venous walls are a feature that is passed on from parents.
In addition to hereditary factors, vascular damage is promoted by:
- overload during sports training;
- sedentary work and a generally sedentary lifestyle;
- work on feet;
- taking hormonal contraceptives;
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, leading to an increase in venous pressure;
- leg injuries;
- diseases of the pelvic organs;
- weakened immune system;
- excess weight;
- high growth;
- unbalanced diet;
- constipation;
- addiction to alcohol;
- smoking;
- excessive passion for tanning, sauna;
- tight clothes, shoes – uncomfortable or with high heels;
- stress, constant worries;
- elderly age.
It is noteworthy that varicose veins in women are diagnosed twice as often as in men. After all, it is the fair sex who wear high-heeled shoes, bear and give birth to children, and take hormonal contraceptives.
Also read the article varicose veins in men
Skin itching “out of the blue”
The most common reason for visiting a dermatologist is itching. There are cases when there are not even any rashes on the skin, but it itches so much that a person literally tears the skin. The suffering is further aggravated by the fact that everyone around them suspects a simulation or a mental disorder.
And, it would seem, it’s not a big problem - a person scratches himself, and that’s it, there are no specific skin diseases, let him be happy. But itching can indicate very serious problems, not to mention the fact that it greatly worsens the patient’s quality of life. Constant itching can lead to depression and even suicide attempts.
The most serious reason
The most important causes of itchy skin are malignant tumors. Itching may be one of the first signs of a tumor and appear before other symptoms. There have been cases when such a difference was up to 5 years!
Paraneoplastic (tumor-associated) skin itching can occur with any tumor, but more often occurs with carcinoma of the stomach, pancreatic cancer, lung, intestinal, brain, breast and prostate cancer. The whole body itches, but there are areas where the itching is more intense.
With Hodgkin's lymphoma, itching is also one of the most common accompanying symptoms and is observed in 25% of patients suffering from this disease.
If “thanks to the itch” you are examined on time, then cancer can be caught in the early, treatable stages.
Water: helps and provokes
Not as fatal as hidden tumors of internal organs, and perhaps the most common cause of itching is simple dry skin.
Modern hygiene requirements include daily showers. In principle, this is correct, but frequent use of detergents, especially in people whose skin is already prone to dryness (and this problem occurs in large numbers among the elderly), causes drying out of the skin. Soap washes away not only dirt, but also substances that retain moisture. As a result, there is itching, but no rashes.
Stop washing? Adherents of the “back-to-nature” concept, and to be honest, some colleagues (usually with a post-war education) advise exactly this. But bacterial and fungal infections will not keep you waiting, and the smell...
So you need to continue to maintain hygiene, but supplement it with special preparations that soften the skin and retain moisture in it (emollients). There are a huge number of them on the market, and they act in different ways; your doctor will tell you what exactly is right for a particular person.
And further. Some people simply don't drink enough water. Especially old people, whose sense of thirst may be dulled, and due to age, they may not remember or may not get what they want due to weakness (yes, that situation when there is no one to give a glass of water).
This leads to much more significant health problems than itchy skin, but also to that. People caring for the elderly should understand the situation and regularly provide water to their charges.
Unfortunately, as practice shows, such patients are often treated with disdain, believing that out of consultations with specialist doctors, only one is necessary - with a psychiatrist.
Yes, such a patient may also have a mental health disorder. But this does not happen as often as society imagines.
Etiology: announce the entire list
In addition to oncology, dry skin and mental status disorders, itchy skin without rashes can be caused by:
- endocrine diseases: hyper- and hypothyroidism, diabetes, hyper- and hypoparathyroidism;
- — neurological diseases: cerebrovascular accidents, multiple sclerosis, peripheral nerve injuries, postherpetic neuralgia;
- — hematological diseases;
- ——Sjogren's syndrome (a systemic disease associated with pathological dryness of the integument).
And also: chronic renal failure, liver disease, biliary tract obstruction, chronic alcoholism (use of psychoactive substances), pregnancy, drug reactions, parasitic infestations, toxic effects of household and industrial chemicals, HIV infection, etc., etc. P.
