Blood pressure is one of the main indicators of human health. At every appointment with a therapist, blood pressure measurement is part of a set of mandatory diagnostic measures that allow one to get a general idea of the patient’s condition and the clinical picture of existing diseases. Any deviations from normal values are a serious reason for examination by a cardiologist, since hypotension and hypertension can lead to serious consequences and even death.
Situations where blood pressure rises or falls occur quite often in older people. In young patients, you can often observe a picture when the pressure fluctuates - sometimes high, sometimes low. The reasons for this may be physiological or pathological. If pressure surges are caused by diseases or abnormalities in the functioning of organs, the patient requires treatment using medications, so much attention is paid to the diagnosis of such problems.
Reasons for the sharp increase
The situation when blood pressure rises sharply is the most common in patients of any age. If blood pressure rises infrequently and is associated with external factors, the diagnosis of hypertension is not made. With a periodic increase in pressure above 140/90 mmHg, as well as in the presence of concomitant pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, the patient is registered with a cardiologist, and his condition is monitored by a specialist.
There are many reasons why normal blood pressure suddenly changes to high blood pressure. Most often they are associated with the influence of external factors, for example, physical activity. If a healthy person goes for a run, lifts a heavy object, or climbs stairs, the pressure may rise slightly. This situation is considered normal and is associated with increased blood flow and increased resistance of the vascular walls.
Serious emotional shocks, worries, and nervous breakdowns can also cause upward surges in blood pressure, so it is important to control your emotions and avoid reasons for worry. If this cannot be done for objective reasons (for example, when the work involves constant communication with different people and clarification of controversial situations), it makes sense to consult with a therapist, psychologist or neurologist about the possibility of using natural medicines with a sedative effect.
These include:
- "Tenoten";
- "Afobazole";
- "Valerian";
- "Motherwort";
- "Persen."
A sudden rise in blood pressure may be a reaction to certain medications. For example, during treatment with oral contraceptives containing estrogen, hypertension is one of the most common side effects. Almost all antibiotics, drugs for the systemic treatment of mycosis, and some drugs for restoring vision have the same effect.
Other reasons for increased blood pressure to 140/90 or higher include:
- change in climatic conditions (example: flying to countries with a climate opposite to the main place of residence);
- drinking large doses of alcohol (hangover syndrome);
- unfavorable weather conditions (magnetic storms, increased atmospheric pressure).
Important!
In the case of a temporary increase in blood pressure, a return to normal levels should occur within 30-40 minutes. If this does not happen, you should seek help from a doctor, as a sharp increase in pressure can cause a hypertensive crisis.
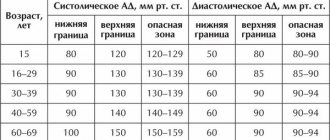
Normal blood pressure and possible deviations
| Normal or disease | Blood pressure readings |
| Norm | 120/80 mmHg |
| Minor deviation within the limits of normal health | 110-130/70-90 mmHg |
| Hypotension | ≤ 110/60 mmHg |
| Hypertension | ≥ 140/90 mmHg |
Pathological causes
Blood vessels are quite elastic and resilient and can cope with increased loads for a long period. Chronic diseases that have a direct impact on the functioning of the circulatory system can occur for a long time without obvious symptoms, but ultimately, the walls of the blood vessels no longer withstand the effects of adverse factors. Clinically, this is manifested by a sharp rise in pressure. In some situations, the pressure may rise so much that the patient will need emergency medical attention (figures of 160/100 mmHg are considered critical).
Pathological causes of a sudden increase in blood pressure include:
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- disorders of the kidneys, in which the renal system retains more moisture and blood thickening occurs;
- blockage of blood vessels with plaques consisting of excess cholesterol.
Important!
In men, sudden surges in pressure can be triggered by benign tumors consisting of glandular tissue (for example, prostate adenoma). In women, a sudden increase in blood pressure is typical for fibroids and uterine polyposis, as well as fibroadenomas - benign tumors of the mammary glands.
Description of the pathology
Patients who have arterial hypertension are forced to constantly adhere to a salt-free diet and take special medications that help control pressure surges and maintain normal levels.
It can increase for various reasons. Values in the upper range from 110 to 139 mmHg and the lower range from 70 to 89 mmHg are considered normal. If they exceed this permissible norm, the pressure is elevated. A change associated with physical or emotional stress should not cause concern, as this is considered the norm. When hypertension manifests itself against the background of serious diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, kidney failure, blood diseases, it is very dangerous for a person. If a patient’s blood pressure has risen sharply, you should pay very close attention to this situation, as this may be a manifestation of a hypertensive crisis. Its whole danger lies in the fact that it can occur in a person who has never suffered from hypertension.
