Since the last quarter of the twentieth century, cardiovascular diseases have steadily occupied a leading position among the most common diseases of mankind. They overtook all possible infectious diseases and even cancer. Cardiovascular diseases are such a widespread phenomenon that scientists, when talking about them, often use the term epidemic, emphasizing their prevalence.
But about a century ago, at the beginning of the twentieth century, they were extremely rare. But by the 50s of the last century, heart disease was already in 10th place in overall statistics. Today, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), they are in sad first place.
Causes of cardiovascular diseases
What is the reason for the incredible prevalence of cardiovascular diseases? First of all, with a change in the way of life of mankind:
- people began to move less : many “office professions” have appeared, where employees spend 8 or more hours in a “sedentary” position. Cars brought not only convenience and speed to travel, but also eliminated the need for walking. The leisure time of a modern person is more often spent watching TV, a computer, a tablet, or with a phone in hand.
- the diet has changed : fruits and vegetables have been replaced by fast carbohydrates (sweets, flour products), fat consumption has increased (fatty meat, lard, sausages, etc.).
- the quality of products has deteriorated : instead of expensive high-quality ingredients, cheap analogues are used, preservatives, dyes, flavors, stabilizers, etc. are added to products.
- smoking has become widespread
Over time, these factors lead to negative consequences: metabolic disorders, obesity, diabetes, accumulation of “bad” cholesterol in blood vessels and, ultimately, atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis is a disease in which cholesterol and its compounds are deposited on the walls of arteries and atherosclerotic plaques form. By sticking, the fatty substance narrows the lumen of the arteries and interferes with the normal flow of blood through them.
Typically, atherosclerosis does not make itself felt until atherosclerotic plaques reach impressive sizes and cover more than 70%
lumen of arteries.
At this time, a person may first experience symptoms of coronary heart disease : shortness of breath, dizziness, chest pain during physical or emotional stress, etc.
It is important to understand that coronary heart disease (CHD) is not one disease, but a general name for a whole group of diseases, including angina pectoris and myocardial infarction . All types of coronary heart disease are characterized by insufficient oxygen saturation of the heart due to narrowing (in some cases spasm) of arterial vessels.
Serious question: what happens to the heart during an angina attack?
Have you heard of such a diagnosis as “angina pectoris”? Such an unusual term actually existed before. So what was it that “compressed the chest” of a person?
With questions about a common disease of modern civilization - angina pectoris, we visited our regular consultant, general practitioner, cardiologist at the Expert Voronezh Clinic, Angelina Anatolyevna Kalinina.
— Angelina Anatolyevna, what is angina pectoris and what is the danger of this disease?
Angina is a syndrome that is manifested by a feeling of discomfort or pain in the chest, often of a squeezing, burning or pressing nature. In most cases, they are localized behind the sternum and can “give” to the left arm, neck, lower jaw, under the scapula, and to the epigastric region. Usually the pain stops with rest after 3-5 minutes or a few seconds or minutes after taking nitroglycerin under the tongue in the form of tablets or spray.
How to distinguish between heart pain and pain due to intercostal neuralgia? The story is told by neurologist, leading specialist of the neurology department of the Expert Kursk Clinic Natalya Vladimirovna Umerenkova
Angina pectoris is one of the types of coronary heart disease (CHD). It is dangerous because there is a risk of myocardial infarction.
Read material on the topic: Coronary heart disease: diagnosis and treatment
- What are the causes of angina?
The cause of classic angina pectoris in more than 90% of cases is atherosclerosis of the heart arteries. Sometimes angina is caused by vasospasm (vasospasm) or functional disorders at the microcirculation level. Often there is a combination of the above reasons.
Risk factors for the occurrence of angina pectoris are divided into so-called modifiable (i.e., those that a person can influence) and non-modifiable (those that cannot be changed).
Modifiable factors include dyslipidemia, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, smoking, excessive consumption of alcohol-containing beverages, physical inactivity, obesity, dietary patterns, etc.
Non-modifiable are male gender, age, hereditary predisposition.
What can cause chest pain? These are cases when a person subjected himself to physical activity, walked quickly, climbed a mountain or stairs, or carried heavy loads. Pain can also appear with increased blood pressure, exposure to low temperatures, overeating, and stress.
Read the material on the topic: It's off scale! Looking for reasons for high blood pressure
— By what signs can angina be recognized?
A detailed interview with the patient is very important. There are typical, probable (or atypical) angina, as well as cardialgia (in which the pain is not associated with a deterioration in the blood supply to the myocardium).
Symptoms of typical angina include chest pain or specific discomfort. Caused by physical activity or psycho-emotional stress. They go away with rest or after using nitroglycerin. With this type of angina, all three manifestations must be present.
