Most passengers experience tinnitus when boarding an airplane. At what pressure value does the same sensation occur under normal conditions and why? A visit to an ENT specialist will help determine the exact cause of the discomfort. Ringing in the ears is a common symptom of inflammation. It is observed with otitis, eustachimitis, sinusitis, sinusitis or maxillary sinus, in some cases it is a symptom of vascular, cardiac pathology.
The effect of human blood pressure on the ears
High or low blood pressure can cause dizziness, noise, and tightness in the ears. The problem with arterial hypertension does not appear overnight; vascular tone worsens gradually.
Hypotonics - in people with low blood pressure, vascular tone decreases every year. The walls of the capillaries become thinner and become permeable. The mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and the cavity of the Eustachian tube swells, which leads to negative pressure in the middle ear and an unpleasant feeling of shortness of breath.
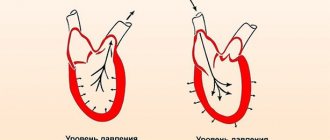
A sharp change in blood pressure (increase, decrease by 10 points or more) leads to impaired cerebral circulation and vasospasm. Hearing is impaired due to differences in pressure between the outer and middle ear. They are separated by the eardrum, which always shifts towards lower pressure, which leads to shortness of breath in the ears:
- as pressure increases, it bulges towards the outer ear;
- and when it descends, it goes to the middle ear.
People with hypertension and hypotension are more likely to experience ear congestion during a sudden change in weather, accompanied by an increase (fall) in atmospheric pressure. Hypotonic people feel weak, drowsy, during cyclones their ears become clogged in such weather, hypertensive people feel bad with similar symptoms during anticyclones.
Ear congestion due to high blood pressure
Blood vessel spasms, which cause high blood pressure, occur for a variety of reasons. Arterial hypertension or another disease accompanied by symptomatic hypertension cannot be excluded. During an embolism caused by high blood pressure, a person experiences throbbing pain in the back of the head and nausea.
Due to increased intracranial pressure, the head begins to spin, the face turns red, tachycardia appears, and the ears become clogged. After blood pressure normalizes, the symptoms disappear, hearing and well-being return. Nasal congestion occurs when upper blood pressure is ≥ 150.
Clogged ears: a sign of illness or congestion
Often, hearing impairment or loss can be due to a cold with complications in the form of the development of inflammatory processes. Clogged ears are a symptom, not a disease, but in any case it is recommended to get examined.
A visit to the doctor is necessary if:
- the cold has passed, but the symptom of congestion remains;
- hearing impairment persists for several days and pain develops;
- discharge appears from the auricle, often purulent;
- dizziness appears.
General weakness, decreased tone, and increased temperature during inflammatory processes may develop.
The presence of these signs poses a certain health risk, so you should visit a doctor and undergo examinations.
Independent treatment measures are contraindicated, because may cause serious complications. Especially in the case of uncontrolled use of medications.
Clogged ears due to low pressure
If blood pressure is low, organs have poor blood supply and lack of oxygen. At the same time, the outflow of carbon dioxide is obstructed. Due to an imbalance in the acid-base balance, metabolic products accumulate in the body and stagnation occurs.
Weak vascular tone disrupts venous outflow, so hypotension is often accompanied by ear congestion. Associated symptoms:
- Eyelashes;
- mild nausea;
- increased drowsiness;
- frequent fainting;
- systematic dizziness.
A person with hypotension gets significantly worse when their blood pressure drops below 60.
Stuffed ear and won’t go away: what to do
When discomfort and a feeling of stuffiness appear in the ear, you cannot immediately take ear sticks and start clearing the passages. Such measures can lead to a worsening of the situation: the plug is pushed in further, becomes denser over time and can cause the development of infectious inflammation and temporary hearing loss.
The following effective ways to “pierce” the ear are practiced:
- use chewing gum or eat candy;
- yawn, straining your vocal cords;
- take a deep breath, cover your nose and mouth with your hands and exhale slowly;
- sharp tilt of the head with straight shoulders. Pull your ear up.
In parallel with the last technique, you can use the following techniques:
- take a deep breath, cover your nose with your hand and slowly exhale through the closed nose, pushing the air;
- hold your nose with your hand and make a swallowing movement;
- strain your vocal cords with your mouth and nose closed.