When a hypertensive crisis occurs, in addition to a sharp jump in blood pressure, the following are noted:
- severe, throbbing headache;
- deterioration of vision, appearance of dots before the eyes;
- gagging caused by nausea;
- excitement, heightened state of fear;
- chest pain;
In the event of a sharp increase in pressure, it is necessary to analyze what factors could influence this condition and immediately call an ambulance. While waiting for the doctors to arrive, you need to calm down and try to relax - nervous tension will only worsen the current situation.
A person’s well-being, performance, activity and mood depend on pressure indicators. If your health suddenly worsens, this may be due to sudden jumps in blood pressure. To understand what provokes changes in indicators and how to ensure their stable level, it is necessary to consider in detail what the lower and upper limits are responsible for.
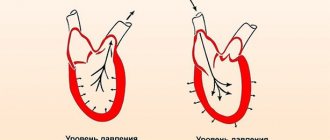
When determining pressure using the Korotkoff method, two pressure indicators are always obtained - systolic and diastolic. The first is the upper one, and it indicates the strength and speed of contraction of the heart muscle. The lower (diastolic) displays the tone and level of elasticity of blood vessels. It occurs as a result of blood pressure in the arteries when the heart muscle contracts.
The difference between the upper and lower values is called pulse pressure. It indicates normal blood supply to organs and tissues, and also indicates the permissible load on the heart. Ideally, the difference should be up to 40 mmHg. If the level has dropped, then we can talk about heart failure.
Increased pulse pressure leads to premature aging of internal organs and the risk of serious heart disease.
A condition in which blood pressure rises above 139/89 is called hypertension, and when it drops to 109/69, it is called hypotension.
Instability of blood pressure is the cause of the development of many dangerous diseases. Its high upper values indicate a strong load on the vascular walls, which can ultimately provoke their rupture. Increased rates cause premature wear of the heart muscle. A sharp decrease in pressure is not too dangerous for the body, but it entails a decrease in performance and cognitive functions.
Indicators can decrease due to insufficient gas exchange in tissues and lungs, and this leads to hypoxia of vital internal organs. A sharp drop in pressure can cause disturbances in brain function, memory loss, coma and even death.
In a healthy person, indicators may change throughout the day. During awakening, they are usually low, and the peak of growth is observed in the evening hours. Therefore, measurements need to be taken several times a day, and at the same time, so as not to miss the unpleasant moment when blood pressure increases or decreases.
Pressure drops sharply: reasons
Exposure to high temperatures (for example, in a bathhouse or sauna) can cause a sudden decrease in blood pressure below normal levels. With vegetative-vascular disorders, hypotension is accompanied by frequent dizziness, which occurs mainly at rest. This phenomenon in medicine is called orthostatic syndrome.
In most cases, in people with normal blood pressure, attacks of hypotension develop under the influence of any disturbances in the functioning of the organs. These include:
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- pathologies of intracerebral circulation;
- chronic hypoxia of brain cells and central nervous system;
- various cardiovascular diseases (heart failure, coronary disease).
In some cases, a drop in blood pressure may occur when the dosage of antihypertensive drugs used to treat blood pressure is incorrectly selected. Self-treatment of any diseases of the heart and blood vessels without monitoring blood pressure and other important indicators is fraught with a critical drop in blood pressure.
In approximately 8% of people, periodic decreases in blood pressure are due to the characteristics of intrauterine development and the formation of the cardiovascular system. Drug correction in this case is ineffective, so such people must carefully monitor their lifestyle and diet to minimize the number of attacks.
Important
! A sharp drop in blood pressure in a healthy person may be a symptom of hidden bleeding (for example, in the stomach or intestines). If the pressure cannot be stabilized within 1 hour using traditional methods or medications, you must go to the hospital.
The pressure drops and rises
In healthy people, slight fluctuations throughout the day are considered normal. During night rest, blood pressure levels drop; during working hours, especially if the activity involves physically hard work, blood pressure may rise. If a person feels normal and deviations from the norm do not exceed acceptable levels, there is no need to worry. But in cases where the pressure jumps sharply, and this happens all the time, you need to consult a doctor and look for the cause. If this is not done, pre-infarction and stroke may develop.
Stress
One of the most common causes of pressure surges is stress. Most often, this situation is typical for young people who spend a lot of time at work or are constantly faced with difficult situations. An unfavorable psychological situation in the family also negatively affects the condition of blood vessels and can cause serious fluctuations. Recently experienced emotional shocks (divorce, death of a loved one, quarrel) can cause a persistent increase in blood pressure with subsequent wave-like jumps.
Important!
If you cannot cope with a stressful situation on your own, it is best to seek help from a qualified psychologist. If you have neurological abnormalities, a tendency to depression, neuroses and psychoses, you may need the help of a psychotherapist.