In atypical angina, only two of the three are present.
With cardialgia, one or none of the above symptoms are noted.
Taking this into account, either a cardiologist or another specialist works with the patient and further searches for the causes of pain in the heart area.
- What is angina pectoris?
The following types are distinguished: stable, unstable and spontaneous.
Separately, there is the so-called cardiac X-syndrome (X-syndrome, otherwise known as microvascular angina). With it, there is a combination of classic signs of angina pectoris with unchanged heart arteries. This species has not yet been fully studied.
— What happens to the heart during an angina attack?
The process develops as follows. Initially, the blood supply to the myocardium is disrupted, later metabolic and electrophysiological “shifts” are noted in it. Then the heart’s ability to relax is impaired, and then to contract. And only then does pain appear and corresponding changes on the electrocardiogram.
Read the material on the topic: Why is ultrasound of the heart prescribed?
— How to provide emergency assistance during an angina attack?
The drugs taken are short-acting nitrates (tablets or spray), under the tongue. It is better to take them in a sitting or lying position (to prevent low blood pressure, dizziness and possible falls associated with this). Tablet dosage: 0.5 mg. In total, up to 3 tablets are taken - 1 tablet every 5-7 minutes. You need to focus on the disappearance of pain.
Nitroglycerin should not be used if the “upper” (systolic) blood pressure is less than 90 mmHg. rt. Art.
This blood pressure should also be monitored while taking nitroglycerin, even if it was initially above 90-100 mm. rt. Art.
If the pain does not subside within 15-20 minutes while taking nitroglycerin, you must call an ambulance to rule out myocardial infarction.
— Are angina pectoris and coronary heart disease the same thing or is there a difference between them?
Angina pectoris is one of the types of coronary heart disease.
— Who has angina pectoris more often: men or women?
In general, its frequency increases with age in both sexes.
In middle age, it is angina pectoris (and not ischemic heart disease in general) that occurs more often in women, probably due to the higher prevalence of vasospasm and cardiac syndrome X. For older age groups, the situation is the opposite, i.e. both ischemic heart disease in principle and angina pectoris as a special case are more often observed in men.
- Who is predisposed to developing angina? What risk factors provoke the development of angina?
These are the modifiable or non-modifiable factors that we talked about earlier.
— Angelina Anatolyevna, how is angina diagnosed?
Firstly, a thorough collection of complaints and anamnesis (with clarification of the nature of the pain, its location, duration, conditions of occurrence, the effect of taking various medications - in particular nitroglycerin, if taken).
Upon examination, signs of atherosclerosis, heart failure, high blood pressure, and obesity may be detected as additional risk factors.
A general blood and urine test, lipidogram (total cholesterol and its fractions, triglycerides), glucose, creatinine clearance are performed. In unstable and acute conditions, markers of myocardial destruction (troponins T and I, creatine phosphokinase (CF fraction).
Instrumental diagnostics. Invasive and non-invasive methods are used here.
The first one is an ECG. How is angina visible on it? These are specific ST segment changes.
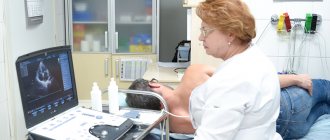
Echocardiography and ultrasound duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries are mandatory.
Load tests - bicycle ergometry and treadmill test.
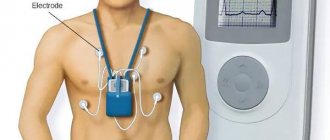
Holter monitoring. It is performed when stress tests are contraindicated, if it is impossible to record an ECG at the time of pain, etc.
Read the material on the topic: Holter (24-hour) ECG monitoring - complete instructions for the patient
Stress echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart under stress).
Perfusion scintigraphy with exercise.
Invasive methods. The “gold standard” for imaging diagnosis of atherosclerosis of the heart arteries is coronary angiography (especially in those at high risk of cardiovascular complications and death), as well as multislice computed tomography with assessment of coronary calcium, or calcium scoring.
— What is the purpose of treatment for angina pectoris? Is this diagnosis an indication for surgery?
The main goals are to eliminate manifestations and improve the prognosis.
If symptoms cannot be eliminated with drug therapy, it is recommended to refer the patient for a consultation with a cardiovascular surgeon to determine the possibility of surgical treatment of angina.
— Is angina responding well to treatment? Is it possible to cure it completely?
Treatment of angina pectoris at the present stage of medical development is effective. You can either significantly reduce its manifestations or eliminate them completely. At the same time, even after surgical treatment with complete restoration of adequate blood supply to the myocardium, drug therapy continues indefinitely, because the risk of cardiovascular complications remains very high.
