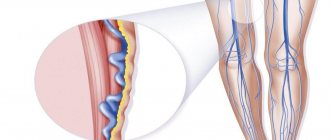
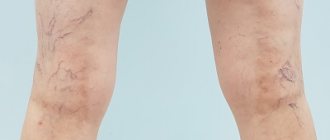
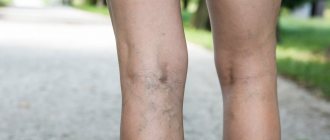
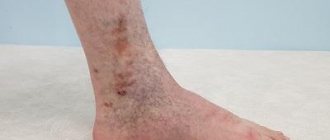
The initial stage of varicose veins is the stage of compensation, in which venous insufficiency is not yet expressed, but symptoms have formed - heaviness in the legs, fatigue; At the initial stage, spider veins and edema are often observed.
In this article, we will look at the reasons for the formation of varicose veins, obvious symptoms and manifestations, and learn about diagnostic and treatment methods.
The stage of initial varicose veins does not appear in diagnoses - this is a name adapted to everyday understanding for mildly expressed venous pathology of the lower extremities (1, English). For a long time, varicose veins were divided into stages, but in 1994 the international classification of chronic venous diseases CEAP was developed and introduced into clinical practice. There is no division of varicose veins into stages; for systematization, classes of increasing severity are used. And the initial stages of the disease correspond to clinical classes C1 and C2, and with the addition of edema, class C3 can be established. In May 2020, the classification was updated, classes C1-C3 remained unchanged (2, English).
Watch the video!
Phlebologists at the center talk about what the initial form of varicose veins is. Find out what the disease is confused with, methods of diagnosis, treatment and prevention.
With initial varicose veins, changes in veins can be of 2 types (3, English):
- Damage to medium-sized vessels that belong to the superficial network. Pathology of the great and small saphenous vein and their tributaries. This is the “classic” type of varicose veins. It is this that leads to physical discomfort in patients due to developing venous stagnation and is prone to further progression.
- Damage to small intradermal vessels is the so-called initial varicose veins. Telangiectasias (spider veins) or a network of reticular varicose veins appear on the skin, which is not accompanied by stagnation of venous blood in the peripheral parts of the lower extremities.
Varicose veins at the initial stage are prognostically more favorable, since they do not lead to clinically significant hemodynamic disturbances in the lower extremities. However, its presence does not exclude the possibility of damage to superficial veins of a larger caliber that lie already under the skin.
Often there is a combination of 2 types of varicose veins; in this case, when making a diagnosis, they focus on more severe manifestations. For example, if there are only spider veins (or reticular varicose veins), they speak of class C1 according to the international classification CEAP. And if against their background signs of damage to the saphenous veins appear, we are talking about class C2, that is, classic varicose veins.
The current classification CEAP, C1 is given in the presence of reticular veins, telangiectasia, that is, initial varicose veins.
Reasons for appearance
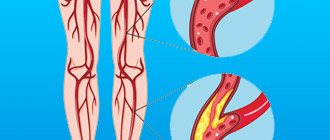
Varicose veins are based on a characteristic persistent and irreversible change in the walls of blood vessels belonging to the superficial venous peripheral network. This is facilitated by venous hypertension (4, English). This increase in pressure is triggered and maintained by many predisposing factors.
At first, venous hypertension is reversible and does not lead to structural changes in blood vessels, but already at this stage pathological processes are launched, which over time or with the addition of other provoking factors lead to deformation of the veins - such irreversible changes are called varicose veins.
Even before the characteristic visible deformation of the veins, pathological processes develop with an increasing effect; consider the sequence (5, English):
- Venous hypertension is accompanied by difficulty in the outflow of blood and a slowdown in its flow. Red blood cells are grouped in the center of the lumen of the vessel, and leukocytes and platelets are pushed to its periphery.
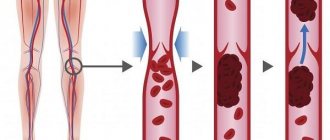
- Redistribution of leukocytes along the inner lining of the veins. The production of endothelial factors is stimulated, which promotes the adhesion (sticking) of leukocytes and their activation. The process of thrombus formation begins, which aggravates the damage to the surface of the venous walls.
- Phlebosclerotic process in the area of venous valves. Normally, when filled with blood, the valves close tightly to each other and block the lumen of the vein. This is necessary to prevent reverse blood flow during cardiac systole. Sclerosis leads to deformation of the valves, and they are no longer able to fully perform their function.
At the earliest stages, all these changes do not yet lead to clinically significant hemodynamic disturbances. And patient complaints are so far limited to cosmetic defects. Over time, visible deformation of the affected area of the vessel begins. The vein acquires pathological bends and lengthens somewhat, local expansions and saccular bulges in the form of varicose nodes appear on it. This is accompanied by worsening valve insufficiency - the valves located in the area of varicose deformation cease to touch each other when filled.