Obesity
Obesity is the main enemy of healthy blood vessels. Overweight people often eat poorly and consume large amounts of food high in fat and carbohydrates. Fats (especially animal fats) are deposited on the walls of blood vessels and form cholesterol plaques, which clog the internal space and interfere with the free flow of blood.
In obese patients, the pressure most often rises above the permissible values, but in some situations, jumps to the lower side are possible, after which an attack of hypertension occurs again.
Bad habits
In people who abuse alcohol and tobacco, pressure surges are a common occurrence. Toxic substances cause spasm of blood vessels. When the vascular walls expand, the pressure drops; when compression occurs, blood pressure readings begin to creep up.
Important!
Pressure changes in themselves are very dangerous for health, and if they occur against the background of chronic intoxication, the life prognosis becomes unfavorable and the risk of developing severe heart diseases increases: coronary artery disease, heart attack, rheumatism, etc.
Vegetative-vascular disorders
VSD is a complex of neurological symptoms that arise from pathologies of the autonomic nervous system. Clinically, vegetative-vascular dystonia is manifested by the following symptoms:
- headache;
- migraine attacks;
- nausea not associated with food intake;
- mood swings;
- pressure surges;
- compression and squeezing in the chest area.
Note!
There is no specific treatment for vegetative-vascular disorders. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of VSD and correcting the lifestyle that the patient leads. A person with signs of VSD should spend more time in the fresh air, include many foods with a high content of vitamins in their diet, stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages, and increase physical activity (taking into account possible contraindications and restrictions).
Video - Why does pressure fluctuate?
Osteochondrosis and diseases of the cervical spine
Dystrophic disorders in the cartilage tissue of the joints of the cervical vertebrae are diagnosed in almost every third person. The development of pathology is facilitated by a sedentary lifestyle, chronic diseases of the endocrine and nervous systems, and abundant nutrition. With osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, compression of blood vessels and nerve endings occurs, which causes sharp fluctuations in pressure.
To get rid of unpleasant symptoms and improve your well-being, it is necessary to perform a set of therapeutic exercises selected by a doctor and treat all diseases and injuries of the spine in a timely manner. In some cases, drug correction with drugs based on lidocaine (for severe pain) and B vitamins can help.
If a patient experiences pressure surges, he should be registered with a local cardiologist, since such fluctuations can lead to serious complications from the cardiovascular system. In cases where a patient is prescribed drugs to treat hypotension or hypertension, the recommended dosage must be strictly followed. If the prescribed treatment does not bring the expected result, you should consult a doctor, but do not make changes to the treatment regimen yourself.
Symptoms and causes of high blood pressure
Pathological hypertension at the initial stage practically does not manifest itself at all or is disguised as signs of fatigue:
- Patients do not tolerate heat and stuffiness well;
- their pulse periodically increases and tachycardia occurs;
- attacks of headache occur with a feeling of pounding in the temples.
With very high tonometer readings, physical weakness, poor coordination of movements, a sharp bursting headache, visual disturbances, and shortness of breath are characteristic. Such conditions can persist for several hours and do not go away on their own, requiring urgent medical correction.
- The most common cause of high blood pressure is primary hypertension. Vascular pathology develops in a chronic form and progresses over time. Its main symptom is a proportional persistent violation of blood pressure. The first stage of the disease lasts asymptomatically; over the years, the condition without drug correction can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
- Cardiovascular pathologies. With atherosclerotic lesions of large vessels, an increase in upper systolic pressure is characteristic. In this case, the indicators on the left and right hands may differ.
- Kidney disease is another common cause of hypertension. The retention of salts and water in the body increases the total volume of fluid and the load on blood vessels. A characteristic sign is the lower indicator - diastolic pressure is usually higher, and systolic pressure may differ little from the norm. Renal hypertension occurs in older and younger people. It can be genetically determined, or develops due to functional disorders, damage or inflammation of organs.
- Severe menopause. In some women, menopause is accompanied by severe hypertension due to hormonal changes: a decrease in estrogen levels.
- Thyrotoxicosis. Disorders of the thyroid gland with an increase in hormone production causes systolic hypertension, and the lower value remains normal. The condition causes a number of characteristic symptoms: irritability, weight loss, insomnia, tremor.
- Pregnancy gestosis. A specific problem that occurs in the later stages. Stress on blood vessels is caused by swelling and hormonal changes. The pressure rises to alarming levels, which can be life-threatening.
- Side effect of taking medications. Therapy with glucocorticoid hormones, painkillers, antidepressants and other groups of drugs often causes an increase in blood pressure. Usually, at the end of the course it normalizes on its own.
In case of hypertension, there are also tumors of the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, and acute intoxication with certain chemicals.