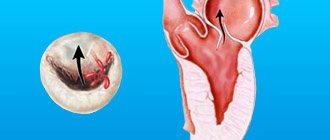
If, as a result of a pathological process, deformation of the valve tissue occurs and the hole through which blood enters the next part of the heart narrows, then such a defect is called stenosis. Deformation can lead to the heart valves not closing due to changes in shape, shortening them as a result of scarring of the affected tissues; this defect is called insufficiency. Valve insufficiency can be functional, resulting from stretching of the chambers of the heart; the area of the unchanged valve is not enough to close the enlarged hole - the leaflets sag (prolapse).
The work of the heart is restructured depending on the changes that have occurred and the needs of blood flow in the body.
Classification of heart defects
Depending on different criteria, PPPs vary:
- By etiology (cause of occurrence):
- rheumatic;
due to bacterial endocarditis;
- syphilitic;
- due to expansion of the heart chambers in heart failure;
- traumatic - during injury or surgery;
- after radiation therapy, oranosis of the chest or mediastinum.
- According to the nature of damage to the heart valves:
- valve narrowing - insufficient opening, preventing the movement of blood from one chamber to another;
valve insufficiency, incomplete closure, blood returns to the heart chamber;
- combined – disruption of several valves;
- isolated – changes in the operation of one valve;
- combined - when the valve does not close tightly enough (valve insufficiency) and does not open completely (stenosis or narrowing of the valve) occur simultaneously in one valve.
- By localization of defects:
- mitral valve;
tricuspid valve;
- pulmonary valve;
- aortic valve.
- For functional impairment:
- prolapse;
failure;
- stenosis.
- According to the state of the cardiovascular system:
- compensated – there is no circulatory failure;
subcompensated - temporary disruption of blood flow (with increased physical activity, during pregnancy, with increased temperature);
- decompensated - there is a circulatory disorder with the slightest effort and at rest.
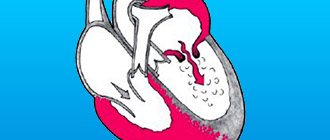
Heart valves and their defects
The heart has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. From the atria, blood enters the ventricles, and then through the valves, with the help of contractions of the heart muscle, enters the arteries. Valves ensure blood flow in the desired direction and quantity. If they close or do not open completely, this prevents normal blood circulation.
As a result, the heart gradually increases in volume and stretches, compensating for blood deficiency and working under constant overload. Exhaustive work of the heart can cause the development of serious cardiovascular diseases, such as arrhythmia or heart failure. In addition, heart valve defects can cause complications due to certain ongoing infectious diseases.
Most often, heart defects are diagnosed in patients over sixty years of age. The reason is that with age, the valves of the valve apparatus lose their elasticity, and the heart increases in size. As a result, blood flow decreases and it unevenly fills the cavities of the heart - heart failure develops.
There are four types of heart valves, and each has a specific function:
- Aortic : prevents blood from flowing from the aorta into the left ventricle of the heart.
- Mitral : prevents the flow of blood from the left ventricle of the heart into the left atrium at the moment when the heart muscle contracts and blood is pushed into the vessels.
- Pulmonary : Prevents the flow of blood from the pulmonary artery into the right ventricle of the heart.
- Tricuspid : valve between the right ventricle of the heart and the right atrium.
If the valves are enlarged, narrowed, loose or torn, it becomes difficult for them to close, and blood flows back with each contraction of the heart. As a result, the heart experiences enormous stress and eventually loses its performance.
Depending on the form of the disease, heart valve defects can manifest as:
- stenosis – narrowing of the lumen (opening) of the vessels through which blood flows. This significantly increases the load on the heart, as it makes it more difficult for blood to be pumped out.
- insufficiency - damage to the heart valve leaflets, resulting in their inability to close completely. In such cases, the blood flows back.