The pathological reverse flow of blood that occurs at this stage is called vertical reflux. This hemodynamic disturbance is one of the key pathogenetic aspects of varicose veins, as it contributes to the formation of chronic venous insufficiency with blood stagnation. It is this that leads to the appearance of the main symptoms of varicose veins. But when small and very small venous vessels in the thickness of the dermis are affected, clinically significant stagnation of blood does not occur.
Features of varicose veins
This pathology, known since the time of Hippocrates, according to the World Health Organization, occurs in more than half of the working population. Varicose veins affect both young people and the elderly, and even teenagers. Some people turn to phlebologists for treatment in a timely manner, while others prefer independent treatment that is not always effective. There are also those who, either from fear of a possible operation, or from an indifferent attitude towards their own health, simply allow the development of varicose veins. By the way, the disease is dangerous due to its complications - the formation of blood clots and trophic ulcers. Phlebeurysm
- a disease that manifests itself in damage to the walls of blood vessels. Due to the weakening of the walls, the veins begin to stretch, visible nodes appear on the surface of the skin, which, in a neglected state, cause disruption of blood flow.
The influence of pregnancy on the formation of varicose veins
During pregnancy, it is important to stop the progression of varicose veins for the health of the mother and the unborn child.
Consultation with a phlebologist is required. Pregnancy creates the prerequisites for the appearance of initial varicose veins and its further development (6, 7 English):
- Hormonal imbalance between estrogens and gestagens. Already from the first days, the level of progesterone in the blood progressively increases, which prevents the onset of the next menstruation. But this hormone affects not only the condition of the endometrium and the entire uterus. Under the influence of progesterone, the tone of the smooth muscle layer in the walls of internal organs and blood vessels, including the veins of the lower extremities, decreases - this contributes to the deterioration of blood evacuation from the peripheral parts of the extremities with the development of venous hypertension.
- The growing uterus causes compression of nearby organs and vessels of the small pelvis. Already from the second trimester of gestation, most women experience difficulty in the outflow of blood through the inferior vena cava system. The resulting increase in pressure in the veins of the legs contributes to the decompensation of existing venous pathology and active remodeling of the vascular walls. There is often concomitant lymphostasis, which aggravates the situation.
- Physical inactivity at the end of the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. With insufficient physical activity, the efficiency of the muscle pump of the legs decreases, and there is a risk of early, initial varicose veins.
During pregnancy, symptoms of both cosmetic and classic varicose veins can develop. Women often do not attach much importance to them, considering them a natural manifestation of pregnancy. Therefore, a consultation with a phlebologist is included in the list of mandatory examinations.
Symptoms and manifestations of varicose veins at the initial stage
The symptoms of initial varicose veins depend on the diameter of the affected vessels and their significance for the general venous outflow.
The “cosmetic” type of the disease is characterized by the presence of only external defects in the form of spider veins (telangiectasia) or a superficial fine mesh. There cannot be any other complaints, since the affected vessels have a very small diameter and are responsible for draining blood only from certain areas of the skin.
With the classic version of varicose veins, the symptoms are more obvious, although physical discomfort in the early stages of the disease is not permanent. The quality of life does not deteriorate significantly, and no serious complications arise. In this form, varicose veins can exist for quite a long time, decompensating and progressing with the addition of additional risk factors.
Severe symptoms of varicose veins
Symptoms of varicose veins affecting the saphenous veins of the legs include (8, English):
- Increased venous pattern in the lower extremities. There is a change in the course of visible superficial vessels and their bulging. But with obesity, this symptom is often masked by overdeveloped subcutaneous tissue. Obvious nodular deformation of blood vessels usually develops in later stages of the disease.
- The appearance of heaviness, a feeling of fullness and fatigue in the legs are signs of decompensation of venous insufficiency. They are usually accompanied by a tendency to slight swelling (pasty) of the legs. Such complaints may appear towards the end of the working day, especially if professional activities involve prolonged standing or sitting. In the early stages of varicose veins, discomfort and swelling disappear soon after taking a horizontal position with legs elevated. Facilitates the condition and performance of a set of exercises to engage the muscle pump of the legs.
- Increased fatigue of the leg muscles, and in some patients a tendency to cramps. This is explained by the beginning of metabolic changes in tissues, which are caused by microcirculation disorders against the background of phlebostasis.
The severity of symptoms may vary. In some patients, varicose veins in the initial stage debut with visible changes in the superficial veins. In others, signs of venous insufficiency initially appear, which is a sign of already existing valve pathology and serves as an indicator of a less favorable course of varicose veins.
Why is it better to treat varicose veins with laser in our MIFC clinic?
