Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the pressure of the fluid that fills the eye. Obviously, ideally it should be normal. Most people are afraid of high blood pressure, but low blood pressure is also bad: the eye cannot maintain its correct shape, and the lack of fluid leads to deterioration in the cleansing of neighboring tissues.
Excessive pressure causes increased inflow or impaired outflow of fluid.
Among the reasons for this deviation from the norm are:
- anatomical features
- heredity
- age-related changes
- problems with the cardiovascular system
If elevated intraocular pressure is not normalized, it can lead to a serious disease - glaucoma. The disease is insidious, in advanced cases it leads to complete and irreversible blindness.
Normal blood pressure is considered to be between 10 and 20 millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
The norm is relative, as, for example, with blood pressure. It is impossible to start from dry population statistics and use them in a stereotyped manner in the treatment of a specific person. There are people whose blood pressure is 20 mm Hg. Art. no glaucoma, but 50% of people with diagnosed glaucoma have pressure below 21 mmHg. Art. The disease depends not only on pressure, but IOP is the only factor that we can influence, lowering it with drops or laser.
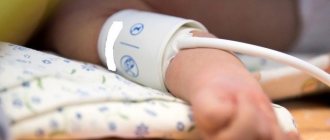
How to measure eye pressure
Methods for measuring IOP are divided into two groups: contact (when there is contact with the cornea of the eye) and non-contact.
- Palpation is the oldest method, requiring highly qualified doctors, experience and special sensitivity of the fingertips. IOP was considered significantly increased if the eyeball felt hard to the touch, and if it was soft, the pressure was normal. Of course, this type of diagnosis (even if you have the necessary skills) does not provide accuracy in determining the degree of deviation from the norm, so it is not used now.
- The tonometric method involves contacting the device with the cornea. For this reason, the measurement is performed under local anesthesia. To visualize the result, dyes are used. The line of contact is clearly visible. The IOP value is calculated using special tables.
- Non-contact is a modern and painless method that makes it possible to accurately measure eye pressure (used in our clinic). Non-contact tonometers have left contact methods behind, because:
- anesthesia and dyes are not needed;
- the possibility of corneal damage, infection or discomfort is excluded;
- the procedure does not take time - IOP is measured in a few seconds;
- all necessary measurements are provided automatically.
Non-contact tonometry is suitable for children and patients with increased sensitivity.
- Icare rebound tonometry is our main method. Indispensable for round-the-clock monitoring of intraocular pressure. Previously, for this control, people were forced to go to the hospital, but now, thanks to the latest technology - the Icare Home tonometer, patients with glaucoma can measure their pressure at home, even every 10 minutes. The rhythm of life remains unchanged, which enhances the veracity of the data obtained. In the hospital, the patient simply lies and does nothing, and the pressure decreases accordingly.
By the way, the demand for this device is so great that we almost never see it in the clinic.
The rebound principle of measurement involves touching the cornea with the lightest (disposable!) sensor literally for an instant. It is a safe, painless and hygienic procedure.
Anesthesia, drops or special skills are not needed for this tonometry.
Methods for measuring intraocular pressure
An approximate assessment of ophthalmotonus can be obtained by palpating the eyeballs. This technique is used in cases of injury to the organs of vision and after operations on them, but only in cases where it is not possible to obtain reliable information using instruments, for example, at home. During this procedure, the doctor presses on the patient's eyeballs with his index fingers, determining the density of the scleral membrane. Its excessive hardness indicates an increase, and its softness indicates a decrease in IOP. Upon receipt of this data, it will be necessary to carry out tonometry using special devices. Today, ophthalmologists use contact and non-contact methods to measure intraocular pressure. The first include the following:
- Maklakov method. It is used for inflammatory ophthalmopathologies and after operations. Before the procedure, anesthetic drops are placed in the patient's eyes. The tonometer is a device consisting of two weights in the form of cylinders weighing 10 grams each. They are moistened in a dye solution and placed on the cornea. After this, the weights are placed on paper. The doctor determines whether the IOP is increased or decreased by the amount of paint remaining on the cornea. At the last stage of the procedure, an antiseptic is instilled into the eyes.