— Can angina be resisted? How to properly prevent this disease and at what age should it start?
The main measures are aimed at preventing the occurrence and progression of atherosclerosis and, accordingly, damage to the arteries of the heart. Those. it is the effect on modifiable risk factors. It is necessary to stop smoking, control weight, and eat rationally. If you have diabetes, you need to achieve your blood glucose targets. Provide rational, regular physical activity. Monitor blood pressure. Regularly take medications prescribed by a cardiologist or cardiac surgeon and be observed by these specialists.
You may also be interested in:
Heart, why don't you want peace? What causes tachycardia?
How to keep your heart healthy?
What do you need to know about health before buying a gym membership?
For reference:
Kalinina Angelina Anatolevna
In 2007 she graduated from the Voronezh State Medical Academy named after. Burdenko.
From 2007 to 2008 she completed an internship in therapy, in 2010 she underwent professional retraining in the specialty “General Medical Practice (Family Medicine)”, and in 2017 – in the specialty “Cardiology”.
Since 2015, he has held the position of general practitioner at Clinic Expert Voronezh. Reception is conducted at the address: st. Pushkinskaya, 11.
What is angina?
Angina pectoris is manifested by pain, a feeling of tightness in the chest . Sometimes the pain is transmitted to neighboring areas of the left side of the body: to the left arm, left shoulder, left side of the neck, left half of the lower jaw, to the area of the left shoulder blade.
In the old days, the disease was called “angina pectoris” because of the way patients described the painful sensation: “as if a huge heavy toad had sat on the chest and was preventing you from breathing freely.”
.
Such symptoms appear mainly during increased work of the heart muscle:
- during physical activity
- emotional outburst
- when the body is cold (the heart goes into overdrive to prevent hypothermia of vital organs)
- when smoking (nicotine contributes to the narrowing of arteries already narrowed by atherosclerotic plaques)
- with increased blood pressure
When working hard, it is important for the heart to receive a sufficient amount of oxygen. However, if the lumen of the arteries through which oxygen is delivered to the heart is narrowed, then the heart begins to experience oxygen starvation and gives an alarm about this in the form of chest pain .
Angina pectoris (1, 2, 3, 4 FC)
Angina pectoris is an attack of chest pain that occurs due to emotional or physical stress. They increase the metabolic needs of the myocardium. Typically, such pain disappears with rest or after taking drugs from the nitrate group. Depending on how a person tolerates physical activity, angina pectoris can be of several functional classes (FC).
Functional classes
- In the first class (angina pectoris FC I), exercise diseases are tolerated well, pain is caused only by certain excessive overloads, which last a long time and are intense.
- In the second class (angina pectoris FC II), walking on level ground for a distance of half a kilometer or climbing more stairs than going up to the second floor may be enough for an attack.
- The third class (angina pectoris FC III) severely limits normal physical activity; for an attack, going to the first floor is enough.
- The fourth class (angina pectoris FC IV) is the most severe, with it it develops even at rest.
What to do if you have an angina attack?
- First of all, you need to try to pull yourself together and calm down
. Sometimes attacks of angina pectoris cause feelings of fear and panic in patients, which leads to an additional release of adrenaline into the blood, an even greater increase in heart rate, and as a result the attack intensifies. It turns out to be a vicious circle. - It is important to take a comfortable sitting or reclining position
. You cannot walk, stand or continue physical activity because... this may make the attack worse. You need complete rest until the pain symptoms go away. - Take the nitrate preparation under the tongue
.
Nitrate drugs dilate blood vessels and thereby stop an attack of angina. This could be, for example, nitroglycerin in tablets or spray form. - If, after taking a nitrate drug, the chest pain does not subside, it is recommended to take a second dose of the drug
(in total, up to 3 doses of the drug are allowed to be taken at intervals of 5 minutes).
If the medicine does not work, the pain does not subside for more than 10 minutes and even intensifies, you must urgently call an ambulance
!
How does the pulse behave in such patients and what can be done about it?
Not only pressure, but also pulse is important during angina.
An increase in heart rate (HR) above 70 beats per minute indicates that the heart is working hard. This means that the muscle's need for oxygen increases. In addition, since the coronary arteries receive blood during relaxation (diastole), when the heart rate increases, the duration of their filling is reduced. Under such conditions, chronic ischemia occurs, which leads to degeneration of the muscle fibers of the heart. If the heartbeat increases sharply during physical and emotional stress, for example, when you are simply catching up with a minibus, the need for oxygen rapidly increases. If against this background an attack of angina occurs with spasm of the coronary vessels, ischemia can have serious consequences.
