To measure blood pressure (BP), automatic or mechanical tonometers are used, which can be purchased at any pharmacy. Self-monitoring and keeping a blood pressure diary motivates the patient to comply with all doctor’s recommendations and increases the effectiveness of treatment by 20%. We highly recommend bringing your BP diary to every doctor's visit.
When measuring blood pressure, a number of conditions must be met:
- Blood pressure must be measured in a sitting position. It is advisable to lean on the back of a chair and relax your legs.
- The hand on which the measurement is being taken should lie freely on the table, without tension.
- The measurement is carried out after a 10-15 minute rest, 2-3 times a day, at approximately the same time. The measurement must be taken twice with a break of 2-4 minutes.
- Initially, the measurement is carried out on both arms in order to identify the arm on which the blood pressure is higher (usually the difference is 5-10 mmHg). In the future, measurements are carried out on the hand on which it turned out to be higher.
- It is advisable not to talk while measuring blood pressure.
- 1 hour before measurement, you should avoid eating and smoking.
- The blood pressure cuff should be the right size for you.
- The lower edge of the cuff should be located 1-2 cm above the elbow.
Measuring blood pressure using the auscultatory method (Korotkoff method) with a mechanical tonometer using a stethoscope requires compliance with several additional rules:
- It is necessary to install the head of the stethoscope 1-2 cm inward from the center of the cubital fossa.
- It is enough to quickly pump air into the cuff; the inflation level should be 20-30 mm. rt. Art. higher than “normal” blood pressure.
- You need to deflate the air from the cuff slowly at a speed of 3-4 mm. rt. Art. per second.
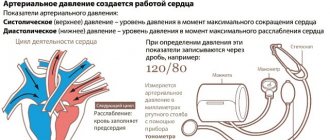
- Record the appearance of the first Korotkoff sound - this will be the systolic blood pressure.
- Record the disappearance of Korotkoff sounds; this corresponds to diastolic blood pressure.
It is important to know!
When measuring blood pressure with any tonometer, mechanical or automatic, with an interval of 2-3 minutes, the values may turn out to be slightly different.
Differences in tonometer readings should not be regarded as manifestations of inaccuracy or malfunction of the devices. The value of blood pressure, like all other parameters of the body, is not constant and is within the limits of physiological fluctuations.
It is also necessary to remember that with physical activity blood pressure increases. This is a physiological mechanism; when the load is stopped, blood pressure normally decreases after a few minutes.
Patient preparation
First of all, you need to be sure that the device used to measure pressure is working properly. If we are talking about a mechanical device, the cuff must be completely deflated and the arrow must be at the zero mark. Otherwise, you should contact a specialist to calibrate the device. It is also important to ensure that the cuff used is fully suitable for the person being examined. The diagnostic results will depend on this.
An hour before measuring blood pressure, you need to give up cigarettes, coffee and other drinks containing caffeine, and alcohol. And physical activity and the use of medications that affect blood pressure levels and heart rate are also not recommended (with the exception of vital conditions, in which the use of such medications is discussed with the attending physician). You can measure blood pressure in a standing, sitting, or lying position. Before the procedure, it is advisable to spend 7-10 minutes in a calm environment, catch your breath, and empty your bladder. The numbers should be measured on both arms (or legs) at intervals of several minutes.
Electronic pressure diary
Many modern blood pressure monitors are equipped with a synchronization function with a smartphone or computer via special applications and Bluetooth technology. This means that the measurement results are automatically sent to a program that organizes the data and stores it.
This option allows you to view the recorded information at any time in a convenient form or display it in the form of graphs and diagrams. You can print all this out and show it to your doctor. With such a pressure diary, it is impossible to forget about entering indicators: this happens automatically.
Difference in blood pressure
Sometimes the diagnosis of other pathologies depends on which hand to measure the pressure on. For example: the kidneys, liver, gastrointestinal tract, pancreas affect the right hemisphere, and the left hemisphere is affected by the lungs, upper limbs and heart. That is why different pressure in the hands has causes not only related to the cardiovascular system, but also to malfunctions of organs.
Finding out the algorithm for measuring blood pressure on different arms is especially important if the difference in indicators is 15 units or more. If such an increase has been observed for a long time, then the chance of complications increases. The patient immediately needs to be examined to find the cause of high blood pressure in the left or right arm.
The affected left or right side of the brain sometimes causes the following symptoms:
- worsening reaction;
- weakness and apathy;
- headaches and dizziness.
People who do not know which arm to measure blood pressure correctly often perform the procedure on one limb. Doctors advise people, especially those with hypertension, to first learn how to measure blood pressure, and then do it on both arms. In this case there should be no error.
Causes of high blood pressure in the left arm
High pressure in the left hand is especially noticeable in left-handed people who actively use the limb. The difference can reach 10-15 units. In people for whom the main right hand is dominant, the indicators on the left limb may also be slightly increased. Doctors explain the deviation as an anatomical feature. On the left arm, nutrition comes directly from the aorta, and on the right – from the brachiocephalic trunk, so the blood pressure level here is lower.
Causes of high blood pressure on the right arm
Blood pressure in the right arm may be slightly higher than the left if the person is right-handed and actively plays sports. Doctors explain this by saying that constant stress on the muscles of the shoulder girdle makes them larger and denser. The arteries passing through this area are compressed, causing blood pressure in the right arm to increase.