- Goldmann tonometer. The measurement is carried out using a slit lamp. This method also requires anesthesia and the use of a dye. The ophthalmologist applies a special prism to the cornea. It leaves colored rings on the eye, which are used to measure pressure using a scale.
- Schiotz method. It involves the use of weights, but without coloring liquid. A tonometer is applied to the eye, which is subjected to pressure from the inside. This leads to the oscillation of the needle on the device. The scale determines the IOP indicator.
- Dynamic contour tonometry. The measuring device is a device with a cavity corresponding to the shape of the cornea. In the center of the tip there is a sensor that measures IOP.
Measuring pressure in the eye using these methods is accurate, but is associated with some discomfort for the person being examined. Today, non-contact methods for measuring intraocular pressure are more popular. They are safer and do not cause discomfort to the patient. Let's take a closer look at them.
Increased eye pressure: symptoms
Direct symptoms are not observed until the pressure exceeds a very high level - 40 or 50 mm. rt. Art. It is then that the patient already feels acute discomfort. This could be a headache, nausea or some other ailment. With average elevation, the eye does not turn red, there is no pain, and it does not affect vision in any way. You can't determine anything at home.
Without regular preventative examinations, it is easy to miss the onset of glaucoma, which is why it has been dubbed the “silent thief of vision.”
Statistics by age
Anyone can get sick, regardless of age. Let us only note the fact that children are less susceptible to this disease than adolescents and adults.
- If you are over 65 years old, you have a 20% chance of having glaucoma.
- From 70 years old – 30%
- From 85 years old – 40%
As we age, the natural drainage of fluid from the eyes becomes worse. The process can be aggravated by cataracts, in which the thickened lens begins to take up more space. As sad as it is, aging is a factor that increases the likelihood of developing glaucoma.
Prevention of irreversible consequences of elevated IOP is an examination by an ophthalmologist, especially after reaching 40 years of age. Ideally, once every 6 months, in extreme cases, at least once a year.
A timely and correct diagnosis is the most important thing. There is no other prevention, and the degree of damage directly depends on the lost time. The earlier the disease is detected, the faster measures are taken to preserve vision. Nowadays, no one should go blind from glaucoma! Blindness occurs when glaucoma is discovered late and the optic nerve is too damaged.
A patient at the reception complains: when I park, I always hit the wall, and even without a car, sometimes I hit my shoulder on the door frame. Lateral vision deteriorates. Unfortunately, this is already an advanced case. Treatment should begin when there are no signs. And in order to “catch” glaucoma at an early stage, you need special equipment, which today can detect the disease 7-8 years earlier than was possible until recently. The patient is armed with knowledge and begins to follow the recommendations, monitor IOP, measure regularly, and, as soon as the pressure rises, treat. Thus, literally changing your destiny, because the importance of vision in everyday life cannot be overestimated.
Non-contact devices for measuring IOP
The most convenient, informative and hygienic method for the patient is a non-contact examination. The directed air flow causes the cornea of the eye to bend. The change in curvature is recorded and processed by a computer program, which produces an accurate result. The method does not cause any discomfort in the patient and is completely safe, as it eliminates accidental damage to the eye or infection.
The procedure for examining the fundus using a non-contact method
- The patient sits on a chair and takes a comfortable position that allows him to remain still for some time.
- The patient's head is fixed in a certain position, the gaze must be kept at a certain point indicated by the doctor.
- The ophthalmologist asks the patient to open the eyelids as wide as possible to increase the area exposed to the air flow.
- The doctor turns on the device, and an air stream begins to flow from the nozzle opposite the eye. The device records the air pressure at which the cornea bends, as well as the degree of its deformation.
- After computer processing, the equipment shows the level of pressure inside the eye.
Characteristics of non-contact tonometers
Let's consider the most important characteristics of the device:
- Range. Popular models are single-range tonometers that perform measurements ranging from 5 mmHg. up to 50 mm Hg
- Error. A deviation of no more than 0.1 mmHg is considered acceptable.
- Trigger. Depending on the design, the meter is triggered automatically during applanation or by a signal given by the doctor. The most convenient models are those that combine both methods.
- Lighting. To reliably record corneal smoothing, the sensitivity of the optical system provided by the illumination is important. A powerful LED, white or red, is used as a light source.