Beta blockers are the drugs of choice in patients with high heart rates. They are included in treatment regimens for arterial hypertension.
Why is angina pectoris dangerous? Transition to myocardial infarction.
An angina attack usually goes away within 2 to 10 minutes.
after the first dose of a nitrate drug.
If an attack lasts more than 20–30 minutes
, it runs the risk of developing into
a myocardial infarction .
necrosis (death) of cells in one or more areas of the heart muscle occurs
Why does necrosis occur in the heart muscle?
Myocardial infarction is the result of severe oxygen starvation of the heart, when blood flow to the heart is reduced to a very low, dangerous level.
In such cases, the body uses compensatory mechanisms: additional small arteries send blood to the heart. But compensatory mechanisms cannot always cope with their task. For example, during a prolonged attack of angina.
In such a situation, first irreversible damage occurs, and then the death of those areas of the heart muscle that do not receive sufficient oxygen.
Blood pressure correction
Hypertension with angina pectoris
The main goal of treating angina with high blood pressure is to reduce the risk of death from myocardial infarction, stroke and kidney failure.
Medicines for angina are also used for hypertension. The drugs cannot completely cure coronary heart disease, but they can reduce the frequency of attacks and their intensity to a minimum. Also, when taken correctly (long-term and regularly), they reduce blood pressure to a safe level. This significantly improves the quality and life expectancy, performance and general psychophysical state and emotional background. The person feels less sick.
Risk factors for developing angina
Factors contributing to the development of angina:
- Physical inactivity (sedentary lifestyle)
- High calorie diet, high in fat and cholesterol
- Obesity
- Increased levels of total cholesterol and in particular “bad” cholesterol in the blood plasma
- Diabetes
- Arterial hypertension
- Smoking
- Heredity
According to statistics, angina pectoris more often affects men under the age of 60–65 years , but after 70 years the ratio of male and female patients levels out. This situation is associated with the peculiarities of the endocrine system .
Oddly enough, cholesterol, considered the basis of all ills, is actually produced by the human body itself
and is involved in the synthesis of steroid hormones, including
sex hormones (testosterone in men, estradiol in women)
.
With age, the level of production of sex hormones decreases. In men, a noticeable decrease occurs at the age of 40–45 years, in women – after menopause (50–55 years).
Consequently, the body's need for cholesterol for the synthesis of sex hormones decreases, but cholesterol production remains at the same level. Thus, unused, “extra” cholesterol
. It is he who is involved in the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, the development of coronary disease and, in particular, angina pectoris.
As can be seen from the figures, a noticeable decrease in the synthesis of sex hormones in men is observed 10 years earlier than in women, which leads to an earlier onset of cardiovascular problems in men.
Medicines with proven effectiveness in treatment
| Acetylsalicylic acid | This is regular aspirin in a dosage of 75-100 mg. The trade name often includes the prefix "cardio". Resists thrombosis. |
| Beta blocker | Blocks the effect of adrenaline on receptors. Reduces the heart's need for oxygen during exercise, which has a positive effect in the treatment of angina pectoris. Lowers systolic and diastolic blood pressure. |
| ACE inhibitors | Suitable for those who have diabetes, preventing the development of nephropathy. Reduce left ventricular hypertrophy. |
| Nitroglycerine | Nitric oxide, which is released from the drug in the vascular wall, dilates the coronary arteries during myocardial ischemia, thereby restoring blood circulation in the muscle area. |
| Calcium antagonists | Prescribed when beta blockers are contraindicated (heart failure, blockade of the conduction system, bronchial asthma) |
| Lipid-lowering therapy | Statins, fibrates and bile acid sequestrants - drugs that normalize cholesterol and lipoprotein levels |
You should not completely rely on medications, because without changing your lifestyle, they partially lose their effectiveness.
Hypotension with angina pectoris
Until recently, it was believed that low blood pressure was better than high blood pressure. However, the statistical analysis suggests that systolic blood pressure 110 and below, and diastolic blood pressure 60 and below are no less a risk factor for the development of myocardial infarction than hypertension.
Hypotension is characteristic of women of reproductive age, as well as patients with severe atherosclerosis. Low blood pressure occurs in patients who mistakenly take high doses of antihypertensive drugs.
As a rule, a person feels that the pressure is low - dizziness, staggering, and fatigue appear. Yes, at the moment the optimal method for correcting this condition is normal physical activity, consuming caffeine-containing products in moderation and wearing compression stockings.
Treatment of angina attacks with hypotension appears to be a difficult task, since most drugs prescribed for this disease exhibit a blood pressure-lowering effect.
