There are six types of neutrophils depending on the stage of their maturation. Immature types include myeloblasts, promyelocytes, myelocytes, metamyelocytes and band cells. The final stage of development is segmented neutrophils (mature cells with a formed nucleus, divided into several segments).
Even at the stages of their initial development, neutrophils are able to resist infection, although mature segmented cells cope with this task much more effectively.
In blood tests of people suffering from severe infectious diseases, immature forms of neutrophils can be detected. This is explained by the fact that in the fight against pathogenic microorganisms, segmented cells die too quickly, and therefore the body is forced to use cells that are not fully mature. But in the blood of a healthy person, predominantly mature neutrophils are found, since they cope well with their task with virtually no help from their young brothers.
Figure 1. Phagocytosis. Image: mikrostoker/Depositphotos
Blood test for neutrophils
To determine the level of neutrophils, a complete blood count is used. To designate neutrophils on the analysis form, the Latin abbreviation NEUT is used, which can be expressed either in absolute (cell content per liter of blood, for example 0.04-0.3 × 109) or as a percentage. For general analysis, capillary blood is usually used. The biomaterial is collected from a finger after puncture with a scarifier. Sometimes blood is drawn from a vein - much depends on the methods the laboratory uses.
Neutrophils - what are they?
Neutrophils play a very important role in human immunity, removing and destroying microorganisms, unnecessary metabolic products, foreign substances, damaged and malfunctioning cells. Neutrophils perform these functions by the method of phagocytosis, that is, by the method of absorbing and eating these substances.
Neutrophils also participate in a very necessary process for the body called proteolysis, which breaks down proteins into their component parts . This is done by adding water to protein molecules. It is worth noting that proteins are very complex substances that consist mainly of amino acids necessary for the renewal and functioning of the human body.
Neutrophils are produced primarily in the bone marrow, which fills cavities in the bones. Once the white blood cells are sufficiently formed, they leave the bone tissue and travel through the blood circulation. Here they are usually divided into two types - segmented and band leukocytes. When they say that a neutrophil is mature, this means that its development has reached its greatest point. This cell goes through several stages in its development:
What does a general blood test show during pregnancy? 34528
- Myeloblast.
- Promyelocyte.
- Myelocyte.
- Metamyelocyte.
- Band forms.
- Segmented, mature form.
The main characteristic of a mature neutrophil is that its nucleus (central structure) is divided into 3-5 sections called nuclei, which do not exist separately, but are connected together by thin threads called chromatin. Under the magnification of a strong microscope, these nuclei are clearly visible.
Indications for analysis
A general blood test is the most common hematological test, so the range of indications for its use is wide. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell whose main task is to destroy pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, the main goal of the analysis for the content of neutrophils is to identify potentially dangerous conditions accompanied by infectious and inflammatory processes. In other words, a blood test for neutrophils can be informative both for colds and for kidney or liver diseases.
Diagnostics
If neutropenia is detected in blood tests, you must consult a general practitioner to find out the cause. At the appointment, the doctor clarifies what medications the patient is taking and whether he is registered for a chronic disease. Important information can be provided by the patient’s life history, for example, if a person has suffered from frequent recurrent infections of the respiratory tract, skin, and genitourinary system since early childhood, the doctor may suspect a hereditary form of neutropenia. Additional studies are prescribed, including:
- General blood analysis.
In a number of diseases, in addition to neutropenia, a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin, the number of red blood cells, and platelets is observed. Infections and autoimmune disorders are accompanied by an increase in ESR. In malignant blood diseases, the presence of immature forms of granulocytes is noted - metamyelocytes, myelocytes, blast cells. - General urine analysis.
Many autoimmune rheumatological pathologies lead to damage to the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys (nephropathy), which is manifested by proteinuria, leukocyturia, and hematuria. - Immunological studies.
In people with hemolytic anemia and hapten neutropenia caused by taking drugs, the Coombs test gives a positive result. In viral hepatitis, serum markers are detected - HBsAg, anti-HCV. - Immunophenotyping.
The study of peripheral blood using flow cytometry allows you to accurately determine the type of leukemia - myeloblastic, monoblastic, megakaryoblastic. - Genetic research.
By identifying mutations in the LYST HAX1 and GFI1 genes, hereditary (primary) forms of neutropenia can be accurately diagnosed. - Histological studies.
If acute leukemia is suspected, a morphological examination of bone marrow obtained by sternal puncture or trepanobiopsy is performed. There is a decrease in the sprouts of normal hematopoiesis and a large number of atypical blast cells.
