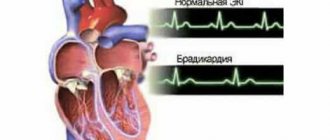
Sinus bradycardia - a decrease in heart rate to 60 beats per minute. This condition is not a pathology. It can be either a variant of the norm or a sign of a serious illness. Bradycardia is often observed in professional athletes. With regular exercise, the heart pumps blood more actively and provides the necessary blood flow through fewer contractions. In swimmers, skiers and track and field athletes, the resting heart rate can reach 30 beats per minute. In this case, this is not considered a deviation. However, if the heart rate is less than normal and other disturbing symptoms are observed, there is a reason to seek advice from a cardiologist.
Symptoms of bradycardia
- dizziness. When the heart rate decreases, systemic blood flow worsens and blood pressure decreases. As a result, the tissues of the body and, above all, the brain, are less well supplied with oxygen. Problems in brain function provoke attacks of dizziness.
- fainting, and in some cases loss of consciousness. The nature of fainting is similar to the causes of dizziness, when the body begins to react acutely to a lack of oxygen.
- dyspnea. Impaired respiratory function appears during physical activity, since with bradycardia, blood circulation slows down and blood stagnation forms in the lungs.
- weakness, increased fatigue, feeling of drowsiness. When, during an attack of bradycardia, the required amount of oxygen does not reach the muscles, they are not able to work as usual and with the necessary strength, which is why weakness, fatigue and other general ailments occur.
- pale skin. Occurs due to low blood pressure.
- there is no significant increase in heart rate during exercise. An increase in heart rate is a normal response of the body during physical activity, even in trained athletes. Failure to adequately increase your heart rate is a symptom of certain heart diseases.
- pain in the chest area . This is a symptom of a serious disorder in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Appears during periods of exercise or when the heart rate drops below 40 beats per minute, when bradycardia is accompanied by a brief attack of deterioration in the blood supply to the heart muscle (angina pectoris). The heart muscle suffers from a lack of oxygen and pain occurs in the chest.
The symptoms listed above may occur to varying degrees. In any case, it is better not to ignore such conditions. This is a reason to consult a doctor who will collect anamnesis, prescribe an examination and, after establishing a diagnosis, determine treatment tactics.
Drug therapy
It is not recommended to use medications before consulting a doctor. Many of them have serious contraindications and severe side effects. Therefore, it is necessary to make an appointment with a cardiologist in advance, only then use therapy methods. Medicines are rarely prescribed; a narrow range of drugs are isolated that normalize the heart rate during bradycardia.
Izadrin
Main forms of production:
- pills;
- injection.
The tablets do not normalize heart rhythm; they are used only as an auxiliary method of therapy to improve the patient's condition. There is a short list of side effects:
Advertising:
- constant thirst caused by dry mucous membranes in the mouth;
- migraine;
- heart rate exceeding normal;
- nausea.
During treatment, the drug is placed under the tongue until completely absorbed. This method is called sublingual. The tablet is held in the mouth until it is completely dissolved. For adults, no more than 5 mg of the drug is recommended per use. You can take up to 3 tablets in 1 day. The duration of therapy is determined depending on the severity of bradycardia.
Isoprenaline
The drugs are used in the form of tablets or solution for intravenous administration. The second form is more effective, but is used in severe cases. The drug has a similar effect on the body to adrenaline. The drug has the following pharmacodynamics:
- increased heart rate;
- increased activity of myocardial adrenergic receptors;
- increased function of the sympathetic nervous system.
The product can be used up to 4 times a day. The dosage is individual for each patient, but usually adults are administered no more than 5 mg of the drug.
Ephedrine hydrochloride
The drug has the following pharmacodynamics:
- narrowing of blood vessels;
- increase in blood pressure.
Ephedrine hydrochloride is a serious drug. It is allowed to be used only in severe cases of bradycardia. Recommendations for use:
- taken only in case of myocardial conduction disturbance;
- take 1 tablet for 1 dose;
- daily dosage is 2-4 tablets;
- The optimal course of treatment is 1 week.
The use of the drug is prohibited if the patient has diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, hypothyroidism, heart failure and other serious pathologies that may cause vasospasm.
Orciprenaline sulfate
According to the mechanism of influence on the body, the drug is similar to Izadrin. Patients with chronic diseases tolerate it better and develop negative reactions less often. The drug is contraindicated only in case of atherosclerosis and individual intolerance. The doctor prescribes tablets or an injection solution.
To increase heart rate, take 1 tablet 4 times a day. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor depending on the patient’s well-being.
Ipratropium bromide
This is the most effective remedy for patients suffering from sinus bradycardia. There is no negative effect on the central nervous system; the drug does not penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Therefore, even after prolonged treatment, drowsiness does not develop. The medicine causes a high-quality effect and is well tolerated by patients. But some of them may develop side effects:
- violation of stool formation;
- polydipsia;
- increased intraocular pressure with the risk of developing glaucoma;
- heart rhythm disturbance.