- a combination of stenosis and insufficiency - the affected valves form an obstacle to the passage of blood. In this case, some of the blood passes through the hole, but returns back into the next phase of the cardiac cycle.
Symptoms of acquired heart disease
Depending on the type of disease, symptoms may vary, but there are several ailments that are common to most heart defects:
- dyspnea;
- fast fatiguability;
- pressing pain in the heart area (especially during physical activity);
- dizziness;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- change in skin color;
- dry cough and hemoptysis;
- interruptions in heart function;
- loss of consciousness.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult your doctor immediately. PPPs are very dangerous and can lead to serious consequences. Including heart failure. There is no need to wait until the disease goes away on its own or try to cope with it on your own. Contact the specialists of the cardiology center of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, and we will conduct the necessary examination
“Blue or white”: what are heart defects in children?
Heart defects require close attention. When faced with such a diagnosis in children, parents may feel confused. Tatyana Mikhailovna Frolova, a pediatric cardiologist at the Expert Clinic Smolensk, will help us understand the issue.
— What is a heart defect in a child and why is it dangerous?
— Heart defects are structural abnormalities of the heart and large vessels. They can be congenital or acquired. Congenital heart defects are more common in children.
Heart defects vary in severity. There are critical defects in which hemodynamic disturbances are incompatible with life. In this case, in the absence of timely assistance, death occurs in the first hours or days after birth. If the heart defect is not critical, it still poses a danger: the heart experiences increased stress, this leads to myocardial dystrophy, chronic heart failure, and early disability.
Heart defects are structural abnormalities of the heart and large vessels. They can be congenital or acquired. Congenital heart defects are more common in children .
— What does “blue/white (pale) type heart defect” mean?
- This is one of the classifications. This division was proposed by the American Heart Association. The white or pale type includes those heart defects in which venous and arterial blood do not mix, or arterial blood enters the venous bed (there is no oxygen starvation of the body). With blue defects, venous blood mixes with arterial blood, as a result of which the oxygen content sharply decreases, cyanosis occurs, and the body experiences significant oxygen starvation. Usually it is the blue type defects that are the most severe.
— Is this division used now?
— Yes, this is one of the possible classifications of congenital heart defects in children.
— What congenital heart defects are especially common?
— The most common types are ventricular septal defect (about 40% of cases), atrial septal defect (about 11% of cases) and patent ductus arteriosus (about 10% of cases).
— Are the symptoms of congenital heart defects always noticeable immediately after the birth of a child?
— It depends on how severe the hemodynamic disturbances are. Severe heart defects are immediately noticeable. If hemodynamic disturbances are minor, there may be no external signs. However, such defects cannot be ignored. For the timely diagnosis of heart defects in children, mandatory screening has been introduced: before the child is one year old, they certainly undergo echocardiography.
“Ultrasound of the heart and echocardiography are the same thing.” Quote from the material “What a heart ultrasound will tell you”
— What are the causes of heart defects in children?
— 90% of congenital heart defects have several combined causes for their development (multifactorial theory of occurrence). The causes of congenital heart defects include maternal diseases (arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, metabolic disorders, previous miscarriages, etc.), bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs), previous infectious diseases, especially in early pregnancy ( After all, the fetal heart is formed already from the 5th week). The most dangerous infections are rubella, Coxsackie virus and cytomegalovirus, viral infections with a rise in temperature in the first trimester of pregnancy in the mother.
Read the material on the topic: What are the dangers of TORCH infections?
We must not forget about the teratogenic effect of some drugs (for example, antiepileptic drugs, lithium, thalidomide, vitamin A, isotretinoin, sulfasalazine, ibuprofen, trimethoprim) and the toxic effect of constant contact with certain substances in hazardous industries (varnishes, paints).
About 8-12% of congenital heart defects are associated with chromosomal abnormalities (Down syndrome, Edwards, Patau, etc.) and only 2% are hereditary (if there are relatives with similar heart defects in the family).
