Blood osmotic pressure (BOP) is the level of force that circulates the solvent (for our body this is water) through the membrane of red blood cells.
Level maintenance occurs on the basis of movement from solutions that are less concentrated to those where the concentration of water is greater.
This interaction is the exchange of water between the blood and tissues of the human body. Ions, glucose, proteins, and other useful elements concentrated in the blood.
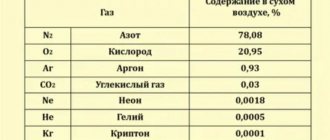
Normal osmotic pressure is 7.6 atm., or 300 mOsmol, which is equal to 760 mmHg.
Osmol is the concentration of one mole of non-electrolyte dissolved per liter of water. Osmotic concentration in the blood is determined precisely by measuring them.
What is osmotic pressure and how does it affect the human body
Osmosis occurs in the human body at the boundary of two different solutions separated by a semi-permeable membrane. One liquid has the ability to penetrate through the walls into the second, which has already been exposed to the first.
Using the example of the human body, we can show the nature of osmotic pressure: water passes through the membrane and enters the blood. Plasma contains a certain concentration of mineral salts, glucose, and proteins. The osmotic pressure indicator lets you know whether the body is sufficiently provided with the exchange of water between the bloodstream and the organs that are located on the outside of the vessels. Osmotic pressure in the human body is the amount of force that forces water to move through the protective membrane of red blood cells.
It is mainly salt that affects osmosis in the blood plasma, because it contains proteins, sugar and urea in small quantities.
The optimal concentration of saline solution in the bloodstream should be 0.9%. This indicator is called isotonic. It is equal to the amount of blood osmosis. When the value exceeds this indicator, the osmotic pressure becomes hypertonic. If this figure is lower, it is hypotonic. In order for the human body to function normally, osmotic pressure must be within optimal values.
It is clear that the osmosis rate cannot be constant, but if the salt concentration is increased or decreased for a short time, then a healthy excretory system can easily remove excess fluid, saline solutions and other substances. In this case, the body itself takes care of the presence of the correct amount of salt inside it. When a person’s health fails and the osmotic pressure is either low or high for a long period, this can cause the occurrence of certain diseases.
Among the most likely consequences is hemolysis. This is a condition in which the membranes of red blood cells burst and they dissolve in the liquid. The appearance of blood containing such dead red cells is slightly transparent. If the parameters of the osmosis force are far from optimal, then the elasticity of cells, tissues and entire organs will disappear. Both with increased osmotic pressure and with decreased pressure, red blood cells have the same fate - destruction.
What happens when there are deviations?
With an increase in blood osmotic pressure, water cells move from red blood cells into the plasma, as a result of which the cells become deformed and lose their functionality. When the concentration of osmoles decreases, the saturation of the cell with water increases , which leads to an increase in its size and deformation of the membrane, which is called hemolysis.
Hemolysis is characterized by the fact that during it the most numerous blood cells - red cells, also called erythrocytes - are deformed, then hemoglobin protein enters the plasma, subsequently making it transparent.
Hemolysis is divided into the following types:
| Type of hemolysis | Characteristic |
| Osmotic | Progresses with the decline of the UDC. Leads to an increase in red blood cells, followed by deformation of their membrane, and the release of hemoglobin |
| Mechanical | This type of hemolysis occurs due to a strong mechanical effect on the blood. As an example, when a test tube with blood is shaken vigorously |
| Biological | Progresses under the influence of immune hemolysis, blood transfusions that do not match the blood group, and with bites of certain types of snakes |
| Thermal | Develops when blood is thawed or frozen |
| Chemical | Progresses under the influence of substances that deform the protein membrane of red cells. Alcoholic drinks, essential oils, chloroform, benzene and others can affect this |
In research, both clinical and scientific, osmotic hemolysis is used to determine the quality indicators of red cells (red cell osmotic resistance method), as well as the resistance of red cell membranes to deformation in solution.
Destruction of the erythrocyte membrane
Which indicators are considered normal and which are considered deviations from the norm?
During this examination of the blood, its freezing point is found. The optimal value for a blood solution is minus 0.56-0.58 degrees. If converted to atmospheric pressure, then normal indicators of the strength of osmosis are 7.5-8 millimeters of mercury. If the indicator is either greater or less than the specified limits, its value will be a deviation from the optimal one.
Proteins, like salts, also create plasma osmotic pressure, but weaker in comparison (its value is 26-30 millimeters of mercury). This pressure is also called oncotic pressure, and it changes the value of the overall indicator.
Plants absorb water from the soil
Type: Endosmos
While plants absorb water throughout their entire surface (leaves, stems and roots), most of the water is absorbed by the root hairs. These root hairs act as a semi-permeable barrier, allowing water molecules (solvent) to move from high concentration (soil) to low concentration (roots).
As a result, root hair cells become more swollen, and their osmotic pressure (ability to absorb solvents) drops.
Water molecules then move into tubes called xylem vessels and are transported to the leaves. Within xylem cells, water molecules exert a strong influence on each other through hydrogen bonds. As water evaporates through the stomata (tiny pores on leaves), more water is released through the xylem cells of the root to replace what was lost.