Therefore, you do not need to undergo a full examination - in this case you will definitely not succeed. You will only waste time, money and nerves. And the reason may remain unclear. Therefore, please leave the search for the cause to your doctor.
How will the doctor deal with this?
At the stage of collecting anamnesis, the doctor will definitely find out the following factors:
- onset (sharp, gradual);
- —flow (continuous, intermittent);
- ——character (stabbing, burning).
—It is also important: whether the itching is localized or “itches everywhere,” how long—it is present and at what time it appears.
The doctor will try to detect provoking factors - is there a connection with the patient’s activity (profession, hobby), perhaps there has been unusual physical activity recently, new pets have appeared, etc. Trips and travel, traumatic situations in the recent past, play a role.
Also important is your sexual history and, finally, what you have already tried to treat yourself.
Remember! Applying a variety of “folk remedies” to scratched skin greatly complicates the establishment of a correct diagnosis and the possibility of carrying out certain tests, and contributes to the development of pustular and other complications.
Stages of initial examination
After collecting your medical history, the doctor will conduct a general examination, take your temperature, find out if you are suffering from excessive sweating, or if you have been particularly tired or losing weight lately.
What are varicose veins
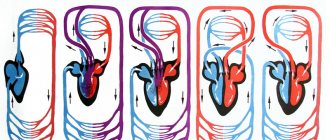
Before moving on to the symptoms and treatment of varicose veins in women, let's look at the anatomical features of the disease. The movement of blood through the vessels is ensured by the rhythmic contraction of the heart. From top to bottom, to the legs, blood flows effortlessly, but its reverse path - up through the veins is possible thanks to special valves inside the veins. Relatively speaking, from a heartbeat, blood rises and is retained by the valve until the next beat. Active upward movement of blood is also facilitated by regular contraction and relaxation of the leg muscles (an obvious benefit of walking!). With varicose veins, the vessel expands, which prevents the valves from closing, and the resulting gap slows down the outflow of blood. Another cause of varicose veins is the loss of elasticity in the veins, which is necessary for the normal narrowing and dilation of blood vessels.
Complications of varicose veins
- phlebitis
Inflamed vessels can lead to thrombophlebitis: in addition to the walls of the vessels, the surrounding tissues also become inflamed, painful symptoms are observed in the legs, the skin in the areas of inflammation turns red, and the body temperature rises.
- venous bleeding
With varicose veins of the lower extremities, blood circulation is disrupted and intravenous pressure increases. As a result, the veins swell and increase in size. Any external impact - a minor injury, a slight bruise - can cause venous bleeding, which, as a rule, goes unnoticed, as it does not cause pain, but can lead to significant blood loss and cause great risks.
- deep vein thrombosis.
Thrombi are blood clots in blood vessels; they are formed as a result of impaired blood circulation and damaged vessel walls. Blood clots block venous channels, leading to deep vein thrombosis.
The disease must be treated in a timely manner, avoiding all kinds of complications. An experienced doctor will identify varicose veins of the lower extremities in its very initial manifestations.
Symptoms and treatment of vein disease in women
At the initial stage, the thought of treatment will not come to mind: the signs of varicose veins in women are almost invisible, appearing only in heaviness and tension in the legs. Heat, itching, cramps in the calf muscles at night - these sensations indicate the development of vascular pathology. At a later stage, the disease is already determined visually: the legs swell, swollen veins become visible, dermatitis and lumps appear on the skin, which can develop into trophic ulcers. Similar symptoms of varicose veins in women in the photo, treatment (comparison: before and after) can most often be seen in advertising brochures of specialized clinics.
When and who to contact
Dangerous manifestations:
- excessive visual appearance of veins;
- painful sensations in the abdomen;
- bowel dysfunction;
- general malaise;
- poor results of blood and urine tests;
- pain on palpation in the abdominal area;
- increase in the size of the liver and spleen.
If a woman observes the development of such symptoms, she should immediately contact a gynecologist who is managing the pregnancy. Additionally, you may need to be examined by a gastroenterologist, vascular surgeon, or endocrinologist.