Prevention of angina
The best method of preventing disease is prevention. If you have at least one of the listed risk factors, except for heredity, which, unfortunately, cannot be influenced, it is advisable to exclude them.
- If you have physical inactivity
(sedentary lifestyle), include in your daily schedule
physical activity
that is suitable for you (for example, fitness, running, Nordic walking or regular walking for at least 30-60 minutes a day). It is not the severity of the physical activity that is important, but the involvement of a large number of muscle groups in the body. - Replace a high-calorie diet
based on eating fatty foods that contain a lot of cholesterol
with a balanced diet
that includes plenty of vegetables and fruits. Limit your salt and sugar intake. Instead of fried foods, choose steamed, boiled or baked foods. - The presence of excess weight
, as a rule, is a consequence of physical inactivity and a diet containing not only a lot of fat, but also a lot of fast carbohydrates.
To cope with extra pounds, daily physical activity
(you don’t have to go to the gym right away, you can start with walking) and
switching to a balanced diet
. It is important to limit the consumption of fatty foods, flour and sweets, and instead choose vegetables, fruits, honey, nuts, and dried fruits in small quantities! - If there is an increased level of cholesterol
in the blood plasma,
diabetes mellitus
or
arterial hypertension
it is important
to consult a doctor
so that a specialist can help you choose the appropriate treatment and give individual dietary recommendations. - It is advisable to quit smoking
, because it can provoke not only angina, but also other, no less dangerous diseases.
Prinzmetal's angina
Symptoms:
- Chest pain characteristic of angina,
- sweating,
- drop in blood pressure,
- loss of consciousness.
Prinzmetal's angina is an uncommon type of the disease, which is also called “variant” or “vasospastic”. It develops at rest and is caused by spasms of the coronary arteries. This type of angina is characterized by severe, prolonged attacks. They usually occur at night or early morning and are intense in nature with a whole group of symptoms.
Angina at rest
It literally arises out of nowhere, without obvious provoking factors. The attack begins in conditions of physical rest, is characterized by duration and severe pain, lack of air, and heart rhythm disturbances. To relieve attacks, complex drug therapy is prescribed. Typically, resting angina occurs with severe, multiple arterial damage. It is dangerous, and often with its symptoms, coronary artery bypass grafting is indicated to create alternative pathways for coronary blood flow. Often, after a few years, the operation must be repeated, since resting angina tends to renew symptoms.
Regardless of stress or rest, sudden chest pain is a consequence of spasm of the vessels that are responsible for supplying blood to the heart muscle. The spasm does not give the heart enough oxygen. Unlike acute myocardial infarction, after which the heart muscle or its fragment cannot be restored, with angina pectoris the disorder of coronary circulation is not permanent.
Progressive angina
Progressive angina (or colloquially “angina pectoris”) is a type of unstable angina. Its cause is a violation of coronary circulation.
Progressive angina can be provoked by:
- excessive smoking,
- alcohol abuse,
- prolonged stress,
- hypertension,
- elevated cholesterol levels.
Doctors also identify internal factors of progressive angina:
- decreased collagen synthesis,
- predominance of the lipid core,
- increase in macrophages (immune system cells),
- other cellular and metabolic changes.
Each of these factors can cause the formation of blood clots over an atherosclerotic plaque. They block the lumen of the artery, and the nutrition of the heart is reduced. Such phenomena are accompanied by a clinical picture of progressive angina pectoris.
It forms against the background of stable angina pectoris, when its course worsens. This can be stated when:
- increased frequency of attacks of chest pain,
- increasing their duration,
- appearance at rest,
- development of new symptoms (nausea or dizziness).
Progressive angina can develop as the severity of the condition increases into different functional classes.
Vasospastic angina
Vasospastic angina develops at rest, which distinguishes it from other types of angina, attacks of which occur during activity. Symptoms of vasospastic angina occur at night, between midnight and dawn. The pain syndrome is pronounced. This type of angina often affects smokers, hypertensive patients and patients with high cholesterol.
The cause of the pain syndrome is spasm of the coronary artery and a sharp slowdown in coronary blood flow. The heart muscle experiences increased stress and begins to hurt. The cause of arterial spasm can be:
- smoking,
- hypertension,
- stress,
- hypothermia of the body,
- elevated cholesterol levels,
- alcohol and drugs.
Moreover, this type of angina develops in patients between 50 and 60 years of age, and men suffer from it 5 times more often than women.
Symptoms of this type of angina include:
- chest pain at rest,
- feeling of tightness in the chest,
- nausea,
- sweating,
- dizziness,
- tachycardia.
The attack lasts from 2 to 20 minutes, attacks can occur at intervals from several weeks to several months.