What affects osmosis rates
The strength of osmosis is influenced by proper nutrition and drinking regime, as well as the healthy functionality of the excretory organs. The amount of salts in the plasma directly affects osmotic pressure. With an excess of them, osmosis will increase, and with a deficiency, it will decrease.
And the rate of fluid intake should be at least 1.5 liters per day, otherwise the body will become dehydrated and the blood will gain increased viscosity.
But, fortunately, when there is a shortage of fluid, a person becomes thirsty and replenishes his water supply. The work of the kidneys, bladder and sweat glands also regulate the amount of salts and solvent in the body, but if the increased concentration of salt is constant, this provokes its retention in the cells. Then the walls of the vessels become thicker, and the lumens of the intercellular space narrow.
As a result, fluid retention occurs, which leads to an increase in the volume of blood moving through the vessels, which provokes an increase in blood pressure. All this negatively affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system and causes the appearance of edema.
What does the osmotic value depend on?
This value is influenced by the amount of electrolytes and non-electrolytes dissolved in the blood plasma. Not less than 60% ionized sodium chloride. Solutions with osmotic pressure close to plasma pressure are called isotonic solutions.
If this value is reduced, such a composition is called hypotonic, and if it is exceeded, it is called hypertonic.
Cell damage occurs when the normal level of solution in tissues changes. Liquids can be administered externally to normalize the condition, and their composition will depend on the nature of the disease:
- A hypertonic solution promotes the outflow of water into the vessels.
- If blood pressure is normal, the drugs are diluted in an isotonic solution, usually sodium chloride.
- A hypotonic concentrated solution may cause cell rupture. Water, penetrating inside the blood cell, quickly fills it. But with the right dosage, it helps cleanse wounds of pus, reducing allergic swelling.
The kidneys and sweat glands maintain this state constantly. They create a protective barrier that prevents metabolic products from interacting with the body.
Therefore, the osmotic pressure in humans is almost always constant; a sharp jump can occur only after intense physical exertion. However, the body itself quickly normalizes the figure.
Measurement methods
There are two most widely used methods for measuring osmosis pressure. Doctors choose which one to use based on the situation.
Cryoscopic method
Since the freezing point of blood directly depends on the amount of substances in it, this method is often used. The more saturated the plasma, the lower the temperature it solidifies. The osmosis indicator is an important parameter in the functioning of the body, and it shows whether the solvent (water) is present in it in optimal quantities.
Osmometer measurement
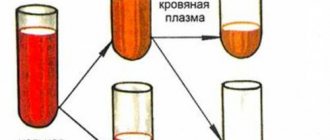
The second measurement option suggests doing this using a special device - an osmometer. It consists of 2 flasks with a partition. The passage between them is partial.
Blood is poured into one of them and covered with a lid with a scale, and solution into the other. It can be hypertonic, hypotonic or isotonic. Look at the scale readings in the vessel.
Types of osmosis
There are usually two types of osmosis:
- Endosmosis: When a cell is placed in a solution with a higher concentration of water than the cell, the solvent (such as water) moves into the cell. This causes the cell to swell or undergo deplasmolysis.
- Exosmosis: When a cell is placed in a solution that has a higher concentration of solute than the cell, the solvent leaves the cell. This causes the cell to become sluggish or undergo plasmolysis.
To better explain this phenomenon, we have listed some very good examples of osmosis that we encounter in everyday life.
Normalization methods
The human body has the ability to self-regulate osmotic pressure. When a corresponding impulse is received from the brain to reduce the volume of intercellular fluid, a hormone is formed that enters the blood. Then the kidneys react to its presence.
Blood also has the ability to bring osmotic pressure parameters to optimal values, acting as a buffer device both when the pressure associated with osmosis increases and when it decreases.
This occurs due to the redistribution of ions between the blood plasma and red cells, and the “ability” of proteins in the blood to attach or release ions.
Meaning
Osmotic pressure plays an important role in the natural environment and human life:
- Delivers moisture along plant trunks.
- Fills human cells with water. As you know, the body largely consists of it.
- Carries out the movement of various fluids throughout the body.
- It is used in various productions and industries.
- Solutions created based on this method are used in medicine. They are administered intravenously during the rehabilitation period of patients after surgery, as well as for disinfection of wounds and decontamination.
Preventive methods
The regulation of the force of osmosis is influenced by the kidneys. If the body needs additional fluid, then the saturation of the blood with active substances will be excessive, and this provokes an increase in pressure. Therefore, you need to be attentive to your feelings, and if thirst arises, it must be quenched immediately.
You should also adhere to proper nutrition:
- Monitor the amount of salt in food. Oversalting and excessive use of spices can lead to a decrease in the permeability of blood vessels due to the presence of salt deposits on their walls.
- Limit drinks such as coffee, Coca-Cola, beer. They can provoke red blood cells to stick together and have a diuretic effect, that is, they actively remove fluid from the body.