Preparing for analysis
The study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach, since food intake causes an increase in the number of neutrophils in the blood. Dinner on the eve of the test is allowed no later than eight o'clock in the evening. 2 days before the study, the patient should follow the following preparation rules:
- stop drinking alcohol;
- limit the consumption of spicy, fried and fatty foods;
- Avoid heavy physical activity and nervous stress.
The morning before the test you should not smoke. It is allowed to drink pure still water.
Figure 2. Preparation for donating blood for analysis.
Some features of the decrease in band neutrophils
Band neutrophils are immature forms of blood cells. Literally a few hours after their origin, they become mature, i.e. segmented. In infants, normal levels range from five to twelve, and in adults - from one to six percent. Among the reasons for the decrease in band neutrophils in a child are:
- excessive physical activity;
- genetics;
- lack of folic acid and cyanocobalamin;
- hormonal imbalance;
- severe stress;
- lead intoxication;
- radiation;
- bad environment;
- the effect of some drugs.
The following diseases also help reduce them:
- autoimmune diseases;
- bone marrow diseases;
- viral and severe bacterial infections;
- erythremia;
- lymphocytic leukemia in chronic form;
- splenomegaly.
Normal levels of neutrophils in the blood
The number of neutrophils in the blood is approximately 40-70% of the total leukocyte mass in both men and women.
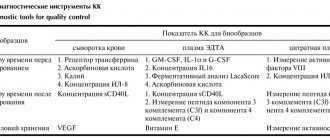
When conducting research, experts primarily pay attention to the content of neutrophils at the middle and full stages of maturation, that is, band and segmented forms. Young cells are of interest if the development of the spread of inflammatory processes is suspected. The table shows the leukocyte formula, which reflects, among other things, the number of neutrophils. Table 1. Leukocyte formula with the number of neutrophils
| Index | × 10x9/l | Share as a percentage of the number of leukocytes | |
| Neutrophils | segmented | 2.0 – 5.5 | 40 — 70 |
| stab | 0.4 – 0.3 | 1 — 5 | |
| Basophils | Within 0.062 | Within 1.0 | |
| Eosinophils | 0.02 – 0.3 | 0.5 — 5 | |
| Lymphocytes | 1.0 – 3.2 | 17 — 38 | |
| Monocytes | 0.07 – 0.5 | 3 — 12 | |
In children of the first year of life, the number of band neutrophils can reach five, then the maximum value is limited to four, as in adults. The smallest number of segmented neutrophils is observed in children 4-5 years old (35-55%). In other age groups it varies between 40-70%.
Note to the patient
It is important to follow basic hygiene rules. Wash your hands before eating. In crowded places you must wear a protective mask. This will help prevent the development of diseases. It is advisable not to communicate with those people who suffer respiratory infections.
If, with low neutrophils, the patient’s general health has deteriorated and the body temperature has increased significantly, then treatment is carried out in a hospital setting under the strict supervision of the attending physician. In this case, self-medication is prohibited, since this can cause the development of serious complications and worsen the general health of the patient.
Now you know that if the test results show a low percentage of neutrophils and an increased percentage of lymphocytes, then these indicators could be influenced by several factors. And only after a complete examination of the patient can we accurately answer what exactly provoked this phenomenon.
Causes of increased neutrophils in the blood
Elevated neutrophil levels can indicate a wide range of illnesses and injuries. Very often, the cause of an increase in neutrophils in the blood is infectious processes of bacterial origin, which can be either focal or generalized (spread throughout the body).
Reasons for increasing the level of neutrophils in the blood:
- upper respiratory tract infections (laryngitis, pharyngitis, sore throat);
- pneumonia;
- kidney diseases;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- local purulent-inflammatory foci (abscesses, abscesses);
- viral diseases (measles, mumps, chickenpox, rubella, etc.);
- oncological diseases;
- taking hormonal medications;
- infections of bacterial origin (dysentery, tuberculosis, cholera, anthrax, etc.);
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- processes of tissue necrosis (gangrene, myocardial infarction, major burns);
- injuries of large organs;
- fractures;
- damage to the skin (cuts, abrasions, etc.);
- gout;
- sepsis (blood poisoning).
Eating canned foods can also cause an increase in neutrophils. This applies to those products in which there are no longer living bacteria left, but the toxic products of their vital activity have been preserved.
Why is it important to know about the leukocyte formula?