Acquired heart defects in children are the result of complications of serious diseases. Most often, the following pathologies lead to the formation of the defect: rheumatic fever, infective endocarditis, systemic connective tissue diseases (including hereditary connective tissue dysplasia), cardiomyopathies (hypertrophic and dilated).
— Tatyana Mikhailovna, in what cases is it worth going to a cardiologist to rule out acquired heart disease? What are the signs of heart disease in a child that should alert parents?
— As I already said, acquired heart defects are the consequences of serious illnesses. Usually, with such diseases, children are already under the supervision of a doctor. Doctors are aware of the possible complications of systemic diseases.
Connective tissue dysplasia requires special attention, since changes in the heart can be asymptomatic for a long time. In this case, parents need to pay attention to such signs as fatigue, decreased tolerance to physical activity, and shortness of breath. Similar manifestations can occur in congenital heart defects that are not diagnosed in time. Therefore, you need to pay attention to such symptoms. And be sure to undergo medical examination in a timely manner.
One of the symptoms of heart disease in a child may be a heart murmur. Read more about this in our article
— Please tell us about the methods of treating heart defects. Is it possible to fully compensate for hemodynamic disorders?
— Treatment methods are divided into surgical and therapeutic. Surgical, in turn, can be radical or auxiliary. Radical operations are aimed at completely eliminating the defect. Blood circulation normalizes, patients can subsequently lead a normal lifestyle and play sports.
If it is immediately impossible to completely eliminate the defect, surgery is performed to correct hemodynamics. An auxiliary operation allows you to reduce the load on the heart and prepare for radical surgery.
Conservative (therapeutic) measures are aimed at reducing the load, improving heart nutrition and preparing for surgery. It is impossible to completely eliminate the defect using conservative methods alone.
You can make an appointment with a pediatric cardiologist here
ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
Interviewed by Daria Ushkova
For reference:
Frolova Tatyana Mikhailovna
Graduate of the pediatric faculty of the Orenburg State Medical Academy in 1997.
In 1998, she completed her internship in the specialty “Pediatrics”.
In 1999-2001 she completed postgraduate studies by correspondence and has an academic degree of Candidate of Medical Sciences.
In 2014 - professional retraining in the specialty "Pediatric Cardiology", in 2017 - in the specialty "Functional Diagnostics".
Currently holds the position of pediatric cardiologist and functional diagnostics doctor at the Expert Clinic, Smolensk. Receives at the address: st. 8 March, no. 20
The editors recommend:
No more sentence! Congenital heart defects in children: identify and treat
Mitral valve prolapse: dangerous or safe?
How to prepare for pregnancy?
Often – how much? A child who is often ill at a pediatrician's appointment
Diagnostics
When diagnosing, it is important to collect as much information as possible about the patient: complaints, symptoms, chronic, hereditary or past infectious diseases. Next, the doctor performs a physical examination: the heart and lungs are listened to, blood pressure is measured, and the liver is palpated and measured.
If, after an initial examination and history taking, the doctor discovers characteristic symptoms of heart defects, the patient is referred for additional instrumental studies:
- ECG;
- daily ECG monitoring;
- Echocardiography – ultrasound examination of the heart;
- chest x-ray;
- CT scan of the heart;
- MRI of the heart.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a cardiologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Electrocardiography (ECG) | 1400 rub. |
| Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) | 3500 rub. |
Prevention
Prevention of PPS involves treating the underlying disease that caused the valve damage. To prevent the development of defects, a cardiotrophic diet and lifestyle correction are additionally prescribed:
- refusal of salty, spicy, fatty foods;
- complete cessation of smoking and drinking alcohol;
- moderately active lifestyle;
- control of infectious diseases, including colds;
- annual monitoring by a cardiologist.
All prescriptions and dietary adjustments must be prescribed by your doctor during the treatment process. In our center, the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, several programs have been developed that will help identify whether you have a heart defect and determine the method of its treatment. You can learn more about the programs here.