We do not want to lag behind the most advanced European technologies and try to be “at the cutting edge” of phlebological care. Therefore, our medical center began to use this laser device for the FIRST time in Russia. And the thousands of years of experience in laser interventions accumulated over many years allowed us to safely perform laser procedures on a new generator with a wavelength of 1940 Nm.
Laser treatment without surgery - new possibilities!
It is also worth noting that despite the need to purchase new expensive equipment for these procedures, we DO NOT RAISE the prices for our services.
In order to learn all the intricacies of working with the new device, we held negotiations with leading European phlebologists from Germany and Latvia who use this laser.
At a master class on laser treatment of varicose veins in Riga with Dr. Uldis Maurins
Our specialists first completed a training cycle with a master class at the Clinic of Dr. Maurins, the president of the Baltic Society of Phlebologists and a recognized leader in the treatment of varicose veins.
We are confident that only the use of the best methods and the constant improvement of our doctors from recognized world leaders will allow us to achieve the highest results in the treatment of varicose veins.
Now the patient has a choice!!! Be treated using established methods or using the latest, more effective technologies. We don't insist - we offer!!!
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of varicose veins, determination of the nature and severity of hemodynamic disorders in the veins of the legs is the prerogative of a phlebologist.
Diagnosis of initial varicose veins includes (9, English):
- clinical examination with functional tests;
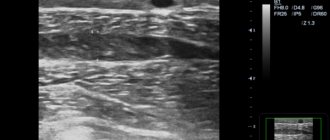
- Ultrasound Doppler Doppler (USD) of the vessels of the lower extremities to assess the nature of blood flow and identify valvular insufficiency in superficial veins and perforators;
- if necessary, consultations with other specialists (gynecologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist) and tests to determine the main causative factor in the development of venous hypertension.
Invasive diagnostic techniques are currently practically not used, since the information obtained with their help does not have much clinical significance. An ultrasound scan is usually sufficient.
Frequently asked questions from patients on the Internet about laser treatment of varicose veins in Moscow
Where is innovative laser treatment for varicose veins performed without surgery in Moscow?
Innovative laser treatment of varicose veins without surgery in Moscow is carried out in city phlebology medical centers. Our innovative phlebology center occupies one of the leading positions in Moscow in conducting modern interventions on veins. Registration is carried out by phone.
What is the advantage of modern methods of treating varicose veins without surgery over conventional surgery in a public hospital?
Today, classical surgical treatment of varicose veins (crossectomy, stripping) is quite widely used in most public medical institutions. However, this method of treatment is considered obsolete by leading European experts. New methods of thermal venous obliteration are distinguished by the minimal trauma of the procedures, rapid recovery and the almost complete absence of a rehabilitation period. An important point is that innovative procedures are carried out under ultrasound visualization with full control of the intervention by a specialist.
How much does laser treatment of varicose veins without surgery cost in Moscow?
The cost of modern laser treatment for varicose veins without surgery in Moscow can vary significantly. Endovenous laser obliteration is a modern high-tech procedure using special consumables (laser light guides). The price of this innovative procedure cannot be too low. In the leading city phlebology centers in Moscow, the cost of laser treatment has fairly similar figures. You can find out prices for laser treatment at the Moscow City Phlebology Center on our website page: , or by phone: +7 (495) 565 35 07.
Is it possible to treat varicose veins without surgery?
Modern innovative procedures that use European treatment protocols can hardly be called operations. Technologies are used that completely eliminate skin incisions. Contrary to the opinions of skeptics who existed just ten years ago, new technologies have proven to be much more effective in removing varicose veins than classical operations. The modern procedure of venous thermoobliteration (laser or radiofrequency) is the most radical treatment of varicose veins without the usual surgical trauma.
Treatment
The treatment methods used for varicose veins are divided into conservative and surgical. Typically, a treatment regimen includes both of these components.
For the treatment of varicose veins at the initial stage, drugs of various groups are widely used, with preference given to phlebotonics in tablet form and as part of ointments. Their regular use in most cases makes it possible to compensate for incipient venous insufficiency, which has a beneficial effect on the patient’s condition (English). Some medicinal plants have approximately the same effect, which explains the frequent use of herbal medicine - both in the form of decoctions and infusions for oral administration, and in the form of herbal preparations.
In addition to drug treatment, the following may be used:
- physiotherapy;
- compression jersey;
- exercise therapy;
- diet therapy - normalizing body weight will reduce the load on the vessels of the lower extremities.
All conservative methods have only a restraining and compensating effect. No drug is capable of restoring sclerotic and deformed veins and the valves located in them.
At the initial stage, an excellent effect can be obtained with sclerotherapy; varicose veins of large diameter are eliminated with a laser - both treatment technologies will relieve not only the unsightly looking vessel, but also the existing venous insufficiency. Healthy deep veins take over the drainage of venous blood. After a short period of adaptation, the blood flow system is completely compensated, phlebostasis is stopped, microcirculation is normalized.