Due to the possibility of negative reactions, the drug is used with caution. Use only a small dosage of 1 tablet 2-4 times a day.
The drug is prohibited for patients with tachycardia and glaucoma. It should not be taken while pregnant.
Causes of bradycardia
There are two groups of reasons: factors not related to heart disease (extracardiac) and factors directly related to pathologies of the cardiovascular system (cardiac).
Extracardiac factors
- persistent lack of thyroid hormones (hypothyroidism);
- stomach and duodenal ulcers;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- head injuries (bruises and swelling);
- rheumatic fever and other systemic connective tissue diseases;
- toxoplasmosis, diphtheria and other infectious diseases;
- prolonged abstinence from food;
- neurocircular dystonia;
- neuroses accompanied by autonomic dysfunction;
- general hypothermia;
- lead poisoning, nicotine;
- reduced body temperature.
Cardiac causes
- myocarditis (inflammation of the myocardium);
- congenital anomalies of the cardiac conduction system;
- cardiosclerosis;
- myocardial dystrophy;
- IBS.
Separately, bradycardia caused by taking medications is distinguished:
- beta blockers;
- cardiac glycosides;
- antiarrhythmic drugs;
- ivabradine.
Emergency care for bradycardia
When the heart rate slows down, there is a danger of hypoperfusion (decreased oxygen saturation) of vital organs, primarily the brain - neurons work poorly when they cannot “burn” glucose.
Therefore, the assistance that others should provide is aimed at “moving” blood from the vessels of the extremities to the head and torso. Pre-medical measures to relieve symptoms of bradyarrhythmia :
- Place the patient on his back, place his legs on a pillow or cushion made from scrap materials. Under the influence of gravity, blood “flows” from the raised limbs to the central organs that need it first.
- Give the person strong tea or coffee. These substances activate the sympathetic part of the autonomic system, which increases the heart rate, bringing the victim to consciousness.
- It is recommended to help the patient perform several physical exercises. The contracted muscles of the limbs will compress the peripheral vessels, redistributing the blood. Adrenaline, which is produced in response to physical activity, has the ability to increase your heart rate.
Treatment of bradycardia
The selection of therapy depends on the reasons that led to this condition. If bradycardia occurs while taking medications, the doctor will recommend stopping or replacing medications that reduce heart rate.
If the cause relates to extracardiac factors, the cardiologist may schedule a consultation with a related specialist who is responsible for the treatment of the pathology that caused the bradycardia.
In some cases, for strict medical reasons, a surgical operation is prescribed, during which a pacemaker is installed.
"Zelenin Drops" for bradycardia
It is not immediately possible to increase your heart rate by using folk remedies prepared with your own hands. Meanwhile, the use of a concentrated herbal tincture can be effective, eliminating the need for medications. Similar “life hacks” include “Zelenin Drops”, reviews of which are quite good, given the long experience of use.
“Zelenin Drops” is a combined preparation based on ethyl alcohol, which consists of tinctures:
- belladonna (belladonna);
- lily of the valley;
- valerian;
- levomenthol.
According to the instructions, the drug is able to increase the pulse during bradycardia at the dose used: 20-25 drops two to three times a day. Children are recommended to take one drop per year of life three times a day.
Symptoms of overdose: dry mouth, tachycardia, dilated pupils, weakness. If such signs appear, you must immediately stop taking the drug.
The use of folk remedies for bradycardia with mild clinical symptoms has many positive reviews. The poor effectiveness of homeopathic elixirs should not detract from the importance of herbal medicine. However, only registered drugs have an evidence base.
Prevention
First of all, you need to be regularly monitored by a cardiologist in order to recognize the pathology in time. In addition, preventive measures include:
- control blood pressure and bring it to normal;
- maintaining adequate weight;
- regular physical activity appropriate for age;
- diet;
- choosing foods high in vitamins and minerals that are good for the heart;
- limiting smoking and alcohol;
- if possible, minimizing stressful situations;
- good sleep, rest and relaxation.
Bradycardia is a symptom that may indicate the presence of serious diseases. Under no circumstances should it be ignored. A timely visit to the doctor will help to avoid complications and begin appropriate treatment in time if necessary.
FIND OUT PRICES
conclusions
Patients with bradycardia should be thoroughly evaluated. This symptom rarely occurs on its own; more often it is secondary (for example, with hypothyroidism, or as a side effect of taking antihypertensive drugs).
Although a person can, after reading the instructions, independently prescribe medications for bradycardia, this does not replace the advice of a qualified specialist. Treatment should always be tailored to each case of bradycardia before it becomes necessary to urgently treat a person experiencing syncope.