- You need to give up various diets and fasting. These experiments on oneself lead to a decrease in the level of proteins in the blood, and this changes the viscosity of the blood and contributes to the occurrence of thrombosis, causes exhaustion and a feeling of fatigue, and a person’s defenses decrease.
The power of osmosis in the human body is responsible for the optimal redistribution of fluid, because the amount of active substances must be at a certain level. This is a very important indicator that illuminates the state of health. In order for its values to be within normal limits, it is useful to drink more water and add salt to food in moderation.
How and when was it opened?
This phenomenon was first discovered and described in 1748. This was done by the French physicist Jean-Antoine Nollet.
His experiment looked like this:
- The container was filled with ethanol and covered with a thin elastic film.
- The vessel was lowered into another, previously filled with water.
- After some time, the thin film begins to swell and inflate. This means that the process of transfer of molecules from one vessel to another has begun.
- They try to swap the vessels: place water in ethanol. The picture is completely opposite: a thin film begins to fall inward.
Jean-Antoine Nollet explained this phenomenon as follows: water, which has a lower density, passes through the film without the slightest resistance. But the higher the concentration, the more difficult it is for molecules to “run across” the barrier.
Food canning
Type: Exosmosis (bacterial cells lose water)
The reason we can enjoy jams and pickles for a long time without fear of spoilage is osmosis. Both are concentrated foods containing large amounts of sugar (in the case of jams), salts, oils, vinegar and other spices (in the case of pickles).
They act not only as flavor enhancers, but also as excellent preservatives, killing bacteria and preventing the growth of other harmful microorganisms.
High concentrations of sugar and salt have a hypertonic effect on bacterial cells. Bacterial cells lose water due to higher concentrations outside and become less conductive to support microbial growth.
Digested food is absorbed in the small and large intestines
Type: Endosmos
When you drink water or eat food, it moves from your mouth through your esophagus to your stomach. Inside the stomach, food breaks down into many small pieces that mix with stomach fluids. The mixture forms a thick semi-liquid mass called chyme. When chyme enters the small intestine, osmosis occurs.
Intestinal epithelial cells (which form the intestinal lining) have a lower concentration than chyme. Thus, to achieve equilibrium, a solvent (water) enters these cells through semi-permeable membranes, taking some nutrients with it.
Next to the epithelial cells are capillaries. Both nutrients and water pass through the capillary cells into the bloodstream.
Water purification
Type: Reverse Osmosis One of the most popular and economical methods of water filtration is reverse osmosis. As the name suggests, this is a reverse osmosis process - the solvent passes through a semi-permeable membrane in the opposite direction to natural osmosis when it is subjected to hydrostatic pressure greater than the osmotic pressure.
Simply put, reverse osmosis is a separation method in which pressure (greater than osmotic pressure) forces a solvent through a semi-permeable membrane, which on one side retains the solvent (contaminants) and on the other allows the pure solvent (drinking water) to pass to the other side.
This process is widely used to remove common contaminants from water, including lead pesticides, nitrates, fluoride, sulfates, arsenic, bacteria and more.
Salt on slugs
Type: Exosmos
Salt and slugs don't mix well. Have you ever wondered why salt kills slugs and snails? The slug's moist skin acts as a semi-permeable membrane. The high concentration of salt on the slug's skin draws water from its cells through osmosis.
The water comes out because it balances the salt concentration between the outside and inside of the slug's skin. Like most other living organisms, slugs need water for maintenance. And when they lose too much water, they shrivel and die.
Sugar on strawberries
Type: Exosmos
The outer membrane of a strawberry acts as a semi-permeable layer between its inside and outside. The inside already contains water and natural sugar. When sugar is sprinkled onto cut strawberries, the greater amount of sugar outside the fruit's cells (combined with the sugar's ability to attract water) causes water to move outward toward the surface of the strawberry.
This process can be used to make delicious products such as macerated strawberries, jellies and jams. It can also be used to extend the shelf life of fruits.
Dry eyes caused by contact lenses
Type: Exosmos
Do you know why we put contact lenses in saline solution? Why not clean water? This is because saline contact lens solution contains the same concentration of salt water as your eye.
When you keep your lenses in the solution, they stay moist, soft and comfortable. Otherwise, they tend to absorb moisture from the eyes through osmosis as they lose water during wear.
Fish absorb water through their skin and gills
Type: endosmosis or exosmosis depending on the type of fish.
If you place saltwater or freshwater fish in water with different concentrations of salt, they will die due to water entering or leaving their cells.
The blood and body fluids of freshwater fish are much saltier than the water in which they swim. Thus, water passes through their gills. Likewise, fish that live in the ocean tend to lose water through their gills.
Just like the human body, the fish body requires a certain concentration of salt to function best. They cannot withstand too much water flowing in or out through the gills. Freshwater fish will burst, and sea fish will dry up.
However, this does not happen because their gills contain specialized cells that selectively pump salt into or out of the blood. Freshwater fish cells regularly transport salt, and saltwater fish cells regularly pump it out. And since ocean water is very salty, fish pump out excess salt through their gills and kidneys.