- Working distance. In all tonometers, the optimal distance is 20 mm. You can move your eye a little closer to the meter, but it is not recommended to exceed the specified interval.
- Location. There are stationary, portable and manual models. Stationary ones are usually installed on a special table or mounted on the wall. Portable and hand-held devices are commonly used during home visits. In the process of measuring intraocular pressure, they are placed on a suitable surface or held in the hands.
- Print information. Modern models are often equipped with a high-speed thermal printer for instant printing of results.
- Display. Screen size is an important parameter that ensures ease of use of the device. Practice shows that if the display diagonal is less than 5 inches, reading measurement results becomes difficult.
- Product weight. A medium-sized stationary ophthalmic tonometer weighs about 18 kg. The weight of the manual model is approximately 1 kg.
Features of choosing a device for measuring pressure
An extensive range of eye tonometers allows you to make the optimal choice taking into account the working conditions of an ophthalmologist.
- Stationary ones are installed in specialized ophthalmology offices in order to properly equip the workplace of the doctor who receives patients. The device is mounted on the wall so that it is convenient to examine a patient sitting on a chair, or installed on the ophthalmologist’s desk. Such devices are characterized by high accuracy, ideal automatic centering, versatility, and a wide operating range.
- Portable meters that allow you to monitor the patient's current intraocular pressure are used primarily in ophthalmic operating rooms.
- Hand-held tonometers are indispensable in the practice of ophthalmological consultants. A small device, comparable in size to a regular ballpoint pen, allows you to measure the level of fundus pressure in any setting, including at the patient’s home. For certain diseases, patients themselves purchase such devices in order to monitor IOP fluctuations and take measures prescribed by the doctor to normalize it.
All of these categories provide measurement accuracy that is quite sufficient for diagnosing the vast majority of diseases associated with changes in pressure. Another distinctive feature of these devices is complete safety for the patient, which is ensured by the absence of direct contact with the working part of the product.
In addition to dimensions, models of ophthalmic tonometers differ in their sets of functions and capabilities, providing accuracy and speed of diagnosis. Additional options include a soft air shot. Devices equipped with this function do not cause patients the slightest discomfort during measurements. Modern devices provide the ability to connect to a computer to upload examination results to the local network of a medical institution.
The service life of a high-quality, reliable tonometer is at least five years, subject to daily active use.
Non-contact eye pressure measuring device 7CR Reichert (USA)
— operating modes: single “shot” and a series of three “shots”; — built-in printer; — data transfer via USB; — measuring range: 7 ~ 60 mm Hg. Art. (standard for tonometers ISO 8612);
Easy to use. Has maximum automatic guidance speed. The process of measuring IOP is comfortable and does not frighten the patient. There is no need for adjustment when positioning the patient. Intuitive color LCD touchscreen display. The best device in its series in terms of price-quality ratio.
And yet, what factors can affect IOP?
Eye fatigue. Vision is a passive process. It doesn't matter if you spend most of your day staring at a computer screen, constantly knitting, or working as a seamstress. Fatigue is manifested by dry eyes - they may begin to water, itch, turn red, “burn”, “prick”, etc. This is due to the fact that those looking at the seam or monitor blink less often. Instead of the norm 10-15 times per minute - only 5-6 times.
It turns out that to avoid the harmful effects of fatigue, all you need to do is blink more often?
Of course, but it is important not to “skip” visiting the doctor. We never tire of reminding you: the patient’s chances in diagnosis, treatment and results are limited by the doctor’s capabilities – his level of education, experience and class of equipment. And there is only one place where we have collected all the newest and best... just kidding, of course, but one of these places is the Vasily Shevchik Clinic, where your vision will be taken seriously.
What to do to reduce blood pressure?
People suffering from ocular hypertension are interested in how to reduce eye pressure. Special drops best cope with this task, but they must be prescribed by an ophthalmologist. If it is not possible to see a doctor in the near future, then reduced with the help of a tincture of sleep grass, wild pear shoots and nettle. A decoction prepared from these herbs should be taken three times a day before meals.
Doctors also recommend instilling a solution made from onion juice and good honey into the eyes.