Possible complications
Deformed veins and the sclerotic valves located in them are not able to recover to their original level under the influence of drug therapy. The changes are irreversible and prone to progression, especially when provoking factors persist and new adverse effects are added.
In the initial stages of the disease, developing venous insufficiency can decompensate - this does not indicate getting rid of varicose veins, but a temporary slowdown in the pathological process. Subsequently, adjacent sections of the vein and other vessels are involved in phlebosclerosis. The greatest clinical significance is the damage to the communicating veins, which provide communication between the superficial venous network of the legs and the deep one. They penetrate (perforate) the fascia located on top of the muscles, therefore they are also called perforators.
Most communicating vessels also have valves, which normally prevent the non-physiological discharge of blood from deep veins to superficial ones, therefore varicose changes in perforators are accompanied by the development of horizontal reflux. This shutdown of the natural mechanism for regulating pressure in the superficial venous system leads to serious consequences:
What happens if varicose veins are not treated?
Turning off the natural mechanism for regulating pressure in the superficial venous system leads to serious consequences (11, German):
- worsening phlebosclerosis and accelerating the process of varicose veins against the background of significantly increased venous hypertension;
- increased phlebostasis, which increases the likelihood of developing intravascular thrombosis;
- disruption of the walls of the capillary network, which is accompanied by an increase in their permeability to plasma and protein molecules, accumulation of metabolic products in tissues and the development of chronic hypoxia.
The addition of horizontal reflux is a factor contributing to persistent decompensation of chronic venous insufficiency. Trophic disorders arise and increase in the skin and soft tissues, swelling and physical discomfort experienced by the patient increase, and the risk of developing thrombophlebitis increases. Varicose veins become complicated, advanced, with a significant area of damage to the veins. And the treatment will no longer give as quick and tangible results as at the early stage.
Microfoam sclerotherapy
Another minimally invasive method that I would like to talk about is echo-controlled microfoam sclerotherapy . This intervention is considered the most “gentle”: obliteration of the lumen of the vein affected by varicose veins is achieved by introducing microfoam sclerosant into the vein.
Under the control of an ultrasound sensor, the phlebologist punctures the vein at the site of its varicose dilatation and injects sclerosant converted into microfoam (different clinics use sclerosant of varying concentrations - however, it is microfoam that allows you to most quickly achieve the obliterating effect).
The introduction of sclerosant stops after the foam “reaches” the anastomosis of the vessel (the process of foam moving through the vessel is clearly visible on the ultrasound monitor). Then the surgeon performs manual manipulation (massage of the limb) in order to speed up the reaction of the sclerosant with the vein endothelium. The massage is performed along the projection of the vein.
Next, an elastic compression is put on the patient’s leg for a period of 3 to 5 days (the mode of wearing the compression is determined individually). Immediately after the procedure, the doctor asks the patient to walk for forty minutes to rid the deep veins of the remnants of the sclerosing substance.
Characteristics and benefits of sclerotherapy:
- Despite the paradoxically low morbidity and simplicity of implementation, microfoam sclerotherapy can be considered a surgical procedure. At least, the effect of its implementation is often quite comparable even with radical surgical interventions - while the patient actually does not have to go to the hospital or subject himself to general anesthesia. In addition, the person does not experience any pain or fear, which is usually associated with traditional “scalpel” surgery.
- After sclerobliteration, there are no scars left on the patient’s skin. The high cosmetic effect is also an important advantage of this procedure – especially for young women.
- Sclerotherapy has a minimum of contraindications, as well as an extremely low risk of side effects - which makes it possible to perform this procedure for elderly patients, as well as people with severe concomitant pathologies for whom traditional phlebectomy is contraindicated.
- Despite the fact that sclerotherapy is considered an innovative method for treating varicose veins, its cost is perhaps the lowest in relation to other types of minimally invasive interventions. Thus, the most affordable case of treating varicose veins with sclerotherapy cost our patient only 3 thousand rubles.
One of the few contraindications to sclerotherapy is a vein diameter greater than 10 mm. In the context of this fact, we once again draw your attention to the importance of timely consultation with a doctor : varicose veins usually expand gradually - so it is not so difficult to capture the moment “up to 10 mm”.
Early treatment is the best result
Pathology in the initial stages can be completely eliminated, avoiding permanent cosmetic defects and complications.
Radical surgery is not required. The use of minimally invasive techniques already at the initial stage of the disease allows you to achieve the same result in literally 1-2 sessions as with surgical removal of a vein. This treatment is not associated with significant physical discomfort and does not require hospitalization, general anesthesia or subsequent dressings.
Author of the article: Zherdev Andrey Vladimirovich Last update: 09/26/2020.