Treatment results for our patients
Disease: varicose veins
Treatment method: EVLT + MINIFLEBECTOMY
Combined treatment of varicose veins. Endovasal laser obliteration of the vein on the left leg (EVL) + Miniphlebectomy
Disease: varicose veins
Treatment method: EVLT + MINIFLEBECTOMY
Laser treatment (EVLT) followed by miniphlebectomy of the tributaries of the great saphenous vein on the thigh and shin of the right leg. Miniphlebectomy of varicose veins.
Disease: Telangiectasia
Treatment method: Foam sclerotherapy
To remove the stars, the patient underwent a session of microfoam sclerotherapy (Foam-Form) of the reticular veins under the control of laser transillumination.
Disease: varicose veins
Treatment method: EVLT + MINIFLEBECTOMY
Upon examination of the patient, varicose veins were diagnosed on the right leg. Combined treatment with EVLT + miniphlebectomy was performed.
I'll wait a little longer Make an appointment
Diagnostics
A reliable diagnosis can only be made after a full examination. Initially, the doctor must listen to the patient’s complaints, study the anamnesis, and conduct an examination.
In this case, it is important to study the external condition of the skin - determine the color, the presence of rosacea, the degree of varicose veins. Additionally, it is necessary to measure blood pressure.
The doctor must determine whether the woman suffers from chronic, genetic diseases. It is important for a woman to tell the truth about her own lifestyle. This will help the specialist determine whether there is a predisposition to varicose veins.
Pregnancy itself is a risk factor. A woman should get tested regularly. The results allow you to monitor the condition of the expectant mother.
Blood tests.
- General analysis.
- Biochemical analysis. Carry out to assess the performance of internal organs.
- Coagulogram. Allows you to determine blood clotting and liver condition.
Urine studies.
- General analysis.
- Daily diuresis.
Additional methods.
- Endoscopy. This method allows you to assess the condition of the gastrointestinal mucosa. Refers to instrumental examinations.
- Ultrasound with Dopplerography. The ability to thoroughly examine the condition of veins and internal organs.
- ECG. For the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases.
If the results are not sufficient to establish a diagnosis, then the doctor may additionally prescribe the following examinations:
- biopsy;
- laparoscopy;
- X-ray;
- MRI;
- CT.
If a vascular network appears on the abdomen during pregnancy, in any case you should consult a doctor. This will reassure the woman and, if necessary, the specialist will choose a safe method to eliminate the problem.
Prevention of varicose veins
Moderate physical activity, regular walks, a balanced diet with a rich set of vitamins, and enough water will help prevent the stage when the veins in a woman’s legs are already protruding and treatment is inevitable. Giving up bad habits and choosing comfortable clothes/shoes will also prolong the health of your blood vessels.
Treatment of vein disease in women
There are two types of treatment for varicose veins in women: conservative and invasive. In the first case, we are talking about measures that are aimed at preventing and stopping the development of the disease: following a diet, wearing compression garments, taking phlebotonics as prescribed by a doctor. Invasive treatment involves surgical interventions such as sclerotherapy, laser coagulation, miniphlebectomy, etc. The treatment method is selected individually by a phlebologist.
What is the treatment for varicose veins after childbirth?
Modern treatment of varicose veins after childbirth is practically no different from the treatment of varicose veins in other situations. The only important difference is some time restrictions inherent in the postpartum period. Most often, radical treatment of varicose veins begins six months after childbirth. It includes the following components:
- Endovascular thermal ablation (laser or radiofrequency).
- Miniphlebectomy.
- Scleroobliteration.
These modern technologies make it possible to treat varicose veins after childbirth quickly and radically. To treat varicose veins after childbirth using the most effective and modern techniques, you need to choose the clinic and doctor wisely.
Treatment of varicose veins after childbirth in our clinic
The specialists of the Innovative Phlebological Center have significant experience and use the most current technologies for the treatment of varicose veins in their practice, which allows them to treat varicose veins after childbirth in the shortest possible time without side effects and strict restrictions.