For information or treatments for glaucoma
Many ophthalmologists begin treatment for glaucoma with eye drops. Drop until the medications begin to lose their ability to reduce the patient's eye pressure. The Sevcik Clinic recommends considering another option: selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT). This is a type of laser surgery designed to treat glaucoma by reducing intraocular pressure by activating the eye's natural drainage pathways. SLT is more often used as the next step in treatment. However, modern studies have shown that additional laser treatment resulted in better and longer-lasting control of IOP on the one hand, and the use of fewer medications by patients, on the other. Depending on the individual characteristics of the disease, SLT may be the best first step of treatment.
Treatment with medications
The doctor prescribes drops that lower IOP and also improve blood circulation and metabolism. Sometimes this is quite enough to stop the progression of the disease.
Surgical treatment
For more serious forms of glaucoma, surgery is prescribed. Depending on the type of glaucoma and the lesion, the operation is performed with a laser or the eyeball is opened. Unfortunately, even surgery does not provide a complete cure. The main goal is to reduce IOP to stop the progression of the disease. To avoid recurrence subsequently, regular ophthalmological examinations are required.
When drawing up a treatment plan, the doctor starts from the stage to which the disease has developed. To correctly assess it, a comprehensive examination is necessary under the supervision of a highly qualified specialist. At the Vasily Shevchik Eye Microsurgery clinic, excellent ophthalmologists work according to the most modern American and European protocols, and they have the latest equipment at their disposal for diagnosing and treating disorders caused by abnormalities in intraocular pressure.
Why does eye pressure rise?
Eye pressure can increase due to a variety of factors. The most common reasons are:
- ailments associated with the cardiovascular system. These include atherosclerosis, varicose veins and a huge number of other diseases that affect the normal functioning of the heart;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- diabetes;
- poisoning with substances of chemical origin;
- kidney disease: a wrinkled kidney and severe glomerulonephritis affect the retina and provoke high eye pressure;
- post-traumatic glaucoma. With glaucoma resulting from mechanical damage to the eyes, ophthalmotonus may be higher than normal;
- spending a long time in front of the display of a tablet or laptop.
These are just the most common factors that provoke an increase in intraocular pressure. People over the age of 40 are also at risk, since the older the person, the more often the disease appears. However, children are also susceptible to the disease, so parents are obliged to closely monitor the health of children and adolescents.
Interesting Facts
- Eye pressure behaves differently in different nationalities and nations.
- African Americans are 10 times more likely to have glaucoma even when the IOP is normal, but people from Eastern Europe often have a special type of glaucoma that behaves very strangely compared to “normal” glaucoma. With the so-called pseudoexfoliation glaucoma, flakes are formed that settle in the drainages of the eye, and their presence provokes the occurrence of cataracts and glaucoma.
- Regular sunglasses cannot be worn if you have glaucoma, because they cause an increase in IOP. In this case, special ones with green lenses are suitable.
- Glaucoma affects almost 9% of the world's population.
- Cases have been described that suggest the likelihood of a viral nature of glaucoma. When the disease simultaneously manifested itself in the same way in people who lived together for a long time in close contact, but were not blood relatives.
Ophthalmotonus - why is it so important?
A change in ophthalmotonus should be considered an alarming symptom that indicates pathological processes in the functioning of the visual organs.
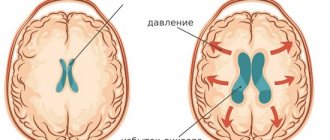
Increased intraocular pressure is a consequence of disturbances in the outflow of fluid that is located under the membrane of the eye. Circulation becomes impossible due to the presence of plugs in the tubules that drain fluid. Moisture gradually accumulates, which leads to increased pressure on the shell.
High pressure inside the eye causes pressure on the fundus vessels. As a result, the retina is injured and the photosensitive elements die. Compression of the optic nerve is also observed, which threatens to disrupt the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to cells. If this happens over a long period of time, the tissues of the organ atrophy, vision gradually decreases and, as a result, disappears completely.
Reduced ophthalmotonus also indicates the development of pathological processes. Low pressure leads to a deterioration in the blood supply to the organ, due to which the tissues atrophy and the eyes gradually cease to see.
Changes in ophthalmotonus may result from problems in the functioning of certain organs and systems. Thus, high intraocular pressure is often observed in people with heart and vascular diseases, and low intraocular pressure may be a concomitant sign of liver failure or the initial stages of retinal detachment.