General information
Acquired defects can manifest themselves in different forms. By origin:
- due to rheumatism, which is a general inflammatory disease of connective tissue that affects the heart; Source: A.N. Kalyagin Features of management of patients with rheumatic heart defects and chronic heart failure // Modern Rheumatology, 2009, No. 3, pp. 24-29
- against the background of syphilis;
- due to an inflammatory process on the inner lining of the heart (endocarditis);
- and due to other systemic diseases leading to damage to the heart muscle or complications to it.
According to the degree of defect, the acquired defect can be:
- local (when the defect is only in 1 valve);
- combined (more than 1 valve is affected);
- combined (both stenosis and insufficiency are observed in one valve).
The defect may be a stenosis due to inflammation, which led to the formation of scars, prolapse (eversion of the valves into the heart cavity), or failure (valve valves do not close completely). In this case, different valves may be defective (aortic, tricuspid, mitral, located on the trunk of the pulmonary artery).
An acquired defect can be expressed in different ways; it has three degrees:
- mild (minor effect on blood circulation);
- moderate;
- heavy.
This group of pathologies entails a number of complications:
- heart failure;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- blood clots
If left untreated or not detected early, heart disease can lead to disability and even death.
How to treat acquired heart disease
Treatment of acquired heart defects is a comprehensive approach, including drug treatment, a special diet, and lifestyle adjustments. If conservative treatment is not enough, surgical intervention is resorted to.
When you contact the center of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of FMBA, our doctors will quickly diagnose your disease and prescribe therapeutic treatment. The center has a therapeutic department, where you will be under the constant supervision of specialists. If after the examination it is determined that surgical correction is needed, you will be referred for a consultation with a cardiac surgeon, who will determine whether you need surgery.
Surgical methods:
- Catheter balloon valvuloplasty is the expansion of a narrowed lumen by inserting a balloon catheter. As a result of the operation, the fusion between the valve leaflets is separated, and the obstruction to blood flow is eliminated;
- Valvotomy (commissurotomy) – dissection of fused valves;
- Valve replacement is the replacement of a damaged valve with an implant. Open heart surgery using a machine that temporarily replaces the work of the heart;
- Percutaneous aortic valve replacement.
The main thing in treatment is timely diagnosis. Don’t put off your health for later, seek advice right now.
Prevention and prognosis for PPS
There are no preventive measures that would protect one hundred percent from acquired heart disease. But there are a number of measures that will reduce the risk of developing heart defects. This means the following:
- timely treatment of infections caused by streptococcus (in particular tonsillitis);
- bicillin prophylaxis in the event of a rheumatic attack;
- taking antibiotics before surgical and dental procedures if there is a risk of infective endocarditis;
- prevention of syphilis, sepsis, rheumatism: sanitation of infectious foci, proper nutrition, work and rest schedule;
- rejection of bad habits;
- presence of moderate physical activity, accessible physical exercises;
- hardening.
The prognosis for the life and ability to work of people with heart defects depends on the general condition, fitness of the person, and physical endurance. If there are no symptoms of decompensation, a person can live and work as usual. If circulatory failure develops, work should either be lightened or stopped; sanatorium treatment at specialized resorts is indicated.
It is necessary to be observed by a cardiologist in order to monitor the dynamics of the process and, as the disease progresses, to promptly determine the indications for cardiac surgical treatment of heart disease.
Causes
Acquired heart pathology occurs due to:
- infective endocarditis;
- syphilis;
- atherosclerosis;
- rheumatism;
- injuries of various types.
The causes of most cases of congenital heart defects are not fully diagnosed by doctors. These diseases can be caused by exposure to radiation in a pregnant woman. Viral and other infections suffered by a woman in the first trimester of pregnancy (hepatitis B, rubella, influenza) are dangerous. Taking drugs, alcohol and certain medications during pregnancy can also cause congenital diseases.