There is a so-called leukocyte formula, which is formed from subtypes of leukocytes: monocytes, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes and neutrophils.
Each species performs its own specific function, although it is based on immune processes.
When we receive the results of a clinical blood test, the level of leukocytes in it may be normal, but it is impossible to say offhand what part of this total indicator is this or that subtype. At the same time, this is very important for planning systemic treatment. That is why oncologists require that blood tests indicate the absolute number of all subtypes of leukocytes. The patient should also pay attention to this when receiving test results.
Neutrophils are of greatest interest to chemotherapists. This subtype of leukocytes plays a very important role in protecting the body from bacterial and fungal infections and a relatively lesser role in protecting against viral infections. Neutrophils play virtually no role in antitumor or anthelmintic defense; other cells participate in these processes.
During chemotherapy, the level of neutrophils is a critically important indicator. If the number of neutrophils falls below 0.5x10*9/l, then normal microflora, which is present, for example, in the mouth or intestines, can cause infections. If the count is reduced to <0.2 x 10*9/L, the inflammatory response may be suppressed and the usual signs of inflammation - leukocytosis or white blood cells in the urine or at the site of infection - may not be observed. Acute severe neutropenia, especially in the presence of another factor (for example, cancer and the fact of anticancer treatment), significantly impairs the function of the immune system and can lead to the development of fulminant fatal infections. The integrity of the skin and mucous membranes, blood supply to tissues, and the patient's nutrition also influence the risk of developing infections.
If chemotherapy is carried out, despite the low level of leukocytes in general and neutrophils in particular, this will lead to complete inhibition of the functioning of the bone marrow, in which our blood cells are formed and mature. This guarantees the development of all sorts of complications, which will have to be fought long and hard with a 50/50 chance of success. Therefore, it is better to postpone treatment for a week to allow the body to recover on its own, than to carry out a cycle and then return to therapy in a month at best.
In the treatment of breast cancer, gastrointestinal tract, oncogynecological diseases, lung cancer and other tumors, various combinations of drugs are used that have varying degrees of toxicity.
Therefore, in each individual case, the attending physician makes a decision on the safety of carrying out the next cycle of chemotherapy individually based on the current situation.
You should not demand or persuade the attending physician to carry out treatment, despite poor blood test results. In this case, the doctor does not want to make you worse, but he realistically assesses the risks and tries to protect you from them.
Causes of low levels of neutrophils in the blood
A decrease in the level of neutrophils in the blood is called neutropenia. The cause of this phenomenon can be diseases of various natures, as well as taking various medications.
Reasons for decreased neutrophil levels:
- infectious diseases (viral hepatitis, typhus, influenza, mononucleosis, etc.);
- autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic vasculitis, Crohn's disease, etc.);
- radiation sickness;
- blood diseases (leukemia, hemolytic and dyserythropoietic anemia).
Separate mention should be made of medications: taking them can also cause neutropenia. This is a very broad group of medications, which includes:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: analgin, amidopyrine);
- antibacterial drugs (cephalosporins, penicillins);
- drugs to lower sugar (chlorpropamide);
- thyreostatic agents (propylthiouracil, Mercazolil);
- antimalarial drugs of synthetic origin (hydroxychloroquine);
- sulfonamides (sulfapyrazone; sulfasalazine);
- cytostatics (chlorambucil, methotrexate);
- antivirals (ganciclovir, zidovudine).
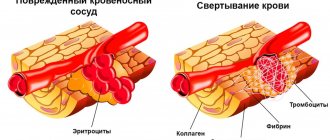
Figure 3. Blood cells in a healthy person and with neutropenia. Image: Sakurra/Depositphotos
What drugs do doctors prescribe?
As a rule, specialists prescribe B vitamins and those medications that contain folic acid. In some cases, among the provoking factors is damage to bone marrow tissue. Under such circumstances, the patient is prescribed medication. Most often, the doctor offers the patient Filgrastim and Lenograstim.
Many people are interested in why the percentage of neutrophils is reduced and lymphocytes are increased? In some cases, this indicates that the body is in the process of removing dead cells.
Consequences of deviation of neutrophils from the norm
A change in the level of neutrophils in the blood is a signal from the body about the presence of inflammatory diseases, injuries or poisoning. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause of the increase or decrease in neutrophils in order to begin treatment in time or eliminate the provoking factor. If this is not done on time, the consequences can be severe (even death). The greatest danger among possible causes is infectious diseases of a bacterial nature, as well as processes of local suppuration and necrotization (death) of tissue.