Stages of the procedure
An optical ophthalmic device measures the fluid pressure inside the eyeball in 10 seconds.
To perform the procedure, the patient must remove glasses and contact lenses. The subject is seated in front of the device, fixing his head. The gaze is directed in front of you to the illuminated point of the device.
Next, a stream of air is supplied at a certain speed, which leads to a change in the shape of the cornea. At this stage, the tonometer processes the results obtained, recording them on a form. Based on the indicators, the diagnostician interprets the results.
Reasons for deviations
When talking about changes in intraocular pressure, we are more likely talking about a situation of increased IOP. This condition is much more common, it causes a number of threatening symptoms and becomes the reason for visiting an ophthalmologist.
There are two main situations in which there is an increase in pressure inside the eye:
- glaucoma is a disease with the development of dangerous changes in the visual system;
- ocular hypertension - implies the absence of a pronounced negative effect on the eyes, but may be a preliminary stage in the development of glaucoma.
Increasing IOP indicators
associated with excess production of aqueous humor, its insufficient outflow, or a combination of these mechanisms.
The reasons for the development of deviations of such processes from the norm can be various factors, ranging from problems directly with the organ of vision and ending with any pathologies in the body that secondarily lead to disruption of the functions of maintaining intraocular pressure. That is why the ophthalmologist carefully collects anamnesis during the appointment - asks not only about visual impairment and specific symptoms of pathologies of his profile, but also clarifies the family history of the disease, the presence of chronic diseases, the presence of additional risk factors, living conditions and features of professional activity. Such information, which is not typical for ophthalmology, helps to establish the cause of the development of glaucoma, and for its successful treatment it is necessary to completely eliminate all factors that increase intraocular pressure.
Any diseases of internal organs can lead to changes in IOP:
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system. The most common disorders of the circulatory system are atherosclerosis, damage to the heart muscle, heart valves, arrhythmias, changes in the system of conducting cardiac impulses, defects, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, changes in lymph flow. Arterial hypertension is especially dangerous - the connection between arterial and intraocular pressure has been proven.
- Vegetovascular dystonia. There has been debate about this diagnosis for a long time, but pathology occurs in cases where it is not possible to identify another objective cause for pressure changes and strong emotional reactions.
- Endocrine diseases. The most common diagnosis that endocrinologists have to deal with is diabetes mellitus. The result of the disease is a disruption of all types of metabolism, including changes in the normal mechanisms of production and outflow of aqueous humor in the chambers of the eye. A common cause of glaucoma is dysfunction of the thyroid gland - its reduced or increased activity affects all types of metabolism in the body.
- Neurological diseases. Diencephalic syndrome, the consequences of acute cerebrovascular accidents, chronic pathologies of the development of the nervous system and other diseases lead to changes in the innervation of the internal structures of the organ of vision, which can cause an increase in IOP.
- Kidney diseases. Changes in the functioning of the renal vessels entail pathologies of the blood supply to all organs.
- Systemic diseases. Vasculitis, lupus, scleroderma and many other severe autoimmune pathologies can cause the development of any disorders, including glaucoma.
Also, trauma, intoxication with various chemical agents and other harmful environmental factors can lead to the formation of increased IOP. It is not always possible to identify the cause of glaucoma. Therefore, ophthalmologists begin universal treatment that helps reduce intraocular pressure, regardless of the reasons for its occurrence.
Applanation tonometry
Screening is carried out similarly to Maklakov’s method. The principle of flattening the cornea is used. The diagnostic method is inexpensive, but there is a high probability of infection in the eye, as with any other contact method.
Goldman tonometry is considered one of the most accurate and reliable research methods. To carry out diagnostics, an applanation tonometer is used, which is installed on a slot frame. The device includes a lens, a slit lamp, and a microscope.
Algorithm for the procedure:
- Apply anesthetic eye drops and a solution that stains the cornea.
- Then the patient is seated on a chair, his head is placed on a special stand of the device and his gaze is directed into the microscope.
- A special prism is placed on the cornea. The ophthalmologist slowly changes the pressure of the prism. After flattening, IOP is determined.
Applanation tonometry has some advantages over other methods. It has a convenient digital display, direct connection to the information system and automatic eye detection.