Diagnostics
The party begins with an examination and interrogation of the patient. The doctor is interested in the history of the development of the disease, this helps to establish an accurate diagnosis. The specialist is interested in:
- symptoms accompanying shortness of breath;
- duration of discomfort;
- their frequency;
- when the first signs of discomfort appear;
- whether one or both ears are swollen.
If the problem is associated with otitis media, the patient experiences high fever, severe pain and intoxication. An ENT examines the ear septum and may refer you for an x-ray of the nasal sinuses. Purulent inflammation is especially dangerous, as it can provoke sepsis.
The combination of dizziness, ear congestion, drop (increase) in blood pressure and headache requires a cardiac examination. X-ray of the spine (cervix) is indicated when the patient experiences an embolism due to changes in atmospheric pressure.
Recognizing spinal pathology and eliminating nerve damage restores normal hearing and alleviates unpleasant symptoms. A feeling of tightness in the ears indicates a migraine or malignant processes in the brain or in the middle ear.
Foreign body in the ear
This usually happens by accident when cleaning the ears, when objects for which they are not intended are used - a match and cotton wool wrapped around it. A part of such a structure can easily break off and end up in a hard-to-reach place. Unfortunately, doctors are faced with episodes where insects crawl into the ears.
Whatever the foreign object, only professionals can get it. Otherwise, your eardrums may be seriously damaged. Certified specialists know how to deal with this problem and will do everything quickly, and most importantly, without consequences.
Methods for relieving congestion
If the cause of tinnitus is high blood pressure, antihypertensive therapy is recommended, which consists of taking diuretics in combination with ACE inhibitors. A person who experiences discomfort due to a sharp increase in blood pressure will need:
- lie down;
- restore breathing;
- take blood pressure medications or any sedatives;
- in case of critical blood pressure values, seek help.
Hypotonic with low blood pressure, noise and congestion in the ears, he definitely needs to lie down, drink a cup of coffee, black tea with sugar. It won't hurt to eat 1-2 slices of dark chocolate. Hypotonic patients are recommended to take hypertensive drugs: Mezaton, Cordiamin. As blood pressure recovers, hearing also normalizes.
Surgical treatment requires frequent surges in blood pressure caused by serious heart pathology, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and nephroprotective drugs - hypertension caused by kidney pathology.
Treatment
Obviously, treatment for ear pressure can only begin after a diagnosis has been made. Until the cause is identified, the otolaryngologist is unlikely to be able to prescribe medications or take any other action. In addition, if the cause of the disease is beyond his competence, then it will not be possible to do without the help of an appropriate specialist (therapist, surgeon, neurologist, etc.).
The reception is conducted by specialists
Kirillov Evgeniy Sergeevich
Audiologist
Cost of services
Initial consultation with an audiologist
1200₽
Repeated consultation with an audiologist
1000₽
Preventive measures
Doctors suggest following a few simple rules so that unpleasant symptoms are not bothered by pressure changes:
- healthy, moderate diet, excluding excess weight;
- Reduce the amount of salt to a minimum;
- physical activity (walking, jogging, physical education);
- Stop smoking and refrain from drinking any alcoholic beverages.
Well-known recommendations will help normalize blood pressure, get rid of tinnitus and ear congestion. Moderate physical activity and proper body weight are the best prevention of cardiovascular pathologies.
What to do if there is wax in your ears?
Often you want to take a cotton swab and just clean out the earwax. You cannot do this if you feel stuffy. It is necessary to make an appointment with a specialist who will assess the degree of congestion and its cause, and then provide professional medical assistance. The ear plug is washed with special tools; this process takes a couple of minutes and does not cause any pain. After rinsing, it is important to follow the rules of ear care; the doctor may also prescribe drops in the ears.
Advantages of treatment at an ENT center
Treatment of ear, nose and throat diseases at the ENT CENTER is a comprehensive and individual approach to each patient. By making a preliminary appointment on the medical center’s website or by phone, you can:
- get face-to-face consultation with a specialist;
- undergo treatment of ENT diseases using progressive techniques;
- receive recommendations for further conservative treatment and prevention of ENT diseases.
Contact the ENT CENTER : here they will help you solve any problem within the competence of ENT doctors as efficiently, safely, quickly and painlessly as possible.