Segmented neutrophils are increased
If neutrophils in the blood are elevated, what does this mean and what is the reason – doctors cannot immediately answer for sure. The only correct statement is the presence of an infection, a pathology complicated by the penetration of pathogenic microbes into the body. In order to accurately establish a reliable cause, a thorough, comprehensive examination of the entire body is required.
However, in most cases, increased segmented neutrophils in the blood are recorded when:
- development of bacterial infection;
- the appearance of a fungal infection;
- mild inflammatory process.
Segmented neutrophils are increased - reasons
An increase in segmented neutrophils is always a reason to examine the body. In such cases, they speak of a shift in the leukocyte formula to the right.
Among the common situations accompanied by this symptomatology, it is necessary to highlight:
- Not related to pathology: physical activity, food intake.
- Pathological: purulent abscesses, burns, trophic ulcers, leukemia, acute inflammatory diseases (pneumonia, tonsillitis, otitis, sepsis, peritonitis), the formation of malignant or benign tumors.
Segmented neutrophils are increased - what to do?
The main task in this case is to determine the reason why increased segmented neutrophils are detected.
The patient is indicated for additional examination, including consultations with the following specialists:
- therapist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- hematologist.
The patient must strictly follow the doctor's instructions and prescriptions. If neutrophilia is caused by a certain pathology, therapy is aimed at its complete cure.
- Reduced neutrophils in the blood
To help your body recover faster, doctors recommend following the following rules:
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Healthy eating.
- Seasonal therapy using multivitamins.
How to reduce the number of neutrophils in the blood
To reduce the number of neutrophils in the blood, it is necessary to influence the cause of this phenomenon, since there are no separate ways to eliminate it. If the increase in neutrophil levels is caused by short-term stress or increased physical activity, then no specific correction is required.
For persistent neutrophilia, depending on the disease that caused it, the following treatment methods are used:
- antimicrobial therapy - antibiotics are used for infections (amoxicillin, cefixime);
- antiplatelet therapy - in case of heart attack and a tendency to blood clots, acetylsalicylic acid and alteplase are prescribed;
- anti-inflammatory therapy - glucocorticosteroids (prednisolone) are used to reduce inflammation that provokes neutrophilia;
- chemotherapy – aimed at combating malignant tumors (cytostatics, antimetabolites).
If there is a local focus of inflammation, surgical treatment can be used. For example, it is relevant for appendicitis or abscesses. The menu should limit the amount of meat products, canned and smoked. The diet should be rich in vegetables and fruits.
To normalize the level of neutrophils in the blood, it is recommended to eat more vegetables and fruits. Photo: sommail / freepik.com
Doctor's recommendations
If the patient has a low level of neutrophils, the doctor informs the patient about lifestyle during the treatment process. First of all, it is necessary to reduce the risk of developing other diseases. It is worth paying attention to your diet. A person who has low neutrophil levels should not consume poorly processed meat products. At first, you need to boil the milk before drinking. Farm products should be excluded from your diet. It is better to buy goods from supermarkets, since products from the market often contain pathogenic microorganisms.
How to increase the number of neutrophils in the blood
To correct neutropenia, it is necessary to identify its cause. If a decrease in neutrophil levels is caused by taking medications, you should first weigh the possible risks of a decrease in neutrophil levels with the importance of the therapeutic effect of the drugs used. In extreme cases, the drug can be replaced with an analogue that does not affect the level of neutrophils in the blood. The underlying diseases that cause neutropenia are treated with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and antiviral drugs.
It is recommended to consume the following products:
- any meat dishes (it is important that they are all well thermally processed);
- hard boiled eggs;
- pasteurized milk;
- cheese (except for varieties with mold);
- potato;
- rice;
- pasta;
- fruits and vegetables;
- alcohol only in consultation with a doctor.
Careful heat treatment of meat and eggs is necessary in order to exclude the possibility of bacteria and microbes entering the body, which actively multiply in poorly fried or undercooked protein dishes.
Functions of band neutrophils
The main functions of immature neutrophils:
- Biological. The cells supply the necessary enzymes to the affected area and thereby activate the process of resorption of necrotic tissue.
- Protective. As a result of phagocytosis, enzyme substances are synthesized, which become an obstacle to dangerous phenomena that threaten the individual’s body.
- They supply antitoxic substances to the blood.
- Participate in fibrinolysis.
It is important to remember that reduced band neutrophils cannot fully perform the necessary functions.