Types of devices for measuring blood pressure
High-precision electronic devices are easy to use, have a stylish design and additional functions. An example of such devices are products from the German company Beurer - high-tech products made from environmentally friendly materials. Buyers are offered 2 types of tonometers for home use:
- Wrist blood pressure monitors
. This is a compact device that is attached to the wrist using a special cuff. After switching on, blood pressure and pulse values appear on the display. In addition to the basic functions, using a special display, the device determines the risk of hypertension and recognizes arrhythmia. An example is the Beurer BC44 model. - Shoulder blood pressure monitors
. The device is equipped with a separate cuff, and the device itself is located on the table. Measures blood pressure and pulse, determines arrhythmia and the risk of hypertension. There are models with built-in ECG function. Example - Beurer BM 95.
Devices placed on the wrist are recommended for use by young people and in middle age, when the blood vessels in the hands are still unchanged. Such products are convenient for mobile use: during training, jogging, walking. Shoulder tonometers are more suitable for older people - measurements are carried out in a calm, stationary environment, and the vessels in the shoulder area are less susceptible to age-related changes, so the values will be more accurate.
Read in the article:
- Why do you need a blood pressure diary?
- What data should be recorded?
- Electronic pressure diary
- How to take measurements correctly?
- Benefits of a pressure diary
Arterial hypertension (hypertension) is a dangerous disease in which the risk of serious complications increases significantly. These include myocardial infarction, stroke, angina, renal and heart failure. To prevent all these consequences, constant monitoring of blood pressure is required. The easiest way to record measurement results is in a self-monitoring diary.
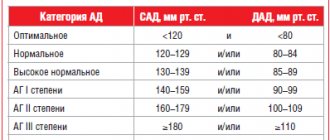
Table of normal pressure by age
Table of normal blood pressure in a person depending on age (average values) according to the Zdrav-answer website:
| Age | Men | Women |
| 20 years | 123 by 76 | 116 by 72 |
| 30 years | 126 by 79 | 120 by 75 |
| 40 years | 129 by 81 | 127 by 80 |
| 50 years | 135 to 83 | 135 by 84 |
| 60-65 years | 135 by 85 | 135 by 85 |
| over 65 years old | 135 to 89 | 135 to 89 |
Additional recommendations
Is it possible to measure blood pressure without a tonometer?
There should be at least 2 minutes between measurement intervals. This is the time needed to restore blood circulation. If strange numbers are recorded on the tonometer, you need to measure blood pressure on the second arm. If both results differ from each other by no more than 5 mmHg. Art., measurements can no longer be taken. Is it possible to measure blood pressure often? This is a painless and safe procedure. It can be carried out as many times as necessary.
To obtain correct diagnostic results in elderly people, it is necessary to take measurements several times in a row. Averages are calculated. Elderly patients are characterized by unstable numbers, which is associated with a decrease in the elasticity of the vascular walls, the development of atherosclerosis and disturbances in the functioning of the blood supply regulation system.
To obtain correct blood pressure results in patients with cardiac arrhythmia, several measurements should be performed in a row, without taking into account results that are obviously incorrect. For example, if the top number is less than 40 mmHg. Art., lower - less than 30 mm Hg. Art., and the difference between them is less than 15 mm Hg. Art.
It is better to record blood pressure numbers in women during pregnancy in a reclining position. Only qualified specialists should measure the pressure of children, using mechanical tonometers or semi-automatic devices with a special children's cuff.
Hand-held device
A manual tonometer for measuring pressure is an air-filled cuff with Velcro, connected by hoses to a rubber pump - a bulb and a meter (manometer). The cuff is wrapped around the patient's shoulder and fastened. The bulb is equipped with a screw-on valve. By compressing it several times, air is pumped into the cuff.
The most common breakdown of a mechanical tonometer is a violation of the seal of the bulb: the bulb bursts, or an invisible crack appears on it over time, which requires replacement of this part of the device.
In addition, some devices come with a phonendoscope for listening to blood impulses in the arteries. These blood pressure monitors are certainly more convenient.
How is ABPM performed?
As a rule, a device for measuring daily pressure is installed in the morning or afternoon. Before installing the device, a person’s blood pressure is first measured using a conventional tonometer, and only after that the daily device is fixed.
A cuff is placed on the lower half of the shoulder and secured, as with a normal pressure measurement with a tonometer. Several test readings are taken. After this, the indicators are checked: if the values concur with a conventional tonometer, the patient is sent home exactly for 24 hours.
Common mistakes and interpretation of results
Getting incorrect results can be caused by the following:
- using a cuff that is too large or too small;
- ignoring the rules of preparation for the examination;
- fixing the cuff to clothing;
- talking, fidgeting in a chair, performing movements with arms and legs;
- full bladder;
- abnormal heart rhythm in the patient;
- device breakdown.
When using any measurement methods, it is important to know the rules for deciphering the results. When recording the final data, two numbers are indicated, for example, 140/95. In this case, 140 is systolic pressure, 95 is diastolic. The difference between them is pulse blood pressure. By the way, the last indicator is also important for monitoring the condition of the heart and blood vessels.