The connection between blood pressure and ears
If a person excludes the occurrence of otorhinolaryngological diseases, he begins to wonder at what pressure the ear becomes clogged.
Most often, this phenomenon is encountered by people with arterial hypertension, who have had a heart attack or acute cerebrovascular accident.
Factors that provoke pressure fluctuations are the following conditions:
- excess weight;
- low level of activity;
- blood loss trauma;
- great effort;
- hereditary predisposition.
These factors create conditions for impaired blood flow and narrowing of blood vessels. Hearing loss is caused by several factors: intracranial, blood pressure and atmospheric pressure.
Removing wax plug at home
Cork differs from simply excess sulfur in that it becomes a thick viscous mass, or even solid in consistency.
- to soften wax, drip hydrogen peroxide (2-3 drops) into the ear, cover the ear with cotton wool or a cloth for several minutes;
- dissolve potassium permanganate in water that is warm to the touch (slightly pink), draw into a large syringe without a needle (sterile);
- inject the solution, trying to direct the stream in different directions of the ear canal, wait for the water to flow out;
- repeat the procedure 2-3 times, but if the cork is old, then washing it out will require many times more manipulations - 20-30.
The sulfur should come out if everything is done carefully and correctly. You can notice this by improving your hearing.
Causes
Let's consider the possible reasons why there is pressure on the ears from the inside.
Migraine
Migraine is a dysfunction of the body of a neurological nature. Most often, migraine manifests itself in regularly occurring episodes of severe headaches that torment a person. The etiology of migraine has not been fully elucidated. Presumably, predisposing factors for migraine, which causes a feeling of pressure in the ears, are:
- genetics;
- neuroses;
- increased stress levels;
- overvoltage;
- eating certain foods that provoke the occurrence of this disease;
- drinking alcohol;
- weather dependence.
Migraine is not accompanied by any other deterioration of a person’s condition, as a rule: there have been no previous blows to the head, concussion, increased pressure in the blood vessels or eye diseases that radiate to the head.
With migraine, there is a narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain, their uneven expansion, and impaired perception of CO2. The risk of migraines increases if relatives suffer from high blood pressure.
Migraines are characterized by throbbing pain inside the head and pressing pain in the ear. As a rule, the pain is long-lasting, from four hours to three days. Most often, only one half of the head is affected, although, in severe cases, the entire head may hurt. With migraine, pressing pain is felt only in one ear on the affected side. Most often the pain is felt on the outside of the ear.
- Pressure in the ears: how it feels and how to get rid of it
Hypertension
Hypertension can cause a feeling of pressure in the ears. Arterial hypertension is characterized by a prolonged increase in blood pressure above the following units: siastolic - above 140, and diastolic - above 90 mmHg. There are many reasons for such a sharp change in pressure:
- taking dietary supplements;
- obesity;
- taking oral contraceptives;
- stress;
- overwork;
- loads that are not comparable with age;
- smoking;
- high blood sugar;
- menopause;
- hereditary predisposition.
Symptoms of arterial hypertension are:
- sudden increase in blood pressure;
- loss of strength, change in complexion;
- perspiration;
- blurred vision;
- patients complain of pain in the back of the head;
- sudden anxiety may occur;
- heart rate increases;
- causeless fear arises;
- often dizziness, fainting;
- pain in the ears is of a pressing nature, with ringing or squeaking, tinnitus, hearing impairment - like deafness.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is another possible cause of ear pressure. This is a disease characterized by impaired metabolism of fats and proteins, resulting in deposits of cholesterol and some types of fats on the walls of blood vessels. Such deposits are called atherosclerotic plaques. The formation of atherosclerotic plaques leads to blockage of blood vessels, and, as a consequence, to disruption of blood flow to the organs.
Causes of atherosclerosis:
- smoking;
- poor nutrition;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- drunkenness;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- menopause;
- poor family history.
Atherosclerosis does not have the ability to develop in a specific organ, and if it has already appeared in the human body, it affects all the vessels of the body. Atherosclerotic plaques penetrate the endothelium of the vessel, and, having the ability to break away from the walls, can lead to rupture of the vessel and subcutaneous hemorrhages. In addition, a detached plaque can simply clog a vessel, completely blocking blood access to a certain human organ. Affecting the vessels of the head and neck, it gradually reaches smaller vessels - the vessels of the ear. By disrupting the blood flow to the ear, it leads to the ear tissue not receiving enough oxygen and necessary substances. The patient may feel that the head is bursting from the inside and the ears are blocked; there is a feeling that there is pressure in the ear.
Otitis
Otitis media is a disease of the hearing organ. There is inflammation of the outer, middle and inner ear. Most often, children are susceptible to otitis media, but adults suffer from it not much less often.
- Inflammation of the outer ear is usually associated with the appearance of a boil in the auricle. Bursting, pressing pain inside the ear in this case is explained by the development of purulent inflammation of the boil. In addition, a person may feel heat in the ears, pain when touching the ear, and tugging pain in the ear. It’s painful to sleep at the cause site, it’s impossible to touch, even straighten your hair. Discomfort persists until the boil breaks out. The inflammatory process can even spread to the eardrum, leading to hearing impairment.
- Inflammation of the middle ear may be purulent, or may not develop into this stage. A person can suffer from inflammation of the middle ear constantly (in chronic form), or temporarily, episodicly and acutely. It is characterized by fever, suppuration from the ear, pressing, bursting pain inside the ear and head. As a rule, otitis media is bacterial in nature. Bacteria can enter the middle ear through the nasal passage in the presence of sinusitis. The hematological route of infection is also possible - through the eardrum. Otitis media can develop with the flu, then bloody discharge will be observed from the ear. And also with scarlet fever, in which case the suppuration will be very profuse, and the pain in the ear will be very severe.
If you suspect that you are developing inflammation of the middle ear, you should immediately consult a doctor: in favorable cases, pus breaks through and exits through the ear canal. But there is a very high risk that the pus will not find a way out through the ear and will spread inside the head, which can lead to the development of meningitis or purulent damage to the brain tissue.
Reference. Inflammation of the inner ear is an inflammation of part of the hearing organ - the labyrinth. It is impossible to make such a diagnosis on your own. As with other types of ear inflammation, this disease is characterized by pressing pain in the ear.
Sulfur plug
Ear wax can also be a source of trouble for a person and lead to a feeling of pressure. As a rule, this symptom occurs without pain in the ear. Earwax is the result of wax accumulation inside the ear and leads to blockage of the ear opening. Poor hygiene and/or improper cleaning of the ear from accumulations of wax leads to compaction of wax residues towards the eardrum. In addition, predisposing factors for the formation of ear plugs may be an asocial lifestyle, working on the street or in dusty industries, and lack of awareness of the rules of personal hygiene. Surprisingly, wearing headphones, telephone headsets and hearing aids leads to the formation of ear plugs. Although everything is logical: physiologically, earwax partially falls out of the ear on its own in small particles. This happens when walking, chewing, talking. The use of the above devices closes the ear canal, and wax cannot find a physiological exit from the auricle.
- An adult's ear hurts: causes, what to do and how to treat at home
Forming in the ear, cerumen plugs the ear canal, disrupts the conduction of sound into the ear, and hearing decreases. Adjacent to the eardrum, it can cause inflammation and, consequently, the development of otitis media. The sad companions of wax plug are pain in the ear canal, inflammation, vomiting, headache and, of course, shooting pain inside the ear, pressing pain.
Other reasons
Other causes of pressure and pain in the ears may be a difference in atmospheric pressure. For example, during takeoff and landing of an airplane. Professional scuba divers often experience ear pain and discomfort due to water pressure and pressure differences at the top. They need to be especially careful, because with a sharp change in pressure they can get decompression sickness.
Diagnostic measures
Since the list of diseases that cause clogged ears is known, the diagnosis includes:
- Blood tests;
- examination of the external auditory canal;
- X-ray examination;
- MRI, CT scan;
- angiography;
- measuring blood pressure with a tonometer.
The first examination allows you to find out the presence of an inflammatory process and infection. During the examination, the ENT determines whether it is otitis media or an accumulation of earwax.
X-ray examination allows you to determine the presence of sinusitis and inflammation. The condition of soft tissues, circulatory disorders, and the presence of a tumor are shown by computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging and angiography.
The simplest test method is to measure blood pressure. Performed manually or automatically. A cuff is placed on the arm, and air is pumped into the blood vessels using a bulb.
The beginning of the pulsation is recorded by a phonendoscope, as is its termination. This second number is the diastolic pressure.